Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
EC2045 2 Marks PDF
Încărcat de
arunathangamDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
EC2045 2 Marks PDF
Încărcat de
arunathangamDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
UNIT I
SATELLITE ORBITS
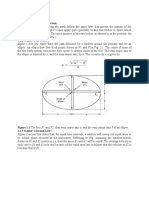
1. State Keplers first law.
It states that the path followed by the satellite around the primary will be
an ellipse. An ellipse has two focal points F1 and F2. The center of mass of the
two body system, termed the barycenter is always centered on one of the foci.
e= a
2
-b
2
a
2. State Keplers second law.
It states that for equal time intervals, the satellite will sweep out equal
areas in its orbital plane, focused at the barycenter.
3. state Keplers third law.
It states that the square of the periodic time of orbit is perpendicular to
the cube of the mean distance between the two bodies.
a
3
/n
where, n= Mean motion of the satellite in rad/sec.
= Earths geocentric gravitational constant.
With the n in radians per sec.the orbital period in second is given by,
4. Define apogee and perigee.
The point farthest from the earth is known as apogee.
The point closest from the earth is known as perigee.
5. What is line of apsides?
The line joining the perigee and apogee through the center of the earth is
known as line of apsides.
www.5starnotes.com
www.5starnotes.com
w
w
w
.
R
e
j
i
n
p
a
u
l
.
c
o
m
6. Define ascending and descending node.
Ascending node: The point where the orbit crosses the equatorial plane
going from south to north.
Descending node: The point where the orbit crosses the equatorial plane
going from north to south.
7. Define inclination.
The angle between the orbital plane and the earths equatorial plane. It is
measured at the ascending node from the equator to the orbit going from east to
north.
8. Define mean anomaly and true anomaly.
Mean anomaly: It gives an average value of the angular position of the
satellite with reference to the perigee.
True anomaly: It is the angle from perigee to the satellite position,
measured at the earths center.
9. Mention the apogee and perigee height.
R
a
= a(1+e)
R
p
= a(1+e)
H
a
= r
a
-R
p
H
p
= r
p
-R
p
10. State Newtons First law.
It states that the gravitational force of attraction between two bodies
proportional to the product of their masses M and m and inversely proportional
to the square of the distance r between them.
F= -GMmr
r
2
Where, G = Universal gravitational constant
r= unit vector.
11. What is meant by azimuth angle?
www.5starnotes.com
www.5starnotes.com
w
w
w
.
R
e
j
i
n
p
a
u
l
.
c
o
m
It is defined as the angle produced by intersection of local horizontal
plane and the plane passing through the earth station, the satellite and center of
earth.
12. State Newtons second law.
Second law of motion states that the acceleration of the body is directly
proportional to the force acting on it and inversely proportional to the mass.
F=ma
13. Find a range and antenna elevation angle for the satellite parameter
R=6371km; a
Gso
=42164m; b=36.23
o
.
Solution:
Range, d= R
2
+a
2GSO
-2Ra
Gso
cosb
d= (6371)
2
+(42164)
2
-2(6371)(42164)cos(36.23
0
)
d=37215km.
Antenna elevation angle,
El=arc cos(
sinb)
El=Cos
-1
(
sin (36.23
0
))
El=48
0
.
14. Write the expressions of nozzle expansion.
From the nozzle expression, the equation can be written as given below.
F=-
Ve+(Pe-Pa)Ae.
Where, Pe=exhaust pressure at the exit plane.
Pa= ambient pressure of the atmosphere.
This equation says that the total thrust of the rocket is compossed of the
momentum thrust and the pressure thrust.
15. Define sub-Satellite point.
www.5starnotes.com
www.5starnotes.com
w
w
w
.
R
e
j
i
n
p
a
u
l
.
c
o
m
The point on the earth vertically under the satellite is called sub-satellite
point . The height of the terrain above the reference ellipsoid at the sub-satellite
point is denoted by H
ss
. The height of the satellite above this is denoted by h
ss.
Thus the total height is,
h= H
ss
+h
ss
16. Define sun transit outage.
The sun comes with the beam width of the earth station antenna is known
as sun transit outage. During this period, the sun behaves as extremely noisy
source and it is blanks out all signals from satellite. This effect is known as sun
transit outage.
17. Write short notes on station keeping.
It is the process of maintaining the satellites attitude against different
factors that can cause drift with time. Satellites need to have their orbits
adjusted from time to time, because, the satellite is initially placed in the correct
orbit. But, natural forces induce a progressive drift.
18. Define specific impulse.
The characteristic that is used to describe the propellant performance is
called specific impulse ISP. It is defined as,
ISP=
.
19. Write short notes on atmospheric Drag.
The atmospheric drag is significant for near earth satellite below or above
1000km. This drag radius the velocity at the perigee because of this the satellite
does not reach the same apogee height on successive revolution. So that the
semi major axis and eccentricity are reduced.
a=a
0
)
2/3
20. Define Prograde orbit and Retrograde orbit.
Prograde orbit: An orbit in which the satellite moves in same direction as
the earth rotation. It is also known as the direct orbit.
www.5starnotes.com
www.5starnotes.com
w
w
w
.
