Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Zafar 14 PDF
Încărcat de
SomiZafar0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
46 vizualizări1 paginăThe vertebral column forms the main part of the axial skeleton. Vertebral foramen is circular and smaller than the foramina of cervical and lumbar vertebrae. The longissimus, a deep or intrinsic back muscle, is innervated by dorsal rami.
Descriere originală:
Titlu original
zafar 14.pdf
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentThe vertebral column forms the main part of the axial skeleton. Vertebral foramen is circular and smaller than the foramina of cervical and lumbar vertebrae. The longissimus, a deep or intrinsic back muscle, is innervated by dorsal rami.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
46 vizualizări1 paginăZafar 14 PDF
Încărcat de
SomiZafarThe vertebral column forms the main part of the axial skeleton. Vertebral foramen is circular and smaller than the foramina of cervical and lumbar vertebrae. The longissimus, a deep or intrinsic back muscle, is innervated by dorsal rami.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 1
Answers and Explanations
1. (E) The vertebral column forms the main part
of the axial skeleton (Moore, p 432).
2. (D) The articular processes contain superior
facets directed superoposteriorly (Moore, p 439).
3. (B) The vertebral foramen is circular and smaller
than the foramina of cervical and lumbar verte-
brae (Moore, p 441).
4. (A) The body is massive and kidney-shaped
when viewed superiorly. The vertebral foramen
is triangular and larger than the foramina in tho-
racic vertebrae and smaller than those in cervi-
cal vertebrae. The transverse processes are long
and slender and contain accessory processes.
The articular processes contain mammillary pro-
cesses. The spinous processes are short, thick,
and broad (Moore, p 442).
5. (E) There is no intervertebral disc between the
C1 and C2 vertebrae (Moore, p 451).
6. (D) The posterior longitudinal ligament helps
prevent hyperexion of the vertebral column
(Moore, p 451).
7. (A) Spinal arteries supplying the vertebrae are
branches of the vertebral and ascending cervical
arteries in the neck, posterior intercostal arteries
in the thorax, subcostal and lumbar arteries in
the lumbar region, and iliolumbar and lateral
and medial sacral arteries in the pelvis (Moore,
p 467).
8. (E) The longissimus, a deep or intrinsic back
muscle, is innervated by dorsal rami. All super-
cial or extrinsic back muscles except the trape-
zius, which is innervated by the accessory nerve,
are innervated by ventral rami (Moore, p 467).
9. (A) The serratus posterior inferior is an inter-
mediate extrinsic back muscle (Moore, p 467).
10. (A) The splenius capitis and cervicis, when act-
ing together, extend the head and neck (Moore,
p 468).
11. (C) The erector spinae muscles extend the ver-
tebral column and head when acting bilaterally,
control exion of the back by gradually length-
ening their bers, and bend the vertebral column
laterally when acting unilaterally (Moore, p 470).
12. (C) The spinalis is a member of the erector spinae
muscles, which comprise the intermediate mus-
cle layer of the back (Moore, p 470).
13. (C) The transversospinalis muscles do not ele-
vate the ribs to assist inspiration (Moore, p 470).
14. (E) The spinalis inserts on spinous processes
not transverse processes. The semispinalis, multi-
fidus, rotatores, and intertransversarii all attach to
transverse processes of vertebrae (Moore, p 470).
15. (A) The longus colli exes the cervical inter-
vertebral joints but does not bend them laterally
(Moore, p 473).
16. (C) Because of their small size and lack of
mechanical advantage, it has been proposed
that the rotatores are likely to be organs of pro-
prioception instead of producers of motion
(Moore, p 474).
