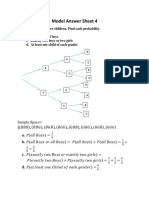
Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Matric 10 Yrs
Încărcat de
Syed Mairaj Ul HaqDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Matric 10 Yrs
Încărcat de
Syed Mairaj Ul HaqDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
P a g e | 1
`
Compiled by: Faizan Ahmed math.pgseducation.com
7075594, 7690630 7075996, 7095650
X MATHEMATICS
10 YEARS PAST PAPERS
S E T S
If Ux[xe, x10], A 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 ] and B 3, 6, 9, 10], then prove that (AUB)`A`B`.
(2012)
If A 1, 2, 3, 4] and B 2, 4, 6, 8], then show that (AUB)(AB) A B. (2011)
If A 1, 2, 3, 5, 6] and B 2, 4, 6, 7], find A B. (2010)
If { {{ { } }} } { {{ { } }} } { {{ { } }} } / ^ 10 1, 3, 5, 7 1, 5, 6, 8 U x x N x A and B = = = = = = = = = = = = Prove that ( (( ( ) )) ) ' ' ' A B A B = == = I U I U I U I U (2009)
If { {{ { } }} } { {{ { } }} } { {{ { } }} } / ^ 20 , 2, 4, 6, .....20 1, 3, 5, ....,19 U x x N x A and B = = = = = = = = = = = = verify that
( (( ( ) )) ) ' ' ' A B A B = == = I U I U I U I U (2008)
If { {{ { } }} } { {{ { } }} } { {{ { } }} } / ^ 12 2, 4, 6, 8,10,12 3, 6, 9,12 U x x N x A and B = = = = = = = = = = = = Prove that
( (( ( ) )) ) ' ' ' A B A B = == = I U I U I U I U (2007, 2004)
If { {{ { } }} } { {{ { } }} } { {{ { } }} } / ^1 12 1, 2, 5, 9 2, 3, 8, 9,10 U x x N x A B = = = = = = = = = = = = Prove that ' ' A B I II I (2005)
If { {{ { } }} } { {{ { } }} } { {{ { } }} } / ^ 10 2, 3, 5, 7 2, 4, 6, 8,10 U x x N x A B = = = = = = = = = = = = verify that ( (( ( ) )) ) ' ' ' A B A B = == = U I U I U I U I
(2006, 2002)
If { {{ { } }} } { {{ { } }} } { {{ { } }} } 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 , 1, 2 2, 4, 6 U A and B = = = = = = = = = = = = Prove that ( (( ( ) )) ) ' ' ' A B A B = == = I U I U I U I U (2003)
If { {{ { } }} } { {{ { } }} } / ^1 12 , 2, 4, 6, 8,10,12 U x x N x A = = = = = = = = and { {{ { } }} } 2, 3, 5, 7,11 B = == = then find ' ' A B U UU U
(2001)
{ {{ { } }} } { {{ { } }} } / ^ 10 2, 4, 6, 8 U x x N x A = = = = = = = = and { {{ { } }} } 2, 3, 5, 7 B = == = Verify that ( (( ( ) )) ) ' ' ' A B A B = == = U I U I U I U I (2000)
If { {{ { } }} } 0,1 A = == = and { {{ { } }} } 1, 2 B = == = prove that A B B A (2003)
If { {{ { } }} } 2, 3, 4 A = == = and { {{ { } }} } , B a b = == = find A B (2009)
If ( (( ( ) )) ) , , A a b c = == = find ( (( ( ) )) ) P A . (2007, 2004)
Find P (B) when { {{ { } }} } , , B x y z = == = (2008, 2009)
If { {{ { } }} } { {{ { } }} } , 2, 3 A a b B = = = = = = = = and { {{ { } }} } 3, 4 C = == = Find the value of ( (( ( ) )) ) A B C U UU U (2006)
If { {{ { } }} } { {{ { } }} } , 8, 9 A a b B = = = = = = = = and { {{ { } }} } 9,10 C = == = then find ( (( ( ) )) ) B C A U UU U (2001)
If ( (( ( ) )) ) ( (( ( ) )) ) 10, 4 2 3 , 2 2 x y x y + = + + = + + = + + = + Find the values of x and y (2005)
If { {{ { } }} } 1, 2, 3 S = == = then find P(S). (2002)
B L A N K S
AAB ________: (AUB, AB, (AB) - (AUB), (AUB) - (AB) )
(A`)` _______: (A, A`, 0, U)
If R(1,2), (2,3), (3,4)] Domain R ______: (1], 1,2], 1,2,3], 2,3])
0, 1, 2, . . .] is the set of ______: (Prime number, Even number, whole number, odd number)
The null set is considered to be a SUBSET of every set.
{ {{ { } }} } 0,1, 2, 3.... is a set of WHOLE NUMBERS.
If a` is a real number then the point (0, a) lies on Y-AXIS.
If a relation is given by ( (( ( ) )) ) ( (( ( ) )) ) ( (( ( ) )) ) { {{ { } }} }
0,1 , 1, 2 , 3, 4 R = == = then Range is { {{ { } }} } 1, 2, 4 .
P a g e | 2
`
Compiled by: Faizan Ahmed math.pgseducation.com
7075594, 7690630 7075996, 7095650
The Y coordinate of every point on x axis is zero.
If { {{ { } }} } , , , A a b c d = == = then P(A) has 16 elements.
If a set has 3 elements the number of its possible subsets is 8.
If set A has 2 elements and set B has 3 elements then A B has 6 elements.
The ordered pair ( (( ( ) )) ) 3, 4 lies in IV quadrant.
If the elements of P(A) are 16 then the number of elements of set 4 A = == = .
SYSTEM OF REAL NUMBERS,
EXPONENTS AND RADI CAL S
Simplify:
l m m n n l
l m n
m n l
x x x
x x x
+ + + + + + + + + + + +
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
\ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \
(2012)
If P3+22, find the value of P
2
+
1
P
2
(2012)
Simplify: [
x
2a
x
a+h
[
x
2h
x
h+c
[
x
2c
x
c+a
(2011)
Simplify:
l m m n n l
l m n
m n l
x x x
x x x
+ + + + + + + + + + + +
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
\ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \
(2010)
Simplify:
2 2 2 a b c
a b b c c a
x x x
x x x
+ + + + + + + + + + + +
| || || | | || || | | || || | | || || |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
\ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \
(2008, 2007)
If 2 3 x = + = + = + = + , find the value of
1
x
x
+ ++ + (2007, 2003)
Simplify:
( (( ( ) )) )
4 .
a b b c
a b
a c
c a
b c
x x
x x
x x
+ + + + + + + +
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
\ \ \ \ \ \ \ \
(2006, 2009)
( (( ( ) )) )
( (( ( ) )) )
1
2 3
2
125 8
64
| | | | | | | |
| | | |
| | | |
\ \ \ \
(2005, 2004)
2 2 2
p q q r r p
p q r
p q q r r p
x x x
x x x
+ + + + + + + + + + + +
+ + + + + + + + + + + +
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
\ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \
(2003)
( (( ( ) )) ) ( (( ( ) )) )
( (( ( ) )) )
2 / 3 / 6
/ 2
27 8
18
n n
n
(2002)
2 2 2
a b b c c a
a b c
a b b c c a
x x x
x x x
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
\ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \
(2001)
2 2 2 2 2 2
a ab b b bc c c ca a
a b c
b c a
x x x
x x x
+ + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + +
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
\ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \
(2000)
B L A N K S
-1(-1)
5
]
2
_________ (-1, 1, 0,2)
Multiplicative inverse of (a h) is: (a+b, -a+b,
1
a-h
,
1
a+h
)
If
2
2 3 x then x = + = = + = = + = = + =
P a g e | 3
`
Compiled by: Faizan Ahmed math.pgseducation.com
7075594, 7690630 7075996, 7095650
The additive inverse of
1
a b
is
1
a b + ++ +
.
