Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
171011-170901-Inter Connected Power System PDF
Încărcat de
Palak Ariwala0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
61 vizualizări2 paginiGUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY b. E. VII th Semester-Examination - Nov-2011 Total Marks: 70 Instructions: 1. Attempt all questions. 2. Make suitable assumptions wherever necessary. 3. Figures to the right indicate full marks.
Descriere originală:
Titlu original
171011-170901-Inter Connected Power System.pdf
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentGUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY b. E. VII th Semester-Examination - Nov-2011 Total Marks: 70 Instructions: 1. Attempt all questions. 2. Make suitable assumptions wherever necessary. 3. Figures to the right indicate full marks.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
61 vizualizări2 pagini171011-170901-Inter Connected Power System PDF
Încărcat de
Palak AriwalaGUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY b. E. VII th Semester-Examination - Nov-2011 Total Marks: 70 Instructions: 1. Attempt all questions. 2. Make suitable assumptions wherever necessary. 3. Figures to the right indicate full marks.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 2
1
Seat No.: _____ Enrolment No.______
GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
B. E. VII
th
SemesterExamination Nov- 2011
Subject code: 170901
Subject Name: Inter Connected Power System
Date:19/11/2011 Time: 10:30 am 01:00 pm
Total Marks: 70
Instructions:
1. Attempt all questions.
2. Make suitable assumptions wherever necessary.
3. Figures to the right indicate full marks.
Q.1 (a) Derive the expression for B-coefficients in case of two generating plants
connected to an arbitrary number of loads through a transmission network.
07
(b) Discuss the procedure for solving the swing equation using point by point
method.
07
Q.2 (a) Compare the GS and NR methods of load flow study. 07
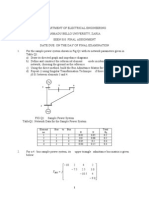
(b) The following figure shows a simple 4-bus system.
1 2
3 4
0.05+j0.15
0.05+j0.15
0.15+j0.45
Line G, pu B, pu
1-2 2.0 6.0
1-3 1.0 3.0
2-3 0.666 2.0
2-4 1.0 3.0
3-4 2.0 6.0
The shunt admittances at all the buses are assumed negligible.
1) Find Y
BUS
assuming that the line shown dotted is not connected.
2) What modifications need to be carried out in Y
BUS
if the line shown dotted
is connected?
07
OR
(b) A system consists of four identical 400 MVA generating units feeding a total load
of 1016 MW. The inertia constant of each unit is 5 on 400 MVA base. The load
changes by 1.5% for a 1% change in frequency. When there is sudden drop in
load by 16 MW, obtain the power system time constant (T
p
) with constants H and
D expressed on 1600 MVA base.
07
Q.3 (a) A power system has two generating plants and power is being dispatched
economically with P
1
= 150 MW and P
2
= 275 MW.
The loss coefficients are:
2 1
11
2 1
12
2 1
22
0.10 10 MW
0.10 10 MW
0.13 10 MW
B
B
B
=
=
=
08
2
To raise the total load on the system by 1 MW, an additional cost of 200 Rs./hour
will be incurred. Find;
a) The penalty factor of plant:1
b) The additional cost per hour to increase the output of plant:1 by 1 MW.
(b) Give reasons:
1) One of the buses is taken as slack bus in load flow studies.
2) Bus admittance matrix is a spare matrix.
3) An acceleration factor is commonly used in load flow studies using GS
method.
06
OR
Q.3 (a) Give the algorithm with flow chart for a fast decoupled load flow solution. 07
(b) Write a short note on Load Dispatch Centre. 07
Q.4 (a) What is power system islanding? Why it is needed? What is ideal procedure to
restore the grid? Discuss the effects of islanding.
07
(b) Derive a mathematical model of turbine speed governing system. 07
OR
Q.4 (a) A 100 MVA, 50 Hz synchronous generator having inertia constant of the machine
as 5 kW-sec per kVA. The load suddenly increases by 50 MW. Due to delay in
governor action there is a delay of 0.6 seconds in opening of steam valve. Find the
frequency deviation.
07
(b) Distinguish between steady state, dynamic and transient stability. Derive power
angle equation sin
e m
P P = . State the assumptions made.
