Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
5142 Facies
Încărcat de
Nandy RayaDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
5142 Facies
Încărcat de
Nandy RayaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Sedimentation and Stratigraphy
Geology 5142
Dr. Thieme
Lecture 11: Facies and
Environments of Deposition
Facies
Sedimentary rocks or rock
characteristics which indicate a
particular depositional environment
Walther's Law
The vertical succession of facies in a
stratigraphic column through time
corresponds to a lateral migration of those
facies over space (also referred to as
space-time substitution)
Facies
Different sediments accumulate adjacent
to one another at the same time
Sediment facies (lithofacies) differ in
those characteristics which indicate the
depositional environment
physical (i.e. sedimentological)
chemical (salinity, pH, etc...)
The changes between adjacent lithofacies
tend to be gradual
Lithofacies
Lithofacies descriptions should include
sedimentary structures
dimensions (particularly thickness)
biogenic content (ooids, peloids, shells,
plant remains, etc... ) and its physical
condition
composition (minerals, rocks, other sed
particles)
grain size
Biofacies, Ichnofacies
Facies may also be identified and
described based upon:
the latter are most likely to directly
coincide with the lithofacies identified
Trace fossils present in the rock
(ichnofacies)
Fauna and/or flora present at the time
and place of deposition (biofacies)
Facies Models
general enough to indicate depositional
environment, but
specific enough to be applied in the
interpretation of stratigraphic sections
typically combine lithofacies, ichnofacies,
and biofacies (where applicable)
often define a lithofacies association
channel lag / overbank / buried soil are all
associated with "meandering stream" facies
Transgression (Onlap)
Regression (Offlap)
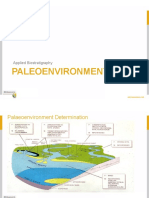
Depositional Environment
A geographic setting where sediment
is accumulating
Determines the nature of the
sediments that accumulate (grain
size, grain shape, etc.)
Depositional Environments
Continental
Dominated by erosion and deposition
associated with streams
Glacial
Wind (eolian)
Marine
Shallow (to about 200 meters)
Deep (seaward of continental
shelves)
Sedimentary Environments
Transitional (shoreline)
Tidal flats
Lagoons
Deltas
Transitional (Shoreline) Environments
Sedimentary structures tell us where we are on
the transect from mean high water across the
shoreface to offshore depositional environments
Calcite Compensation Depth (CCD)
Photic Zone -
Photosynthesis by
marine plants and
algae in the upper
part of the water
column provides
food for organisms
that build shells and
skeletons deposited
in limestones on the
sea floor.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Tuana The Anthropocene and The Body of EthicsDocument26 paginiTuana The Anthropocene and The Body of EthicsscgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercise 7: Historical Geology and Fossils: Earth and Beyond - An Introduction To Earth-Space Science Lab ManualDocument15 paginiExercise 7: Historical Geology and Fossils: Earth and Beyond - An Introduction To Earth-Space Science Lab ManualAtubrah PrinceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fasies N Deps EnvDocument24 paginiFasies N Deps EnvMuhammad Ary IsmoehartoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Piquer 2015Document30 paginiPiquer 2015WilsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- FIRST Lecture Petroleum GeologyDocument7 paginiFIRST Lecture Petroleum Geologyيا ابا صالح المهديÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Deductive Method For The Selection of Geomorphosites Sellier2015Document15 paginiA Deductive Method For The Selection of Geomorphosites Sellier2015Alexandru StefanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11 Facies and TimeDocument92 pagini11 Facies and TimemukakuÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7B SchlagerHandoutv3Document148 pagini7B SchlagerHandoutv3Farrukh QayyumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shallow-marine Sandstone Reservoirs, Depositional Environments, Stratigraphic Characteristics and Facies Model: A Review Numair Ahmed Siddiqui, Abdul Hadi A. Rahman, Chow Weng Sum, Wan Ismail Wan Yusoff and Mohammad Suhaili bin Ismail Department of Geoscience, Faculty of Geoscience and Petroleum Engineering, Universiti Teknologi