Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Goblet Cell
Încărcat de
Muhammad ZairulfikriDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Goblet Cell
Încărcat de
Muhammad ZairulfikriDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Goblet cell
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Goblet cell
Schematic illustration of a goblet cell in close up, illustrating different
internal structures of the cell.
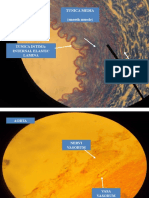
Transverse section of a villus, from the humanintestine. X 350.
a. Basement membrane, here somewhat shrunken away from the
epithelium.
b. Lacteal.
c. Columnar epithelium.
d. Its striated border.
e. Goblet cells.
f. Leucocytes in epithelium.
f. Leucocytes below epithelium.
g. Blood vessels.
h. Muscle cells cut across.
Latin exocrimohsinocytus caliciformis
Code TH H3.04.03.0.00009;
H3.04.03.0.00016
H3.05.00.0.00006
Anatomical terminology
A goblet cell is a glandular simple columnar epithelial cell whose function is to secrete gel
forming mucins, which are the major component of mucus. The goblet cells use
both apocrine and merocrine methods for secretion.
The majority of the cell's cytoplasm is occupied by mucinogen granules, except at the bottom,
where rough endoplasmic reticulum,mitochondria, the nucleus, and other organelles are
concentrated. The apical plasma membrane projects microvilli to increase surface area for
secretion.
Contents
[hide]
1 Structure
o 1.1 Histology
2 Function
o 2.1 Types of secretion
o 2.2 Role in oral tolerance
3 Clinical significance
4 History
o 4.1 Etymology
5 References
6 External links
Structure[edit]
They are found scattered among the epithelial lining of organs, such as
the intestinal and respiratory tracts.
[1]
They are found inside thetrachea, bronchus, and
larger bronchioles in respiratory tract, small intestines, the colon, and conjunctiva in the upper
eyelid. (Goblet cells are the chief source of tear mucus. These occur throughout the conjunctiva,
especially the plica semilunaris. These are most dense in nasal conjunctiva, least dense in upper
temporal fornix and absent in palpebral mucocutaneous junction and limbus.)
They may be an indication of metaplasia, such as in Barrett's esophagus.
Histology[edit]
The nuclei of goblet cells tend to be displaced toward the basal end of the cell body, leading to
intense basophilic staining.
In mucicarmine stains, deep red mucin found within goblet cell bodies. Goblet cells can be seen
in the examples below as the larger, more pale cells.
An intestinal gland from the human intestine with goblet cells visible.
Goblet cell in ileum
section of mouse intestine. Mucus of goblet cells in blue.
Section of mucous membrane of humanstomach, near thecardiac orifice. X 45.
c. Cardiac glands.
d. Their ducts.
cr. Gland similar to theintestinal glands, withgoblet cells.
mm. Mucous membrane.
m. Muscularis mucosae.
m. Muscular tissue within the mucous membrane.
Function[edit]
The main role of goblet cells is to secrete mucus in order to protect the mucosae where they are
found.
Types of secretion[edit]
Basal secretions. This is the normal base level secretion of mucus, which is accomplished
by cytoskeletal movement of secretory granules.
Stimulated secretion. Secretion may be stimulated by dust, smoke, etc. Other stimuli include
viruses, bacteria, etc.
[citation needed]
Role in oral tolerance[edit]
Oral tolerance is the process by which the immune system is prevented from responding to
antigen derived from food products, as peptides from food may pass into the bloodstream via the
gut, which would in theory lead to an immune response. A recent paper published in Nature, has
shed some light on the process and implicated goblet cells as having a role in the process.
[2]
It
was known that CD103 expressing dendritic cells of the lamina propria had a role to play in the
induction of oral tolerance (potentially by inducing the differentiation of regulatory T cells), and
this paper suggests that the goblet cells act to preferentially deliver antigen to these
CD103
+
dendritic cells.
[2]
Clinical significance[edit]
Goblet cell carcinoid - a tumor that has a component that is similar to goblet cells
History[edit]
Etymology[edit]
The term goblet refers to these cells' goblet-like shape. The apical portion is shaped like a cup,
as it is distended by abundant mucinogen granules; its basal portion is shaped like a stem, as it
is narrow for lack of these granules.
