Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Oral Liquid Manufacturing PDF
Încărcat de
Ricardo BernardDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Oral Liquid Manufacturing PDF
Încărcat de
Ricardo BernardDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
ORAL LIQUID MANUFACTURING
INTRODUCTION
Oral liquid market size in India is estimated at Rs. 2,176 crore accounting for about 10% of the
total domestic pharmaceutical industry. The oral liquids are consumed in about 9 major
therapeutic segments in India.
Top 6 therapeutic segments accounts for about 73% of the total domestic oral liquid sales. The
total oral liquid market in NER is estimated at around Rs. 86 crore in the year 2001-02. The NER
oral liquid market is about 4% of the total domestic oral liquid market.
As far as oral liquids are concerned, high prevalence of common cough and cold in NER, makes
it very large and attractive market. Also, the NER suffers from diseases related to hygiene and
cleanliness problems like Malaria, Diarrhoea, etc.
Substantial portion of the population suffers from acute acidity problems. Among other common
health-related problems identified are Vitamin deficiency, Anaemia, J oint-pain and
inflammation, etc. among others, which can be catered by the Oral Liquid manufacturing unit.
Based on the demand-supply analysis, common disease prevalent and other health-related
problem, the following categories are identified, which have significant demand in the North-
East Region (NER) as well as at national level.
Cough Preparations
Cold Preparations
Antianaemic Preparations
Vitamins
Antacids
In case of the oral liquid products, with the same infrastructure, a unit can manufacture a
multiple therapeutic segments without significant changes in the equipment, tools and processes.
MARKET POTENTIAL
Exhibit 1 provides the major oral liquid therapeutic segments and their sizes in terms of All India
domestic oral liquid market and NER oral liquid market.
Exhibit 1
(Unit: Rs. crore)
Major Therapeutic Segments for Oral Liquid Market
Particulars All India
Market Size
NER Market
Size
Cough and Cold Preparation 804 27
Antianaemic Preparations 271 8
Vitamins 206 10
Antacid, Antiflatulents 165 8
Antibiotic, Antibacterial 82 2
Antiinflammatory, Antirheumatic 60 2
Total 2,176 86
Source: AFF Research
Cough and cold preparations are the most important therapeutic segment as far as the oral liquids
are concerned. It accounts for about 37% of the all India oral liquid market size and about 31%
of NER oral liquid market size. Antianaemic preparations and Vitamins and Antacids,
Antiflatulents are other important categories in oral liquids.
The estimated growth rate for all India oral liquid market is about 4 to 5% while in NER it is
estimated to be growing at about 16 to 18% over past 5 years. Considering the same growth rate,
the domestic oral liquid market in India is estimated to be Rs. 3,380 crore in the year 2011-12.
The NER oral liquid market is estimated to grow at about 16% over next 10 years. In the year
2011-12, the NER market for oral liquids is estimated to be Rs. 378 crore.
PLANT CAPACITY AND PRODUCTION TARGETS
Plant capacity and production targets for the proposed unit have been arrived at based on
following factors:
Product Mix (based on various therapeutic segments proposed for manufacturing)
Demand : Supply Gap (in the North East Region)
Minimum Economic Plant Size- The economic size for manufacturing for NER region is
500 litre batch size (Based on the discussion with large pharmaceutical manufacturers and
various units involved in contract manufacturing).
Rated Capacity of the key equipment
The proposed plant will have a batch size of 500 litres in one shift and will operate on a single
shift basis. With sales realisation of Rs. 3.06 crore, the manufacturing unit will be accounting for
about 6 to 8% of the total NER oral liquid market (considering sales realisation for the contract
manufacturing units about 50 to 60% of the actual retail value of the products, as the units are
involved in contract manufacturing).
It is proposed that the unit would be involved in contract manufacturing for a larger
pharmaceutical company. It would primarily cater to the needs of the NER. But would not be
restricted to the NER alone.
Taking an optimistic outlook, there is potential for about 15 to 16 oral liquid manufacturing units
of similar size in NER, which could leverage the opportunity in the NER. The manufacturing
potential is based on the following
Sales realisation for contract manufacturing unit (and the retail value of the same)
Demand-supply gap existing in NER
Number of large pharmaceutical players active in the NER oral liquid market (as contract
manufacturing will be considered for only large players and also, one contract
manufacturer would be engaged in manufacturing oral liquid for only one players as
secrecy of formulation is critical issue in pharmaceutical industry) and manufacturing
products, which are non-competing in nature.
Summing up:
Batch Size: 500 Litres on a single batch basis (one batch per day)
Plant Capacity: 29 lac bottles per annum (50 ml per bottle)
Capacity Utilisation: 25% (Year 1)
Full Capacity Utilisation: Year 3
RAW MATERIALS AND INPUTS
Raw Materials
Raw materials used in the process depend upon the drug manufactured. Typically, in any drug
manufactured there are two types of raw materials used:
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs)
Excipients
Water
The requirement of water for 500-litre batch oral liquid-manufacturing unit is approximately
3,500 Litres per day.