PETRONAS, Perak, MalaysiaDocument27 paginiShallow-marine Sandstone Reservoirs, Depositional Environments, Stratigraphic Characteristics and Facies Model: A Review Numair Ahmed Siddiqui, Abdul Hadi A. Rahman, Chow Weng Sum, Wan Ismail Wan Yusoff and Mohammad Suhaili bin Ismail Department of Geoscience, Faculty of Geoscience and Petroleum Engineering, Universiti Teknologi PETRONAS, Perak, MalaysiaCris TinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NOAA Technical Report ERL 238-AOML 8Document51 paginiNOAA Technical Report ERL 238-AOML 8Marselinus Satrio WicaksonoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brilha 2015Document18 paginiBrilha 2015Jorge D. MarquesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Part-02 BiostratigraphyDocument50 paginiPart-02 BiostratigraphyDavid John MarcusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geomorphosites: Emmanuel Reynard, Paola Coratza and Géraldine Regolini-Bissig (Editors)Document16 paginiGeomorphosites: Emmanuel Reynard, Paola Coratza and Géraldine Regolini-Bissig (Editors)Diana BorosÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6-Sedimentary PPTminimizerDocument25 pagini6-Sedimentary PPTminimizerapi-3823621Încă nu există evaluări
- Clastic DiagenesisDocument106 paginiClastic DiagenesisPrasanti Plaban Dash100% (1)
- EGN Magazine Issue 12Document56 paginiEGN Magazine Issue 12Lesvos Petrified Forest, Greece100% (3)
- Geology II Lecture SlidesDocument62 paginiGeology II Lecture Slidesbikki rayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Petroleum Geology - Petroleum System: Jeremiah OkoromaDocument16 paginiPetroleum Geology - Petroleum System: Jeremiah OkoromaRashid AhmedovÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gamma Ray LogDocument96 paginiGamma Ray LogzckreprbÎncă nu există evaluări
- Source Rock Evaluation in July Field Gulf of Suez Egypt by Gamal Ragab GaafarDocument22 paginiSource Rock Evaluation in July Field Gulf of Suez Egypt by Gamal Ragab GaafarDr. Gamal Ragab Gaafar0% (1)
- Introduction PDFDocument8 paginiIntroduction PDFPelangi Nadira ArifatunnisaÎncă nu există evaluări
- QAB2033 - Topic 7 - Deep Marine CarbonatesDocument80 paginiQAB2033 - Topic 7 - Deep Marine CarbonatesredwanasisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formation Evaluation Julius 1Document41 paginiFormation Evaluation Julius 1Fosu AdomÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carbonate Sequence Stratigraphy 6-4-14Document44 paginiCarbonate Sequence Stratigraphy 6-4-14Arjun WadhawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 20 Hydrocarbon Accumulation in An Inverted Segment of The Andean Foreland, San Bernardo Belt, Central PatagoniaDocument16 pagini20 Hydrocarbon Accumulation in An Inverted Segment of The Andean Foreland, San Bernardo Belt, Central Patagoniafiorela anait vera parqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPWLA-1994-GGG - Pitfalls of Picket Plots in CarbonatesDocument25 paginiSPWLA-1994-GGG - Pitfalls of Picket Plots in CarbonatesPedroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydrocarbon Traps and SealsDocument30 paginiHydrocarbon Traps and SealsAbu NaserÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3d Seismic Data Interpretation HorizonsDocument57 pagini3d Seismic Data Interpretation HorizonsAz SalehÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 4 Seismic InterpretationDocument55 paginiLecture 4 Seismic InterpretationChristian Rogel De TorresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Properties of CarbonatesDocument35 paginiProperties of CarbonatesnftwoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction Well LoggingDocument40 paginiIntroduction Well LoggingTajuddin MohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydrocarbon Origins and OccurrencesDocument22 paginiHydrocarbon Origins and OccurrencesTri Haryanta100% (1)
- CarbonateDocument42 paginiCarbonateMaria MawarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seismic Survey: University of Zakho College of Engineering Petroleum Engineering DEPDocument35 paginiSeismic Survey: University of Zakho College of Engineering Petroleum Engineering DEPLulav BarwaryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering Geology Presentation PDFDocument65 paginiEngineering Geology Presentation PDFBenjamin AttwellÎncă nu există evaluări
