Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Ecologic Model
Încărcat de
Shermane Criszen F. SallanTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Ecologic Model
Încărcat de
Shermane Criszen F. SallanDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
VI.
Ecologic Model
A. Hypotheses
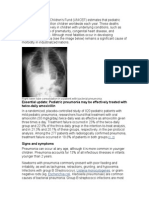
Pneumonia is an inflammation of the one or both lungs, usually caused by an infection.
Three common causes are bacteria, viruses and fungi. You can also get pneumonia by
accidentally inhaling liquid or other microorganisms and sometimes by physical and
chemical irritants. People most at risk are older than 65 or younger than 2 years of age,
or already have health problems. ach individual is unique in their degree of reactivity to
environmental triggers. This naturally influences the type and dose of medication
prescribed, !hich may vary from one individual to another. Pneumonia is caused by
environmental and genetic factors, !hich can influence ho! severe pneumonia is and
ho! !ell it responds to medication. "nderlying both environmental and genetic factors is
the role of the upper air!ay in recogni#ing the perceived dangers and protecting the
more vulnerable lungs by shutting do!n the air!ay.
$ommunity %cquired Pneumonia is an acute infection of the pulmonary parenchyma that
is associated !ith at least some symptoms of acute infection, accompanied by the
presence of an acute infiltrate on a chest radiograph, or auscultatory findings consistent
!ith pneumonia, in a patient not hospitali#ed or residing in a long term care facility for &
'( days before onset of symptoms.
B. Predisposing Factors
Host
- lderly )*( years +ld,
- -ecurrent pneumonia
- .ip /racture
- .istory of $olon $ancer
Environment
- 0ed ridden. "nable to turn. 1evelopment of bacteria
Agent
- Presence of S. pneumoniae,
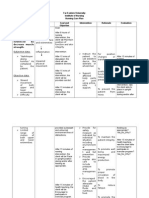
B. Ecologic Model
Agent-Host Environment
D. Analysis
This is useful for e2amining causes of disease in an individual. 3t is useful in predicting
illness rather than promoting !ellness, although identification of risk factors that result
from the interaction of agent, host environment are helpful in promoting and maintaining
health. 0ecause each of the agent4host4environment factors constantly interacts !ith
others, health is an ever4changing state.
The agent4host4environment model is primarily used in predicting illness rather than
promoting !ellness, although identification of risk factors that result from the interaction
of agent, host, and environment are helpful in promoting and maintaining health.
0ecause each of the agent4host4environment factors constantly interacts !ith others,
health is an ever changing state. .ealth is seen !hen all three elements are in balance
!hile illness is seen !hen one, t!o, or all three elements are not in balance.
)/undamentals of 5ursing by 6o#ier 277(,
8hen pneumonia is caused by bacteria, an infected adult9elder usually becomes sick
relatively quickly and e2periences the sudden onset of high fever and unusually rapid
Environment
Bed ridden.
Unable to
turn.
Development
of bacteria
Host
-Elderly
- Recurrent
Pneumonia
-Hip Fracture
-History of
Colon cancer
Agent
-Presence of S.
pneumoniae,
breathing. 8hen pneumonia is caused by viruses, symptoms tend to appear more
gradually and are often less severe than in bacterial pneumonia. 8hee#ing may be more
common in viral pneumonia.
)6ids .ealth from 5ermour by Yamini 1urani 27'',
3f you:re age 65 or older, particularly if you have other conditions that make you
more prone to developing pneumonia, you:re at increased risk of pneumonia. People
!ho are hospitali#ed have a higher risk for developing pneumonia than those !ho are
not. .ospitali#ed patients are particularly vulnerable to gram4negative bacteria and
staphylococci, !hich can be very dangerous, particularly in people !ho are already ill.
-ecurrent pneumonia, if a person inhales fluid )aspirates, from the esophagus into the
lungs, it may trigger inflammation in these upper passages.
E Conclsion and !ecommendations
3t can be inferred in the statements above that the client is suffering from
Pneumonia, and can probably be caused by the lo!ered immune system of the client
from the identified pre4disposing risk factors.
8e therefore conclude that our hypothesis is correct because the client had
$ommunity %cquired Pneumonia $omplained !ho complained of difficulty of breathing,
patient had productive cough, 8hee#ing sounds in the lungs and crackles sounds in the
lungs.
