Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Engine Dynamic Properties - 2
Încărcat de
Gthulasi78Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Engine Dynamic Properties - 2
Încărcat de
Gthulasi78Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Reciprocating engine dynamic properties
Scuola di Dottorato di Ricerca 2010 - Road vehicle and engine engineering science
6
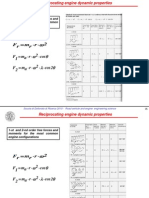
Considerations on gas forces
In multiple cylinder engines, the torque curve of the individual cylinders are
superimposed with a phase shift dependent on the numbers of cylinders,
their configuration, crankshaft design and firing sequence. The resulting
composite curve is characteristics of the engine design and covers a full working
cycle.
Harmonic analysis can lead to a torsional harmonics by a series of sinusoidal
oscillations featuring whole-number multiples of the basic frequencies.
Il Motore come sorgente di vibrazioni e rumore
Fig. 1.4
Effetto del frazionamento sullirregolarit di coppia
Effetto del frazionamento sullirregolarit di coppia
Fig. 1.4a Fig. 1.4b
Analisi delle zone di emissione di un motore
Analisi delle zone di emissione di un motore
The cyclic torque fluctuation leads to a variations of the
crankshafts rotation speed, called cyclic variation and
defined as:
Energy storage devices, as the flywheel and the clutch
spring, must be design to adequately compensate for the
variations of rotation speed in normal applications.
min
min max
Concetti generali
Progettazione meccanica motori Alessandro Piccone 2004/2005
7
Engine Orders
Engine orders are simply the amplitudes of the frequency components which are the multiples
of the rotating frequency. Engine orders, which are determined by an order analysis are
extensively used in the vibration and noise work to identify the source of excitation (order) and,
hence, its frequency of an engine induced problem. For example, a four cylinder in-line engine
will always has its second order component as the dominant excitation.
2E
In four-cylinder four-stroke engines this notation is often used to denote an engine order
where the frequency is two times the engine rotational speed.
3E
Basic firing frequency of a six-cylinder four-stroke engine.
4E
Two times engine firing frequency of a four-cylinder four-stroke engine. It is the basic firing
frequency of an eight-cylinder four-stroke engine.
Engine order meaning
Reciprocating engine dynamic properties
Scuola di Dottorato di Ricerca 2010 - Road vehicle and engine engineering science
8
Engine Excitation Mechanisms (Single Cylinder Engine) 1/5
Inertia Force - The displacement of the piston with respect to crank angle can be derived from simple
trigonometry. This can then be differentiated to yield velocity and acceleration of the piston. The expressions
obtained tend to be very complicated and can be simplified into the expression containing only first order
(once per revolution), second order (twice per revolution), and a negligible fourth order.
where
F
i
= Inertia force [N]
M
REC
= Reciprocating mass (piston mass plus approximately 2/3 conrod mass)
= Crank angle (zero at top dead centre)
R = Crankshaft radius [m]
L = Conrod length [m]
N = Rotational speed [rpm]
Note: if R/L<0.3 it is accurate enough to use just the
first two terms.
Inertia force is obtained by multiplying the piston acceleration by the reciprocating mass and acts only in
the line of the cylinders.
Reciprocating engine dynamic properties
Scuola di Dottorato di Ricerca 2010 - Road vehicle and engine engineering science
Gas Forcing
The rate of rise and peak cylinder pressure of the diesel (13MPa at approximately 20 after TDC) are
approximately twice that of the gasoline with the angle the peak occurs at typically 5earlier.
Diesel and gasoline combustion is random even at full load, worse at part load and particularly poor at
idle. Therefore, it is normal to talk about the average peak cylinder pressure (P
max mean
) and standard
deviation of P
max
. This variability both cycle to cycle and cylinder to cylinder is one source of half order
excitation.
Equilibriumof Forces
The gas force that acts on the piston also acts on
the cylinder head. The force on the piston splits into
two components, one acting down the rod and one
acting sideways on the cylinder wall. The forces are
reacted at the main bearing but a couple exists
between the horizontal reaction at the bearing and
the piston side force. This couple is equal to the
crankshaft output torque, so the crankshaft torque
is reacted by forces on the engine structure.
The gas force components of the vertical force at the
bearing is equal and opposite to the force acting on
the cylinder head, but of course the inertia component
is unbalanced.
Engine Excitation Mechanisms (Single Cylinder Engine) 2/5
Reciprocating engine dynamic properties
Scuola di Dottorato di Ricerca 2010 - Road vehicle and engine engineering science
10
Torque resulting from piston motion alone for a single cylinder engine.