07
Q.5 (a) A single area consists of two generating units, rated at 400 and 800 MVA, with
speed regulation of 4% and 5% on their respective ratings. The units are operating
in parallel, sharing 700 MW. Unit 1 supplies 200 MW and unit 2 supplies 500
MW at 1.0 per unit (50 Hz) frequency. The load is increased by 130 MW.
Assume there is no frequency-dependent load. Find the steady-state frequency
deviation and the new generation on each unit.
07
(b) Explain the following:
1) Bus incidence matrix
2) Primitive network
07
OR
Q.5 (a) A 50 Hz generator of reactance of 1.2 pu is connected to an infinite bus bar
through a line reactance of 0.6 pu. |E| = 1.2 pu and |V| = 1.0 pu. The inertia
constant is 4 MW-sec per MVA. The generator is loaded to 50% of its maximum
power limit. Find the frequency of natural oscillations.
07
(b) Write a short note on Automatic Voltage Control. 07
*************
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Service Guide Rev E - Invivo Expression PDFDocument96 paginiService Guide Rev E - Invivo Expression PDFBalaji BalasubramanianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rudhiprayog Ane Kahevat Sangrah - GujaratiDocument389 paginiRudhiprayog Ane Kahevat Sangrah - GujaratiHarshad Ashodiya Interior Designer57% (14)
- Power, Testing, and Grounding of Electronic SystemsDe la EverandPower, Testing, and Grounding of Electronic SystemsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power System Control QuestionDocument8 paginiPower System Control QuestionMATHANKUMAR.SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power System Simulation Lab - QuestionsDocument13 paginiPower System Simulation Lab - QuestionsMATHANKUMAR.SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Instruments NotesDocument116 paginiInstruments Notesprithvih4Încă nu există evaluări
- VSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsDe la EverandVSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Investigation of the Usefulness of the PowerWorld Simulator Program: Developed by "Glover, Overbye & Sarma" in the Solution of Power System ProblemsDe la EverandInvestigation of the Usefulness of the PowerWorld Simulator Program: Developed by "Glover, Overbye & Sarma" in the Solution of Power System ProblemsÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9A02602 Power System AnalysisDocument4 pagini9A02602 Power System Analysissivabharathamurthy100% (1)
- THYSSEN (Maquina Mini Gearless DAF-270)Document76 paginiTHYSSEN (Maquina Mini Gearless DAF-270)migmarel86% (7)
- Lecture 11 - Power-Flow StudiesDocument28 paginiLecture 11 - Power-Flow StudiesdhanunjayudunasikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Danfoss Scroll Compressors in Parallel Installation SMSYSZDocument48 paginiDanfoss Scroll Compressors in Parallel Installation SMSYSZNikolas Chionas100% (1)
- Measurements & Electronic Instruments Laboratory Experiment ManualDocument3 paginiMeasurements & Electronic Instruments Laboratory Experiment Manualfirst lastÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power System AnalysisDocument5 paginiPower System AnalysisVidyavihar ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)De la EverandPower System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)Încă nu există evaluări
- Inter Connected Power System - CombinedDocument11 paginiInter Connected Power System - CombinedPalak AriwalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Instructions: 1. Attempt All Questions. 2. Make Suitable Assumptions Wherever Necessary. 3. Figures To The Right Indicate Full MarksDocument2 paginiInstructions: 1. Attempt All Questions. 2. Make Suitable Assumptions Wherever Necessary. 3. Figures To The Right Indicate Full MarksAmit PandeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Instructions: 1. Attempt All Questions. 2. Make Suitable Assumptions Wherever Necessary. 3. Figures To The Right Indicate Full MarksDocument2 paginiInstructions: 1. Attempt All Questions. 2. Make Suitable Assumptions Wherever Necessary. 