The additive inverse of a b is b a .
( (( ( ) )) ) ( (( ( ) )) )
7 2 2 7 2 2 + = + = + = + =
( (( ( ) )) ) ( (( ( ) )) )
2 2 7 2 2 7 + = + = + = + =
9 8
5 5 5 = = = =
is an irrational number.
( (( ( ) )) )
1/ 2
49 121 77 = = = =
1 1
3 2
8 36 8 = = = =
1 1
15 15
o
x
= == =
Degree of polynomial
2 3 2 5 2 7
8 5 x y x y x y is
1
a a a
= = = =
LOGARI THMS
With the help of log tables, find the value of
.87
(28.9)(.785)
. (2012)
With the help of log tables, find the value of
.73548.27
(1.18)
2
. (2011)
With the help of log tables, find the value of
85.7 2.47
8.89
. (2010)
Find the value of
( (( ( ) )) ) ( (( ( ) )) )
2
86.2 37.37
591
with the help of log tables. (2009, 2002)
( (( ( ) )) ) ( (( ( ) )) )
0.87
28.9 0.785
(2008)
82.2 88.6
2.25
(2007)
( (( ( ) )) )
2
780.6 3.0
4.0
(2006)
( (( ( ) )) ) ( (( ( ) )) )
1
3
3
9310
1.08 62.4
| | | | | | | |
| | | |
| | | |
\ \ \ \
(2005)
( (( ( ) )) ) ( (( ( ) )) )
48.7
83.8 3.14
(2004)
Solve
( (( ( ) )) ) ( (( ( ) )) )
2
0.96 87.5
4850
(2003, 2001)
Solve
( (( ( ) )) ) ( (( ( ) )) )
2
0.96 87.5
4850
(2000)
B L A N K S
P a g e | 4
`
Compiled by: Faizan Ahmed math.pgseducation.com
7075594, 7690630 7075996, 7095650
lug
4
x =
3
2
, then x = ________ (
1
8
, 8,
1
,
1
9
)
lug
1
1 = y, then y = ________ ( 1, 3, 5, )
lug
a
x
3
y
z
2
= ________ (A). lug
a
x
3
+lug
a
y lug
a
z
2
(B). 3lug
a
x + lug
a
y 2lug
a
z
(C). 3lug
a
x lug
a
y +2lug
a
z (D).
3lug
a
x-2lug
a
z
lug
a
y
If
81
log 9 x then x = = = = = = = = If log 32 5
x
then x = = = = = = = =
If
3
4
81
log x then x = = = = = = = = If log 81 4
x
then x = == =
If
2
3
8
log x then x = = = = = = = = If log 49 2
x
then x = = = = = = = =
The characteristic of 0.00396 is -3. log 3 + log 6 - log 2 log 9
If log 36 2
x
then x = = = = = = = =
AL GEBRAI C EXPRESSI ONS
None. (2012)
Find the value of a
3
1
a
3
when a
1
a
= 4. (2011)
If a + b 5 and a - b 3, find the value of a
2
+ b
2
. (2010)
If 9, 20 a b ab + = = + = = + = = + = = then find the value of
2 2
a b + ++ + . (2009, 2004)
If 9 a b c + + = + + = + + = + + = and
2 2 2
29 a b c + + = + + = + + = + + = then find the value of ab bc ca + + + + + + + + . (2008)
Find
2 2
a b + ++ + when 7 a b + = + = + = + = and 12 ab = == = . (2007, 2003)
If 8 a b + = + = + = + = when 2 a b = = = = find the values of
2 2
a b and ab + ++ + . (2005)
Find a b + ++ + when 5 21 a b and ab = = = = = = = = . (2001)
Find
3
3
1
x
x
= == = when
1
4 x
x
= = = = . (2006, 2002)
Find the value of
2
2
1 1
6 x when x
x x
+ + = + + = + + = + + = (2000)
B L A N K S
Degree of the polynomial x
2
+xy
2
+y is: (2,3,4,1)
x
2
+64 can be made a perfect square by adding _________.
(a) 4x
2
(b) 8x
2
(c) 2x
2
(d) 16x
2
(x-4)(x-6) __________
(a) x
2
+10x-24 (b) x
2
-10x-24 (c) x
2
+10x+24 (d) x
2
-10x+24
If a+b2 and ab2 then value of a
2
+b
2
is:
(a) -1 (b) 2 (c) 4 (d)
3
2
( (( ( ) )) ) ( (( ( ) )) )
2 2
4 a b a b ab + = + = + = + = . ( (( ( ) )) ) ( (( ( ) )) ) ( (( ( ) )) )
2 2
2 2
2 a b a b a b + + = + + + = + + + = + + + = + .
