Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Present Perfect and Continuous
Încărcat de
ledracDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Present Perfect and Continuous
Încărcat de
ledracDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
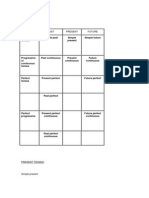
Present Perfect Simple Present Perfect
Progressive
Form
Present Perfect Simple Present Perfect Progressive
irregular verbs: form of 'have' + 3rd column of
irregular verbs
Example:
I / you / we / they have spoken
he / she / it has spoken
regular verbs: form of 'have' + infinitive + ed
Example:
I / you / we / they have worked
he / she / it has worked
form of 'have' + been + verb + ing
Example:
I / you / we / they have been speaking
he / she / it has been speaking
Exceptions
Exceptions when adding 'ed' :
when the final letter is e, only add d
Example:
love - loved
after a short, stressed vowel, the final
consonant is doubled
Example:
admit - admitted
final l is always doubled in British English (not in
American English)
Example:
travel - travelled
after a consonant, final y becomes i (but: not
Exceptions when adding 'ing' :
silent e is dropped. (but: does not apply for -ee)
Example: come - coming
aber: agree - agreeing
after a short, stressed vowel, the final
consonant is doubled
Example: sit - sitting
after a vowel, the final consonant l is doubled in
British English (but not in American English).
Example: travel - travelling
final ie becomes y.
Example: lie - lying
after a vowel)
Example:
worry - worried
but: play - played
See also explanations on Present Perfect Simple and Present Perfect Progressive
Use
Both tenses are used to express that an action began in the past and is still going on or
has just finished. In many cases, both forms are correct, but there is often a difference in
meaning: We use the Present Perfect Simple mainly to express that an action is
completed or to emphasise the result. We use the Present Perfect Progressive to
emphasise the duration or continuous course of an action.
Result or duration?
Do you want to express what has happened so far or how long an action has been going
on yet?
Present Perfect Simple Present Perfect Progressive
Result (what / how much / how often)
I have written 5 letters. / I have been to London
twice.
Duration (how long)
I have been writing for an hour.
Certain verbs
The following verbs are usually only used in Present Perfect Simple (not in the
progressive form).
state: be, have (for possession only)
Example: We have been on holiday for two weeks.
senses: feel, hear, see, smell, taste, touch
Example: He has touched the painting.
brain work: believe, know, think, understand
Example: I have known him for 3 years.
Emphasis on completion or duration?
Do you want to emphasise the completion of an action or its continuous course (how
has somebody spent his time)?
Present Perfect Simple Present Perfect Progressive
Emphasis on completion
I have done my homework. (Meaning: My
homework is completed now.)
Emphasis on duration
I have been doing my homework. (Meaning: That's
how I have spent my time. It does not matter
whether the homework is completed now.)
Result or side effect?
Do you want to express that a completed action led to a desired result or that the action
had an unwanted side effect?
Present Perfect Simple Present Perfect Progressive
desired result
I have washed the car. (Result: The car is clean
now.)
unwanted side effect
Why are you so wet? - I have been washing the car.
(side effect: I became wet when I was washing the
car. It does not matter whether the car is clean
now.)
Time + negation: last time or beginning of an action?
In negative sentences: Do you want to express how much time has past since the last
time the action took place or since the beginning of the action?
Present Perfect Simple Present Perfect Progressive
since the last time
I haven't played that game for years. (Meaning: It's
years ago that I last played that game.)
since the beginning
I haven't been playing that game for an hour, only
for 10 minutes. (Meaning: It's not even an hour ago
that I started to play that game.)
Permanent or temporary?
If an action is still going on and we want to express that it is a permanent situation, we
would usually use the Present Perfect Simple. For temporary situations, we would
prefer the Present Perfect Progressive. This is not a rule, however, only a tendency.
Present Perfect Simple Present Perfect Progressive
permanent temporary
James has lived in this town for 10 years.
(Meaning: He is a permanent resident of this town.)
James has been living here for a year. (Meaning:
This situation is only temporary. Maybe he is an
exchange student and only here for one or two
years.)