R
e
j
i
n
p
a
u
l
.
c
o
m
Retrograde orbit: An orbit in which the satellite moves in counter to
direction of earth rotation.
UNIT II
SPACE SEGMENT AND SATELLITE LINK DESIGN
1. Write short notes on attitude control system.
It is the system that achieves and maintains the required attitudes. The
main functions off attitude control system include maintaining accurate satellite
position throughout the life span of the system.
2. Describe the spin stabilized satellites.
In a spin stabilized satellites, the body of the satellite spins at about 30 to
100 rpm about the axis perpendicular to the orbital plane. The satellites are
normally dual spin satellites with a spinning section and a despun section on
which antennas are mounted. These are kept stationary with respect to earth by
counter rotating the despun section.
3. What are the main functions of a space craft management .
The main functions of a space craft management are given below.
1. To control the orbit and attitude of the satellite.
2. To monitor the status of all the sensors in the satellite.
3. To switch on/off some sections in communication system.
4. Write short notes on telemetry.
The telemetry system is present in the satellite, this subsystem collects
data from many/all sensors present in the satellite and retransmit it into the earth
station.
5. Write short notes on tracking.
Tracking is nothing but to find the position of the satellite in space.
Tracking is very important during the transfer orbit and drift phase of the
satellite launch. We know that lots of disturbing forces may change the attitude
www.5starnotes.com
www.5starnotes.com
w
w
w
.
R
e
j
i
n
p
a
u
l
.
c
o
m
and orbit of a satellite, so it is necessary to track the satellite and send correction
signals.
6. Write the equations of Link-Power Budget.
The power output of the link is power at the receiver the major source of
loss in any ground satellite link is the free space spreading loss.
[LOSSES]=[FSL]+[RFL]+[AML]+[AA]+[PL]
Where, FSL=Free Space Spreading Loss(dB)
RFL=Receiver Feeder Loss(dB)
AML=Antenna Misalignment Loss(sB)
AA= Atmospheric Absorption(dB)
PL= Polarization mismatch Law(dB)
7. What is an EIRP?
EIRP means Equivalent Isotropic Radiated Power. It is a measure of
radiated or transmitted power of an antenna.
8. What is an intermodulation noise?
Intermodulation distortion in high power amplifier can result in signal
product which appear as noise and it is referred to as Intermodulation noise.
9. What is an system noise?
Noise temperature is very important concept in receivers. By using this,
thermal noise which is generated by active and passive devices in the receiver
can be calculated.
The noise power is given by,
P
n
=KT
n
B
Where, P
n
=Noise power
K=Boltzmans constant
T
n
=Noise temperature of source(in Kelvin)
B=Bandwidth in Hz
www.5starnotes.com
www.5starnotes.com
w
w
w
.
R
e
j
i
n
p
a
u
l
.
c
o
m
10. What is an antenna loss?
It is added to noise received as radiation and the total antenna noise
temperature is the sum of the equivalent noise temperature of all these sources.
11. Define sky noise.
It is a term used to describe the microwave radiation which is present
throughout universe and which appears to originate from matter in any form, at
finite temperature.
12. Define noise factor.
An alternative way of representing amplifier noise is by means of its
noise factor. In defining the NF of an amplifiers, usually taken as 290K.
13. Define saturation flux density.
The flux density required at the receiving antenna to produce saturation
of TWTA is termed the saturation flux density.
14. Define Satellite uplink.
The link through which the earth station transmits the signal and the
satellite receive the same is known as uplink. [C/No] equation in the last title
carrier to noise ratio can be applied to uplink.
[
]
u
= [EIRP]
u
+[
]-[L]
u
-[K]
Here, the subscript u is used to denote the uplink.
[C/No] ratio appears at satellite receiver.
[EIRP]
u
=Earth station EIRP.
[G/T]
u
= satellite receiver G/T
15. Define satellite downlink.
The link through which the satellite transmit the signal and the earth
station receive it,
Subscript D is used to indicate the downlink in the following equation.
[
]
D
= [EIRP]
D
+[
]
D
-[L]
D
-[K].
www.5starnotes.com
www.5starnotes.com
w
w
w
.
R
e
j
i
n
p
a
u
l
.
c
o
m
16. Define Carrier to Noise Ratio.
The performance of satellite line is measured by carrier to noise ratio, it is
given as CNR or C/N.
C/N in db is given as [C/N]
[
] =[P
R
]-[P
N
]
[C/N0]= [EIRP]+[G/T]-[L]-[K] dB. Hz.
17. A transponder require a saturation flux density of -110 d Bw/m
2
, operating
frequency of 14 GHz. Total loss =200dB Find [EIRP].