There are other cells that secrete mucus (as in the foveolar cells of the stomach
[3]
), but they are
not usually called "goblet cells" because they do not have this distinctive shape.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Notes From Dental Articles ANATOMYDocument6 paginiNotes From Dental Articles ANATOMYpatelpurvivÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intrdoduction Gis 2 (Associated Organs) : Maya Tejasari Histology DepartmentDocument24 paginiIntrdoduction Gis 2 (Associated Organs) : Maya Tejasari Histology DepartmentIpan YustiartaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cells: USC Messed Up The Following QuestionsDocument119 paginiCells: USC Messed Up The Following Questionsopeyemi idaeworÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toxicopathological Effects of Intravenous Injection of Layer Double Hydroxide (LDH) Nanoparticles in Male Rats.Document16 paginiToxicopathological Effects of Intravenous Injection of Layer Double Hydroxide (LDH) Nanoparticles in Male Rats.Amar AmarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Endocytosis ExocytosisDocument5 paginiEndocytosis ExocytosisMiska Fairuz100% (1)
- DPP XI Chapter - 16 Digestion and Absorption 12Document12 paginiDPP XI Chapter - 16 Digestion and Absorption 12Riya MondalÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Introduction To The Gastrointestinal SystemDocument7 pagini1 Introduction To The Gastrointestinal SystemLinh Phan100% (1)
- Bioprocess Considerations in Using Animal Cell CulturesDocument25 paginiBioprocess Considerations in Using Animal Cell CulturesDidem Kara100% (1)
- Histology of BreastDocument2 paginiHistology of BreastIbrahim SugiyonoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Histology Lecture: Minerva Diana A. Dichoso, RMTDocument108 paginiHistology Lecture: Minerva Diana A. Dichoso, RMTVernadel ApolloÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 Cell Structure Prokaryotes VMCDocument31 pagini3 Cell Structure Prokaryotes VMCapi-302494239Încă nu există evaluări
- Histology of Urinary SystemDocument53 paginiHistology of Urinary SystemA1205Angelica GloryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presentasi Jurnal LaryngoceleDocument13 paginiPresentasi Jurnal LaryngoceleTiara Rachmaputeri AriantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Morphology and Cytology of BacteriaDocument22 paginiMorphology and Cytology of BacteriaNura GudetaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell DefinitionDocument2 paginiCell DefinitionjudyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Histo Slides Volume IIDocument21 paginiHisto Slides Volume IIKristian CadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial Biology FGS0044 Answer All Questions. Diagram of An Animal Cell. Label The PartsDocument3 paginiTutorial Biology FGS0044 Answer All Questions. Diagram of An Animal Cell. Label The PartsPreeti RajasegarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 135 2022F U1 Cells&Tissues LISDocument17 pagini135 2022F U1 Cells&Tissues LISChung Trần Quang Bách 9AÎncă nu există evaluări
- Connective TissuesDocument45 paginiConnective TissuesAbrar osmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Auditory NerveDocument31 paginiAuditory NerveI Nengah Aditya PramanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Histo Slides Volume IDocument67 paginiHisto Slides Volume IKristian CadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- VIII. Special SensesDocument21 paginiVIII. Special SensesSkyNayvieÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCQs On GITDocument3 paginiMCQs On GITsamuel waiswaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Structure Kgis Grade 11Document64 paginiCell Structure Kgis Grade 11Katie Al HodaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 26: The Urinary System: Chapter Objectives Overview of Kidney FunctionDocument14 paginiChapter 26: The Urinary System: Chapter Objectives Overview of Kidney FunctionAnkit SwainÎncă nu există evaluări
- THEORIES OF SHOOT APICAL MERISTEM NotesDocument11 paginiTHEORIES OF SHOOT APICAL MERISTEM NotesAbhimanyu Pandey100% (2)