Signal words
Present Perfect Simple Present Perfect Progressive
how often
... times
how long
since
for
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Present Perfect SimpleDocument3 paginiPresent Perfect SimpleMadeley CuevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present Perfect Simple Vs Present Perfect ProgressiveDocument3 paginiPresent Perfect Simple Vs Present Perfect ProgressiveAnca MorosanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present Perfect Simple Vs Present Perfect ContinuousDocument8 paginiPresent Perfect Simple Vs Present Perfect ContinuousDaniela NagedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sesión 12 Present Perfect Vs P. P. ContinuousDocument5 paginiSesión 12 Present Perfect Vs P. P. ContinuousfernandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5B Present Prefect& ContinuousDocument14 pagini5B Present Prefect& ContinuousKHALEDALSHARAIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dynamic and Stative Verbs PDFDocument7 paginiDynamic and Stative Verbs PDFDiego TrejoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simple Present vs Present Perfect ProgressiveDocument2 paginiSimple Present vs Present Perfect ProgressivezenzenblueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contrasting the Simple Past and Present Perfect TensesDocument8 paginiContrasting the Simple Past and Present Perfect TensesHayleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simple Past. Vs PPdocxDocument3 paginiSimple Past. Vs PPdocxNagore MonteroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simple Past vs Present Perfect Form and UseDocument3 paginiSimple Past vs Present Perfect Form and UseChristian JaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tenses UietDocument27 paginiTenses UietMohitÎncă nu există evaluări
- English Test Simple Present and Present ProgressiveDocument17 paginiEnglish Test Simple Present and Present Progressivecontes_alinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present Perfect and Simple PastDocument3 paginiPresent Perfect and Simple PastElaine Ricardo CândidoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present Perfect Simple and ContinuousDocument3 paginiPresent Perfect Simple and ContinuousHuyền NgânÎncă nu există evaluări
- Traditiile Romei AnticeDocument13 paginiTraditiile Romei AnticeAnonymous XsOfDozHauÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present Simple TenseDocument18 paginiPresent Simple TenseirmafpdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Teach Past Simple vs Present PerfectDocument7 paginiTeach Past Simple vs Present PerfectMiley Kaltrina FetahuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simple Past Vs Present PerfectDocument3 paginiSimple Past Vs Present PerfectMatilda EftimovaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simple PastDocument5 paginiSimple Pastledrac0% (1)
- Present Perfect Simple and ContinuousDocument2 paginiPresent Perfect Simple and ContinuousDaniela BlagojevicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present Perfect Simple - P Perfect ContDocument6 paginiPresent Perfect Simple - P Perfect ContAntonia AntoÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Past Continuous Tense Is Most Often Used For Actions Happening at Some Time in The PastDocument4 paginiThe Past Continuous Tense Is Most Often Used For Actions Happening at Some Time in The PastAndreea-Cristina DraganescuÎncă nu există evaluări
- PPS VS PPCDocument4 paginiPPS VS PPCCristinaianc100% (1)
- Present Perfect Vs ContinuousDocument4 paginiPresent Perfect Vs ContinuousAmeliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Past Simple or ContinuousDocument4 paginiPast Simple or ContinuousirmafpdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present Perfect Simple X ContinuousDocument2 paginiPresent Perfect Simple X ContinuousMaria MouraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Past Simple vs Continuous SeminarDocument3 paginiPast Simple vs Continuous SeminarCaTa LiNaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linguistics (3 Week)Document4 paginiLinguistics (3 Week)Timo GomezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present Perfect Continuous - English VersionDocument2 paginiPresent Perfect Continuous - English VersionAzahara Márquez ZamoranoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simple Present - Present ProgressiveDocument4 paginiSimple Present - Present Progressivedanieladeras_2002Încă nu există evaluări
- Present Continuous and Simple Present TensesDocument17 paginiPresent Continuous and Simple Present TensessherinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PresentperfectDocument12 paginiPresentperfectapi-252190418Încă nu există evaluări
- Present Perfect Vs Present Perfect ContinuousDocument2 paginiPresent Perfect Vs Present Perfect ContinuousNaitali MalikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simple Present Present Progressive: in General or Right Now?Document3 paginiSimple Present Present Progressive: in General or Right Now?Nadia Nur AmeliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present Progressive NotesDocument5 paginiPresent Progressive NotesFauzan 'AzimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Appendices: Clean Clean Clean Clean Clean Clean Clean Clean Clean CleanDocument5 paginiAppendices: Clean Clean Clean Clean Clean Clean Clean Clean Clean CleanDiego Alejandro MunguíaÎncă nu există evaluări