Torsional Excitation of Crankshaft and Engine Structure - The total torque acting on the crankshaft of
the single cylinder engine results from the effect of the gas and inertia forces on the crank slider
mechanism.The torque resulting from piston motion is often called the INERTIA torque and is
represented by the equation:
where
t
i
= Inertia torque [Nm]
Engine Excitation Mechanisms (Single Cylinder Engine) 3/5
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Manual Transmission - 2Document6 paginiManual Transmission - 2Gthulasi78Încă nu există evaluări
- Manual Transmission - 1Document6 paginiManual Transmission - 1Gthulasi78Încă nu există evaluări
- Engine Dynamic Properties-1Document5 paginiEngine Dynamic Properties-1Gthulasi78Încă nu există evaluări
- Weibull Tutorial 1Document5 paginiWeibull Tutorial 1Gthulasi78Încă nu există evaluări
- Brushless DC Motors Are A Type of Synchronous MotorDocument5 paginiBrushless DC Motors Are A Type of Synchronous MotorGthulasi78Încă nu există evaluări
- BLDC 3Document4 paginiBLDC 3Gthulasi78Încă nu există evaluări
- BLDC 4Document5 paginiBLDC 4Gthulasi78Încă nu există evaluări
- Engine Dynamic Properties-2Document5 paginiEngine Dynamic Properties-2Gthulasi78Încă nu există evaluări
- Weibull Tutorial 2Document6 paginiWeibull Tutorial 2Gthulasi78Încă nu există evaluări
- The Steady State Magnetic FieldDocument28 paginiThe Steady State Magnetic FieldRashmi HarishÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sensorless BLDC Motor Control With BEMF Zero-Crossing DetectionDocument6 paginiSensorless BLDC Motor Control With BEMF Zero-Crossing DetectionGthulasi78Încă nu există evaluări
- Synchronous PM Motors: Stator Field Needs To Be Close To Orthogonal (90°) To Rotor Field To GetDocument4 paginiSynchronous PM Motors: Stator Field Needs To Be Close To Orthogonal (90°) To Rotor Field To GetGthulasi78Încă nu există evaluări
- BLDC 5Document7 paginiBLDC 5Gthulasi78Încă nu există evaluări
- BLDC 2Document4 paginiBLDC 2Gthulasi78Încă nu există evaluări
- BLDC 3Document4 paginiBLDC 3Gthulasi78Încă nu există evaluări
- SensorlessBLDCControl 2Document7 paginiSensorlessBLDCControl 2Gthulasi78Încă nu există evaluări
- BLDC 3Document4 paginiBLDC 3Gthulasi78Încă nu există evaluări
- SensorlessBLDCControl 2Document7 paginiSensorlessBLDCControl 2Gthulasi78Încă nu există evaluări
- 3-Phase Sensorless BLDC Motor Control Using MC9S08MP16: PresentationDocument7 pagini3-Phase Sensorless BLDC Motor Control Using MC9S08MP16: PresentationGthulasi78Încă nu există evaluări
- Rotor Sectional View and Commutation SequenceDocument5 paginiRotor Sectional View and Commutation SequenceGthulasi78Încă nu există evaluări
- Brushless DC Motors Are A Type of Synchronous MotorDocument5 paginiBrushless DC Motors Are A Type of Synchronous MotorGthulasi78Încă nu există evaluări
- BLDC 2Document4 paginiBLDC 2Gthulasi78Încă nu există evaluări
- ECE 753 Fault Tolerant Computing Reliability ModelingDocument6 paginiECE 753 Fault Tolerant Computing Reliability ModelingGthulasi78Încă nu există evaluări
- Brushless DC Motors Are A Type of Synchronous MotorDocument5 paginiBrushless DC Motors Are A Type of Synchronous MotorGthulasi78Încă nu există evaluări
- Engine Dynamic Properties - 4Document5 paginiEngine Dynamic Properties - 4Gthulasi78Încă nu există evaluări
- Engine Dynamic Properties - 5Document5 paginiEngine Dynamic Properties - 5Gthulasi78Încă nu există evaluări
- V6 Engine Dynamic PropertiesDocument3 paginiV6 Engine Dynamic PropertiesGthulasi78Încă nu există evaluări
- Engine Dynamic Properties - 6Document5 paginiEngine Dynamic Properties - 6Gthulasi78Încă nu există evaluări
- Engine Dynamic Properties - 3Document5 paginiEngine Dynamic Properties - 3Gthulasi78Încă nu există evaluări
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5782)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (72)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol.-2013-Amanapu-P362-7 - EUV Work With SEMATECHDocument6 paginiECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol.-2013-Amanapu-P362-7 - EUV Work With SEMATECHUmarameshKÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eating Habits in VietnamDocument3 paginiEating Habits in Vietnamsuachuamatong2501Încă nu există evaluări