FACTORI ZATI ON
Resolve the following into factors: r
2
(s-t)+s
2
(t-r)+t
2
(r-s) (2012)
x
6
-64, (ab+cd)
2
(ac-bd)
2
, x
2
+15x100 (2012)
18x
2
+9x20, 27x
3
-1+8y
6
+18xy
2
: (2011)
Resolve the following into factors: (2010)
( (( ( ) )) ) ( (( ( ) )) ) ( (( ( ) )) ) x y z y z x z x y
2 2 2
+ + + + + + + +
2
10 17 6 x x + + + + . (2009)
P a g e | 5
`
Compiled by: Faizan Ahmed math.pgseducation.com
7075594, 7690630 7075996, 7095650
2
ab amx bx mx + + + + . (2009, 2005, 2001, 2000)
2 2
16 64 x y xy + + + + . (2009)
6 6
a b . (2009)
4 2
11 1 x x + + + + . (2009)
2 2
14 15 9 x xy y . (2003)
3 2
2 x x + + + + . (2011, 2009, 2007, 2006, 2004)
2
x yz xy xz + + + + . (2008, 2007, 2004)
2
4 5 21 x x + + + + . (2008)
4
4 a + ++ + . (2011, 2008)
( (( ( ) )) )
2 2
1 2ab a b + + + + + + + + . (2008, 2007, 2004)
3 3
2 8 x x y y + + + + . (2008, 2001)
3 3 3
27 9 a b c abc . (2008)
2
12 5 2 x x + + + + . (2007, 2004)
4
64 x + ++ + . ( 2007, 2006, 2004, 2002)
3 3
8 1 6 x y xy + + + + + + + + . (2007, 2004)
3 2 2
ax ax bx bx cx c + + + + . (2006)
2 2
16 64 x y xy + + + + . (2006)
2 3
2 8 x x y y + + + + . (2006)
3 6 2
27 64 1 36 a b ab . (2006)
2 2
12 17 5 a ab b . (2005)
2
64 25 80 m m + + + + + + + + . (2005)
7 5 3
m n n m . (2005)
8 4
1 x x + + + + + + + + . (2005, 2012)
3 3
27 8 1 18 a b ab + + + + + + + + . (2005)
2 2
16 40 25 a ab b + + + + . (2003)
3 3
27 64 x y + ++ + . (2003)
4
4 1 y + ++ + . (2003)
2 2
4 4 x x y + + + + + + + + . (2003)
3 3 3
27 8 18 a b c abc + + + + + + + + . (2003)
2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
6 12 9 8 a x b y b x a y + + + + . (2002)
3 3 3
8 6 x y z xyz . (2002)
2
2 15 x x + + + + . (2002)
2 2
25 9 30 a b ab + + + + . (2002)
2 7
x y xy . (2002)
2 2
25 4 20 a b ab + + + + . (2001)
3 3
8 1 6 a b ab + + + + + + + + . (2001)
2
3 7 6 a a . (2001)
4
4 81 y + ++ + . (2001)
2 2
16 40 25 a ab b + + + + . (2000)
3 3
27 8 x y + ++ + . (2000)
2 2
2 1 x x y + + + + + + + + . (2000)
3 3 3
8 6 a b c abc + + + + + + + + . (2000)
P a g e | 6
`
Compiled by: Faizan Ahmed math.pgseducation.com
7075594, 7690630 7075996, 7095650
2 2
13 30 x xy y + + + + . (2000)
For what values of a and b, x
4
+4x
3
+10x
2
+ax+b will be a perfect square? (2012)
For what values of q`, 4x
4
+12x
3
+25x
2
+24x+q will be a perfect square? (2011)
What should be added to
4 3 2
4 10 14 5 x x x x + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + to make it a perfect square? (2009)
What should be subtracted from
4 3 2
2 3 2 x x x x + + + + + + + + + + + + so that it becomes a perfect square?
Find the value of x also. (2008, 2006, 2002)
If
4 3 2
4 12 21 9 x x x ax + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + is a perfect square. Find the value of ' ' a ? (2007, 2003)
For what values of a and b will the expression
4 3 2
4 12 21 x x x ax b + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + be a perfect square?
(2005)
For what values of a and b will the expression
4 3 2
4 12 25 x x x ax b + + + + + + + + be a perfect square?
(2004)
If
4 2
2 4
8 4
4 x x q
x x
+ + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + is a perfect square then find the value of q . (2001)
For what value of p will the expression
4 3 2
4 16 24 16 x x x x p + + + + + + + + become a perfect square.
(2000)
REMAINDER THEOREM
x
3
-x
2
-14x+24 (2012)
x
3
+3x2+4x-28 (2011)
x x x
3 2
11 36 36 + + + + (2010)
3 2
5 2 24 x x x + + + + . (2009, 2004, 2001)
2 2
14 24 x x x + + + + . (2008)
3 2
6 11 6 x x x + + + + . (2007, 2003)
3 2
6 32 x x + + + + . (2006)
3 2
2 5 4 3 x x x + + + + . (2005)
3
17 26 x x + + + + . (2002)
SIMPLIFY
2
4
1
2 2
a b a
a b a ab
+ ++ + | | | | | | | |
| | | |
\ \ \ \
. (2009)
2 2
4 3 1
9 4 3 2
x y
x y x y
. (2008)
2 2 2 2
1 b a
a b a b a b
+ + + +
. (2007, 2004)
2 2 2 4
1 1 2
1 1 1
a
a a a a a a
+ + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + +
. (2006)
2
4
1
2 2
x y xy
x y x xy
| | | | | | | | + ++ +
+ + + +
| | | |
\ \ \ \
. (2005)
2 2
1 1 1
4 2 2 x y x y x y
+ + + + + + + +
. (2000)
2
2
1 1 1
4
2 2
b
a b a b a
+ + + + + + + +
+ + + +
. (2002)
Find the second polynomial when one polynomial is
2
5 14, x x G.C.D is 7 x and
L.C.M.
3 2
10 11 70 x x x + + + + + + + + . (2001)
B L A N K S
P a g e | 7
`
Compiled by: Faizan Ahmed math.pgseducation.com
7075594, 7690630 7075996, 7095650
G.C.D of
5 2 3 4
18 12 x y and x y is
4
64 x + ++ + can be made perfect square by adding
2
16 . x
9
4
should be added to
2
3 a a to make it a perfect square.
L.C.M. of
2
4 5 x and x is
2
2x should be added to
4
4 x + ++ + to make it a perfect square.
2
b should be added to
2
16 8 a ab + ++ + to make it a perfect square.
2 y should be added to
2
1 y + ++ + to make it a perfect square.
2
4b should be added to
4
4 a ab to make it a perfect square.
To make
2
8 x x a perfect square 16 should be added.
MATRI CES
By using Cramer`s Rule, solve the equations: (2012)
2x+5y9, 4x-2y1
If Aj
3 2
1
[; prove that: A.A
-1
I (2011)
Apply Cramer`s Rule to solve the given equations:
x y 4 2 + = + = + = + =
x y 7 2 3 + = + = + = + =
If
3 2
5 6
A
| | | | | | | |
= == =
| | | |
\ \ \ \
find
1
A
and PROVE THAT
1
AA I
= == = . (2009, 2008)
If
2 1
3 2
A
| | | | | | | |
= == =
| | | |
\ \ \ \
find
1
A
. (2007, 2003)
If
6 2
4 3
A
| | | | | | | |
= == =
| | | |
\ \ \ \
find
1
A
and PROVE THAT
1
AA I
= == = . (2006, 2002)
If
5 3
2 1
A
| | | | | | | |
= == =
| | | |
\ \ \ \
then find
1
A
and PROVE THAT
1
AA I
= == = . (2001)
Solve the following equations with the help of matrices.
2 3 1 x y = = = = (2004)
4 6 x y + = + = + = + =
2 2 x y = = = = (2005)
2 3 x y + = + = + = + =
2 5 x y + = + = + = + = (2000)
3 7 x y + = + = + = + =
B L A N K S
If A_
1 2
3 p
_ is a singular matrix, the value of p is: (5,6,1,-1)
Scalar matrix is :
(a) j
3
3
[ (b) j
1
1
[ (c) j
3
3 3
[ (d) j
1
1 1
[
If number of rows and columns is not equal then matrix is called rectangular matrix.
If
1 2
3
A then p
p
| | | | | | | |
= = = = = = = =
| | | |
\ \ \ \
P a g e | 8
`
Compiled by: Faizan Ahmed math.pgseducation.com
7075594, 7690630 7075996, 7095650
If
2 3
4 x
| | | | | | | |
| | | |
\ \ \ \
is a singular matrix then x
If
1 2 1 2
3 4 3 4
A and B
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
= = = = = = = =
| | | | | | | |
\ \ \ \ \ \ \ \
then A + B is a 0 matrix.