ELECTRICITY
Approximate power requirement of a 500-litre batch oral liquid-manufacturing unit is 30 kW,
which can be availed from the nearest sub-station of respective State Electricity Board (SEB).
MANUFACTURING PROCESS
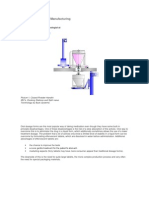
The flow chart for the manufacturing process is as shown below in the Exhibit .
Exhibit
Flow Chart for Oral liquid Manufacturing Process
The oral liquid manufacturing process is a batch process. Initially, the raw material goes through
a Quality Check (QC) and if approved various Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (API) and
Excipients are dispensed for processing.
Sugar Syrup Preparation
(Tank 1)
Mixing of API
(Tank 2)
Storage before Bottle Filling
(Tank 3)
QC
Test
Co Mill and
Homogenizer
QC Not Approved
Reject
Recover
Inspection
Labeling Machining
Cup Dispensing
(If required)
IPQC
QC Not
Approved
Reject
Bottle Filling & Capping
M/C
QC Approved
Secondary Packing
QC Approved Product
Not Approved
Reject
Recover
Raw Material
Handling and
Mixing
Bottling
Labelling
Product Packing
In the tank 1 all the excipients are mixed with the sugar syrup. The mixture of sugar syrup and
excipients is taken to the tank 2 where Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) are mixed.
The solution from the tank 2 is taken to the co-mill and homogenizer where all the raw materials
are mixed uniformly to form a homogeneous solution. This solution is pumped into the tank 3
where it is stored before filling in the bottles.
At this stage, a Quality Check is carried out to check various quality-related aspects of the raw
materials. It the solution is approved during the quality check, it is taken to the filling section.
In the filling section, the bottles are filled as per the requirement where the specified quantity is
dispensed by the machine. After filling the bottle, the capping takes place and the bottle is
sealed. The sealed bottle, is taken for inspection where the bottle is checked for quality related
aspects like
Right amount of liquid filled in the bottle
Bottle is air tight and sealed properly
Any cracks in the bottle
Leakage of liquid from the bottle, etc.
After filling the bottle, the labelling takes place. In labelling section, the various manufacturing
details are printed onto the primary pack like batch number, date of manufacturing, maximum
retail price of the therapeutic, etc. as required by Food and Drugs Act.
Additionally, secondary packing is done for the oral liquids in cardboard boxes and in corrugated
boxes. The packed oral liquids go through QC for final inspection.
QUALITY, STANDARDS AND TECHNOLOGY
The plant should adhere to the norms laid out in Indian Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP)
standards. Additionally, if the unit is set-up for export of pharmaceutical products then should
meet the norms of US FDA, UK MCA, WHO, etc. as required in the export markets.
It should be noted that as the proposed unit would be involved in contract manufacturing, the
manufacturing process related technology would be provided by the principal organisation for
which the contract manufacturing would be carried out. The proposed unit would not be involved
in the basic formulations related research in the initial years.
Additionally, the manufacturing technology for NE region would not differ from other regions as
the same is not region specific. As far as the oral-liquid manufacturing equipment is concerned,
the process equipment is widely available in the country.
KEY ASSUMPTIONS
The key assumptions made while preparing the project profile are detailed below:
The plant is a single assembly line unit. Unit operates in a single shift basis. Eight working
hours per shift.
Unit operates for 300 working days in a year
Unit has a batch size of 500 litres
The land for the unit is assumed to be in a notified area. The land is taken on a long-term
lease. As per the norms, fixed charges for land development are considered at Rs 250 per
sq. mtr. Additionally, lease rentals are assumed at Rs. 3.5 per sft.
The costs of the raw materials, packing materials, utilities like fuel, electricity, etc are
considered constant for simplicity purpose. Cost of various other activities like manpower
is assumed to be constant. Sales realisation for finished goods is also assumed constant for
10 years from the year of commencement .
Sr.
No.
Items Value Basis
1. Land development Development
charges: Rs. 250
per sq. mtr.
Lease Rentals:
Rs. 3.5 per sft.
2. Machinery and equipment
cost
--- Costs of leading machinery
suppliers inclusive of installation
charges
3. Miscellaneous fixed assets --- Industry norm
4. Provision for contingency 10% of total
capital
expenditure
Assumption
5. Raw material prices --- Landed cost (including
transportation)
6. Labour --- Prevalent rate in NER (Guwahati,
Assam)
7. Power and fuel --- Prevalent charges in Assam
8. Repair and maintenance --- Industry norm
9. Inventory: Raw materials
(RM)
2 Months Industry norm
10. Inventory: Finished goods
(FG)
1 Month Industry norm
11. Bills receivable 1 Month Industry norm
12. Creditors 1 Month Industry norm
13. Product distribution
expenses
7% Taking into consideration average
distribution costs.