Solution:
Here, [s]=-110dB
F=14GHz
[L]=200dB
[A]=-(21.45+20logf)=-44.37
[EIRP] =[ s]+[A]+[L]
[EIRP]=-110-44.37+200
[EIRP]=45.63 dB.
18. What is noise weighting?
The method used to improve the post detection signal to noise ratio is
referred to as noise weighting.
19. Write short notes on body stabilization.
The body stabilization is also known as three axis satellite. The
stabilization is achieved by controlling the moment of the satellite along the 3-
axis. (i.e) yaw,pitch,r oll With respect to the reference.
20. What is meant by Pitch angle?
An angle produced by the movement of a spacecraft about an axis which
is perpendicular to its longitudinal axis is known as Pitch angle.
www.5starnotes.com
www.5starnotes.com
w
w
w
.
R
e
j
i
n
p
a
u
l
.
c
o
m
UNIT III
SATELLITE ACCESS
1. What are methods of multiple access techniques?
Two methods of multiple access techniques are given below.
FDMA (Frequency division multiple access techniques)
TDMA(Time division multiple access techniques)
2. What is CDMA? And its types?
In this method, each signal is associated with a particular code that is
used to spread the signal in frequency and time. Its types are:
Spread spectrum multiple access.
Pulse address multiple access.
3. What is an TDMA? What are the advantages?
Only one carrier uses the transponder at any one time, and therefore
intermodulation products, which results from the non-linear amplification of
multiple carriers are absent.
Advantages: The transponder traveling wave tube can be operated at maximum
power output.
4. Define multiple access.
Various earth stations may transmit more number of carriers. At that
time, a transponder is loaded with more than one number of carriers. This is
known as multiple access.
5. What is CBR?
An un modulated carrier wave is provided during the first part of the
carrier and bit-timing recover (CBR) time slot. It is used as a synchronizing
signal for local oscillator in the detector circuit. In the remaining part of CBR
time slot, the carrier is modulated by a known phase change sequence.
6. What is BCW?
www.5starnotes.com
www.5starnotes.com
w
w
w
.
R
e
j
i
n
p
a
u
l
.
c
o
m
The copy of burst code word (BCW) is stored in all the earth stations.
Incoming bits in the burst are compared with the BCW. The receiver detects the
group of received bits matched with BCW. Then, accurate time reference for
the burst position in frame is provided.
7. What is amplitude modulation?
The modulated signal may be expressed as,
am(t)={ka
s
(t)+1}Ac sin(ct+)
For special case where the modulating signal in sine wave with angular
frequency cos and letting k=m,above equation becomes
am(t)=(msinst+1)Ac sin ct
where, m=modulation index.
8. What are the analog transmission technique.
The analog transmission techniques are given as,
Amplitude modulation
Frequency division multiplexing.
Frequency modulation.
9. What are the components of encryption?
The symmetric encryption has 5 components. They are,
Plain text
Encryption algorithm
Secret key
Cipher-text
Decryption algorithm.
10.What are the types of vedio signals?
Generally two types of signals are transmitted through the satellite
circuits.
Broadcast equality commercial television.
Television used for business conferencing.
www.5starnotes.com
www.5starnotes.com
w
w
w
.
R
e
j
i
n
p
a
u
l
.
c
o
m
11. What are the disadvantages of FDMA.
Sensitive to fading
Stabilization is difficult.
Sensitive to random frequency modulation.
Sensitive to inter modulation distortion.
12. Write short notes on voice.
Voice is a telephone speech signals. Generally bandwidth upto 20 Hz.
Telephone handset acts as the acoustic electric transmission. Which converts
voice/sound signal to electrical signal.
13. What are the limitations of FDMA-satellite access?
If the traffic in the downlink is much heavier than that in the
uplink, then FDMA is relatively inefficient. So, bandwidth of the
uplink channel is not fully used.
Compared with TDMA, FDMA has less flexibility in reassigning
channels.
Carrier frequency assignments are hardware controlled.
14. distinguish between pre-assigned and demand-assigned TDMA satellite
access.
Preassigned TDMA Demand assigned TDMA
Example for preassigned TDMA is
CSC for the SPADE network. CSC
can accommodate upto 49 earth
stations in the network and 1 reference
station.
In TDMA,reassigning of channels is
more flexible. Different methods are
used to provide traffic flexibility.
All bursts are of equal length. Each
burst contains 128 bits. The bit rate is
138kb/s,
The burst length may be kept constant
and the number of bursts per frame
used by the given station is varied
when the demand is varied.
15. Mention the merits and demerits of TDMA over FDMA.
In TDMA, only one carrier uses the transponder at any time. So,
intermodulation noise is reduced.
16. What is an multiple access technique?
www.5starnotes.com
www.5starnotes.com
w
w
w
.
R
e
j
i
n
p
a
u
l
.
c
o
m
A transponder to be loaded by a number of carriers. These may originate
from a number of earth stations. This mode of operation known as multiple
access technique.
17. What is meant by space division multiple access?
The satellite as a whole to be accessed by earth stations widely separated
geographically but transmitting on the same frequency i.e. known as frequency
reuse. This method of access known as space division multiple access.