If
1 1
2 2
a a
A and B then A B
b b
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
= = = = = = = = = = = =
| | | | | | | | | | | |
\ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \
.
AL GEBRAI C SENTENCES
Solve graphically the following sets of equations. (Find four ordered pairs)
(1)
x y
x y
5 7 13
7 6 3
+ = + = + = + =
+ = + = + = + =
(2010)
(2)
4 5
5 17
x y
x y
= = = =
+ = + = + = + =
(2009)
(3)
3 7 2
5 3
x y
x y
= + = + = + = +
+ = + = + = + =
(2008, 2006, 2001)
(4)
3 5
2 7 3
x y
x y
= = = =
+ = + = + = + =
(2007, 2004)
(5)
3 5 21
4 11
x y
x y
+ = + = + = + =
+ = + = + = + =
(2005)
(6)
8 29
2 11
x y
x y
= = = =
+ = + = + = + =
(2003)
(7)
2 12
3 2 4
x y
x y
+ = + = + = + =
= = = =
(2002)
(8)
7 3
3 13
x y
x y
= = = =
+ = + = + = + =
(2002)
(9) x2y3, 2x+y14 (2011)
(10) 4xy100, 3x+5y190 (2012)
Solve the following equations:
2x+5
3 = 1, (2011)
8 5
1 3
2
x + ++ +
= = = = (2009)
25 6 4 3 x x = + = + = + = + (2011, 2009, 2007, 2006, 2004)
2
10 24 0 x x + = + = + = + = (2009)
2 1
2 0
3
x
= = = = (2008, 2002)
3 5
2 10
2
x
+ = + = + = + = (2008)
2
6 40 0 x x + = + = + = + = (2008, 2007, 2004)
P a g e | 9
`
Compiled by: Faizan Ahmed math.pgseducation.com
7075594, 7690630 7075996, 7095650
2 3
2 8
3
x + ++ +
= = = = (2007, 2006, 2004)
( (( ( ) )) ) ( (( ( ) )) ) 5 1 2 2 17 x x + = + = + = + = (2006, 2003)
5 3 6 3 x = = = = (2005, 2001)
( (( ( ) )) ) 4 3 1 2 8 x x = + = + = + = + (2005, 2001)
2
2 7 15 0 x x = = = = (2005)
2
8 15 0 x x + + = + + = + + = + + = (2003)
x x
2
2 7 6 0 + = + = + = + = (2010)
x x 4 5 3 7 = + = + = + = + . (2010)
3 5 1 8 x + = + = + = + = (2003, 2000)
2 3 6 , x x x N > + > + > + > + (2002)
2
3 10 2 0 x x + = + = + = + = (2002)
2
3 10 6 0 x x + = + = + = + = (2001)
2
6 5 1 0 x x + + = + + = + + = + + = (2000)
2 1
2 5
3
a
= = = = (2000)
B L A N K S
Sol set of { {{ { } }} } 4 2 x is = = = = Sol set of { {{ { } }} } 2 2 3 x is + = + = + = + =
EL I MI NATI ON
Find a relation independent of t` from the following equation: (2012)
x =
a(1-t
2
)
1+t
2
, y =
h(1-t
2
)
2t
2
Find a relation independent of x` from the following equation: (2011)
x +
1
x
= 2a, x
3
+
1
x
3
= h
3
Eliminate x ` from the following equations and find the new relationship: (2010)
x p
x
x q
x
1
2
1
2 1
+ = + = + = + =
= + = + = + = +
Find relation free of x (2009)
2
x a
b
a x
+ = + = + = + =
2
x a
c
a x
= = = =
Eliminate t
2 3
, x at y bt = = = = = = = = (2008)
If
2
2
1
2 x p
x
+ = = + = = + = = + = = and
2
1
3 x q
x
+ = + = + = + = find relation free from x . (2006)
Eliminate t (2005)
5 7 2 x t and y t = = = = = = = =
Find relation independent of x . (2004)
1
x t
x
+ = + = + = + =
P a g e | 10
`
Compiled by: Faizan Ahmed math.pgseducation.com
7075594, 7690630 7075996, 7095650
1
2
t
x
x
= = = =
If
1 1
2 2 x t and x t
x x
+ = + = + = + = + = + = + = + = find the relation free from x . (2003)
Eliminate
1
: 2 x x p
x
+ = + = + = + = . (2002)
1
2 1 x q
x
= + = + = + = +
Eliminate : x (2001)
1
2 x a
x
= = = =
2 2
2
1
x b
x
+ = + = + = + =
Eliminate : x (2000)
2 2
2
1 1
2 x p and x q
x x
= + = = + = = + = = + =
RATI O AND PROPORRTI ON
If
a
h+c
=
h
c+a
=
c
a+h
and a+b+c= , prove that abc (2012)
If
a c e
b d f
= = = = = = = = , prove that (a
2
+ c
2
+e
2
)(h
2
+d
2
+
2
) = (ah +cd + e)
2
(2011)
If
a c e
b d f
= = = = = = = = , prove that
a b a e e f a
b b f f b
4 2 2 2 4 4
6 2 2 5 4
+ + + +
= == =
+ + + +
. (2010)
I NF ORMATI ON HANDLI NG
Marks obtained by some students in a computer science exam are given below. Find the
median of their marks: (2012)
Marks Obtained 20 - 24 25 - 29 30 - 34 35 - 39 40 - 44 45 - 49
No. of Students 25 28 32 25 13 12
The marks obtained by 84 students in an examination are given below. Find mean. (2011)
Marks Obtained 25 - 29 30- 34 35 - 39 40 - 44 45 - 49
No. of Students 9 18 35 17 5
The marks obtained by some students in a Chemistry examination are given below. Find the
median of their marks: (2010)
Marks Obtained 25 - 29 30 - 34 35 - 39 40 - 44 45 - 49
No. of Students 9 18 35 17 5
Find variance from the given information. (2009)
2
12.5, 6666 x x = = = = = = = =
The marks obtained by some students in a subject are below. Find mean. (2009)
Marks Obtained 15-19 20-24 25-29 30-34 35-39
No. of Students 9 18 35 17 5
Find the variance of the following set of numbers. (2008, 2000)
3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13 X = == =
The following are the marks obtained by 10 students in Mathematics: (2008)
23,15, 35, 48, 41, 5, 8, 9,11, 51 X = == = . Find the median of the marks of the students.
The marks obtained by 60 students in an examination are given below. Find their mode. (2007)
P a g e | 11
`
Compiled by: Faizan Ahmed math.pgseducation.com
7075594, 7690630 7075996, 7095650
Marks 40-42 43-45 46-48 49-51 52-54
No. of Students 10 12 30 6 2
A hospital is six storied. The number of rooms in each storey is 35, 32, 31, 34, 38, 33. Find the
standard deviation of the data. (2007)
The marks obtained by 100 students are given below. Find their arithmetic mean. (2006,03,01)
Marks 30-34 35-39 40-44 43-49 50-54 55-59
No. of Students 14 16 18 23 18 11
The weight measurements of 12 medicines (in grams) are 43, 54, 45, 44, 58, 47, 50, 52, 51, 45,
48, 46. Calculate their standard deviation. (2006)
Ten students took a test in Mathematics (out of 100) they got 66, 46, 50, 52, 60, 63, 64, 51, 61
and 55 marks. Find the variance of their marks. (2005)
A set of data contains the values as 148, 145, 160, 157, 156 and 160. Prove that Mode > Median
> Mean. (2005)
The following are the marks obtained by 10 students in English. Find standard deviation of
marks. (2004)
46, 50, 52, 60, 63, 64, 51, 55, 66
Following are the heights of 40 students in inches: Find the mode of the heights of students.