14. Other Expenses --- Includes cost of conversion during
manufacturing (i.e. utilities) and
variable product distribution costs
15. Interest on working capital 9% 3% subsidy on working capital
loan under the Central Interest
Subsidy Scheme, 1997
16. Subsidy on plant and
machinery
15% Under the Central Capital
Investment Subsidy Scheme,
1997
17. Subsidy on insurance
premium
100% Under the Central Comprehensive
Insurance Scheme, 1997
18. Subsidy on Income Tax 100%
19. Debt : Equity ratio 60 : 40 Industry norm
20. RM cost Landed cost at the factory gate
(inclusive of transportation cost
and excise duty)
FINANCIAL ASPECTS
Sr.
No.
A. LAND AND SITE DEVELOPMENT
Particulars Units Unit Rate Total (Rs.)
1. Land and Site
Development
250 sq. m. Rs. 250/ sq. m. 62,500
Total 62,500
Sr.
No
.
B. BUILDING AND CIVIL WORKS
Particulars Units Unit Rate Total (Rs.)
1. Building and Civil Work
200 sq. m. Rs. 7,500/ sq. m. 1,500,000
Total 1,500,000
Sr.
No.
C. PLANT AND MACHINERY
Particulars Quantity
(Nos.)
Unit Cost
(Rs.)
Total Cost
(Rs.)
Manufacturing Equipment
1 Manufacturing Vessels 3 nos. 300,000 900,000
2 Co-mill and Homogenizer 1 nos. 200,000 200,000
3
Rotary bottle washing machine
(60 bottles per minute)
1 nos. 300,000 300,000
4
Automatic Bottle Filling and
Capping Machine
1 nos. 900,000 900,000
5
Inspection Machinery (2
Station)
1 nos. 100,000 100,000
6
Labeling Machine (120 bottles
per minute)
1 nos. 250,000 250,000
7
Cups Dispensing Machine
(Automatic)
1 nos. 150,000 150,000
Testing Equipment
8 PH Meter 1 nos. 10,000 10,000
9 Balances 1 nos. 30,000 30,000
10
UV Spectrophotometer 1 nos. 100,000 100,000
11 HPLC 1 nos. 1,300,000 1,300,000
12 IR Spectrophotometer 1 nos. 150,000 150,000
13 Dissolution Tester 1 nos. 120,000 120,000
14 Other Testing Machinery 1 nos. 203,000 203,000
Utilities/ Misc. Other Equipment
15
Air Handling Units, Ventilation,
AC Ducting, etc.
6,000,000
16
Electrification, Control Panels
and Cabling, Transformer, etc.
3,000,000
17
Water Plant, Generation and
Distribution
2,500,000
Sr.
No.
Particulars Quantity
(Nos.)
Unit Cost
(Rs.)
Total Cost
(Rs.)
18
Steam Generation Units,
Compressors
600,000
Total Machinery, Utilities and
Equipment
16,813,000
Note: Above-mentioned equipment is indicative list for the proposed oral liquid-manufacturing unit
Sr. No.
D. MISCELLANEOUS FIXED ASSETS
Particulars Total (Rs.)
1 Furniture and Fittings 25,000
2 Office Equipment 100,000
3 Fire Fighting Equipment 50,000
4 Cost Of Tube-well 20,000
Total Misc. Fixed Assets 195,000
Sr. No.
E. PRELIMINARY AND PRE-OPERATIVE EXPENSES
Particulars Total Cost (Rs.)
1 Detailed Techno-economic Feasibility Study 100,000
2 Loan Processing Fees 10,000
3 Establishment expenses 200,000
Total Preliminary & Preoperative Expenses 310,000
Provision for contingency- @ 10% of the Total Capital Investment
F. PROVISION FOR CONTINGENCY
OPERATING COSTS
Raw materials consumed differ significantly from product to product in pharmaceutical industry.
Hence, average cost of raw materials is considered for simplicity purpose.
A. RAW MATERIAL
Sr. No. Particulars Units Total
1 Average cost of raw material Rs. per
kg. 102
2 Raw materials consumed per batch Kg. 500
3 Number of batches per year Nos. 300
Total raw materials consumed per annum Rs. 15,300,000
Note: Above raw material consumption pattern is calculated at 100% capacity utilisation of the
manufacturing unit working for 300 days per annum and a single shift per day basis.
B. LABOUR
Sr.
No.
Particulars Qualification Nos. Salary
per
Month
(Rs.)
Annual
Manpower
Cost
(Rs.)
Direct Labour
1 Factory Manager BE/B.Tech +
MBA/MMS
1 20,000 264,000
2 Production Manager BE/B.Tech 1 15,000 198,000
3 Chemists BE/B.Tech 6 12,000 950,400
4 Engineer and Technicians BE/B.Tech 3 10,000 396,000
5 Skilled Workers BE 4 5,000 264,000
6 Semi-skilled and Un-skilled Workers Matriculate 8 3,000 316,800
7 Other Misc. Personnel 6 2,500 198,000
Total Direct Labour Cost 29 2,587,200
Indirect Labour
8 Finance Manager MBA/MMS +
CA
1 15,000 198,000
9 Accountant CA 1 10,000 132,000
10 Business Development Executives Graduate 1 8,000 105,600
11 Security Personnel 3 3,000 118,800
Total Indirect Labour 6 554,400
Total Cost of man-power 35 3,141,600
Note: (1) Manpower cost also includes Perks @ 10% of annual salary
(2) There is no specific requirement of other highly skilled and specifically trained manpower apart from
the normally available qualified manpower as mentioned above at the proposed manufacturing location.