18. What is burst code word and burst position acquisition?
Burst code: It is a binary word, a copy of which is stored at each earth
station.
Burst position acquisition: A station just entering, or reentering after a
long delay to acquire its correct slot position is known as burst position
acquisition.
19. Define guard time.
It is necessary to prevent the bursts from overlapping. The guard time
will vary from burst to burst depending on the accuracy with which the various
bursts can be positioned within each frame.
20. Write short notes on open-loop timing control.
It is a method of transmit timing. In this method, according to burst time
plan, a station transmits at a fixed interval. Necessary guard time is allowed to
absorb the variations in propagation delay.
UNIT IV
EARTH SEGMENT
1. What are the components of Earth station?
The earth station comprises set of equipment, which is used to make a
link with satellite mainly the used components are,
Transmitters
Receivers.
www.5starnotes.com
www.5starnotes.com
w
w
w
.
R
e
j
i
n
p
a
u
l
.
c
o
m
Antennas
Tracking System.
Terrestrial interface.
Primary power.
Test equipment.
2. Write short notes on MATV.
MATV is a Master Antenna TV System. It is used to provide reception of
DBS TV channels to the user group. It consists of one outdoor unit and various
indoor units. Each user can independently access all the channels. It has a low
signal to noise ratio. The receiver antenna diameter is 2m-3m.
3. Write short notes on CATV.
CATV is a Community Antenna TV system. As in MATV system, it
consists of one outdoor unit and separate feeds for each sense of polarization.
The channels are then combined by using combiner block. The combined
signal is a multiplexed signal which is transmitted through the cable to the
users. The signal is retransmitted from a low power VHF TV transmitter.
4. Define Y-factor.
Y-factor is the ratio of output noise measured when the receiver is
connected to a hot noise to the output noise measured when connected to the
cold source(Tc).
The receiver excess noise Te is related to the Y-factor by
T
w
=(T
b
-Y
Tc
)/(Y-1)
5. Write the expressions of universal antenna.
The universal antenna formula is
and
If a is atmospheric absorption at zenith then the elevation angle 0 is given
by
www.5starnotes.com
www.5starnotes.com
w
w
w
.
R
e
j
i
n
p
a
u
l
.
c
o
m
sin
Where, A= correction factor.
6. What is an EIRP?
EIRP means Equivalent Isotropic Radiated Power. It is a measure of
radiated or transmitted power of an antenna.
7. Define Carrier to Noise Ratio.
The performance of satellite line is measured by carrier to noise ratio, it is
given as CNR or C/N.
C/N in db is given as [C/N]
[
] =[P
R
]-[P
N
]
[C/N0]= [EIRP]+[G/T]-[L]-[K] dB. Hz.
8. What is a monopulse?
If the antenna generates different patterns with nulls on the axis, in
azimuth and elevation planes, then it is called monopulse tracking method. The
monopulse antenna presents a low systematic pointing error or the order of
0.1 . The monopulse technique is more complex and highly expensive.
Hence it is not used popularly.
9. What are the basic requirements of an earth station antenna?.
The basic requirements of an earth station antenna are listed below.
The antenna must have a low noise temperature. The ohmic losses
of antenna must also be maximum.
The antenna must be rotated or steered easily so that a tracking
system can be employed to point the antenna beam accurately.
The antenna radiation must have a low side lobe level to reduce
interference from unwanted signals and also to minimize
interference into other satellites and terrestrial systems.
The antenna must have a high directive gain.
www.5starnotes.com
www.5starnotes.com
w
w
w
.
R
e
j
i
n
p
a
u
l
.
c
o
m
10. Write short notes on TVRO.
The TVRO is a Receive Only Home TV systems. TVRO transmission
takes place in Ku- band. Single mesh type reflector may be used which focuses
the signal into a single feed horn, which has 2 separate outputs, one for c-band
signals and other for ku-band signals.
11. What is a tracking?
The tracking is an important operation of the earth station. The efficiency
of earth station depends as to how efficiently it points the antenna beam to the
satellite both in the transmit and receive mode.
12. Write a short notes on step by step technique.
The step by step technique is the most popular technique used for
tracking. In this technique maximum reception of the received signal is needed
and it is performed by moving and checking the beam continuously. This
tracking gives a systematic pointing of the order of 0.20
3db.
13. A transponder require a saturation flux density of -110 d Bw/m
2
, operating
frequency of 14 GHz. Total loss =200dB Find [EIRP].
Solution:
Here, [s]=-110dB
F=14GHz
[L]=200dB
[A]=-(21.45+20logf)=-44.37
[EIRP] =[ s]+[A]+[L]
[EIRP]=-110-44.37+200
[EIRP]=45.63 dB.
14. A satellite downlink at 12 GHz operates with a transmit power of 6 W and
an antenna gain of 48.2 dB. Calculate the EIRP in dBW.