- Bacterial Cell - 220220 - 072643Document106 paginiBacterial Cell - 220220 - 072643Hernandez NicoleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercise 3 Phylum CoelenterataDocument34 paginiExercise 3 Phylum CoelenterataClemence Marie FuentesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Membrane TransportDocument24 paginiMembrane Transportolawandeilo123Încă nu există evaluări
- 1st Lecture On The Histology of Urinary System by DR RoomiDocument14 pagini1st Lecture On The Histology of Urinary System by DR RoomiMudassar RoomiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thecytoskeleton PPTDocument11 paginiThecytoskeleton PPTseenu mohapatraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch. 4-5 Mock Test Answer KeyDocument14 paginiCh. 4-5 Mock Test Answer KeybuddybbuddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aldwin A. Yaneza, MD Course Director. Gross AnatomyDocument40 paginiAldwin A. Yaneza, MD Course Director. Gross AnatomyfilchibuffÎncă nu există evaluări
- Difference Between Sterilization and DisinfectionDocument4 paginiDifference Between Sterilization and Disinfectiontaz_taz3Încă nu există evaluări
- Mammalian Histology AssignmentDocument9 paginiMammalian Histology AssignmentSana Sultana100% (1)
- ATCC Primary Cell Culture GuideDocument35 paginiATCC Primary Cell Culture GuideAlemayehu LetÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy of Male Rep. SysDocument89 paginiAnatomy of Male Rep. Syszodo_izyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thoracotomy Through The Auscultatory Triangle - Ann Thorac Surg.1989Document2 paginiThoracotomy Through The Auscultatory Triangle - Ann Thorac Surg.1989Adriana PavelÎncă nu există evaluări
- White Blood Cells (WBC) PDFDocument3 paginiWhite Blood Cells (WBC) PDFPerry SinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathology B - Gastrointestinal Tract (Esguerra, 2015) PDFDocument18 paginiPathology B - Gastrointestinal Tract (Esguerra, 2015) PDFJem QuintoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Histology of Cerebrum and CerebellumDocument22 paginiHistology of Cerebrum and CerebellumUloko ChristopherÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lectures No 4 Introduction & Method of Tissue Preparation & Specimen Reception & FixationDocument27 paginiLectures No 4 Introduction & Method of Tissue Preparation & Specimen Reception & FixationAbdallah AlasalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch. 3 Tissues Test: NameDocument5 paginiCh. 3 Tissues Test: Namestephanieyoung07Încă nu există evaluări
- MED3ATA Immunology Lecture CombinedDocument253 paginiMED3ATA Immunology Lecture CombinedLeona KerenÎncă nu există evaluări
- MetaplasiaDocument6 paginiMetaplasiaMd Ahsanuzzaman PinkuÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8.TEETH LECTURE For Dentistry Students 2011Document49 pagini8.TEETH LECTURE For Dentistry Students 2011ahmed yousefÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cucurbitacins and Cancer A Review On in Vitro, in Vivo, in Silico Analysis of Compounds Against Estrogen Receptor (ER) For A Better TreatmentDocument7 paginiCucurbitacins and Cancer A Review On in Vitro, in Vivo, in Silico Analysis of Compounds Against Estrogen Receptor (ER) For A Better TreatmentInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology100% (5)
- The Abdominal OrgansDocument56 paginiThe Abdominal OrgansAjeng FikihÎncă nu există evaluări
- Standard Operating ProceduresDocument3 paginiStandard Operating ProceduresPrasanna BabuÎncă nu există evaluări
- PituitaryDocument15 paginiPituitaryBivek PokhrelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lymphoid System MCQDocument8 paginiLymphoid System MCQAbduladheemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scope Biochemistry 2015Document31 paginiScope Biochemistry 2015prima octafiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument6 paginiProkaryotes and Eukaryoteshussainm1234Încă nu există evaluări
- Pathanatomy Lecture - 02 Cell InjuryDocument41 paginiPathanatomy Lecture - 02 Cell InjuryChris QueiklinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Histology Practical Manual Part 1 2021Document124 paginiHistology Practical Manual Part 1 2021khushikumari1407Încă nu există evaluări
- Biochemistry - Enzymes Review NotesDocument4 paginiBiochemistry - Enzymes Review NotesKenneth100% (1)
- Comparative Anatomy of Integumentary Glands in VertebratesDocument3 paginiComparative Anatomy of Integumentary Glands in VertebratesViswadeep Das100% (1)