Particulars
C. POWER AND FUEL
Units Consumption
per day
Unit Cost
(Rs.)
Annual Cost
(Rs.)
Electricity (30 kW) Units 717 6 1,290,000
Furnace Oil Litres 75 8 180,000
Water Litres 3,500 0 0
Total 1,470,000
Source: It is assumed that ground water is tapped through tubewell and hence water is considered free of
cost.
Sr. No.
D. OTHER EXPENSES
Particulars Total Cost
(Rs.)
Fixed
1 Repairs and maintenance 1,415,000
2 Business Development expenses 500,000
3 Lease rent for land 105,000
4 Office Administration and other misc. expenses
100,000
5 Professional and legal fees 300,000
6 Bank charges and commissions 20,000
7 Printing and stationary 100,000
8 Insurance and taxes 100,000
Total other expenses 2,640,000
E. Total Working Capital
The working capital requirement for the manufacturing unit is as indicated below.
Particulars Norms Total (Rs.)
Raw Materials 2 Months of raw materials 2,550,000
Packing
Materials
2 Month of packing materials
765,000
Finished Goods 1 Month of cost of production 1,861,500
Bills Receivables 1 Month of sales value 2,550,000
Outstandings 1 Month of Raw Material and Packing Material 1,657,500
Total 6,069,000
Note: 1. Working capital requirement indicated above is at 100% capacity utilisation.
2. Margin money @ 25% of total Working Capital Rs. 1,517,250
The capital investment required for the project is Rs. 2.23 crore. The break-up of the capital
investment is indicated in below.
CAPITAL INVESTMENT
Sr. No. Particulars Total Value (Rs.)
1 Land and Site Development Cost 62,500
2 Building and Civil Works 1,500,000
3 Plant and Machinery 16,813,000
4 Misc. Fixed Assets 195,000
5 Preliminary and Pre-operative Expenses 310,000
6 Provisions for Contingency 1,888,050
7 Margin Money for Working Capital 1,517,250
Total Cost of the Project 22,285,800
Debt and Equity Structure
Total Cost of Project Rs. 22.28 lakhs
Promoters Equity: Rs. 8.91 lakhs
Debt Funds: Rs. 13.37 lakhs
A. Cost of Production
Sr. No. Particulars Total (Rs.)
1 Raw materials 15,300,000
2 Packing materials 4,590,000
3 Administrative overheads 2,587,200
4 Other overheads 1,470,000
5 Interest on working capital 409,658
Total cost of production 24,356,858
Note: Cost of production indicated above is at 100% capacity utilisation.
B. Turnover
Annual sales realisation of the manufacturing unit with the assumed product mix is illustrated
below. Sales realisation at 100% capacity utilisation are around Rs. 3.06 crore.
Sr.
No.
Particulars Annual Capacity-
No. of Oral Liquid
Bottles (Lakhs)
Sales
Realisation per
Bottle (Rs.)
Total Sales
Realisation
(Rs.)
1 Cough Preparation 12 12 14,400,000
2 Cold Preparation 9 8 7,200,000
3 Antianaemic Preparation
and Vitamins 6 8 4,800,000
4 Antacid 3 14 4,200,000
Total 30 30,600,000
C. Profit and Loss Statement for 10 Years
(Unit: Rs. lacs)
Particulars Formula Yr 1 Yr 2 Yr 3 Yr 4 Yr 5 Yr 6 Yr 7 Yr 8 Yr 9 Yr 10
Capacity Utilisation 25% 75% 100% 100% 100% 100% 100% 100% 100% 100%
Sales Realisation A
70 217 300 306 306 306 306 306 306 306
Operating Costs B
Raw Material and
Packaging Material
46 141 195 199 199 199 199 199 199 199
Selling and
Administration OH
31 31 31 31 31 31 31 31 31 31
3. Other Overheads
5 12 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 15
Interest on Working
Capital
1 3 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4
Gross Profit incl.
Transport Subsidy
C=A-B -13 30 55 57 57 57 57 57 57 57
Interest D 14 14 13 11 9 8 6 5 3 2
Depreciation E 29 25 22 19 16 14 12 10 9 8
PBT F=C-(D+E)
-57 -10 20 27 31 35 38 42 45 47
Tax G 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
PAT H=F-G
-57 -10 20 27 31 35 38 42 45 47
Cash Profit I=H+E -27 16 42 46 47 49 51 52 54 55
GP Margin J =C/A -19% 14% 18% 19% 19% 19% 19% 19% 19% 19%
NP Margin K=H/A -81% -4% 7% 9% 10% 11% 13% 14% 15% 16%
Note: Figures indicated above are rounded-off
Return on Investment (ROI): 11%
D. Breakeven Analysis
The breakeven analysis for the proposed oral liquid-manufacturing unit is indicated below. The
unit does not achieve operational break-even point in first two-years of operation. From third
year onwards, the unit achieves operational breaks-even.