EIRP means Equivalent Isotropic Radiated Power. It is a measure of
radiated or transmitted power of an antenna.
www.5starnotes.com
www.5starnotes.com
w
w
w
.
R
e
j
i
n
p
a
u
l
.
c
o
m
EIRP=10log6+48.2
EIRP=56dBW.
15. What is a transponder?
In a communication satellite, the equipment which provides the
connecting link between the satellites transmit and receive antennas is referred
to as the transponder.
16. What is meant by input back off of a transponder?
The operating point of TWT must be shifted closer to the linear portion of
the curve to reduce the intermodulation distortion. So, input power is reduced.
This is known as input backoff.
17. What is TWTA?
TWTA means travelling wave tube amplifier. The TWTA is widely used
in transponder to provide the final output power required to the transtube and its
power supplies.
18. Give the formulae to compute the uplink carrier to noise ratio.
Uplink carrier to noise ratio is [C/N0]
u
[C/N0]= [EIRP]
u
+[G/T]
u
-[L]
u
-[K]
[L
u
]=Losses in dB.
[K]=constant=-228.6
19. What is meant by intermodulation distortion?
When multiple carriers are passed through the device with the non-linear
transfer characteristic, more serious form of distortion is introduced known as
intermodulation distortion.
20. What is polarization interleaving?
Overlap occurs between channels, but these are alternatively polarized
left hand circular and right hand circular to reduce interference to acceptable
levels. This is referred to as polarization interleaving.
www.5starnotes.com
www.5starnotes.com
w
w
w
.
R
e
j
i
n
p
a
u
l
.
c
o
m
UNIT V
SATELLITE APPLICATIONS
1. Write short notes on INTELSAT.
INTELSAT stands for International Telecommunication Satellite. In
april 6, 1965 first INTELSAT was launched. It is nicknamed as Early Bird.
Initially 11 members are made in present; there are more than 155 members and
700 earth station. INTELSAT-6 uses microprocessor with switching process.
These are used for whether, DTH, telex etc.
2. What does INTELSAT,INMARSAT,INSAT stands for.
INTELSAT stands for International Telecommunication Satellite.
INSAT stands for Indian National Satellite system.
INMARSAT stands for International Marine Satellite Organization.
3. What are the satellite mobile services?
The satellite mobile services are
Mobile Satellite Service.(MSAT)
Very Small Aperture Terminal(VSAT)
Direct Broadcast Satellite (DBS)
Global Positioning System(GPS)
Microsats
Orbcomm
Iridium.
4. What are VSATs?
VSAT is a Very Small Aperture Terminal System. It provides two way
communication facilities. Typical user groups include banking and financial
institutions, airline, hotel booking agencies and large retail stores with
geographically dispersed outlets.
5. Write short notes on INMARSAT.
www.5starnotes.com
www.5starnotes.com
w
w
w
.
R
e
j
i
n
p
a
u
l
.
c
o
m
It stands for International Marine Satellite Organization. It founded in the
year 1979. It provides voice and data service. It is used in marine assessment
for disaster management.
6. What are the INMARSAT services?
The INMARSAT services are
Telephony
Telex
Facsimile
E-mail
Slow speed data for marine
Aeronautical
Landmobile
Telephony
7. Define LEO.
LEO stands for Low Earth Orbit. It is defined as orbit within the locus
extending from the earth surface upto an altitude of 2000 km, the commonly
accepted definition for LEO is between 160-200 km above the earth surface.
8. Define MEO.
MEO stands for Medium Earth Orbit. It lies between 8000km and
18000km above the earth surface. MEO satellite ranges for orbital period for
about 2 to 12 hrs. Some MEO orbits are in near perfect circles and therefore
have constant altitude and travel at a constant speed.
9. Define Satellite Navigational System.
Satellite Navigation are SATNAV system is a system of satellite that
provides autonomous geospatial positioning with global coverage. It allows
electronic receivers to determine the latitude, longitude and attitude position
within a few meters using timing signals transmitted from a line of sight by
radio from the satellite.
10. What are the services and features of GSM?
The GSM services are classified into 2.
www.5starnotes.com
www.5starnotes.com
w
w
w
.
R
e
j
i
n
p
a
u
l
.
c
o
m
Tele services.
Data services.
Features of GSM:
Subscriber Indentity Module (SIM)
On the air privacy.
11. What is a direct broadcasting satellite?
Satellite used for direct broadcasting is called DBS. These Service
include audio, TV,internet services. Satellite and antenna footprint can be made
to cover large area of earth.
12. What are the INSAT services.
The INSAT provides 3 main services
Long distance communication
TV and Radio broadcasting.
Meterology.
13. Write a short notes on digital audio broadcast.
The digital audio broadcasting through satellite is used to provide, high
quality audio signals to the consumers. In early days, it was called as digital
audio broadcast. Now it is commonly termed as
SDARS (Satellite Digital Audio Radio Service)
DARS (digital Audio Radio Service).
14. What are the applications of GPS?
Mobile communication to provide position updates.