7
0523-01 Chap 1 7/17/02 3:25 PM Page 7
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Anatomy and Physiology of The SpineDocument12 paginiAnatomy and Physiology of The SpineKinahZildredBibitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Osteology Vertebra ServicalDocument3 paginiOsteology Vertebra ServicalDefaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter Two 2.1 Anatomy of The Human NeckDocument24 paginiChapter Two 2.1 Anatomy of The Human NeckOppong Kwadwo SamuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spine AnatomyDocument8 paginiSpine Anatomyvishramki2009Încă nu există evaluări
- Answers and Explanations: (Moore, P 846)Document1 paginăAnswers and Explanations: (Moore, P 846)SomiZafarÎncă nu există evaluări
- AD 5 Vertebral AnatomyDocument37 paginiAD 5 Vertebral AnatomyLintang ZerlinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11 Axial Division of The Skeletal SystemDocument10 pagini11 Axial Division of The Skeletal SystemMira Chariza Therese A. - BSN 1- CÎncă nu există evaluări
- Skeletal System OutlineDocument7 paginiSkeletal System Outlineapi-294104473Încă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy PcketDocument16 paginiAnatomy PcketHanya BelajarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy 2Document2 paginiAnatomy 2Adrienne Chelsea GabayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maktab Rendah Sains Mara Pengkalan Hulu, Perak.: Biology Notes (CHAPTER 2-4)Document38 paginiMaktab Rendah Sains Mara Pengkalan Hulu, Perak.: Biology Notes (CHAPTER 2-4)Nurul Aisyah ZakariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vertebra: StructureDocument9 paginiVertebra: StructureayudhyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human Muscle SystemDocument5 paginiHuman Muscle SystemBan DitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bab IDocument18 paginiBab ISulvina IbrahimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spine Biomechanics: Mer/Bio Soft Tissue Mechanics SB-1Document11 paginiSpine Biomechanics: Mer/Bio Soft Tissue Mechanics SB-1Sarah Magdy100% (1)
- Spinal Plates and Rods OverviewDocument4 paginiSpinal Plates and Rods OverviewAbby SerranoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit VIIIb Lecture NotesDocument4 paginiUnit VIIIb Lecture NotesSteve Sullivan100% (1)
- Zoology Act 4Document3 paginiZoology Act 4Marrion PenieroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vertebral TechniquesDocument24 paginiVertebral TechniquesOnofrei Oana ElenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1-Musculoskeletal SystemDocument113 paginiChapter 1-Musculoskeletal SystemWang Ming YaÎncă nu există evaluări
- StructureDocument7 paginiStructureNeirfla WassabiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ex7 Libres Frix PhBioSci18Lab 1BDocument8 paginiEx7 Libres Frix PhBioSci18Lab 1BFrix LibresÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2ND Grading Laboratory SheetsDocument16 pagini2ND Grading Laboratory SheetsAllecia Leona Arceta SoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Myofascial Meridians Trigger Points Tend To Develop Along "Myofascial Meridians"Document4 paginiMyofascial Meridians Trigger Points Tend To Develop Along "Myofascial Meridians"Corduneanu MonalisaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Form 5 Biology (Chapter 2: Locomotion & Support)Document14 paginiForm 5 Biology (Chapter 2: Locomotion & Support)NorhalizaIsmailÎncă nu există evaluări
- ANATOMYDocument6 paginiANATOMYFawzi JarkinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dental Distress Syndrome QuantifiedDocument29 paginiDental Distress Syndrome QuantifiedNenad Petrövic100% (1)
- Shoulder: Jump To Navigation Jump To Search Shoulder (Disambiguation)Document6 paginiShoulder: Jump To Navigation Jump To Search Shoulder (Disambiguation)GeorgeÎncă nu există evaluări
- NeuroanatomyDocument34 paginiNeuroanatomyAnonymous -Încă nu există evaluări
- Muscle Origin Insertion Innervation ActionDocument6 paginiMuscle Origin Insertion Innervation ActionmcwnotesÎncă nu există evaluări
- LabSci1 Lab Ex15Document10 paginiLabSci1 Lab Ex15Hannah MondillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spinal Curves ScoliosisDocument22 paginiSpinal Curves ScoliosisJennifer Mann100% (1)
- The Dental Distress Syndrome QuantifiedDocument37 paginiThe Dental Distress Syndrome QuantifiedDentalbay GrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human Anatomy Physiology Chapter 4 Osseous System NotesDocument17 paginiHuman Anatomy Physiology Chapter 4 Osseous System Notesmanku9163Încă nu există evaluări