Particulars Unit Yr 1 Yr 2 Yr 3 Yr 4 Yr 5 Yr 6 Yr 7
Capacity Utilisation (%) 25% 75% 100% 100% 100% 100% 100%
Sales Realisation Rs. lakhs 70 217 300 306 306 306 306
Variable Cost of Sales
Direct Material Rs.
lakhs 35 108 150 153 153 153 153
Packing Cost Rs.
lakhs 11 33 45 46 46 46 46
Conversion Cost Rs.
lakhs 6 17 24 24 24 24 24
Direct Labour Rs.
lakhs 26 26 26 26 26 26 26
Interest on Working
Capital
Rs.
lakhs 1 3 4 4 4 4 4
Total Variable Costs Rs. lakhs 78 187 249 253 253 253 253
Contribution Rs. lakhs -8 30 51 53 53 53 53
Fixed Costs
Other overheads (excl .
Repairs and Maintenance)
Rs.
lakhs
4 9 11 11 11 11 11
Repairs and Maintenance Rs.
lakhs 14 14 14 14 14 14 14
Manpower Cost Rs.
lakhs 6 6 6 6 6 6 6
Interest on Term Loan Rs.
lakhs 14 14 13 11 9 8 6
Total Fixed Cost Rs. lakhs 38 43 44 42 40 39 37
Break Even Point Rs. lakhs 334 311 256 244 235 226 217
Actual Sales Realiastion Rs.
lakhs
70 217 300 306 306 306 306
Break Even Sales at % of
Capacity
%
109% 101% 84% 80% 77% 74% 71%
Note: 1. Figures indicated above are rounded-off
2. Annual sales values indicated above are after taking into consideration opening and closing stocks
SOURCE OF RAW MATERIALS AND PACKING MATERIALS
The raw materials and packaging materials that are required for manufacturing pharmaceutical
products are not locally available in NER. The closest source for procuring raw materials and
packing materials is Hyderabad or Delhi.
Additionally, the raw materials and packing materials can be procured from West Cluster
(Mumbai, Daman, etc) but the cost of transportation will increase substantially.
Mentioned below are few sources of raw materials-
Ajanta Chemicals
21, Cloth Commercial Centre, Kalupur, Ahmedabad- 380002
Tel: +(91)-(079)- 2335755, 2384605
Fax: +(91)-(079)- 22121182
Alkyl Amines Chemicals Limited
207-A, Kakad Chambers, 132, Dr. A. B. Road, Worli, Mumbai- 400018
Tel: +(91)-(022)- 24925564, 24930699
Fax: +(91)-(022)- 27671932
Email: aac.vsh.@alkyl.sprintrpg.ems.vsnl.net.in
Abbott Labs (India) Limited
17 R, Kamani Marg, Mumbai- 400001
Tel: +(91)-(022)- 256319797
Email: webmaster@abbott.co.in
Gufic Chemical Private Limited
Subhash Road, A, Vile Parle (E), Mumbai- 400037
Tel: +(91)-(022)- 28341521/22, 28344523
Fax: +(91)-(022)- 28369008
Gujarat Organic Chemicals
32, GIDC, Vithal Udyognagar, Kaira, Gujarat- 388121
Tel: +(91)-(02692)- 231478, 231489
Impex India
8-2-333/ 14-A, Road No. 3, Banjara Hills, Hyderabad- 500034
Tel: +(91)-(040)- 23548409
Fax: +(91)-(040)- 23548409
Email: impex.india@gnhyd.globalnet.ems.vsnl.net.in
Indian Drugs and Pharmaceuticals Limited
P.O. Virbhadra- 249202 (Rishikesh), Utter Pradesh
Jayant Vitamins Limited
12, Bhargava Lane, Civil Lines, Delhi- 110054
Tel: +(91)-(011)- 22911653, 22519414
Lake Chemicals Private Limited
12, Ravi Kiran, Plain Street, Bangalore- 560001
Tel: +(91)-(080)- 22860394, 22866353
Fax: +(91)-(080)- 22867734
Email: md@lake.india.com
Mentioned below are few sources of packing materials-
Ajanata Packing Company
8939/1, Multani Dhanda, Paharganj, New Delhi- 110055
Tel: +(91)-(011)- 23629420, 23514419
Fax: +(91)-(011)- 23629420
Email: ajantabottle@usa.net
Boxcare Packaging Pvt. Ltd.