Spot beam identification.
Used in ships
Scientists, surveyors, etc.
15. What is ECEF?
The geocentric equatorial coordinate system is used with the GPS system.
It is called as earth centered, earth fixed coordinate system.
www.5starnotes.com
www.5starnotes.com
w
w
w
.
R
e
j
i
n
p
a
u
l
.
c
o
m
16. What is dilution of precision?
Position calculations involve range differences and where the ranges are
nearly equal; any error is greatly magnified in the difference. This effect,
brought a result of the satellite geometry is known as dilution of precision.
17. What is PDOP?
With the GPS system, dilution of position is taken into account through a
factor known as the position dilution of precision.
18. What is a transponder capacity?
DBS television is also known as DTH TV. It needs more channels. So,
audio and video components of a TV program are digitized. So, compression
technique is used. Bandwidth is reduced due to this compression symbol rate
which can be transmitted in a given bandwidth is given by
Rs=BIF/(1+)
= Roll off factor.
19. What is the difference between a geostationary orbit and a geosynchronous
orbit?
In the geostationary orbit, a satellite appears stationary relative to the
earth. The satellite follows the same speed as the earth, so it seems to appear
stationary from the earth.
20. What is the orbital spacing of satellites?
For high power satellites orbital spacing 9
0
. This orbital spacing is
required to avoid adjacent interference.
www.5starnotes.com
www.5starnotes.com
w
w
w
.
R
e
j
i
n
p
a
u
l
.
c
o
m
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- QBDocument8 paginiQBSoundararajan RajagopalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Satellite Systems Applications and ServicesDocument18 paginiSatellite Systems Applications and Servicesgayathiridevi RÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ec1015 Satellite CommunicationDocument13 paginiEc1015 Satellite Communicationainugiri100% (1)
- SC 2 Marks 2015 PDFDocument14 paginiSC 2 Marks 2015 PDFRama SubramanianÎncă nu există evaluări
- SATELLITE COMMUNICATION Question and AnswersDocument7 paginiSATELLITE COMMUNICATION Question and AnswersRubini RavichandranÎncă nu există evaluări
- SATELLITE COMMUNICATION GUIDEDocument157 paginiSATELLITE COMMUNICATION GUIDEShayaan PappathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Space Segment and Link Design FundamentalsDocument3 paginiSpace Segment and Link Design FundamentalsIISRTÎncă nu există evaluări
- Selvam College of Technology, Namakkal: Department of Ece Two MarkDocument16 paginiSelvam College of Technology, Namakkal: Department of Ece Two MarkVijay Prashaant SweetÎncă nu există evaluări
- Satellite Communication Two Marks Question and Answers-2012-2013Document27 paginiSatellite Communication Two Marks Question and Answers-2012-2013shankar100% (15)
- Satellite Communication Two Marks Questions & Answers Unit - I Satellite OrbitDocument3 paginiSatellite Communication Two Marks Questions & Answers Unit - I Satellite OrbitKarthick NpÎncă nu există evaluări
- CommmDocument157 paginiCommmsuganyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Need of Satellite Communication Overcomes Distance LimitationsDocument49 paginiNeed of Satellite Communication Overcomes Distance Limitationsmayuriprajapati100% (2)
- Satellite Communication: Topic: Orbit DynamicsDocument18 paginiSatellite Communication: Topic: Orbit DynamicsMohit SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Satellite of OrbitsDocument23 paginiSatellite of OrbitsyuvasreeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Satellite Communication OrbitsDocument156 paginiSatellite Communication OrbitsKunal DixitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kepler's First Law: 11) A) I) State The Kepler's Laws. Discuss Its Importance in Satellite CommunicationsDocument16 paginiKepler's First Law: 11) A) I) State The Kepler's Laws. Discuss Its Importance in Satellite CommunicationsSoundararajan RajagopalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Satellite CommunicationsDocument202 paginiSatellite CommunicationsSachin Korgaonkar50% (2)
- Kepler's Laws: 1.2.1 Kepler's Law IntroductionDocument6 paginiKepler's Laws: 1.2.1 Kepler's Law IntroductionsubbuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Satellite Orbital MechanicsDocument29 paginiSatellite Orbital MechanicsmojammeljoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Satellite Communication LECTURE NOTESDocument202 paginiSatellite Communication LECTURE NOTESSindhu Velayudham100% (1)
- NovDec 2015 EC 2045Document27 paginiNovDec 2015 EC 2045Rathna Assistant ProfessorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Satellite Parameters Trajectories Module1Document134 paginiSatellite Parameters Trajectories Module1Neil LewisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Satellite Unit I Two MarksDocument3 paginiSatellite Unit I Two Marksbhavanisankari sÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Satellite Communication:: Unit I Satellite OrbitsDocument22 paginiIntroduction To Satellite Communication:: Unit I Satellite OrbitsjagadishÎncă nu există evaluări
- Satellite CommunicationDocument157 paginiSatellite CommunicationMadhu SurapureddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- UNit-4 (Satellite Communication)Document15 paginiUNit-4 (Satellite Communication)Kunal ChoudharyÎncă nu există evaluări