3. Figures To The Right Indicate Full MarksPalak AriwalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Merged DocumentDocument25 paginiMerged DocumentAshokAbiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1792Document7 pagini1792Mohd AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- 171212-170901-Inter Connected Power System PDFDocument3 pagini171212-170901-Inter Connected Power System PDFPalak AriwalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SEO-Optimized Title for Electrical Machines & Electronics Remedial Exam DocumentDocument2 paginiSEO-Optimized Title for Electrical Machines & Electronics Remedial Exam DocumentJignesh PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment PSEDocument5 paginiAssignment PSEdipakk beraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power Systems Computer Methods DocumentDocument7 paginiPower Systems Computer Methods DocumentsuhrudkumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- May 2010Document8 paginiMay 2010Viswa ChaitanyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- APznzaZv YDIffTO4n4O AOwn AvRtnudzBl0remzAumPE9jRsmywQlsaYGS49ODmr8 KgaT1XsShBOB BilLGkWkoZtCjCt2 V5ry9nbm6 BUfcCuhaPFsi1y6nDocument3 paginiAPznzaZv YDIffTO4n4O AOwn AvRtnudzBl0remzAumPE9jRsmywQlsaYGS49ODmr8 KgaT1XsShBOB BilLGkWkoZtCjCt2 V5ry9nbm6 BUfcCuhaPFsi1y6nDaniel Lopes Dias SilvaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Faculty of Environment & Technology: DR H Nouri UFME7M-15-M Modern Power SystemsDocument5 paginiFaculty of Environment & Technology: DR H Nouri UFME7M-15-M Modern Power SystemsLibraryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Be Winter 2020Document2 paginiBe Winter 2020Rushikesh PandyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 07a70203 PowersystemoperationandcontrolDocument8 pagini07a70203 PowersystemoperationandcontrolSamiullah MohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- B.Tech Power System Operation and Control Exam QuestionsDocument8 paginiB.Tech Power System Operation and Control Exam QuestionsMedha AravindÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rr310205 Electromechanics IIIDocument8 paginiRr310205 Electromechanics IIISRINIVASA RAO GANTAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Btech Ee 7 8 Sem Power System Operation and Control A3035 Dec 2018Document2 paginiBtech Ee 7 8 Sem Power System Operation and Control A3035 Dec 2018Raj KamalÎncă nu există evaluări
- R05410204-Power System Operation and ControlDocument6 paginiR05410204-Power System Operation and ControlSRINIVASA RAO GANTAÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE2404 Power System Simulation Lab ProgramsDocument121 paginiEE2404 Power System Simulation Lab ProgramsSachin Samy0% (1)
- Practical ExamDocument2 paginiPractical ExamIrfan AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- OPTIMIZED LOAD SCHEDULINGDocument4 paginiOPTIMIZED LOAD SCHEDULINGShakthi BoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nr-410204-Power System Operation and ControlDocument8 paginiNr-410204-Power System Operation and ControlSrinivasa Rao GÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power System Control-1Document6 paginiPower System Control-1Venkatesh KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- FirstRanker's Choice 1Document8 paginiFirstRanker's Choice 1Jaipaul CheernamÎncă nu există evaluări
- QP Nov - 2010 4 1 Eee PsocDocument8 paginiQP Nov - 2010 4 1 Eee PsocMohammed AlhakeemiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power System Operation and Control ExamDocument4 paginiPower System Operation and Control ExamDr. Gollapalli NareshÎncă nu există evaluări
- KL University Power System Operation & Control AssignmentDocument2 paginiKL University Power System Operation & Control AssignmentVijaya Aditya TadepalliÎncă nu există evaluări
- 498 610 PDFDocument5 pagini498 610 PDFhafiz858Încă nu există evaluări
- II B. Tech II Semester Regular Examinations April/May - 2013 Electrical Machines - IiDocument8 paginiII B. Tech II Semester Regular Examinations April/May - 2013 Electrical Machines - IiAR-TÎncă nu există evaluări
- Subject: Power System Analysis - 2 Subject Code: 15EE71 Model Question Paper MarksDocument2 paginiSubject: Power System Analysis - 2 Subject Code: 15EE71 Model Question Paper MarksVinod KohliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eel301 2022Document2 paginiEel301 2022rraj09102002Încă nu există evaluări
- Psa ModelDocument2 paginiPsa ModelSyed MeerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ee306 ADocument3 paginiEe306 AAparna JoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eeen 810 Final Assignment - 21012012Document5 paginiEeen 810 Final Assignment - 21012012Kabir MohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power SystemDocument3 paginiPower SystemMogaka LucasÎncă nu există evaluări
- X10407EE8702 WatermarkDocument4 paginiX10407EE8702 WatermarkP.Barani Tharan -EEEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document3 paginiQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.Jagadish Babu KondraguntaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Code Analysis of BTech Electromechanical ExamDocument10 paginiCode Analysis of BTech Electromechanical ExamRupesh Kumar SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Department of Electrical &electronics Engineering: Unit: I & IiDocument5 paginiDepartment of Electrical &electronics Engineering: Unit: I & IiArun MariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gujarat Technological University: InstructionsDocument2 paginiGujarat Technological University: Instructionssameer_m_daniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 11 - Power-Flow StudiesDocument28 paginiLecture 11 - Power-Flow StudiesVipin WilfredÎncă nu există evaluări