83, B & C Sheth Govindrao Smruti, Dr. A. B. Road, Worli, Mumbai- 400018
Tel: +(91)-(022)- 24960985, 24960986
Flexible Packaging Company
128/129, New Sadguru Nashik Industrial Estate, Goregaon (E), Mumbai- 400063
Tel: +(91)-(022)- 28733602
Fax: +(91)-(022)- 28734856
Email: vilam@bom4.vsnl.net.in
Wonderpack Industries (Pvt) Limited
PO Box No. 29127, TV Indl. Estate, S. K. Ahire Road, Worli, Mumbai- 400025
Tel: +(91)-(022)- 24936496, 24949580
Fax: +(91)-(022)- 24938796
Email: wonder@bom3.vsnl.net.in
SOURCE OF MACHINERY AND EQUIPMANT
PROCESS EQUIPMENT
Alliance Engineering Company
97, Trisandhya Building, D. Phalke Road, Mumbai- 400014
Tel: +(91)-(022) 24112461, 24156510
Fax: +(91)-(022) 24138307
Pharmalab Engineering India Limited
Star Metal Compound, L. B. S. Road, Vikhroli (W), Mumbai- 400083
Tel: +(91)-(022) 25782559
Fax: +(91)-(022) 25775219
Email: poma@gbom.3vsnl..net.in
Tapasya Engineering Works Private Limited
A-212, Road No. 30, Wagle Industrial Estate, Thane, Mumbai- 400604
Tel: +(91)-(022)- 25823250
Unipack Machines Private Limited
B-270, Joshi Wadi, Off Manpada Road, Dombivali (E), Mumbai- 421201
ABMA Machines
Plot No. 40/1, Phase I, GIDC, Ahmedabad- 382445
Ambica Engineering Works
Plot No. 1804, Phase-III, GIDC Industrial Area, Vatva, Ahmedabad- 382445
Tel: +(91)-(079) 25894796, 25830729
Gansons Limited
The Shopping Mall, Arjun Marg, DLF Qutab Enclave (Phase-I), Gurgaon- 122002
Tel: +(91)-(0124) 2359596/7
Fax: +(91)-(0124) 2359041
Neomachine Mfg. Co. Private Limited
39/2A, Purna Das Road, Kolkata- 700053
AUXILIARY EQUIPMENT
Thermax (India) Limited
Thermax House, 4, Mumbai-Pune Road, Shivajinagar, Pune- 411019
Tel: +(91)-(020)- 25512122
Fax: +(91)-(020)- 25512242
Website: www.thermaxindia.com
Atlas Copco (India) Limited
Sevanagar, Dapodi, Pune- 411012
Tel: +(91)-(020)- 27146416/17
Fax: +(91)-(020)- 27146637
Website: www.atlascopco.com
Aquatech India Limited
Plot No. 3, Baner Park, Near D. P. Road, Aundh, Pune- 411007
Tel: +(91)-(020)- 27292103, 27291104
Fax: +(91)-(020)- 7291805
Website: www.aquatech.com
Email: asa@aquatech.com
Alfa Laval (India) Limited
Shivajinagar, Pune- 4110112
Tel: +(91)-(020)- 27147721
Fax: +(91)-(020)- 27147711
Ion Exchange, Mumbai
Tiecicon House, Dr. E. Moses Road, Mahalaxmi, Mumbai- 400011
Tel: +(91)-(022)- 24939520/23/25
Fax: +(91)-(022)- 24938737
Website: www.ionindia.com
Email: ho.commun@ho.ionxchng.co.in
Courtesy:NEDFi
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Metformin FormulationDocument6 paginiMetformin Formulationsujit50% (2)
- The DR Sebi Diet Cookbook With Pictures The Nutrit - 231120 - 113343Document210 paginiThe DR Sebi Diet Cookbook With Pictures The Nutrit - 231120 - 113343suzanne100% (1)
- Master Formula Brimolol SolutionDocument3 paginiMaster Formula Brimolol SolutionSarfarazpk1Încă nu există evaluări
- Impact of Packaging Materials On Product Stability - FinalDocument54 paginiImpact of Packaging Materials On Product Stability - Finalhenrykayode4100% (1)
- Ointment BMRDocument22 paginiOintment BMRspp80% (5)
- 2 Leozinc B SyrupDocument2 pagini2 Leozinc B SyrupShagorShagorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample BMRDocument16 paginiSample BMRspp93% (15)
- Guide To Master Formulae Final 2012Document119 paginiGuide To Master Formulae Final 2012MohamedRefaatMohamedÎncă nu există evaluări
- All About You Fun Activities Games Games 57864Document1 paginăAll About You Fun Activities Games Games 57864Marce RendónÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prepared by Production: Approved by QA/QC:: NVIDAZOLE® 2500 BolusDocument17 paginiPrepared by Production: Approved by QA/QC:: NVIDAZOLE® 2500 BolusLegese HailuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Actpro Al Drysyrup 3b001Document48 paginiActpro Al Drysyrup 3b001joerichladÎncă nu există evaluări
- Care Intensive Drug Pharmaceutical CompanyDocument1 paginăCare Intensive Drug Pharmaceutical CompanyMajd Kittaneh100% (1)
- Pharmaceutical PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT FLOWCHARTDocument2 paginiPharmaceutical PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT FLOWCHARTAsif Hussain100% (15)
- Co Dabamal Tablet 9m606001Document22 paginiCo Dabamal Tablet 9m606001joerichladÎncă nu există evaluări
- 14 Ways to Improve Spoken English Without a PartnerDocument7 pagini14 Ways to Improve Spoken English Without a PartnerUmadevi ManiÎncă nu există evaluări
- MFRDocument9 paginiMFRHarshal PawarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acitral Syrup 1000litDocument4 paginiAcitral Syrup 1000litAhmad HussainÎncă nu există evaluări