- Journal of African Earth Sciences: Khaled Albriki, Feiyu Wang, Meijin Li, Rajab El ZarougDocument25 paginiJournal of African Earth Sciences: Khaled Albriki, Feiyu Wang, Meijin Li, Rajab El ZarougSYED TAWAB SHAHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Provenance, Tectonic Setting, Source Area Weathering & Paleoredox Condition-Ise SandstoneDocument16 paginiProvenance, Tectonic Setting, Source Area Weathering & Paleoredox Condition-Ise SandstoneHenry MYÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intro Carbonate 2 Carbonate SystemDocument23 paginiIntro Carbonate 2 Carbonate SystemAngel AmpuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seismic Methods PDFDocument12 paginiSeismic Methods PDFandreas yordanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Climate Change - : The Stone Tape'Document16 paginiClimate Change - : The Stone Tape'mdalgamouniÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Investigations in Geophysics - 20) Gerard T. Schuster - Seismic Inversion (2017, Society of Exploration Geophysicists) - Libgen - LiDocument377 pagini(Investigations in Geophysics - 20) Gerard T. Schuster - Seismic Inversion (2017, Society of Exploration Geophysicists) - Libgen - LimayurnawalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reservoir Characterization: Classification of CarbonatesDocument5 paginiReservoir Characterization: Classification of CarbonatesahmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alug Et Al., 2014Document18 paginiAlug Et Al., 2014Amr DeafÎncă nu există evaluări
- Development GeologyDocument114 paginiDevelopment GeologyAsif Akber JÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stratigraphy, Palynology Lower Chile: and of ofDocument14 paginiStratigraphy, Palynology Lower Chile: and of ofMG Snchez RÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basin AnalysisDocument16 paginiBasin Analysissergiu_24100% (1)
- Badin ThesisDocument12 paginiBadin ThesisRaheelKhan0% (1)
- Hydrogen EmbrittlementDocument10 paginiHydrogen EmbrittlementEvans Azka FÎncă nu există evaluări
- QAB2033 Topic 9 DiagenesisDocument73 paginiQAB2033 Topic 9 DiagenesisredwanasisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Impact of Depositional Environment On Petrophysical Reservoir Characteristics in Obaiyed Field, Western Desert, Egypt PDFDocument14 paginiImpact of Depositional Environment On Petrophysical Reservoir Characteristics in Obaiyed Field, Western Desert, Egypt PDFMohamed Abdel-FattahÎncă nu există evaluări
- VelocityModeling UGM August 27 2015Document22 paginiVelocityModeling UGM August 27 2015Naga Lakshmi VasaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exploration Techniques Geophysical Methods H. RueterDocument45 paginiExploration Techniques Geophysical Methods H. RueterBruno Pereyra QuirogaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Norwegian Basins Article OSDocument6 paginiThe Norwegian Basins Article OSNG KMÎncă nu există evaluări
- QAB2033 - Topic 3 - Texture, Classification & Pore TypesDocument34 paginiQAB2033 - Topic 3 - Texture, Classification & Pore TypesredwanasisÎncă nu există evaluări
- CI Facies Analysis - OverviewDocument29 paginiCI Facies Analysis - OverviewPrisaca Cristian100% (1)
- Petroleum Geology: 1 Prepared By: M. TalimbayDocument10 paginiPetroleum Geology: 1 Prepared By: M. TalimbayClark Holden MacasaetÎncă nu există evaluări
- Logging Interpretation Method - Basic Approaches: Quick Look Log Interpretation With Shaly Sand FormationDocument47 paginiLogging Interpretation Method - Basic Approaches: Quick Look Log Interpretation With Shaly Sand FormationhafideÎncă nu există evaluări
- Symposium on Geochemistry of Groundwater: 26th International Geological Congress, Paris, 1980De la EverandSymposium on Geochemistry of Groundwater: 26th International Geological Congress, Paris, 1980Încă nu există evaluări
- Deepwater Sedimentary Systems: Science, Discovery, and ApplicationsDe la EverandDeepwater Sedimentary Systems: Science, Discovery, and ApplicationsJon R. RotzienÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geology of Carbonate Reservoirs: The Identification, Description and Characterization of Hydrocarbon Reservoirs in Carbonate RocksDe la EverandGeology of Carbonate Reservoirs: The Identification, Description and Characterization of Hydrocarbon Reservoirs in Carbonate RocksÎncă nu există evaluări
- Narrative Report On Tree Planting Activities SCHOOL YEAR 2019-2020 IDocument3 paginiNarrative Report On Tree Planting Activities SCHOOL YEAR 2019-2020 Imae80% (5)