- Govt. Girls High School Pura Heeran, SialkotDocument7 paginiGovt. Girls High School Pura Heeran, SialkotFizza cooks foodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Illustrating The Relationship Between Humidity and WoodDocument13 paginiIllustrating The Relationship Between Humidity and Woodmoa memÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practice Exam-30000 SeriesDocument11 paginiPractice Exam-30000 SeriesJuan Romero61% (33)
- Anatomy of The Rectum and Anal Canal: The Rectum Is The Part of The Colon Between The Sigmoid ColonDocument25 paginiAnatomy of The Rectum and Anal Canal: The Rectum Is The Part of The Colon Between The Sigmoid ColonJoy GhoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- DownloadDocument12 paginiDownloadAdemar Espírito SantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fundamentals of Physics Extended 10e CH 3 SolutionsDocument6 paginiFundamentals of Physics Extended 10e CH 3 Solutionssin8310% (1)
- Coil Handling Equipment UNCOILER SystemsDocument28 paginiCoil Handling Equipment UNCOILER SystemsKarya Bangunan0% (1)
- Rapid Test Pro Instruction V2Document2 paginiRapid Test Pro Instruction V2desi AdelinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Element Cube, Create A Superhero. Color The Periodic TableDocument6 paginiElement Cube, Create A Superhero. Color The Periodic Tableah5600100% (1)
- Catalogo Raychem PararrayosDocument12 paginiCatalogo Raychem PararrayosEvertMiguelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Micro Cold Storage: Ecozen SolutionsDocument2 paginiMicro Cold Storage: Ecozen SolutionsVikram DeshmukhÎncă nu există evaluări
- A5. Ficha Técnica S4E500AM0301Document6 paginiA5. Ficha Técnica S4E500AM0301Ruben3012Încă nu există evaluări
- Concrete Technology, Basics of ConcreteDocument80 paginiConcrete Technology, Basics of ConcreteAhsan Rabbani100% (3)
- Service Manual Sigma Air Control Plus: Article Number: 7.7740.0 7.7741.0 7.7742.0Document47 paginiService Manual Sigma Air Control Plus: Article Number: 7.7740.0 7.7741.0 7.7742.0Evandro Jva compressoresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aptitude Probability Concepts and FormulasDocument4 paginiAptitude Probability Concepts and FormulasSamuel DebebeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Architects Choise Design Number 3 DollhouseDocument10 paginiArchitects Choise Design Number 3 Dollhouseminutemen_us100% (2)
- NETWORK ANALYSIS MODELS LINKS NODESDocument14 paginiNETWORK ANALYSIS MODELS LINKS NODESTamilmani Natarajan100% (3)
- History 6Sem621History English HistoryandCulDocument207 paginiHistory 6Sem621History English HistoryandCul12nakulÎncă nu există evaluări
- 247 DIN EN 13858 Engl PDFDocument15 pagini247 DIN EN 13858 Engl PDFAlejo Leal100% (4)
- Math 3Eng-T Engineering Data Analysis Problem Set #4 Due Date: Sep 24, 2020 (12 NN) Justin M. Marquez BET-Automotive General InstructionsDocument5 paginiMath 3Eng-T Engineering Data Analysis Problem Set #4 Due Date: Sep 24, 2020 (12 NN) Justin M. Marquez BET-Automotive General InstructionsDeniell Joyce MarquezÎncă nu există evaluări
- BS en 61746-2-2011 (2014)Document48 paginiBS en 61746-2-2011 (2014)melisbbÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 Computers & You: Computers Are Your Future, 10e (Coyle)Document10 paginiChapter 1 Computers & You: Computers Are Your Future, 10e (Coyle)Tú Nguyễn100% (1)
- The Poet's Dream of Nature's PeaceDocument3 paginiThe Poet's Dream of Nature's PeaceMeher KapoorÎncă nu există evaluări
- SEM TheoryDocument50 paginiSEM TheoryKamiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Arts and Crafts of Bagobo and ManoboDocument6 paginiArts and Crafts of Bagobo and ManoboSnyx75% (4)
- Module1 Measles&RubellaDocument52 paginiModule1 Measles&Rubellasakshi gÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advances in engineering technologiesDocument11 paginiAdvances in engineering technologiesSudarshan AhireÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gate Chemistry 2007Document21 paginiGate Chemistry 2007uvir iitmÎncă nu există evaluări