- 01 BMR Placebo TabletsDocument10 pagini01 BMR Placebo TabletsIris Patrisha Abigail BalutocÎncă nu există evaluări
- Finished Product - Test ProcedureDocument13 paginiFinished Product - Test ProcedureShagorShagor100% (3)
- 10 DOH Approved Herbal Meds HandoutDocument1 pagină10 DOH Approved Herbal Meds Handoutnicole alignoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presentation Marketing and Distribution ChannelsDocument15 paginiPresentation Marketing and Distribution Channelsavtarsingsadaf_28176Încă nu există evaluări
- Production of Tablets and CapsulesDocument32 paginiProduction of Tablets and Capsulesraviteja79173% (15)
- Aphrin PFS Batch Manufacturing RecordDocument13 paginiAphrin PFS Batch Manufacturing RecordShagorShagorÎncă nu există evaluări
- SOP - Operation of Semi-Automatic Capsule Filling MachineDocument3 paginiSOP - Operation of Semi-Automatic Capsule Filling MachineKrishelle Anne Obispo75% (4)
- Batch Manufacturing Record SAMPLEDocument8 paginiBatch Manufacturing Record SAMPLETrilochan Ayurveda67% (6)
- Master Formula RecordDocument39 paginiMaster Formula RecordAbhijit kanavaje100% (1)
- GMP DOCUMENTSDocument23 paginiGMP DOCUMENTSAnonymous yBhOAi5UH100% (1)
- BMR of Vericef 500capsuleDocument17 paginiBMR of Vericef 500capsuleShagorShagor100% (1)
- Guide To Master FormulaeDocument39 paginiGuide To Master FormulaeAshok KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vatakulantka Rasa TabletDocument7 paginiVatakulantka Rasa Tabletreflectprakash3610Încă nu există evaluări
- SOP For Operation of Carton Coding MachineDocument3 paginiSOP For Operation of Carton Coding MachineJayant Kumar JhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Leon Pharmaceuticals Raw Material SpecificationsDocument11 paginiLeon Pharmaceuticals Raw Material SpecificationsShagorShagor0% (1)
- Process Validation of Ointment/Cream FormulationDocument40 paginiProcess Validation of Ointment/Cream FormulationGursharanjit Singh Shinh100% (2)
- Tablet Section Cost DR SabDocument6 paginiTablet Section Cost DR SabAbdul SamadÎncă nu există evaluări
- BIS CreamsDocument13 paginiBIS CreamsNAVNEET BAGGA100% (2)
- Masterformularecord 180319024817Document20 paginiMasterformularecord 180319024817Mucharla Praveen KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2017-02-08 Flow Process Chart SyrupsDocument1 pagină2017-02-08 Flow Process Chart Syrupsreflectprakash361075% (4)
- What Is BMR (Batch Manufacturing Record)Document2 paginiWhat Is BMR (Batch Manufacturing Record)Prince Moni100% (1)
- Production of Tablet ProjectDocument72 paginiProduction of Tablet ProjectKunal Malawat100% (1)
- Final Business PlanDocument35 paginiFinal Business Planjeanuel100% (1)
- 5-Operation & Cleaning of Ropp Sealing MachineDocument3 pagini5-Operation & Cleaning of Ropp Sealing MachineananthÎncă nu există evaluări
- Feasibility Study On Beef Cattle Development in TeDocument9 paginiFeasibility Study On Beef Cattle Development in TeMichelle Ann SoledadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aphrin 500 MG Capsule BPR 2Document16 paginiAphrin 500 MG Capsule BPR 2ShagorShagor100% (2)
- Stability Studies of Pharmaceutical & Cosmetic ProductsDe la EverandStability Studies of Pharmaceutical & Cosmetic ProductsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Training in PharmaDocument4 paginiTraining in PharmaPrince MoniÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Safire WoodDocument18 paginiThe Safire WoodPip TurenÎncă nu există evaluări
- BMR - fp025-01 v-1 Azinil Pfs 35mlDocument14 paginiBMR - fp025-01 v-1 Azinil Pfs 35mlShagorShagorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Master Formula and Manufacturing RecordsDocument7 paginiMaster Formula and Manufacturing RecordsTrilochan Ayurveda100% (1)
- Table For Cleaning SolutionsDocument1 paginăTable For Cleaning Solutionsreflectprakash3610Încă nu există evaluări
- Ratlam Training ReportDocument81 paginiRatlam Training Reportapi-1998598367% (3)
- Ointment Process ValidationDocument25 paginiOintment Process ValidationMuqeet Kazmi75% (12)
- Aphrin Pfs BPR p1 v-1Document13 paginiAphrin Pfs BPR p1 v-1ShagorShagorÎncă nu există evaluări
- cGMP Current Good Manufacturing Practices for PharmaceuticalsDe la EverandcGMP Current Good Manufacturing Practices for PharmaceuticalsEvaluare: 1 din 5 stele1/5 (2)
- HPTLC: Factors Influencing The TLC / HPTLC Separation and Resolution of SpotsDocument8 paginiHPTLC: Factors Influencing The TLC / HPTLC Separation and Resolution of Spots0921pyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Batch Manufacturing Record - Capsule FinalDocument6 paginiBatch Manufacturing Record - Capsule FinalAkik Sasmal100% (1)