Typically, oral antibiotics, rest, fluids, and home care are sufficient for complete
resolution. .o!ever, people !ho are having trouble breathing, !ith other medical
problems, and the elderly may need greater care. 3f the symptoms get !orse, the
pneumonia does not improve !ith home treatment, or complications occur, then
hospitali#ed may be recommended. +2ygen therapy, 5ebuli#ation, %ntibiotic therapy,
and 3ntravenous /luid therapy may be needed. +ver the counter cough medicine has not
been found to be helpful in pneumonia.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Chronic CoughDe la EverandDiagnosis and Treatment of Chronic CoughSang Heon ChoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ecologic Model of PneumoniaDocument2 paginiEcologic Model of PneumoniaShermane Criszen F. SallanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ecologic ModelDocument3 paginiEcologic ModelHazel Regencia RodriguezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study PneumoniaDocument53 paginiCase Study PneumoniaWilliam Agoncillo100% (1)
- 3 PneumoniaDocument17 pagini3 PneumoniaMohamed Na3eemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pneumonia: DR Abdul Ghani WaseemDocument20 paginiPneumonia: DR Abdul Ghani WaseemFarwaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PnuemoniaDocument102 paginiPnuemoniaRegineCuasSulibÎncă nu există evaluări
- REQ - PneumoniaDocument6 paginiREQ - PneumoniaAira AgolongÎncă nu există evaluări
- I SearchresearchpneumoniaDocument7 paginiI Searchresearchpneumoniaapi-277487340Încă nu există evaluări
- Nur 111 Session 3 Sas 1Document8 paginiNur 111 Session 3 Sas 1Zzimply Tri Sha UmaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- NURSING CARE PLAN PneumoniaDocument38 paginiNURSING CARE PLAN PneumoniaLuna JadeÎncă nu există evaluări
- PneumoniaDocument3 paginiPneumoniaEdward McSweegan, PhD100% (1)
- PneumoniaDocument10 paginiPneumoniaJohn Philip M. Lacas RNÎncă nu există evaluări
- CASE STUDY: Bronchial Asthma in Acute Exacerbation: EtiologyDocument35 paginiCASE STUDY: Bronchial Asthma in Acute Exacerbation: EtiologyMishiel Castillo100% (1)
- Revise PneumoniaDocument7 paginiRevise PneumoniaMelai AvilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Definition of PneumoniaDocument4 paginiDefinition of PneumoniaEmylia Ananda PutriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abstract PneumoniaDocument2 paginiAbstract PneumoniaAlissa MaghopoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pneumonia: - Is An Infection of One or Both Lungs Which Is Usually Caused by BacteriaDocument10 paginiPneumonia: - Is An Infection of One or Both Lungs Which Is Usually Caused by Bacteriajdvea12Încă nu există evaluări
- Paul Christian C. Paragas March 15, 2013 BSN - MSC Mrs. Maridel M. Juarez Pneumonia Updates Key FactsDocument3 paginiPaul Christian C. Paragas March 15, 2013 BSN - MSC Mrs. Maridel M. Juarez Pneumonia Updates Key FactsMichael UrrutiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aspiration PneumoniaDocument18 paginiAspiration PneumoniaRaja Alfian IrawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Corynebacteria.: Student Name Institution Affiliation Course Name Professor's Name Due DateDocument6 paginiCorynebacteria.: Student Name Institution Affiliation Course Name Professor's Name Due DateRamso SoppahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Causes of PneumoniaDocument4 paginiCauses of Pneumoniailke akdenizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eman YousifDocument9 paginiEman Yousifsheka mÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Bronchitis... The OneDocument35 paginiAcute Bronchitis... The One'mYk FavilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is Pneumonia?: Patient EducationDocument2 paginiWhat Is Pneumonia?: Patient EducationDian Putri NingsihÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Management 103 Cap MRDocument9 paginiNursing Care Management 103 Cap MRkarenfaye00Încă nu există evaluări
- 1 Running Head: Disease Report On Causes and Prevention of PneumoniaDocument4 pagini1 Running Head: Disease Report On Causes and Prevention of PneumoniawaweruhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 1: PneumoniaDocument45 paginiTopic 1: PneumoniaNektarios TsakalosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pneumonia Disease Risk FactorsDocument3 paginiPneumonia Disease Risk FactorsPedialy AvilesÎncă nu există evaluări
- 584 1130 1 PBDocument3 pagini584 1130 1 PBAlden Lui SevillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trinity University of Asia St. Luke'S College of Nursing Case Study (Opd) NAME: Marie Deborah Kay B. Chakas CASE: Pneumonia (Pedia)Document19 paginiTrinity University of Asia St. Luke'S College of Nursing Case Study (Opd) NAME: Marie Deborah Kay B. Chakas CASE: Pneumonia (Pedia)MARIE DEBORAH KAY CHAKASÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pennsylvania Department of Health 2013 Plague Fact SheetDocument3 paginiPennsylvania Department of Health 2013 Plague Fact SheetSean SimonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eco ModelDocument3 paginiEco ModelMary Joyce Juat DayotÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practice Essentials: Pediatric Pneumonia MedicationDocument56 paginiPractice Essentials: Pediatric Pneumonia MedicationAnonymous HgX3mN1oÎncă nu există evaluări
- Febrile SeizureDocument5 paginiFebrile SeizureGilny RantungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pneumonia With Pleural EffusionDocument24 paginiPneumonia With Pleural EffusionMund CheleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group I OxygenationDocument75 paginiGroup I OxygenationSheryl Ann Barit PedinesÎncă nu există evaluări