- VSB Engineering College QuestionsDocument48 paginiVSB Engineering College QuestionsJ JulietÎncă nu există evaluări
- Esa Ue20ee101 II Sem August 2021Document3 paginiEsa Ue20ee101 II Sem August 2021Shashank BakshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psa Question Bank 2Document9 paginiPsa Question Bank 2Krishnakumar IesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Machinery IIDocument2 paginiElectrical Machinery IINEERAJÎncă nu există evaluări
- EC3T5 - PVP 12 Code: EC3T5 B.Tech I Sem May 2016 Electrical Tech ExamDocument3 paginiEC3T5 - PVP 12 Code: EC3T5 B.Tech I Sem May 2016 Electrical Tech ExamHarishReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- NR - 410203 - Computer Methods in Power SystemsDocument6 paginiNR - 410203 - Computer Methods in Power SystemsSrinivasa Rao GÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Machines - IIIDocument9 paginiElectrical Machines - IIILourence Adriel DimaunahanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unbalanced Three-Phase Distribution SystemDocument5 paginiUnbalanced Three-Phase Distribution SystemIraj Az IraniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorDe la EverandSimulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorÎncă nu există evaluări
- 47 March 2018 GyanparabDocument30 pagini47 March 2018 GyanparabPalak AriwalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tie Up Hospital Esic SuratDocument4 paginiTie Up Hospital Esic SuratPalak AriwalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class VII Question Bank English"TITLE "Chief Patron Shri U.N.Khawarey Guide Class VII English" TITLE "Contributors Kendriya Vidyalaya Question Bank Class VIIDocument68 paginiClass VII Question Bank English"TITLE "Chief Patron Shri U.N.Khawarey Guide Class VII English" TITLE "Contributors Kendriya Vidyalaya Question Bank Class VIIAparna Kalla MendirattaÎncă nu există evaluări
- RRB SSE Question Paper 2015 - Day 3 - Slot 2Document53 paginiRRB SSE Question Paper 2015 - Day 3 - Slot 2Palak AriwalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- GTU Electrical Machine Design Exam QuestionsDocument2 paginiGTU Electrical Machine Design Exam QuestionsPalak AriwalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fig: 1 Different SectorDocument2 paginiFig: 1 Different SectorPalak AriwalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- HTTP 164.100.129.99 Mts Pdfprint VerifyprintDocument2 paginiHTTP 164.100.129.99 Mts Pdfprint VerifyprintPalak AriwalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gujarati Grammer 4 PDFDocument17 paginiGujarati Grammer 4 PDFJennifer CarlsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bank Po PaperDocument10 paginiBank Po Paperzipsy53Încă nu există evaluări
- RRB SSE Question Paper 2015 - Day 3 - Slot 2Document53 paginiRRB SSE Question Paper 2015 - Day 3 - Slot 2Palak AriwalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 04Document61 paginiLecture 04gurutheboss1100% (3)
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument2 paginiGujarat Technological UniversityPalak AriwalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument1 paginăGujarat Technological UniversityPalak AriwalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power System Practice and DesignDocument1 paginăPower System Practice and DesignMeet Joshi50% (2)
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument2 paginiGujarat Technological UniversityPalak AriwalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guidelines Regarding Departmental Elective.Document1 paginăGuidelines Regarding Departmental Elective.Jay ThakarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument1 paginăGujarat Technological UniversityPalak AriwalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- P UtilizationDocument1 paginăP UtilizationPalak AriwalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Machine Design IIDocument1 paginăElectrical Machine Design IIMeet JoshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- P Electronics IIDocument1 paginăP Electronics IIPalak AriwalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- GTU BE ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING COMMISSIONING EQUIPMENTDocument3 paginiGTU BE ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING COMMISSIONING EQUIPMENTPalak AriwalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pessor and ControllersDocument2 paginiPessor and ControllersPalak AriwalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 09 Teaching SchemeDocument1 pagină09 Teaching SchemeRahul TilekarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advance Java TechnologyDocument2 paginiAdvance Java TechnologySagar LodhiyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Power System IIDocument2 paginiAdvanced Power System IIdurgesh_ahirÎncă nu există evaluări