- Movement and LocomotionDocument8 paginiMovement and LocomotionRonnith NandyÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Moore, P 1016) .: 7: The Head and NeckDocument1 pagină(Moore, P 1016) .: 7: The Head and NeckSomiZafarÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Intrinsic Back Muscles - Attachments - Actions - TeachMeAnatomyDocument5 paginiThe Intrinsic Back Muscles - Attachments - Actions - TeachMeAnatomymohammed abidieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Locomotion 2Document21 paginiLocomotion 2medina ainabaevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 4-6 Lesson Summarty Pe 1Document7 paginiUnit 4-6 Lesson Summarty Pe 1Vergel CallejaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biomechanics of The Vertebral ColumnDocument44 paginiBiomechanics of The Vertebral ColumnVijay PradeepÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4th Report SkeletonDocument14 pagini4th Report SkeletonAndi NurhidayahÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2nd Grading Activity SheetsDocument22 pagini2nd Grading Activity SheetsXella RiegoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy 2019 1Document6 paginiAnatomy 2019 1YMORÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Extrinsic Muscles of The Back - Anatomy of The TorsoDocument1 paginăThe Extrinsic Muscles of The Back - Anatomy of The TorsoNasan ShehadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bones of The Trunk LessDocument22 paginiBones of The Trunk LessYakshender AhlawatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thoracic Vertebrae Articulate Ribs Rib CageDocument4 paginiThoracic Vertebrae Articulate Ribs Rib CageNeirfla WassabiÎncă nu există evaluări
- A2 AnatomyDocument3 paginiA2 AnatomyAmir HaziziÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Form 5 Chapter 2:locomotion and Support: To: Mrs AnnamalDocument25 paginiBiology Form 5 Chapter 2:locomotion and Support: To: Mrs AnnamalAnnamal ArulnathanÎncă nu există evaluări
- GROUP 8 - Chapter 10 - Muscular System Gross AnatomyDocument145 paginiGROUP 8 - Chapter 10 - Muscular System Gross Anatomygooglegirl18Încă nu există evaluări
- Biomechanics of Human SpineDocument41 paginiBiomechanics of Human Spinebisnismail88Încă nu există evaluări
- About Erector SpinaeDocument10 paginiAbout Erector SpinaeAnnas Diah L.Încă nu există evaluări
- Skeletal System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument21 paginiSkeletal System Anatomy and PhysiologyCherie Mae SuazoÎncă nu există evaluări
- ProQuestDocuments 2022 03 01Document11 paginiProQuestDocuments 2022 03 01Éoghan McCulloughÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cervical SpondylosisDocument46 paginiCervical SpondylosisWalter Burton100% (1)
- Bones & JointsDocument18 paginiBones & Jointsroychanchal562Încă nu există evaluări
- ACT 5 - Skeletal - Lab Sheet 2 Copy KoDocument12 paginiACT 5 - Skeletal - Lab Sheet 2 Copy KoMariah Ray RintÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.review OsteoarthritisDocument22 pagini1.review OsteoarthritisGERSON RYANTOÎncă nu există evaluări
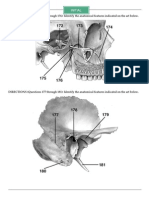
- DIRECTIONS (Questions 157 Through 161) : Identify The Anatomical Features Indicated On The Art BelowDocument1 paginăDIRECTIONS (Questions 157 Through 161) : Identify The Anatomical Features Indicated On The Art BelowSomiZafarÎncă nu există evaluări
- DIRECTIONS (Questions 147 Through 151) : Identify The Anatomical Features Indicated On The Art BelowDocument1 paginăDIRECTIONS (Questions 147 Through 151) : Identify The Anatomical Features Indicated On The Art BelowSomiZafarÎncă nu există evaluări
- DIRECTIONS (Questions 152 Through 156) : Identify The Anatomical Features Indicated On The Art BelowDocument1 paginăDIRECTIONS (Questions 152 Through 156) : Identify The Anatomical Features Indicated On The Art BelowSomiZafarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zafar 147Document1 paginăZafar 147SomiZafarÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Moore, P 1016) .: 7: The Head and NeckDocument1 pagină(Moore, P 1016) .: 7: The Head and NeckSomiZafarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Answers and Explanations: 109-156Document1 paginăAnswers and Explanations: 109-156SomiZafarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zafar 143Document1 paginăZafar 143SomiZafarÎncă nu există evaluări
- DIRECTIONS (Questions 172 Through 176) : Identify The Anatomical Features Indicated On The Art BelowDocument1 paginăDIRECTIONS (Questions 172 Through 176) : Identify The Anatomical Features Indicated On The Art BelowSomiZafarÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Back: QuestionsDocument1 paginăThe Back: QuestionsSomiZafarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zafar 141Document1 paginăZafar 141SomiZafarÎncă nu există evaluări
- DIRECTIONS (Questions 162 Through 166) : Identify The Anatomical Features Indicated On The Art BelowDocument1 paginăDIRECTIONS (Questions 162 Through 166) : Identify The Anatomical Features Indicated On The Art BelowSomiZafarÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Moore, P 846) .: Answers and Explanations: 1-39Document1 pagină(Moore, P 846) .: Answers and Explanations: 1-39SomiZafarÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Moore, P 486) .: 1: The BackDocument1 pagină(Moore, P 486) .: 1: The BackSomiZafarÎncă nu există evaluări