- PHYS122 University of WaterlooDocument174 paginiPHYS122 University of WaterlooEddy LiuÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2-Satellite - Systems 2 - Orbits IIIDocument42 pagini2-Satellite - Systems 2 - Orbits IIIمهيمن الابراهيميÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module1 - Satellite Communication VTU 7th SemDocument127 paginiModule1 - Satellite Communication VTU 7th Semrohan gowdaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1 Satellite CommDocument81 paginiUnit 1 Satellite CommNivitha AnjuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction to Satellite Communication Orbits and ParametersDocument15 paginiIntroduction to Satellite Communication Orbits and Parametersapollo eceÎncă nu există evaluări
- SatelliteDocument8 paginiSatelliteRifat ahmmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1-Satellite CommunicationDocument100 paginiUnit 1-Satellite CommunicationvenugopalÎncă nu există evaluări
- SC PPT-MMM1Document70 paginiSC PPT-MMM1ManjunathÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit IiDocument36 paginiUnit Iipradnya patilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Space DynamicsDocument4 paginiSpace DynamicsShubham ShekharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Satellite CommunicationDocument46 paginiSatellite CommunicationChandra MathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 1 - Satellite Orbits and TrajectoriesDocument28 paginiModule 1 - Satellite Orbits and Trajectoriescc bbÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2Document68 paginiChapter 2arebuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment - 1Document21 paginiAssignment - 1shoyeb ahmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kepler's Laws Reveal Satellite MotionDocument6 paginiKepler's Laws Reveal Satellite MotionPulkit SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 3Document18 paginiLecture 3TyDolla ChicoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ilcev ICEEOT Pg4505-4513 2016Document9 paginiIlcev ICEEOT Pg4505-4513 2016Eslam SaeedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sol EndDocument8 paginiSol EndBorn MaDÎncă nu există evaluări
- UNIT 1 Satellite CommunicationDocument12 paginiUNIT 1 Satellite CommunicationRõçky StrâñgëÎncă nu există evaluări
- Satellite Communication Systems ExplainedDocument55 paginiSatellite Communication Systems ExplainedIndraysh Vijay [EC - 76]Încă nu există evaluări
- Ece-Vi-Satellite Communications (10ec662) - Notes PDFDocument50 paginiEce-Vi-Satellite Communications (10ec662) - Notes PDFHilmi Sanusi80% (10)
- Chapter 6: Blackbody Radiation: Thermal Emission: Eventual Absorption: Acts Like A Black BodyDocument38 paginiChapter 6: Blackbody Radiation: Thermal Emission: Eventual Absorption: Acts Like A Black Bodyvenkat_09Încă nu există evaluări
- Earth observation satellite orbital parameters and geostationary orbit calculationsDocument9 paginiEarth observation satellite orbital parameters and geostationary orbit calculationsAakansha SuchittaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Communicate via satellitesDocument46 paginiCommunicate via satellitesJason MiralloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pratt & Bostian - PPDocument3 paginiPratt & Bostian - PPapi-26783388Încă nu există evaluări
- Artificial Satellites: Sunil Kumar SinghDocument8 paginiArtificial Satellites: Sunil Kumar SinghSarah AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Orbital Mechanics and LaunchersDocument53 paginiOrbital Mechanics and Launchersali70ymailÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lectures on Stellar StatisticsDe la EverandLectures on Stellar StatisticsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zero Point Energy Per Stereo Radian and the Distribution of Gravitational Acceleration of Planets Throughout the Solar System.: The Origin and Cause of GravitationDe la EverandZero Point Energy Per Stereo Radian and the Distribution of Gravitational Acceleration of Planets Throughout the Solar System.: The Origin and Cause of GravitationÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unified Field Theory in a Nutshell1: The Quest for the Theory of EverythingDe la EverandUnified Field Theory in a Nutshell1: The Quest for the Theory of EverythingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Full Free Motion of Celestial Bodies Around a Central Mass - Why Do They Mostly Orbit in the Equatorial Plane?De la EverandFull Free Motion of Celestial Bodies Around a Central Mass - Why Do They Mostly Orbit in the Equatorial Plane?Încă nu există evaluări
- Tnpscmar12 495333Document1 paginăTnpscmar12 495333Prabhu KomarapalayamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class: Iii Year - It Subject: Digital Signal Processing: A) Text Books: (TX)Document4 paginiClass: Iii Year - It Subject: Digital Signal Processing: A) Text Books: (TX)arunathangamÎncă nu există evaluări
- EC2354 2 Marks PDFDocument24 paginiEC2354 2 Marks PDFarunathangamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ec2353 2 Marks PDFDocument15 paginiEc2353 2 Marks PDFpsjayakumarmeÎncă nu există evaluări
- I&CDocument48 paginiI&CarunathangamÎncă nu există evaluări