- ROLE OF WAREHOUSEDocument6 paginiROLE OF WAREHOUSEPrince MoniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Get Smart Plus 1 FlashcardsDocument331 paginiGet Smart Plus 1 FlashcardsElena Ned0% (1)
- Manufacturing Formula: Product: Ctzine SyrupDocument6 paginiManufacturing Formula: Product: Ctzine SyrupMohammed ZubairÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manufacturing Formula: PRODUCT: Neuropal Suspension (Pyritinol Dihydrochloride 100mg)Document6 paginiManufacturing Formula: PRODUCT: Neuropal Suspension (Pyritinol Dihydrochloride 100mg)Mohammed ZubairÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manufacturing Formula: Product: Univit SyrupDocument6 paginiManufacturing Formula: Product: Univit SyrupMohammed ZubairÎncă nu există evaluări
- Regulation of Cosmetics in Japan PDFDocument32 paginiRegulation of Cosmetics in Japan PDFMucharla Praveen KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Procedure for release of Drug Substance and ProductsDocument4 paginiProcedure for release of Drug Substance and Productsom shankar JhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.Pv Semisolid FDADocument37 pagini2.Pv Semisolid FDARahayu Maulida RÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manufacturing Formula: PRODUCT: Medgel Suspension (Sucralfate)Document5 paginiManufacturing Formula: PRODUCT: Medgel Suspension (Sucralfate)Mohammed ZubairÎncă nu există evaluări
- GMP New PDFDocument51 paginiGMP New PDFMeha RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- BMR - Elfexo 120 TabletDocument13 paginiBMR - Elfexo 120 TabletShagorShagor100% (1)
- Effervescent Dosage ManufacturingDocument5 paginiEffervescent Dosage ManufacturingResk CavalierÎncă nu există evaluări
- SOP On Transferring Finished Products To Finished Goods StoresDocument3 paginiSOP On Transferring Finished Products To Finished Goods StoresRainMan7550% (2)
- 1285212273JH 092310 - WebDocument12 pagini1285212273JH 092310 - WebCoolerAdsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sandpoint Residents - Sheet1Document2 paginiSandpoint Residents - Sheet1Joseph NietubiczÎncă nu există evaluări
- Please Elaborate The DEFINITIONDocument3 paginiPlease Elaborate The DEFINITIONhector aceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simple Present Tense in The NegativeDocument3 paginiSimple Present Tense in The NegativecarlosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class-X Subject-English Enquiry Letter (Writing) Online AssignmentDocument94 paginiClass-X Subject-English Enquiry Letter (Writing) Online AssignmentPiyush Sharma 9-FÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class11 Nutrition Health and Well BeingDocument21 paginiClass11 Nutrition Health and Well Beingshreyanshsaha439Încă nu există evaluări
- Milling Catalogue - RevisedDocument20 paginiMilling Catalogue - Revisedpurchase Core CarbÎncă nu există evaluări
- TRADITIONS OF CHRISTMAS EVEDocument19 paginiTRADITIONS OF CHRISTMAS EVEAdrian CojocaruÎncă nu există evaluări
- 15 Days Diet Chart (Non-Veg)Document19 pagini15 Days Diet Chart (Non-Veg)amar.mygovÎncă nu există evaluări
- Patrik 1Document342 paginiPatrik 1NanoCellÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plant PartsDocument49 paginiPlant Partsshahzad18400% (1)
- Agriculture Business WeekDocument10 paginiAgriculture Business WeekadajariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Warsash Private AccommodationDocument8 paginiWarsash Private AccommodationLovepreet ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- 24604-Article Text-87708-1-10-20230805Document6 pagini24604-Article Text-87708-1-10-20230805saniaajibahÎncă nu există evaluări
- 676 - 22 Aloe VeraDocument5 pagini676 - 22 Aloe VeraZairi ZakariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Milky Mushroom Cultivation Project ReportDocument21 paginiMilky Mushroom Cultivation Project Reportuvabd15122001Încă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry, Salt Analysis and IndexDocument10 paginiChemistry, Salt Analysis and IndexRahul RajputÎncă nu există evaluări
- English - Lidia's LessonsDocument7 paginiEnglish - Lidia's LessonsValentina CabreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gerund InfinitiveDocument14 paginiGerund InfinitiveGuțaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Te: Evaluación Final, Unidad 4 (20%) : AnswerDocument5 paginiTe: Evaluación Final, Unidad 4 (20%) : AnswerESTER LEMOSÎncă nu există evaluări
- BreastfeedingDocument68 paginiBreastfeedingteabagmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ademiluyi Et AlDocument8 paginiAdemiluyi Et AlsunilbholÎncă nu există evaluări