Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
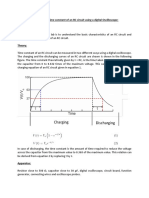
Experiment No.1: Hartley Oscillator
Încărcat de
Bhadresh RenukaTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Experiment No.1: Hartley Oscillator
Încărcat de
Bhadresh RenukaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
A.V.P.T.I. / E.C.
department /AE Page 1
EXPERIMENT NO.1
Hartley oscillator
AIM :
To build Hartley oscillator circuit, measure its frequency of oscillation and compare it
with the theoretical value.
APPARATUS :
1) D.C regulated power supply 0-30v, 2A, 1No.
2) Digital Voltmeter , 1No.
3) CRO,dual trace ,1 No.
4) Bread board.
5) Connecting wire.
COMOPNENT :
1) Transistor: BC107 or 2N3903 or 2N3904 or equivalent,1No.
2) Carbon resistor: each 1/2W, 1 No each 27k, 2.7k, 1.2k, 120k.
3) Capacitor: 0.1F, 2 no, 0.015F 1 No., 3.3F, 1 No.
4) Inductor: 200H, 1 No., 100H 1 No.
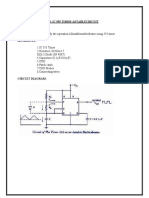
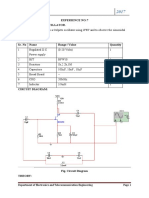
CIRCUIT
A.V.P.T.I. / E.C. department /AE Page 2
THEORY :
Circuit of a Hartley oscillator is shown in figure. Q is an NPN type transistor. R
1
and
R
2
are the biasing resistors. R
E
is the resistance connected in the emitter circuit for bias
stabilization. C
E
is the bypass capacitor. Oscillator energy is coupled to the tank circuit
formed by the two inductors L
1,
L
2 and
capacitor C. It decides the frequency of oscillation.
. R
c
is the resistance in the collector circuit.Cc
1
is the input coupling capacitor through
which the voltage developed at output is coupled to the base via tank circuit. Tank circuit
gives a phase shift of 180 degree ,so the positive feedback is given to input. This
capacitor also prevents DC entering in to the tank circuit from the base. Cc
2
is the output
coupling capacitor. Oscillation energy is coupled to the tank circuit by this capacitor this
capacitor also blokes d.c. entering the tank circuit. This is necessary because otherwise
the Q factor of the tank circuit is reduced. Output is taken as shown.
Frequency of oscillator is given by f
Where L = L
1
+ L
2
If L is in henry , C is in Farad ,f will be in Hz
PROCEDURE :
1) Prepare CRO for operation.
2) Connect the circuit as shown in the circuit diagram.
3) Apply +Vcc = 9V from the power supply.
4) Connect the CRO probes across the output terminals.
5) Obtain the waveform on the screen.
6) Measure the time period T of one complete wave and calculate the frequency of
oscillation. f=1/T hz , where T is in second
7) Calculate the theoretical value of the frequency of oscillation, f
8) Compare Meadured ( Actual frequency ) with theoretical value of the frequency
9) Switch off the supply.