- EC2252 2 Marks PDFDocument17 paginiEC2252 2 Marks PDFarunathangamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linear IC and ApplicationsDocument27 paginiLinear IC and ApplicationsarunathangamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ec 1993 PDFDocument19 paginiEc 1993 PDFarunathangamÎncă nu există evaluări
- 05 Chapter 03 LFSIMDocument97 pagini05 Chapter 03 LFSIMarunathangamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Int 3 QPDocument1 paginăInt 3 QParunathangamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Get TRDocDocument5 paginiGet TRDocarunathangamÎncă nu există evaluări
- System-Level Training of Neural Networks For Counting White Blood CellsDocument6 paginiSystem-Level Training of Neural Networks For Counting White Blood CellsarunathangamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Relationship of Z-Transform and Fourier TransformDocument9 paginiRelationship of Z-Transform and Fourier TransformarunathangamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Relationship of Z-Transform and Fourier TransformDocument9 paginiRelationship of Z-Transform and Fourier TransformarunathangamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electronics Question BankDocument9 paginiElectronics Question BankHoney SriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vlsi 2Document39 paginiVlsi 2arunathangamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic VLSI Design: + Drain VDD - N Type Silicon SourceDocument74 paginiBasic VLSI Design: + Drain VDD - N Type Silicon SourceNeelam RamanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Welcome To The Session On: VerilogDocument27 paginiWelcome To The Session On: VerilogarunathangamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Environment N Its ComponentsDocument2 paginiEnvironment N Its ComponentspupulgoelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gulika and MandiDocument3 paginiGulika and MandishivarhÎncă nu există evaluări
- INPhO2017 Solution 20170131Document8 paginiINPhO2017 Solution 20170131ShivamKumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carnahan Squadron - Jun 2008Document6 paginiCarnahan Squadron - Jun 2008CAP Unit NewslettersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Archimedes - WikipediaDocument24 paginiArchimedes - WikipediaAlice DarwinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Polarization 4Document11 paginiPolarization 4tarunjinÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 Basic GK Questions for Kids Aged 3-6Document28 pagini10 Basic GK Questions for Kids Aged 3-6zarinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chronology of Revelation Earth by CobraDocument39 paginiChronology of Revelation Earth by CobraAdriela100% (1)
- Bill Gates Vedic Birth ChartDocument11 paginiBill Gates Vedic Birth ChartDisha TÎncă nu există evaluări
- Astrology BooksDocument3 paginiAstrology BooksRavin Taira Pal50% (4)
- De Ave Phoenice Phoenix: FelixDocument8 paginiDe Ave Phoenice Phoenix: FelixTyler N. PattersonÎncă nu există evaluări
- IOAA 2015 Data Analysis Problems Ver 20150730 - 1851Document22 paginiIOAA 2015 Data Analysis Problems Ver 20150730 - 1851Raja PalasaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Space SlutsDocument1 paginăSpace Slutsapi-47774943Încă nu există evaluări
- Physics 11th Sample Question On System of PariclesDocument2 paginiPhysics 11th Sample Question On System of PariclesAbhishek AsthanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical Science Summative Test FinalDocument2 paginiPhysical Science Summative Test FinalNATHANIEL GALOPO100% (1)
- FWD Mahesh Parashara PDF .. Let Me Know If I Missed Any PagesDocument107 paginiFWD Mahesh Parashara PDF .. Let Me Know If I Missed Any Pagesmahesh_850564621Încă nu există evaluări
- A Flight of Fantasy Task SheetDocument5 paginiA Flight of Fantasy Task SheetRushil BhandariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Friday Funday PDF Solar System Mercury ActivitiesDocument19 paginiFriday Funday PDF Solar System Mercury ActivitiesAmit SachanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Light PollutionDocument28 paginiLight PollutionRamanathan Mohan100% (1)
- Annunaki and Quran and BibleDocument31 paginiAnnunaki and Quran and Biblefingerbang9392100% (7)
- Reading Practice 9-11Document5 paginiReading Practice 9-11Thành HưngÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trigonometry TimelineDocument1 paginăTrigonometry TimelineAj GomezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bridgmanita PDFDocument2 paginiBridgmanita PDFAnibal Urango AlcantaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ready VirgoDocument52 paginiReady VirgomaizecarolinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formation of The EarthDocument3 paginiFormation of The EarthAbhishek yadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gravity Lesson PlanDocument22 paginiGravity Lesson PlanLoran Prelya TengayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Descendants of The AN.UNNA.KIDocument30 paginiDescendants of The AN.UNNA.KIedisaha100% (1)
- Tithi PRAVESHADocument38 paginiTithi PRAVESHAdbbircs100% (1)
- Progress Test 2A (Units 4-6)Document7 paginiProgress Test 2A (Units 4-6)SvetlanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Goldwing Paint ColorsDocument13 paginiGoldwing Paint ColorsRingo AlmafuerteÎncă nu există evaluări