(2004)
Heights (inches) 48-50 50-52 52-54 54-56 56-58 58-60
No. of Students 5 7 10 9 6 3
The heights of 11 players of a football team are as under. Find variance of the heights. (2003)
57, 61, 60, 64, 59, 55, 58, 63, 65, 61, 56
Find S.D from the following information: (2002)
2
19.5, 195, 5555 x x x = = = = = = = = = = = =
The following are the marks obtained by 10 students in English. Find the median. (2002)
23,15, 48, 41, 5, 8, 9,11, 51, 3 X = == =
Find the variance 5, 13,15, 25,12,18, 17, 19, 20,16, 3 X = == = (2001)
On the prize distribution day 84 students of a school brought pocket money with them as
under. Find A.M. (2000)
Rupees 15-19 20-24 25-29 30-34 35-39
No. of Students 9 18 35 17 5
B L A N K S
The median of 0,2,4,6,8,9 is _______. (4,6,8,5)
Of -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, the mean is 0.
In series 0, 1, 4, 6, 7, 9, 12 the median is 6.
The variance is the square of the standard deviation.
The sum of 5 observations is 125, the mean is 25.
/ x n is the formula of arithmetic mean.
The median of 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12 is 7.
3 median - 2 mean mode.
The value which appears most in the data is called MODE.
If the arithmetic mean of 20 numbers is 100 then their sum is 2000.
4 6 5 6 9 0
2 8 7 4 9 4
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
+ = + = + = + =
| | | | | | | | | | | |
\ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \
The median 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12 is 7.
TRI GONOMETRY
Prove that: cut +tan = cutxec
2
(2012)
P a g e | 12
`
Compiled by: Faizan Ahmed math.pgseducation.com
7075594, 7690630 7075996, 7095650
Prove that: sin
2
0 +cos
2
0 1 (2011)
Find the value of the trigonometric ratios of 30
o
. (2010)
Find all the trigonometric ratios of 45
o
. (2009, 2004)
Find the trigonometric ratios of 30
o
. (2005)
Find the trigonometric ratios of 60
o
. (2006)
Prove that:
1 cos
1 cos sin
Sin
+ ++ +
= == =
(2009)
sin260 cos 260 1
o o
+ = + = + = + = . (2008)
( (( ( ) )) )
2
cos sin 2sin . cos 1 + = + = + = + = . (2007)
1 cos cos
sin
cos 1
= + = + = + = + (2006)
( (( ( ) )) ) tan cot sin cos 1 + = + = + = + = . (2005, 2002)
( (( ( ) )) )
2 2 2
cosec 1 sin cos = = = = . (2004)
2 2
1 cot cosec + = + = + = + = . (2003)
Derive
2 2
sin cos 1 + = + = + = + = . (2001)
The foot of a tower is at a distance of 210 dm from a point on the earth. The angle of elevation of the
tower from the point is 60
o
. Find the height of the tower. (2008)
A tree 90 dm high on the bank of a river makes an angle of 30
o
from a point directly on the opposite
bank of a river. Find the width of a river. (2002, 2000)
A ladder makes an angle of 60
o
with the floor and reaches a height of 6 meters on the wall. Find the
length of the ladder. (2001)
Solve the triangle ABC in which m<C 90
o
, m<B 60
o
and b 4 cm. (2007)
B L A N K S
The reciprocal of sin cosec = == = .
If in a rt. Triangle ABC m<B 90o and measures of sides a, b, c are 6, 10 and 8 respectively then tan
m<A .
2
1 cot 2 Cosec = = = =
(1)
2
60
3
o
Cosec = == = (2) . Sin Sec = == = (3) tan60 3
o
= == =
(4) tan . cot 1 = == = (5) cosec . tan sec = == = (6)
1
cot 60
3
o
= == =
(7)
2
1 cos sin = = = = (8) 30 2
o
Cosec = == = (9)
1
tan30
3
o
= == =
BLANKS FROM GEOMETRY (10 Years
The sum of all angles of a cyclic triangle is 360
o
.
A line cannot be PARALLEL to two intersecting lines.
Each of the supplementary angles can be a right angle.
The angle inscribed in major arc is an acute angle.
The line which meets circle in only one point is called TANGENT.
P a g e | 13
`
Compiled by: Faizan Ahmed math.pgseducation.com
7075594, 7690630 7075996, 7095650
An angle inscribed in a semi circle is right angle.
The angle inscribed in minor arc is obtuse.
If a st. line intersects a circle in two points the st. line is called SECANT.
A line segments whose end points lie on circle is called CHORD.
The measure of each angle of an equilateral triangle is 60
o
.
The vertical angles formed by two intersecting lines are Congruent.
The circle passing through the vertices of a triangle is called Circum circle.
A chord passing through the centre of a circle is called the DIAMETER of a circle.
If the sum of measures of two angles is 180
o
then the angles are called SUPPLEMENTARY.
I MPORTANT !UESTI ONS
CHAPTER # 1: Examples 1.22, 1.6 Ex. 1.1 (6, 9) Ex. 1.2 (12, 14, 17, 18, 20) Ex. 1.3 (1, 3, 5)
MISCELL. (4, 11, 12)
CHAPTER # 2: Examples (pg. 20, 3 (pg. 39), 2, 3 (pg. 43), 1, 2, 3 (pg 44-45) 2 (pg. 47)
Ex.2.1 (3) Ex. 2.3 (10, 11, 12, 13) Ex. 2.4 (7-12) Ex. 2.6 (10-14) 2.7 (5-14)
Ex.2.8 (2-10) Miscellaneous Ex. (6, 8, 10)
CHAPTER # 3: Examples 3, 4 (pg. 55) 5, 6 (very important) (pg. 56) 1 (pg. 62) 2, 3 (pg. 64)
2 (pg. 66) 3, 1 (pg. 67) 2.3 (pg. 68).
Ex. 3.1 (Objectives 1 - 12) Ex.3.2 (11-25 especially 20, 21, 22) Ex.3.4, 3.5,
3.6 Miscellaneous Ex. (5, 6, 7, 8, 10)
CHAPTER # 4: Example 1 (pg. 84) 2, 3 (pg. 85) 4 (pg. 86) 3, 4 (pg. 87) 3, 4 (pg. 89)
2 (pg.92) Ex. 4.1 (4) Ex. 4.4 (9-12) Ex. 4.5 (3) Ex. 4.7
Ex. 4.8 (2) Ex. 4.9 (2-5) Ex. 4.10 (7, 8, 9) Miscell. (4, 6, 8, 9, 11, 12)
CHAPTER # 5: Examples 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 (pg. 96-97) 1, 2 (pg. 98) 1, 2 (pg. 100) 1, 2, 3 (pg.101-
102) 1, 2 (pg. 103-104) 1, 2 (pg. 106) 1, 2 (pg. 118) 2 (pg. 120) 1(pg.122), 3,
4 (pg.127-128) Ex.5.1 to Ex.5.7, Ex.5.10 (11-15) 5.11(4, 5, 6, 8), 10 (2, 3, 4,
5) 11(1, 2, 3) 12 (1, 3).