- English Grammar in A Nutshell BookDocument70 paginiEnglish Grammar in A Nutshell Bookdavidco66200157% (7)
- English Present Simple and COntinousDocument4 paginiEnglish Present Simple and COntinousLaura MuñozÎncă nu există evaluări
- English Tense SystemDocument26 paginiEnglish Tense SystemJordan CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Future Perfect Continuous TenseDocument8 paginiFuture Perfect Continuous TenseAtriyusri HanafahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present Perfect Simple ContinuousDocument17 paginiPresent Perfect Simple ContinuousLiliana RaduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simple Present vs Perfect ProgressiveDocument9 paginiSimple Present vs Perfect Progressivenistor mariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grammar GuideDocument21 paginiGrammar GuideAfrica ArcayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Listed Below Are Uses With Examples, and The Structure of The Present Simple TenseDocument6 paginiListed Below Are Uses With Examples, and The Structure of The Present Simple TenseUma KalyaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present Tense PaperDocument18 paginiPresent Tense PaperMega PuspiytaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tenses Part - 1 Simple Present TenseDocument5 paginiTenses Part - 1 Simple Present Tensesiva kumar100% (1)
- Complete Grammar For First Certificate in EnglishDocument231 paginiComplete Grammar For First Certificate in EnglishDana Bleoca100% (3)
- Present Perfect Simple & ContinuousDocument20 paginiPresent Perfect Simple & Continuousbuendia8986% (7)
- Present SimpleDocument6 paginiPresent SimpleGranada CamiloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simple Present and Present Continuous TensesDocument43 paginiSimple Present and Present Continuous TensesFrancisca Ponce HilleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lightweight introduction to Communicative English GrammarDocument42 paginiLightweight introduction to Communicative English Grammarsdenhelle100% (1)
- English Papers on Past Perfect Tense, Present Perfect Continuous Tense, Direct and Indirect Speech, and PrepositionsDocument13 paginiEnglish Papers on Past Perfect Tense, Present Perfect Continuous Tense, Direct and Indirect Speech, and PrepositionsRatihAyerIndartoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Verb Tense Tutorial: Complete List of Simple Present FormsDocument43 paginiVerb Tense Tutorial: Complete List of Simple Present FormsRoxana TudoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present Perfect Unfinished TimeDocument5 paginiPresent Perfect Unfinished TimePedro MujicaÎncă nu există evaluări
- English Grammar ExplanationsDocument13 paginiEnglish Grammar ExplanationsНикола Каранфиловски100% (3)
- Active VoiceDocument13 paginiActive VoiceIan Iswara MadhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- How Do We Use This TenseDocument8 paginiHow Do We Use This TenseFlorentina DespoiuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Master English Tenses: A Short & Comprehensive GuideDe la EverandMaster English Tenses: A Short & Comprehensive GuideÎncă nu există evaluări
- Easy Italian: Lower Intermediate Level - Vol. 1De la EverandEasy Italian: Lower Intermediate Level - Vol. 1Evaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- ESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideDe la EverandESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideÎncă nu există evaluări
- Verb and Preposition CollocationsDocument6 paginiVerb and Preposition CollocationsledracÎncă nu există evaluări
- Much, Many, A Lot Of, Lots Of: QuantifiersDocument8 paginiMuch, Many, A Lot Of, Lots Of: QuantifiersledracÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inversion RulesDocument11 paginiInversion RulesledracÎncă nu există evaluări
- Future Perfect ProgressiveDocument6 paginiFuture Perfect ProgressiveledracÎncă nu există evaluări
- BesidesDocument4 paginiBesidesledracÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summary Charts of English TensesDocument6 paginiSummary Charts of English TensesledracÎncă nu există evaluări
- Verb TensesDocument5 paginiVerb TensesledracÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quanti FiersDocument6 paginiQuanti FiersledracÎncă nu există evaluări
- Verb TensesDocument5 paginiVerb TensesledracÎncă nu există evaluări
- Future Perfect ContinuousDocument3 paginiFuture Perfect ContinuousledracÎncă nu există evaluări
- Causative Form (Active and Passive Causative)Document5 paginiCausative Form (Active and Passive Causative)ledracÎncă nu există evaluări
- English Verb TensesDocument5 paginiEnglish Verb TensesledracÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Continuous FormsDocument6 paginiThe Continuous FormsledracÎncă nu există evaluări
- Either / or Versus Neither / Nor: - LEDRA - CV - 1Document5 paginiEither / or Versus Neither / Nor: - LEDRA - CV - 1ledracÎncă nu există evaluări
- 15 Most Useful Phrasal VerbsDocument3 pagini15 Most Useful Phrasal VerbsledracÎncă nu există evaluări
- PronounsDocument3 paginiPronounsCarla FilipeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Connector SummaryDocument18 paginiConnector SummaryledracÎncă nu există evaluări