- HistoDocument8 paginiHistoFatima AmaliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phylum Coelenterata ClassificationDocument3 paginiPhylum Coelenterata ClassificationSudesh Rathod100% (1)
- Cyclone HaroldDocument7 paginiCyclone HaroldMuhammad ZairulfikriÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Study On Dress Code For College Students: SSRN Electronic Journal January 2014Document23 paginiA Study On Dress Code For College Students: SSRN Electronic Journal January 2014Muhammad ZairulfikriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cellular Differentiation: Mammalian Cell TypesDocument7 paginiCellular Differentiation: Mammalian Cell TypesMuhammad ZairulfikriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reading Jurnal TipsDocument1 paginăReading Jurnal TipsMuhammad ZairulfikriÎncă nu există evaluări
- National Aeronautics and Space Administration: For Other Uses, SeeDocument21 paginiNational Aeronautics and Space Administration: For Other Uses, SeeMuhammad ZairulfikriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Negligence: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument14 paginiNegligence: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchMuhammad ZairulfikriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concept Time Value of MoneyDocument15 paginiConcept Time Value of MoneyFariz Imran Mohd ShaariÎncă nu există evaluări
- PSCF9 03carterDocument7 paginiPSCF9 03carterMuhammad ZairulfikriÎncă nu există evaluări
- En The Four Juristic SchoolsDocument196 paginiEn The Four Juristic SchoolsMuhammad ZairulfikriÎncă nu există evaluări
- En The Four Juristic Schools PDFDocument196 paginiEn The Four Juristic Schools PDFMuhammad ZairulfikriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hugo ChavezDocument7 paginiHugo ChavezMuhammad ZairulfikriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Part A: 20 Multiple Choice Questions (Topic 4: Completing The Accounting Cycle)Document5 paginiPart A: 20 Multiple Choice Questions (Topic 4: Completing The Accounting Cycle)Muhammad ZairulfikriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oireachtas National ParliamentDocument6 paginiOireachtas National ParliamentMuhammad ZairulfikriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Investment: VerificationDocument4 paginiInvestment: VerificationMuhammad ZairulfikriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Part A: 20 Multiple Choice Questions (Topic 4: Completing The Accounting Cycle)Document5 paginiPart A: 20 Multiple Choice Questions (Topic 4: Completing The Accounting Cycle)Muhammad ZairulfikriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research ConceptDocument1 paginăResearch ConceptMuhammad ZairulfikriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic For IMT GT SeminarDocument1 paginăTopic For IMT GT SeminarMuhammad ZairulfikriÎncă nu există evaluări
- JWP A172 0304 Utk HebahDocument98 paginiJWP A172 0304 Utk HebahMuhammad ZairulfikriÎncă nu există evaluări
- BIDAYUH: Customs and TraditionDocument29 paginiBIDAYUH: Customs and TraditionMuhammad ZairulfikriÎncă nu există evaluări
- John BoyegaDocument9 paginiJohn BoyegaMuhammad ZairulfikriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dhaka EconomyDocument2 paginiDhaka EconomyMuhammad ZairulfikriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Product Development'S ManualDocument3 paginiProduct Development'S ManualMuhammad ZairulfikriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Malaysia Is A Beautiful Country To Live inDocument2 paginiMalaysia Is A Beautiful Country To Live inMuhammad ZairulfikriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Star WarDocument17 paginiStar WarMuhammad ZairulfikriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Red SeaDocument13 paginiRed SeaMuhammad Zairulfikri100% (1)
- Gulf of SuezDocument3 paginiGulf of SuezMuhammad ZairulfikriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Metamorphosis: EtymologyDocument5 paginiMetamorphosis: EtymologyMuhammad ZairulfikriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Potency: TotipotencyDocument4 paginiCell Potency: TotipotencyMuhammad ZairulfikriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cellular Differentiation: Mammalian Cell TypesDocument7 paginiCellular Differentiation: Mammalian Cell TypesMuhammad ZairulfikriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Re Led Basics Higher OrderDocument3 paginiRe Led Basics Higher OrderMuhammad ZairulfikriÎncă nu există evaluări