- 76953125005465Document43 pagini76953125005465Palak AriwalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- GTU BE Semester VIII Advanced Power System II ExamDocument1 paginăGTU BE Semester VIII Advanced Power System II ExamPalak AriwalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Power System Questions Part3Document1 paginăAdvanced Power System Questions Part3vagoliyoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tiger TO-92 Plastic Transistor SpecsDocument3 paginiTiger TO-92 Plastic Transistor SpecsVinod kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Forward Converter Design and AnalysisDocument56 paginiForward Converter Design and AnalysisJeanTsunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Description and Classification of Electromagnetic Environments - Revision of IEC 61000-2-5Document5 paginiDescription and Classification of Electromagnetic Environments - Revision of IEC 61000-2-5AAAAAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ds SSG 8 Baur En-GbDocument2 paginiDs SSG 8 Baur En-Gbrupesh kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- ASUS Sound Card GuideDocument1 paginăASUS Sound Card GuideilabuloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ecad Lab Manual PDFDocument55 paginiEcad Lab Manual PDFSubrahmanyam VjsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Foundry Technologies 180-Nm Cmos, RF Cmos and Sige Bicmos: High-Performance Devices For A Wide Range of ApplicationsDocument4 paginiFoundry Technologies 180-Nm Cmos, RF Cmos and Sige Bicmos: High-Performance Devices For A Wide Range of Applicationssandeep_sggsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vec 1180 KDocument35 paginiVec 1180 Kyu3zaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3GPP TS 36.101: Technical SpecificationDocument223 pagini3GPP TS 36.101: Technical SpecificationsomberriÎncă nu există evaluări
- BGR PSRRDocument3 paginiBGR PSRRsachin saxenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- LC 22 Le 320Document367 paginiLC 22 Le 320Yanto SaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fusion: User ManualDocument283 paginiFusion: User ManualAndresÎncă nu există evaluări
- It Information Technology Department - B.E., ANNA UNIVERSITY Important Question and Answers - Regulation 2013,2017 - STUDY MATERIAL, NotesDocument5 paginiIt Information Technology Department - B.E., ANNA UNIVERSITY Important Question and Answers - Regulation 2013,2017 - STUDY MATERIAL, NotesKali ThaashÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 8 State Space AnalysisDocument22 paginiChapter 8 State Space AnalysisAli AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- SG30 - 33 - 40 - 50CX User ManualDocument110 paginiSG30 - 33 - 40 - 50CX User ManualAntonio Ruiz JiménezÎncă nu există evaluări
- History and Working Principle of Solar CellsDocument4 paginiHistory and Working Principle of Solar Cellszamzul ariefÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 5 Series and Parallel CircuitsDocument3 paginiLab 5 Series and Parallel CircuitsJimmyPowellÎncă nu există evaluări
- VLT Micro DriveDocument11 paginiVLT Micro DriveMiguel E RosasÎncă nu există evaluări
- SJ-20200929135033-015-ZXA10 C680&C600&C650&C620 (V1.2.1) Optical Access Aggregation Equipment Routine Maintenance - 996110Document44 paginiSJ-20200929135033-015-ZXA10 C680&C600&C650&C620 (V1.2.1) Optical Access Aggregation Equipment Routine Maintenance - 996110paulo gadelhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heat SensorDocument27 paginiHeat SensorRasaq Eneji Jimoh100% (2)
- MR 198CVS Video Processor User Manual V1.0 20140505 PDFDocument120 paginiMR 198CVS Video Processor User Manual V1.0 20140505 PDFMauricio DiazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Casio CTK-2000 Service Manual and Parts ListDocument27 paginiCasio CTK-2000 Service Manual and Parts ListEngkiong Go100% (3)
- P54d en 2048 PDFDocument8 paginiP54d en 2048 PDFSi DidiksÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final ProjectDocument10 paginiFinal Projectapi-271770058Încă nu există evaluări