Ex. 5.12 (1, 4, 5) Ex. 5.14 (9-14) Miscell. (1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, 10, 11)
CHAPTER # 6: Example 1 (pg.148) example (pg. 154) example (pg.156) example 1
(pg. 159) example 1 (pg.163) Ex.6.4 (4, 5, 6) Ex. 6.5 (By Cramer`s Rules)
Miscell. (1, 8).
CHAPTER # 1: Examples 1 (pg.1) 2 (pg.5) 3 (pg.6) 1 (pg.7) 2 (pg.8) example (pg.9) 3
(pg.10) 4 (pg.11) 1, 2 (pg.13) 1, 2 (pg.14-15) 1 (pg.17) 2 (pg.18) Ex.1.1 (1)
1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 1.5 (1-10) 1.6 (9-16) 1.8 Miscell. (1, 2, 3, 4, 10).
CHAPTER # 2: Example 1 (pg.21) 4, 1 (pg.4) 1, 2 (pg. 24-25) Ex.2.1 1 (i, iv, v) 2, 3, 4 (i, ii,
iii, iv), 5, 7(i, ii), 8]
CHAPTER # 3: Example (pg.30) 1, 2, 3 (pg.3) 1, 2, 4, 5 (pg.40-41) 1, 2, 3 (pg.43-44) Ex.3.1
(2, 3, 9, 10, 11, 12, 16, 17) Ex. 3.2, Ex. 3.3 (1-7) Miscell. (8, 15, 17).
CHAPTER # 4: Examples 1 (pg.72), 2 (pg.73) 3, 4 (pg.74) 10 (pg.78) 1, 2 (pg.80-81) 3,
4(pg.82) 1, 2 (pg.84) 3, 4 (pg.85) 1 (93) Ex.4.3 (2, 4, 6, 7, 8, 10) Ex. 4.4 (1, 2,
4, 6, 9) Miscell. (4, 12 (i, ii, iii), 19, 21).
CHAPTER # 8: Ratios of 60
o
, Examples 1, 2, 3, 4 (pg.174-175) 1, 2, 3, 4 (pg.176-179) 1, 2,
3, 4, 7 (pg.181-185) Ex.8.3 (2(ii, ii, vi, vii, viii, ix, xi), 3, 4) Ex. 8.4 (2, 3)
Ex.8.5 (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 10, 11, 13, 14, 17, 18) Miscell. (2(iv,vi), 3, 4, 5, 7, 8)
F ORMUL AE
( (( ( ) )) ) ' ' ' A B A B = == = U I U I U I U I ( (( ( ) )) ) ' ' ' A B A B = == = I U I U I U I U
NO. OF SUBSETS 2
n
NO. OF BINARY RELATIONS: m n
P a g e | 14
`
Compiled by: Faizan Ahmed math.pgseducation.com
7075594, 7690630 7075996, 7095650
A B ( (( ( ) )) ) ( (( ( ) )) ) A B A B A B = = = = U I U I U I U I 1
o
a = == =
1
1
a
a
= == =
1
1
a
a
= == =
log log log
a a a
m n mn + = + = + = + = log log log
a a a
m
m n
n
= = = =
log log
n
a a
m n m = == =
log
log
log
n
b
n
a
a
b
= == =
( (( ( ) )) ) ( (( ( ) )) ) ( (( ( ) )) )
2 2
2 2
2 a b a b a b + + = + + + = + + + = + + + = + ( (( ( ) )) ) ( (( ( ) )) )
2 2
4 a b a b ab + = + = + = + =
( (( ( ) )) ) ( (( ( ) )) )
2 2
4 a b a b ab + = + + = + + = + + = + ( (( ( ) )) ) ( (( ( ) )) )
2 2
4 a b a b ab = + = + = + = +
( (( ( ) )) )
2
2 2 2
2 2 2 a b c a b c ab bc ca + + = + + + + + + + = + + + + + + + = + + + + + + + = + + + + + ( (( ( ) )) ) ( (( ( ) )) )
3 3 2 2
a b a b a ab b + = + + + = + + + = + + + = + +
( (( ( ) )) ) ( (( ( ) )) )
3 3 2 2
a b a b a ab b = + = + = + = + ( (( ( ) )) ) ( (( ( ) )) )
3
3 3
3 a b a b ab a b + = + + + + = + + + + = + + + + = + + +
( (( ( ) )) ) ( (( ( ) )) )
3
3 3
3 a b a b ab a b = = = =
( (( ( ) )) ) ( (( ( ) )) )
3 3 3 2 2 2
3 a b c abc a b c a b c ab bc ca + + = + + + + + + = + + + + + + = + + + + + + = + + + +
PRODUCT OF POLYNOMIALS H.C.F L.C.M
1
/ A Ad A A
= == =
DETERMINANT OF MATRIX ad - bc
Quadratic Formula:
2
4
2
b b ac
x
a
= == =
Arithmetic mean for grouped data / fx f
Median for grouped data /
2
n
l h f c
| | | | | | | |
+ + + +
| | | |
\ \ \ \
Mode for grouped data
( (( ( ) )) )
( (( ( ) )) ) ( (( ( ) )) )
1
1 2
l fm f h
fm f fm f
+ + + +
+ + + +
Mean for ungrouped data / x n
Median for ungrouped data If n is odd then Median
1
2
n + ++ +
= == =
If n is even then Median
1 2
2 2 2
n n
th th
+ ++ + | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
+ ++ +
` ` ` `
| | | | | | | |
\ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ ) ) ) )
item.