- MediaDocument3 paginiMediamediatrixgasmenÎncă nu există evaluări
- A. Current Trends About The Disease ConditionDocument35 paginiA. Current Trends About The Disease ConditionVina LaurelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pediatric Community Acquired Pneumonia: PresentorsDocument34 paginiPediatric Community Acquired Pneumonia: PresentorsEvelyn MedinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1Document30 paginiChapter 1Ayro Business CenterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medical Terms Kind of IlnessDocument11 paginiMedical Terms Kind of IlnessFani KimerliÎncă nu există evaluări
- PneumoniaDocument35 paginiPneumoniaAlina Batalà100% (1)
- Pneumonia Case Pres Level 2 Group 4Document43 paginiPneumonia Case Pres Level 2 Group 4Archie Punzalan67% (3)
- Case Study For PneumoniaDocument11 paginiCase Study For PneumoniaGabbii Cinco100% (1)
- Epidemiology of TBDocument4 paginiEpidemiology of TByam pdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Review of Literature - Anusha BhandarkarDocument26 paginiReview of Literature - Anusha BhandarkarAnushaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Management 1Document8 paginiNursing Management 1Melai AvilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pneumonia WrittenDocument12 paginiPneumonia WrittenFereli Joy SupanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Preventive Medicine Part IaDocument4 paginiPreventive Medicine Part IarustonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clinical Presentation On PnemoniaDocument37 paginiClinical Presentation On PnemoniasreekalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Name: Yeti Muliani Class: 1A Nim: 20.043 Subject: English Lecturer: Ririn Yosep Hanna. S. Pane, M.Pd. Assignment: Skimmming and Scanning TextDocument6 paginiName: Yeti Muliani Class: 1A Nim: 20.043 Subject: English Lecturer: Ririn Yosep Hanna. S. Pane, M.Pd. Assignment: Skimmming and Scanning TextYeti MulianiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Updated September 2016: PneumoniaDocument5 paginiUpdated September 2016: PneumoniaYidnekachew Girma Assefa100% (1)
- Pleural EffusionDocument38 paginiPleural EffusionMela VincoÎncă nu există evaluări
- EMT Case StudyDocument10 paginiEMT Case StudymkasimkatuziÎncă nu există evaluări
- Essential Update: Pediatric Pneumonia May Be Effectively Treated With Twice-Daily AmoxicillinDocument54 paginiEssential Update: Pediatric Pneumonia May Be Effectively Treated With Twice-Daily AmoxicillinYostesara Maurena SantosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oleh: Ns. Hana Ariyani, M. KepDocument23 paginiOleh: Ns. Hana Ariyani, M. KepMuhammad Rizal alimuddinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kaushal - Pneumonia DiseaseDocument10 paginiKaushal - Pneumonia DiseaseKaushal PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hospital Acquired Pneumonia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDe la EverandHospital Acquired Pneumonia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Opd Case PresDocument25 paginiOpd Case PresShermane Criszen F. SallanÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCPPimpaired DocleaderDocument4 paginiNCPPimpaired DocleaderShermane Criszen F. SallanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Leadership and ManagementTableofcontentsDocument1 paginăLeadership and ManagementTableofcontentsShermane Criszen F. SallanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drugs Feunrmf OpdDocument12 paginiDrugs Feunrmf OpdShermane Criszen F. SallanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seminar - Budget ProposalDocument2 paginiSeminar - Budget ProposalShermane Criszen F. Sallan0% (1)
- Tranexamic AcidDocument2 paginiTranexamic AcidShermane Criszen F. SallanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Body Parts Assessment Technique Interpretation Analysis: Assessment of Head To ToeDocument15 paginiBody Parts Assessment Technique Interpretation Analysis: Assessment of Head To ToeShermane Criszen F. SallanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample AttendanceDocument2 paginiSample AttendanceShermane Criszen F. SallanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seminar - Budget ProposalDocument2 paginiSeminar - Budget ProposalShermane Criszen F. Sallan0% (1)
- The Writing ProcessDocument17 paginiThe Writing ProcessShermane Criszen F. SallanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Family Health NursingDocument15 paginiFamily Health NursingShermane Criszen F. SallanÎncă nu există evaluări
- RFBDocument1 paginăRFBShermane Criszen F. SallanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocument4 paginiPathophysiology of PneumoniaShermane Criszen F. Sallan100% (4)
- Ecologic Model of PneumoniaDocument3 paginiEcologic Model of PneumoniaShermane Criszen F. SallanÎncă nu există evaluări
- GoalDocument5 paginiGoalShermane Criszen F. SallanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity IntoleranceDocument4 paginiActivity IntoleranceShermane Criszen F. SallanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ecologic Model and Pathophy1Document2 paginiEcologic Model and Pathophy1Shermane Criszen F. SallanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ecologic Model and Pathophy1revisedDocument2 paginiEcologic Model and Pathophy1revisedShermane Criszen F. SallanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDocument1 paginăPathophysiology of Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverShermane Criszen F. SallanÎncă nu există evaluări