A.V.P.T.I. / E.C. department /AE Page 3
OBSERVATION TABLE :
Time
period T
Frequency
Measured f=
Calculated f
CALULATION :
L = L
1
+ L
2 : =
C =
f
CONCLUSION :
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Experiment No.2: Colpitt OscillatorDocument3 paginiExperiment No.2: Colpitt OscillatorBhadresh Renuka50% (2)
- Lab3 DC Power Supply Design1588856969Document3 paginiLab3 DC Power Supply Design1588856969badalabhinav10Încă nu există evaluări
- Lab Assignment #2 Due: Oct. 5, 20 Materials Needed: Sep. 30, 20 Fall 2020Document5 paginiLab Assignment #2 Due: Oct. 5, 20 Materials Needed: Sep. 30, 20 Fall 2020api-482290211Încă nu există evaluări
- Astable Multivibrator: Non Linear Applications:-A) Astable Multivibrator B) Mono Stable MultivibratorDocument15 paginiAstable Multivibrator: Non Linear Applications:-A) Astable Multivibrator B) Mono Stable MultivibratorFarhan AkhterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Expt 6 - Colpitts Oscillator (2020)Document4 paginiExpt 6 - Colpitts Oscillator (2020)samarthÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oscillator ManualDocument22 paginiOscillator ManualckooipgÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.RC CircuitsDocument7 pagini1.RC CircuitsNaveen ChÎncă nu există evaluări
- Expt 7 - Hartley Oscillator (2020)Document4 paginiExpt 7 - Hartley Oscillator (2020)samarthÎncă nu există evaluări
- Expt 9 - Astable-Multivibrator (2020)Document5 paginiExpt 9 - Astable-Multivibrator (2020)samarth100% (1)
- Capacitor When SwitchingDocument4 paginiCapacitor When SwitchingAli AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indian Institute of Technology Ropar Electrical Engineering DepartmentDocument3 paginiIndian Institute of Technology Ropar Electrical Engineering Departmentrahul.23eez0004Încă nu există evaluări
- 120EI0884 - SamyakHinge CSL Lab RecordDocument51 pagini120EI0884 - SamyakHinge CSL Lab Recordpappu singhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wein Bridge OscillatorDocument6 paginiWein Bridge Oscillatorinspectornaresh100% (1)
- Ae Exp 9 To Design Monostable Multivibrators Using 555 IcDocument6 paginiAe Exp 9 To Design Monostable Multivibrators Using 555 IcPriyanshu KumawatÎncă nu există evaluări
- RC Circuits - George Ricarrson 2501987261Document9 paginiRC Circuits - George Ricarrson 2501987261George RYÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vco WDocument8 paginiVco Wapi-3725139Încă nu există evaluări
- Astable Multivibrator ExperimentDocument5 paginiAstable Multivibrator ExperimentShivakumar goud100% (1)
- Capacitors and Time-Dependent Signals: ConceptDocument6 paginiCapacitors and Time-Dependent Signals: ConceptsriÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7 Hartly & Collpit PDFDocument13 pagini7 Hartly & Collpit PDFengineerluv100% (1)
- Durgapur: National Institute of TechnologyDocument10 paginiDurgapur: National Institute of TechnologyBishal SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Expt - 10. Astable MultiDocument3 paginiExpt - 10. Astable Multirathod avinashÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hartley and Colpitt - S OscillatorDocument7 paginiHartley and Colpitt - S OscillatorT BlackÎncă nu există evaluări
- aeclAB 1Document41 paginiaeclAB 1ayjagadishÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab ManualDocument38 paginiLab ManualsivaÎncă nu există evaluări
- RC Phase Shift Oscillator and RC Coupled Ce Amplifier - Lab ExperimentDocument8 paginiRC Phase Shift Oscillator and RC Coupled Ce Amplifier - Lab ExperimentMani BharathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hartley OscillatorDocument3 paginiHartley OscillatorJunaid AleemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 06 RC, RL, and RLC Transients-2Document11 paginiLab 06 RC, RL, and RLC Transients-2Ece KayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Laboratory Exercise 3Document7 paginiLaboratory Exercise 3BenedictÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mit Aec Labmanula 10esl37Document45 paginiMit Aec Labmanula 10esl37anon_70724250Încă nu există evaluări
- Transient Response of RC CircuitDocument5 paginiTransient Response of RC CircuitJayesh Ruikar100% (1)