1
cosec
Sin
= == =
1
sec
Cos
= == =
sin
cos
!an
= == =
2 2
cos 1 Sin + = + = + = + =
2 2
1 tan sec + = + = + = + =
2 2
1 cot cosec + = + = + = + =
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Use of Trigonometry in NavigationDocument5 paginiThe Use of Trigonometry in NavigationJanPoulPoscabol100% (2)
- GEOMETRIC REASONING SKILLS FOR SOLVING PROBLEMSDocument33 paginiGEOMETRIC REASONING SKILLS FOR SOLVING PROBLEMSOliver Price-WalkerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Math 30-1 Diploma ReviewDocument25 paginiMath 30-1 Diploma ReviewHeidy ChauÎncă nu există evaluări
- Energy Notes 3 - Conservation of EnergyDocument5 paginiEnergy Notes 3 - Conservation of EnergySyed Mairaj Ul HaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Instructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYDe la EverandInstructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYÎncă nu există evaluări
- Equilibrium of Force SystemDocument89 paginiEquilibrium of Force SystemKimberly TerogoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageDe la EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageÎncă nu există evaluări
- PREC 2nd Quarter APBDocument6 paginiPREC 2nd Quarter APBJae JinÎncă nu există evaluări
- MATH 10 Q2 WEEKS 1 8 63 PagesDocument63 paginiMATH 10 Q2 WEEKS 1 8 63 PageskairaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tangent Lines and Circles ExplainedDocument5 paginiTangent Lines and Circles Explainedmarygrace idanan67% (3)
- Signal Detection and Estimation - Solution ManualDocument169 paginiSignal Detection and Estimation - Solution ManualSolidstate Raman64% (14)
- Angle and distance measurementsDocument10 paginiAngle and distance measurementsJenny Rose Cornejo100% (1)
- Law of Sine CosineDocument52 paginiLaw of Sine Cosineangel coralesÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11 MatricesDocument13 pagini11 MatricesSri DÎncă nu există evaluări
- Homework 7 (Bonus!) Abelian GroupsDocument3 paginiHomework 7 (Bonus!) Abelian GroupsHafiz AzeemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Isomorphic PDFDocument3 paginiIsomorphic PDFHafiz AzeemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hsslive HSS XI-maths-engDocument39 paginiHsslive HSS XI-maths-engPranavi MuthusamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linearna Algebra - Rjesenja, ETFDocument44 paginiLinearna Algebra - Rjesenja, ETFmarkovukÎncă nu există evaluări
- TE AMO AMORCITOOO!Document7 paginiTE AMO AMORCITOOO!Jann Eduardo PadillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Smarandache PartitionsDocument4 paginiSmarandache PartitionsRyanEliasÎncă nu există evaluări
- R R A S: Quantitative MethodsDocument9 paginiR R A S: Quantitative MethodsMehmoodulHassanAfzalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Laplace transform problemsDocument5 paginiLaplace transform problemsNorma Montes FonsecaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Movie Segment: InstantaneousDocument9 paginiMovie Segment: Instantaneousrehan_sadiq1991Încă nu există evaluări
- AnswersDocument33 paginiAnswersRaj kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cbse 2014 DelhiDocument17 paginiCbse 2014 DelhiharshdalalÎncă nu există evaluări
- NACA Five-Digit-Airfoil SeriesDocument9 paginiNACA Five-Digit-Airfoil SeriesKivanc Ali ANILÎncă nu există evaluări
- S6 Assignment I On CH 1 To 3Document3 paginiS6 Assignment I On CH 1 To 3rehankatyal05Încă nu există evaluări
- 2011 Set B Mock Paper 1 SolutionsDocument15 pagini2011 Set B Mock Paper 1 SolutionsJordan TiongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sakshi: Section - A (Mathematics)Document14 paginiSakshi: Section - A (Mathematics)swamy ChinthalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Danish Math Exercise on Sets & RelationsDocument15 paginiDanish Math Exercise on Sets & RelationsMurk ShaikhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stepeni (Potencije) Operacije Sa StepenimaDocument32 paginiStepeni (Potencije) Operacije Sa StepenimaHugo FitzgeraldÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Overview of Numerical AnalysisDocument59 pagini2 Overview of Numerical AnalysisVashish RamrechaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CENG 196 - CE Competency Appraisal I Problem Set 1 SetsDocument4 paginiCENG 196 - CE Competency Appraisal I Problem Set 1 SetsKurt Francis AcostaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mi h2 Math Solutions p1Document10 paginiMi h2 Math Solutions p1jimmytanlimlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lopitalovo praviloDocument5 paginiLopitalovo praviloAlbina ImamovicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Probability Concepts: 1.1 The Given Sets AreDocument21 paginiProbability Concepts: 1.1 The Given Sets AreSudipta GhoshÎncă nu există evaluări
- International Journal of Engineering and Science Invention (IJESI)Document9 paginiInternational Journal of Engineering and Science Invention (IJESI)inventionjournalsÎncă nu există evaluări
- AnalisisDocument5 paginiAnalisisJhon SanjinesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Set Theory - DPP 02 - Arjuna JEE 2024Document2 paginiSet Theory - DPP 02 - Arjuna JEE 2024anshikashukla2925Încă nu există evaluări
- QM Problem Set 1Document9 paginiQM Problem Set 1Aniruddha GhoshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Surds and Indices: I. Laws of Indices: I) A Xa A (A) A (Ab) A BDocument19 paginiSurds and Indices: I. Laws of Indices: I) A Xa A (A) A (Ab) A BArunachalam NarayananÎncă nu există evaluări
- Model Answer Sheet 4 .Document6 paginiModel Answer Sheet 4 .looooooooooolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 S 1Document16 paginiChapter 2 S 1Fahad HussainÎncă nu există evaluări
- CENG 196 - Problem Set 1.1Document2 paginiCENG 196 - Problem Set 1.1Apple AterradoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modified Activity OperationsOnSetsDocument3 paginiModified Activity OperationsOnSetsMarc Andre Cuizon SaberonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Destacamento Jake - Problem Set 3Document5 paginiDestacamento Jake - Problem Set 3Generose PurolÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1995 2019Document31 pagini1995 2019Zayyan AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Correction Enset 2018Document14 paginiCorrection Enset 2018Salah Din AbbadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Namma Kalvi 10th Maths - Public Exam 2012-2018 Repeated Questions EMDocument37 paginiNamma Kalvi 10th Maths - Public Exam 2012-2018 Repeated Questions EMpurshotthaman dÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ryan Christian Diokno (Assignment)Document2 paginiRyan Christian Diokno (Assignment)Ryan Christian DioknoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mid IDocument11 paginiMid IpassmefoolÎncă nu există evaluări
- RI H2 Maths 2013 Prelim P1 SolutionsDocument13 paginiRI H2 Maths 2013 Prelim P1 Solutionsnej200695100% (1)
- RT Solutions-Practice Test Papers XIII VXY 1 To 6 SolDocument40 paginiRT Solutions-Practice Test Papers XIII VXY 1 To 6 Solvishal110085Încă nu există evaluări
- Integral Solution of The Biquadratic Equation: S.Vidhyalakshmi, T.R.Usha Rani and M.A.GopalanDocument4 paginiIntegral Solution of The Biquadratic Equation: S.Vidhyalakshmi, T.R.Usha Rani and M.A.GopalanInternational Journal of computational Engineering research (IJCER)Încă nu există evaluări
- NCERT Exemplar - Class 11 Chapter 2 Relations and Functions ExercisesDocument15 paginiNCERT Exemplar - Class 11 Chapter 2 Relations and Functions ExercisesNIROY CHADHAÎncă nu există evaluări
- HCI H2 Math Prelim Paper 1 SolutionsDocument12 paginiHCI H2 Math Prelim Paper 1 Solutionsnej200695Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 Relations and FunctionsDocument16 paginiChapter 2 Relations and FunctionsSharmila devi B, PRT-MathsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Classwork Activity #11 With SolutionsDocument2 paginiClasswork Activity #11 With SolutionsChala1989Încă nu există evaluări