- DIRECTIONS (Questions 182 Through 186) : Identify The Anatomical Features Indicated On The Art BelowDocument1 paginăDIRECTIONS (Questions 182 Through 186) : Identify The Anatomical Features Indicated On The Art BelowSomiZafarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zafar 12Document1 paginăZafar 12SomiZafarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zafar 13Document1 paginăZafar 13SomiZafarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zafar 10Document1 paginăZafar 10SomiZafarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zafar 11Document1 paginăZafar 11SomiZafarÎncă nu există evaluări
- One Best-Answer-Single Item QuestionDocument1 paginăOne Best-Answer-Single Item QuestionSomiZafarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Answers, Explanations, and References: Zinsser's Microbiology. 20th Ed. Norwalk, Conn: AppleDocument1 paginăAnswers, Explanations, and References: Zinsser's Microbiology. 20th Ed. Norwalk, Conn: AppleSomiZafarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zafar 9Document1 paginăZafar 9SomiZafarÎncă nu există evaluări
- This Page Intentionally Left BlankDocument1 paginăThis Page Intentionally Left BlankSomiZafarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zafar 2Document1 paginăZafar 2SomiZafarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zafar 149Document1 paginăZafar 149SomiZafarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zafar 4Document1 paginăZafar 4SomiZafarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Appleton & Lange Review of Anatomy, Sixth Edition: NoticeDocument1 paginăAppleton & Lange Review of Anatomy, Sixth Edition: NoticeSomiZafarÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Case Study On Exley Chemical CompanyDocument12 paginiAn Case Study On Exley Chemical CompanyChristian JimmyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chromium ProcessDocument5 paginiChromium Processgalati12345Încă nu există evaluări
- T Box 12-280Document4 paginiT Box 12-280Bibi DanilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Installing Windows 7: Part 1: Setting BiosDocument5 paginiInstalling Windows 7: Part 1: Setting BiosChristine143Încă nu există evaluări
- 04 - Dynanet I PDH UpdateDocument6 pagini04 - Dynanet I PDH Updatematt1606Încă nu există evaluări
- Etiology of Malocclusion Local FactorsDocument13 paginiEtiology of Malocclusion Local FactorsAshis BiswasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stressors Daily HasslesDocument2 paginiStressors Daily Hasslesdebbie96Încă nu există evaluări
- Light ScratteringDocument27 paginiLight ScratteringKenix ChanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fifa World Cup 2022Document25 paginiFifa World Cup 2022paraschiv_alexandruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 11 Menu Engineering and AnalysisDocument8 paginiChapter 11 Menu Engineering and AnalysisArifin FuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pittman GM9236S027Document0 paginiPittman GM9236S027Nicola's SacÎncă nu există evaluări
- Megazyme Brewing Flyer 2011Document2 paginiMegazyme Brewing Flyer 2011Megazyme International IrelandÎncă nu există evaluări
- Common Base CharaDocument3 paginiCommon Base Charamaheswarysreenath100% (1)
- Curled Metal Inc CalculationDocument3 paginiCurled Metal Inc CalculationOnal Raut50% (2)
- Simple Carburetor OperationDocument6 paginiSimple Carburetor OperationHassan Mehdi100% (1)
- Reduction and Oxidation ActivityDocument3 paginiReduction and Oxidation ActivitysharinhanumÎncă nu există evaluări
- DBXLH 6565a VTMDocument4 paginiDBXLH 6565a VTMAlem MeleseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Outline For Each TopicDocument2 paginiOutline For Each TopicJuan LamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Air SpeedsDocument2 paginiAir SpeedsmgskumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clearances From Electric Supply LinesDocument6 paginiClearances From Electric Supply LinesPrashant MohokarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sss20102011 Slide Otoacoustic EmissionsDocument11 paginiSss20102011 Slide Otoacoustic EmissionsWendi Perd'sÎncă nu există evaluări
- Timetable and Traffic 2008 AbDocument1 paginăTimetable and Traffic 2008 AbDwi Beni IswadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Construction ProcessDocument3 paginiConstruction Processchandanbansal94Încă nu există evaluări
- Astm A325Document2 paginiAstm A325ingsabrinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECE141Document4 paginiECE141Shiela UbalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bunker SiloDocument1 paginăBunker SiloRedouane FirdaoussiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Distributor Installation: Crankshaft Position Sensor RemovalDocument2 paginiDistributor Installation: Crankshaft Position Sensor RemovalKeyboardMan1960Încă nu există evaluări
- Your Partner in Condition MonitoringDocument22 paginiYour Partner in Condition MonitoringAnonymous ffje1rpaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phone Service Browser Web BrowserDocument3 paginiPhone Service Browser Web Browserrudy_423522658Încă nu există evaluări
- Acuerdo Entre Argentina y El Club de ParisDocument2 paginiAcuerdo Entre Argentina y El Club de ParisINFOnewsÎncă nu există evaluări