- Basic Electronics Lab (Experiment 2 Report) : Submitted By: Group: G7 Ashutosh Garg (2018MEB1213) Ashwin Goyal (2018MEB1214)Document8 paginiBasic Electronics Lab (Experiment 2 Report) : Submitted By: Group: G7 Ashutosh Garg (2018MEB1213) Ashwin Goyal (2018MEB1214)Ashutosh GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- RC Time Constant LabDocument5 paginiRC Time Constant LabLucas CasagrandeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eca Lab-Min PDFDocument87 paginiEca Lab-Min PDFAkashita SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exp5 ColpittsDocument5 paginiExp5 Colpittsmanish gowdaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Expt - 7 :transistorized Astable MultivibratorDocument4 paginiExpt - 7 :transistorized Astable Multivibratorsamarth100% (1)
- ColpittsDocument8 paginiColpittsRavi Teja100% (1)
- Recombination Time in DiodesDocument4 paginiRecombination Time in Diodesluis palominoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Daycounter Inc - Snubber Circuit Design CalculatorsDocument5 paginiDaycounter Inc - Snubber Circuit Design CalculatorsLaercio Marques100% (1)
- Experiment Guide For RC Circuits 1. CapacitorsDocument9 paginiExperiment Guide For RC Circuits 1. CapacitorsShafiqul Islam ShafiqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Low Voltage Fara TrafDocument8 paginiLow Voltage Fara TraftyutyuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Colpitts OscillatorDocument3 paginiColpitts OscillatorSakshi GosaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Astable CircuitsDocument9 paginiAstable CircuitsRavindranath ShrivastavaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application of IC 555Document6 paginiApplication of IC 555ManojkumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dwarkadas. J. Sanghvi College of EngineeringDocument8 paginiDwarkadas. J. Sanghvi College of EngineeringAbir DeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- ST - Joseph College of Engineering: SriperumbudurDocument45 paginiST - Joseph College of Engineering: SriperumbudurSuryaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 241 RLC Circuit Ac SourceDocument14 pagini241 RLC Circuit Ac SourceWsma AmswÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heartly OscillatorDocument10 paginiHeartly OscillatorMr. Kumar AilaboinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Applied Electronics Lab 2Document9 paginiApplied Electronics Lab 2Rickel RoweÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circuits Docs Labs Lab3 First and Second Order ResponsesDocument8 paginiCircuits Docs Labs Lab3 First and Second Order ResponsesCesar Santiago Bolaño SalazarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ec FinalDocument46 paginiEc FinalManjunath YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electronics Lab ManualDocument86 paginiElectronics Lab ManualLogeeswaran MurugappanÎncă nu există evaluări
- EC Lab ManualDocument27 paginiEC Lab ManualMohan KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 2 BJT SwitchDocument6 paginiExperiment 2 BJT Switchprop_kcp50% (2)
- EI Lab Exp XDocument6 paginiEI Lab Exp XtrialÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2De la EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Încă nu există evaluări
- ELEN 214 Lab Manual 7-1Document7 paginiELEN 214 Lab Manual 7-1Ratnesh ChaturvediÎncă nu există evaluări
- ADE Lab Manual - Analog Part PDFDocument21 paginiADE Lab Manual - Analog Part PDFJk RinkuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Astable Multi Vibrator: Prior To The Lab SessionDocument5 paginiAstable Multi Vibrator: Prior To The Lab SessionRiya Saluja100% (1)
- 110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorDe la Everand110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- Muhammad Firdaus - A Review of Personal Data Protection Law in IndonesiaDocument7 paginiMuhammad Firdaus - A Review of Personal Data Protection Law in IndonesiaJordan Amadeus SoetowidjojoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Car Section 2 Series (H) Part-IiDocument6 paginiCar Section 2 Series (H) Part-Iipandurang nalawadeÎncă nu există evaluări
- " Suratgarh Super Thermal Power Station": Submitted ToDocument58 pagini" Suratgarh Super Thermal Power Station": Submitted ToSahuManishÎncă nu există evaluări