- PDF of ProtectionDocument28 paginiPDF of ProtectionAROOJ ASLAMÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy of The Abdominal VisceraDocument7 paginiAnatomy of The Abdominal VisceraRabia ManzoorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nasal Cavity and Paranasal Sinuses: Anatomy and FunctionDocument17 paginiNasal Cavity and Paranasal Sinuses: Anatomy and FunctionVictor EnachiÎncă nu există evaluări
- AmelogenesisDocument18 paginiAmelogenesisDeepa RayÎncă nu există evaluări
- GSC 101 Final Term Past Paper 1Document8 paginiGSC 101 Final Term Past Paper 1Abdullahkhan abdullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathology Mcqs (4th Year)Document9 paginiPathology Mcqs (4th Year)usmandumassar100% (7)
- 1976 - Creeping Attachment After Free Gingival GraftDocument6 pagini1976 - Creeping Attachment After Free Gingival GraftTien Li AnÎncă nu există evaluări
- PolycythemiaDocument45 paginiPolycythemiaatik mayasariÎncă nu există evaluări
- The A To Z of Surface AnatomyDocument236 paginiThe A To Z of Surface AnatomyAspenPharma83% (6)
- Cells Immune System Click Learn WorksheetDocument3 paginiCells Immune System Click Learn WorksheetAngie Gabriela Rivera RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biotechnology - Module 1-Final VersionDocument17 paginiBiotechnology - Module 1-Final VersionColourBlueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oral Histology CompendiumDocument197 paginiOral Histology Compendiumdaw022Încă nu există evaluări
- Sistem Pencernaan RuminansiaDocument37 paginiSistem Pencernaan RuminansiaIndah Fitri Sakinah LimbongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fugl-Meyer Assessment Upper Extremity (Fma-Ue) Assessment of Sensorimotor FunctionDocument3 paginiFugl-Meyer Assessment Upper Extremity (Fma-Ue) Assessment of Sensorimotor FunctionRaquel GomesÎncă nu există evaluări
- 300 MUST DO Important Topics by DR AshishDocument11 pagini300 MUST DO Important Topics by DR AshishshreyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11.2) Dihybrid Inheritance 11.3) Genes and Alleles 11.4) Inheritance in HumansDocument33 pagini11.2) Dihybrid Inheritance 11.3) Genes and Alleles 11.4) Inheritance in HumansCarmen RianaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tissues, Organs, & Organ Systems (Article) - Khan AcademyDocument28 paginiTissues, Organs, & Organ Systems (Article) - Khan AcademyImtiax LaghariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Massage 101Document33 paginiMassage 101Vladislav KotovÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fascial SpacesDocument79 paginiFascial SpacesArun MamachanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Laboratory High School Third Quarterly Exam Science and TechnologyDocument3 paginiLaboratory High School Third Quarterly Exam Science and TechnologyEsther Suan-LancitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- INTRAPARTAL CARE - MaternalDocument8 paginiINTRAPARTAL CARE - MaternalMae CalicaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biomechanics Unit 3Document24 paginiBiomechanics Unit 3RajuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Out 9Document7 paginiOut 9Ilvita MayasariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tessa Thomas - The 10-Minute Facelift - Lessen The Signs of Ageing The Natural Way-Hamlyn (2001)Document132 paginiTessa Thomas - The 10-Minute Facelift - Lessen The Signs of Ageing The Natural Way-Hamlyn (2001)Defne Güller100% (1)
- Placental AbnormalitiesDocument3 paginiPlacental AbnormalitiesThakoon TtsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 6 - Tissues Revision NotesDocument4 paginiChapter 6 - Tissues Revision NotesAbhishek100% (1)
- Muscle Testing: Knee Flexion + ExtensionDocument38 paginiMuscle Testing: Knee Flexion + ExtensionHaruka HaganeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Orthopedic Surgical InstrumentsDocument91 paginiOrthopedic Surgical InstrumentsDelvine AderoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physiologic Changes in Aging Affecting Various SystemsDocument27 paginiPhysiologic Changes in Aging Affecting Various SystemsMina75% (4)