- Global Warming Questionnaire AnalysisDocument11 paginiGlobal Warming Questionnaire AnalysisA8cent_8Încă nu există evaluări
- Manfred - Lenzen PublicationsDocument13 paginiManfred - Lenzen PublicationsGlen GurayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Before We Proceed: Here Are Some Video Clips of The Effects OFDocument18 paginiBefore We Proceed: Here Are Some Video Clips of The Effects OFClaudette Ligo SantosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eco ResortDocument2 paginiEco ResortKousalyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mod 1 EcologyDocument86 paginiMod 1 EcologyrfgvgfÎncă nu există evaluări
- Navares, Mabette S.-pdd1Document6 paginiNavares, Mabette S.-pdd1Mabette NavaresÎncă nu există evaluări
- The La Mesa Eco ParkDocument3 paginiThe La Mesa Eco ParkJan DrakeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guimaras State CollegeDocument5 paginiGuimaras State CollegeBabarianCocBermejoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit-V GIS ApplicationsDocument66 paginiUnit-V GIS ApplicationsJithesh DharmadasÎncă nu există evaluări
- BSBSUS501 Sample Sustainability PolicyDocument2 paginiBSBSUS501 Sample Sustainability Policytauqeer akbarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Report Karnataka Elephant Task ForceDocument150 paginiReport Karnataka Elephant Task ForceNaresh KadyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 1 Introduction To Water Resources Systems Planning and ManagementDocument67 paginiLecture 1 Introduction To Water Resources Systems Planning and ManagementmelakuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stronza & Durham 2008 - Ecotourism and Conservation in The AmericasDocument292 paginiStronza & Durham 2008 - Ecotourism and Conservation in The AmericasCasafranca NilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sustainable Fashion PPT 1 Aug 27 2020 Oct 10Document99 paginiSustainable Fashion PPT 1 Aug 27 2020 Oct 10Sunitha VichurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Forest Types of PakistanDocument13 paginiForest Types of Pakistanbutterfily80% (46)
- Estuarine Fish Diversity of Manakudy Estuary, Kanyakumari DistrictDocument6 paginiEstuarine Fish Diversity of Manakudy Estuary, Kanyakumari DistrictJournal of Environment and Bio-SciencesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research PaperDocument8 paginiResearch PaperJohn Paulo GregorioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Environmental Inspection For Crane Barge Check ListDocument1 paginăEnvironmental Inspection For Crane Barge Check ListMuhammad Ali WafaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SITE PLANNING & SELECTION v1.0Document58 paginiSITE PLANNING & SELECTION v1.0Alex AnderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wet LandDocument258 paginiWet LandLe Ngoc DungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microsoft Word - Monografia - Diagnostico Do Escoamento Pluvial em Luanda - Maio 2013Document40 paginiMicrosoft Word - Monografia - Diagnostico Do Escoamento Pluvial em Luanda - Maio 2013Vivaldo Palanga100% (1)
- Contamination in Pasir Gudang Area, Peninsular Malaysia: What Can We Learn From Kim Kim River Chemical Waste Contamination?Document4 paginiContamination in Pasir Gudang Area, Peninsular Malaysia: What Can We Learn From Kim Kim River Chemical Waste Contamination?Leow Chee Seng100% (1)
- Super Teacher Worksheets People and Earths EcosystemDocument4 paginiSuper Teacher Worksheets People and Earths EcosystemRodmar SumugatÎncă nu există evaluări
- MAPEH Q1 Week 1Document21 paginiMAPEH Q1 Week 1Humphrey Noel NerizonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rice, Water, and Power: Landscapes of Domination and Resistance in The Lowcountry, 1790 - 1880Document19 paginiRice, Water, and Power: Landscapes of Domination and Resistance in The Lowcountry, 1790 - 1880fuck offÎncă nu există evaluări
- Go Green Together Review WorksheetDocument2 paginiGo Green Together Review Worksheet장시현0% (1)
- BarangayDocument2 paginiBarangayTifanny Kristel Ann GalaponÎncă nu există evaluări
- Age of StupidDocument2 paginiAge of Stupidapi-376424331Încă nu există evaluări
- Please Oppose SB 175 A Bill To Partially Fund The Proposed Shooting Complex of GFP at Elk Vale RD Near Elk Creek in Meade CountyDocument7 paginiPlease Oppose SB 175 A Bill To Partially Fund The Proposed Shooting Complex of GFP at Elk Vale RD Near Elk Creek in Meade CountyNancy HildingÎncă nu există evaluări