- Auditing Multiple Choice Questions and Answers MCQs Auditing MCQ For CA, CS and CMA Exams Principle of Auditing MCQsDocument30 paginiAuditing Multiple Choice Questions and Answers MCQs Auditing MCQ For CA, CS and CMA Exams Principle of Auditing MCQsmirjapur0% (1)
- Directorate of Technical Education, Maharashtra State, MumbaiDocument57 paginiDirectorate of Technical Education, Maharashtra State, MumbaiShubham DahatondeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solutions Jet FuelDocument4 paginiSolutions Jet FuelkevinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Defenders of The Empire v1.4Document13 paginiDefenders of The Empire v1.4Iker Antolín MedinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Registration Form - Synergies in Communication - 6th Edition - 2017-Drobot AnaDocument3 paginiRegistration Form - Synergies in Communication - 6th Edition - 2017-Drobot AnaAna IrinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Schematic Circuits: Section C - ElectricsDocument1 paginăSchematic Circuits: Section C - ElectricsIonut GrozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Read The Dialogue Below and Answer The Following QuestionDocument5 paginiRead The Dialogue Below and Answer The Following QuestionDavid GainesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Max9924 Max9927Document23 paginiMax9924 Max9927someone elseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1: Power and Responsibility: 1. Important Leadership QualitiesDocument6 paginiUnit 1: Power and Responsibility: 1. Important Leadership QualitiesTrần Thanh MinhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Revised PARA Element2 Radio LawsDocument81 paginiRevised PARA Element2 Radio LawsAurora Pelagio Vallejos100% (4)
- 103-Article Text-514-1-10-20190329Document11 pagini103-Article Text-514-1-10-20190329Elok KurniaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPWM Vs SVMDocument11 paginiSPWM Vs SVMpmbalajibtechÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Concept of ProbabilityDocument12 paginiBasic Concept of Probability8wc9sncvpwÎncă nu există evaluări
- Operation ManagementDocument4 paginiOperation ManagementHananiya GizawÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mass and Heat Balance of Steelmaking in Bof As Compared To Eaf ProcessesDocument15 paginiMass and Heat Balance of Steelmaking in Bof As Compared To Eaf ProcessesAgil Setyawan100% (1)
- Normal Consistency of Hydraulic CementDocument15 paginiNormal Consistency of Hydraulic CementApril Lyn SantosÎncă nu există evaluări
- OIl Rig Safety ChecklistDocument10 paginiOIl Rig Safety ChecklistTom TaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Project Diary-Wps OfficeDocument4 paginiA Project Diary-Wps OfficeSameer ShaikhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Highway Journal Feb 2023Document52 paginiHighway Journal Feb 2023ShaileshRastogiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cryptography Lab DA-1Document19 paginiCryptography Lab DA-1Gautam Thothathri 19MIC0092Încă nu există evaluări
- SQL TestDocument10 paginiSQL TestGautam KatlaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Denial of LOI & LOP For Ayurveda Colleges Under 13A For AY-2021-22 As On 18.02.2022Document1 paginăDenial of LOI & LOP For Ayurveda Colleges Under 13A For AY-2021-22 As On 18.02.2022Gbp GbpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application of A HAZOP Study Method To Hazard Evaluation of Chemical Unit of The Power StationDocument8 paginiApplication of A HAZOP Study Method To Hazard Evaluation of Chemical Unit of The Power Stationshinta sariÎncă nu există evaluări
- MT Im For 2002 3 PGC This Is A Lecture About Politics Governance and Citizenship This Will HelpDocument62 paginiMT Im For 2002 3 PGC This Is A Lecture About Politics Governance and Citizenship This Will HelpGen UriÎncă nu există evaluări
- SAP Environment, Health, and Safety (EHS)Document13 paginiSAP Environment, Health, and Safety (EHS)SAFETY VOFPLÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clevite Bearing Book EB-40-07Document104 paginiClevite Bearing Book EB-40-07lowelowelÎncă nu există evaluări
- MIDTERM Exam - Programming 2 - 2SEM 2020Document3 paginiMIDTERM Exam - Programming 2 - 2SEM 2020Bab bidiÎncă nu există evaluări