- Nyjc h2 Math p1 SolutionDocument10 paginiNyjc h2 Math p1 SolutionjimmytanlimlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- 薛定宇 高等应用数学问题matlab求解(第三版)课后答案 PDFDocument160 pagini薛定宇 高等应用数学问题matlab求解(第三版)课后答案 PDFAlexandra WangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activities/Assessment: Week 1: Introduction To MatricesDocument5 paginiActivities/Assessment: Week 1: Introduction To MatricesMark Kenneth DiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PS3 Relations PDFDocument2 paginiPS3 Relations PDFElon MuskÎncă nu există evaluări
- RT Solutions-22!01!2012 XIII VXY Paper I Code A SolDocument16 paginiRT Solutions-22!01!2012 XIII VXY Paper I Code A Solvishal110085Încă nu există evaluări
- Jee Main Model Questions: MathematicsDocument2 paginiJee Main Model Questions: MathematicsVijayabhaskarareddy VemireddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- UNO Analysis: Familiarity with the Official UNO Ruleset is assumedDocument14 paginiUNO Analysis: Familiarity with the Official UNO Ruleset is assumeddummy accÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sheet 3 Basis and Dimension of A Vector Space: 1. Determine The Value ofDocument3 paginiSheet 3 Basis and Dimension of A Vector Space: 1. Determine The Value ofMohamed AlfarashÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kinema Tics Mult ChoiceDocument11 paginiKinema Tics Mult ChoiceSyed Mairaj Ul HaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Math 1st Year2Document4 paginiMath 1st Year2Syed Mairaj Ul HaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- New Microsoft Office Powerpoint Presentation-1Document26 paginiNew Microsoft Office Powerpoint Presentation-1Syed Mairaj Ul HaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- GK BcatDocument2 paginiGK BcatSyed Mairaj Ul HaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Weekly test questions on passive voice and indirect speechDocument1 paginăWeekly test questions on passive voice and indirect speechSyed Mairaj Ul HaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Weekly TestDocument2 paginiPhysics Weekly TestSyed Mairaj Ul HaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Professor Jee Collegiate Monthly Test Schdule B.com.b.scDocument2 paginiProfessor Jee Collegiate Monthly Test Schdule B.com.b.scSyed Mairaj Ul HaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mcat Phy2Document2 paginiMcat Phy2Syed Mairaj Ul HaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mcate PhyDocument3 paginiMcate PhySyed Mairaj Ul HaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- X Physics 14 Jun TestDocument1 paginăX Physics 14 Jun TestSyed Mairaj Ul HaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Weekly test questions on passive voice and indirect speechDocument1 paginăWeekly test questions on passive voice and indirect speechSyed Mairaj Ul HaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mcate PhyDocument3 paginiMcate PhySyed Mairaj Ul HaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrostatics, Class 12th Cbse Physics FormulaeDocument2 paginiElectrostatics, Class 12th Cbse Physics FormulaeJake TylerÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 Class Urdu Final CompDocument120 pagini10 Class Urdu Final CompSyed Mairaj Ul HaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Xii CGDocument59 paginiXii CGSyed Mairaj Ul HaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bcom II Management NotesDocument81 paginiBcom II Management NotesSyed Mairaj Ul HaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test Result Sheet - Xi CommerceDocument5 paginiTest Result Sheet - Xi CommerceSyed Mairaj Ul HaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ray OpticsDocument1 paginăRay OpticsVishal SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wave Notes 4 - Refraction1Document5 paginiWave Notes 4 - Refraction1Syed Mairaj Ul HaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Professor Jee Collegiate: Class IxDocument2 paginiProfessor Jee Collegiate: Class IxSyed Mairaj Ul HaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- FormDocument2 paginiFormSyed Mairaj Ul HaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nts TestDocument13 paginiNts TestSyed Mairaj Ul HaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wave Notes 3 - Reflection1Document5 paginiWave Notes 3 - Reflection1Syed Mairaj Ul HaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Proud Faculty of Professor Jee CollegiateDocument1 paginăProud Faculty of Professor Jee CollegiateSyed Mairaj Ul HaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test Result Sheet - Xi CommerceDocument5 paginiTest Result Sheet - Xi CommerceSyed Mairaj Ul HaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- FormDocument2 paginiFormSyed Mairaj Ul HaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Muharram Holidays NotificationDocument1 paginăMuharram Holidays NotificationSyed Mairaj Ul HaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class 2nd Year Commercial Geography Guess Paper CommerceDocument2 paginiClass 2nd Year Commercial Geography Guess Paper CommerceKamran Arif Ch80% (15)
- Fundamental Physical QuantitiesDocument5 paginiFundamental Physical QuantitiesSyed Mairaj Ul HaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Section 4.1 WorksheetDocument2 paginiSection 4.1 WorksheetDanayla WoodsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Perth Academy Straight Line Multiple ChoiceDocument9 paginiPerth Academy Straight Line Multiple ChoiceQwaAlmanlawiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tes of Angle Grade VII SMPDocument1 paginăTes of Angle Grade VII SMPecho_tee_nanÎncă nu există evaluări
- SDS2 EngDocument130 paginiSDS2 EngVladimirAgeevÎncă nu există evaluări
- SSC CGL Tier - II: Pure Maths Handout: Geometry - IDocument4 paginiSSC CGL Tier - II: Pure Maths Handout: Geometry - IKenny CharlesÎncă nu există evaluări
- ME 322 Machine Design Gear and Bearing Design PrinciplesDocument13 paginiME 322 Machine Design Gear and Bearing Design PrinciplesVishak ReguÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aplicacion de Las Proyecciones EstereograficasDocument264 paginiAplicacion de Las Proyecciones EstereograficasIrwing Borja ValdezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 5 (Traversing and Travers Computation)Document21 paginiModule 5 (Traversing and Travers Computation)Marvie NivalÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3GPP TR 36.873Document47 pagini3GPP TR 36.873Jackokie ZhaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2-D AssignmentDocument4 pagini2-D AssignmentChristian David WillÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geometry: Crop CirclesDocument54 paginiGeometry: Crop CirclesVismaya JainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jitimu Maths 2019 BookletDocument116 paginiJitimu Maths 2019 BookletanneojeraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Math10 - Q2 - Summative and Performance 2Document2 paginiMath10 - Q2 - Summative and Performance 2Israel BarcenalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Synthesis of MechanismsDocument16 paginiSynthesis of MechanismsDasika Sunder100% (1)
- 8.1 Understanding Angles P. 514Document14 pagini8.1 Understanding Angles P. 514Melissa WoodruffÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Education Diagnostic Test ReviewDocument16 paginiGeneral Education Diagnostic Test ReviewVaughn GaneloÎncă nu există evaluări
- ORBIS User's ManualDocument26 paginiORBIS User's Manualanhntran4850Încă nu există evaluări
- Relations Between Sets of VariablesDocument57 paginiRelations Between Sets of VariablesRezky Andriady IdhilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Area Related To CirclesDocument18 paginiArea Related To CirclesAlpha Mythical GamingÎncă nu există evaluări
- G9 - Activity - 7D Math Grade 9Document2 paginiG9 - Activity - 7D Math Grade 9Trina PamaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- DLL Math Grade7 Quarter3 Week3Document5 paginiDLL Math Grade7 Quarter3 Week3NolandÎncă nu există evaluări