- Discourse MarkersDocument2 paginiDiscourse MarkersledracÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present Perfect and Simple PastDocument1 paginăPresent Perfect and Simple PastledracÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reglas Reported SpeechDocument4 paginiReglas Reported SpeechKary ShitoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Must, Have To, Have Got To: Positive Sentences Present PastDocument1 paginăMust, Have To, Have Got To: Positive Sentences Present PastledracÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alterações Nos Verbos ModaisDocument4 paginiAlterações Nos Verbos ModaisledracÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparative and Superlative AdjectivesDocument3 paginiComparative and Superlative AdjectivesledracÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simple PastDocument5 paginiSimple Pastledrac0% (1)
- Comparative and superlative adjectives rulesDocument2 paginiComparative and superlative adjectives rulesledracÎncă nu există evaluări
- DespiteDocument2 paginiDespiteledrac0% (1)
- Forming Comparative and Superlative AdjectivesDocument4 paginiForming Comparative and Superlative Adjectivesoe2sayoeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Although/even Though/despite/in Spite Of/thoughDocument2 paginiAlthough/even Though/despite/in Spite Of/thoughledracÎncă nu există evaluări
- Double Object Verbs ExplainedDocument2 paginiDouble Object Verbs ExplainedledracÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adjective ModifiersDocument5 paginiAdjective ModifiersMay Ann DioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prepositions After AdjectivesDocument2 paginiPrepositions After AdjectivesCamila PaulucciÎncă nu există evaluări
- Handout 2 - Pronouns (Kinds and Properties)Document5 paginiHandout 2 - Pronouns (Kinds and Properties)Sangie CenetaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Learn JapaneseDocument18 paginiLearn JapaneseJulz Valdueza100% (2)
- The Digital SAT®-2Document12 paginiThe Digital SAT®-2Asilbek AshurovÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 4 Topic 4 Parts of Speech NewDocument2 paginiAssignment 4 Topic 4 Parts of Speech Newayu nilawatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Романюк О.М. - - стаття PDFDocument4 paginiРоманюк О.М. - - стаття PDFАліна ГуляйгродськаÎncă nu există evaluări
- Voice WorksheetDocument2 paginiVoice WorksheetAnuradha MukherjeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module in TypewriterDocument28 paginiModule in TypewriterzarahjoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compiler Final PDFDocument12 paginiCompiler Final PDFAbu AnsariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adjectives - Comparison - Exercise 1Document5 paginiAdjectives - Comparison - Exercise 1Bianca PistolÎncă nu există evaluări
- French AdjectivesDocument5 paginiFrench AdjectivesIqraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Perfect TensesDocument3 paginiPerfect TensesBeby Febri Kurnia75% (4)
- Lesson Plan Final Demo Final SentencesDocument5 paginiLesson Plan Final Demo Final Sentencesnilo m. bordajeÎncă nu există evaluări
- As AsDocument4 paginiAs AsManoloGarridoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advance English Syllabus 7Document1 paginăAdvance English Syllabus 7drose cachoÎncă nu există evaluări
- AdjectivesDocument12 paginiAdjectivesRasel AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Positive Agreement Using So and TooDocument7 paginiPositive Agreement Using So and TooEga Hidayat AffyatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan Grammar PunctuationDocument3 paginiLesson Plan Grammar PunctuationRosmalia KasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- INGLES INAV 2 Hernandez Ibarra Maria PilarDocument5 paginiINGLES INAV 2 Hernandez Ibarra Maria Pilarz6pn22cd8jÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effective Language in Public SpeakingDocument3 paginiEffective Language in Public SpeakingOanny Oanaa100% (1)
- Modality and The English Modals (PDFDrive)Document233 paginiModality and The English Modals (PDFDrive)Joel I. Meneces Lutino67% (3)
- Once Upon A Time : Activity TypeDocument2 paginiOnce Upon A Time : Activity Typeoscar0% (1)
- Active and Passive Voice - English Exercise - English4uDocument3 paginiActive and Passive Voice - English Exercise - English4uLissseth Carolina CERON SANCHEZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grammar Worksheet: 'Ve Seen Haven't HadDocument2 paginiGrammar Worksheet: 'Ve Seen Haven't HadAndrea Paola Ricardo VanegasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Active and Passive VoiceDocument4 paginiActive and Passive VoiceSalvador Lawrence TogoresÎncă nu există evaluări
- First Certificate Star by Luke ProdromouDocument160 paginiFirst Certificate Star by Luke ProdromouОлеся РаевскаяÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Comparative Study of Structural ParticlesDocument13 paginiA Comparative Study of Structural ParticlesShoon Thadar PaingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technical English Module for Science StudentsDocument7 paginiTechnical English Module for Science StudentsYassine LachouriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Table of English Tenses at a GlanceDocument3 paginiTable of English Tenses at a GlanceViviarviÎncă nu există evaluări