Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Sample Problem PP
Încărcat de
callielizzaTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Sample Problem PP
Încărcat de
callielizzaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Sample problem p p
A (non-rigid) diving bell has an air space of 3.0 m
3
when on the deck of
a small boat. What is the volume of the air space when the bell has been
l d t d th f 50 ? Th d it f t i 1 025
3
lowered to a depth of 50 m? The density of sea water is 1.025 g cm
-3
.
What do we need to assume?
Ideal gas behavior for air
Water temperature is unchanged at 50 m
Constant T so use Boyle: PV=const
Wh i i id i i f i ?
Constant T, so use Boyle: PV=cons t
Why is rigid important information?
1.0 atm
f i
p p gh gh = + = +
Real Gases
- Compressibility Z
PV PV
Z
- Compressibility, Z
PV PV
Z
nRT RT
= =
Z = 1 Ideal Gas behavior
Z < 1 PV less than expected Attractive forces
Z > 1 PV greater than expected Repulsive forces
Z
1
Ar
Ideal Gas Ideal Gas
P
Real Gases data!
Compressibility
PV
PV
Z
nRT RT
m
= =
Z = 1 at all P, T Ideal Gas Behavior
Now look at real gases
Ideal gas
g
at some temperature T
Look at a broader 0 800 atm region
We need new eq of state for each gas
These data are many gases at one T.
So next look at one gas at many T
Boyle Temperature, T
B
y p ,
B
T
B
is the temperature corresponding
( )
Z Z P T =
T
B
is the temperature corresponding
to the greatest extent
of near-ideal behavior.
( )
, Z Z P T
( )
( )
, cZ T P
f
We can determine T
B
analytically.
( )
( )
lim 0
,
0 t th B l t t
+
=
c
p
f T
P
df
T T 0 at , the Boyle temperature = =
B
f
T T
dT
van der Waals equation of state van der Waals equation of state
Physically-motivated corrections to Ideal Gas EoS. y y
For a real gas, both attractive and repulsive intermolecular
forces are present. Empirical terms were developed to help account
for both.
Excluded volume concept (nb)
nRT
P
V b
=
1. Repulsive forces: make pressure higher than ideal gas
Excluded volume concept (nb)
V nb
Volume of one molecule of radius r is V
mol
= (4/3) tr
3
Closest approach of two molecules with radius r is 2r Closest approach of two molecules with radius r is 2r.
ConcepTest #5 ConcepTest #5
Excluded volume
nRT
P =
Excluded volume
P
V nb
=
The volume of one molecule of radius r is V
mol
= 4/3 tr
3
Th l h f l l i h di i 2 The closest approach of two molecules with radius r is 2r.
What is the excluded volume for the two molecules?
A. 2V
mol
B 4V B. 4V
mol
C. 8V
mol
D 16 V D. 16 V
mol
van der Waals equation of state
Physically-motivated corrections to Ideal Gas EoS.
For a real gas, both attractive and repulsive intermolecular
forces are present Empirical terms were developed to help account forces are present. Empirical terms were developed to help account
for both.
1. Repulsive forces: make pressure higher than ideal gas
(or equivalently make the volume smaller)
Do the latter: Excluded volume
nRT
P =
(or, equivalently, make the volume smaller)
Do the latter Excluded volume
V nb
Volume of one molecule of radius r is V
mol
= 4/3 tr
3
Closest approach of two molecules with radius r is 2r Closest approach of two molecules with radius r is 2r.
The excluded volume V
exc
is 2
3
V
mol
= 8V
mol
for two molecules.
So we might estimate that
b 4V N ~
So we might estimate that
A mol
b 4V N ~
This assumes binary collisions only. Always true? NO!
van der Waals equation of state van der Waals equation of state
Physically-motivated corrections to Ideal Gas EoS. y y
For a real gas, both attractive and repulsive intermolecular
forces are present. Empirical terms were developed to help account
for both.
Pressure depends wall collisions, both on frequency
and their force
2. Attractive forces: make pressure lower than ideal gas
and their force.
Not easy to show, but we expect a pressure correction of the
form a(n/V)
2
, giving the van der Waals Equation of State
2
2 2
nRT an RT a
P
V b V V b V
= =
2 2
V nb V V b V
3D van der Waals eqn of state 3D van der Waals eqn of state
T= T/T
c
Real Gases CO
2
CO
2
Look at 20 C isotherm
Look at 50 C isotherm.
Behavior is near ideal gas
2
ABC Compression
At C, liquid condensation begins
Look at 20 C isotherm.
D liquid- vapor mixture at
P
vap
(20 C)
E l d E last vapor condenses
F Steep rise in pressure
A liquid or solid is much less A liquid or solid is much less
compressible than a gas
For T >T there is a single phase For T >T
c
, there is a single phase,
with no liquid formed.
van der Waals Isotherms near T
c
van der Waals Isotherms near T
c
v d W loops are v d W loops are
not physical. Why?
Patch up with Maxwell
construction
van der Waals Isotherms, T/T
c
van der Waals Isotherms near T
cc
Look at one of the van der Waals
isotherms at a temperat re of 0 9 T
1.5
G
isotherms at a temperature of 0.9 T
c
e
s
s
u
r
e
,
P
r
1.0
T
r
=0.9
B
A D compress the gas at constant T,
F G compress the liquid phase
R
e
d
u
c
e
d
P
r
e
0.5
D
B
F
C
A
g, l
(steep and not very compressible)
D F vapor condensing (gas and
liquid coexist)
Thesearestable states
R d d V l V
0.3 0.5 0.7 1 2 3 5 7 10
0.0
A
These are stable states
F C supercooled liquid
D B superheated gas
Th t t bl t t
Reduced Volume, V
r These are metastable states
C B a non-physical artifact of vdW
(patched up with Maxwell construction)
Metastable example:
Use a very clean glass. Add water and heat
for a while with a microwave oven (superheat)
(p p )
o aw ewt a c owaveove (supe eat)
Add a drop of sand or perhaps touch with a spoon.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- ZCS300 ManualDocument24 paginiZCS300 ManualFabricio BorgattaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flextronics Case AnalysisDocument31 paginiFlextronics Case AnalysisGauthamJayanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5 Gas Laws and Kinetic Theory - 2Document43 paginiChapter 5 Gas Laws and Kinetic Theory - 2Rahim RahimunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concentration (Molarity&Dilution) CalculationsDocument19 paginiConcentration (Molarity&Dilution) CalculationscallielizzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multiple Effect EvaporatorDocument45 paginiMultiple Effect Evaporatorcallielizza85% (13)
- Can You Believe It 3Document114 paginiCan You Believe It 3callielizzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- TechnicalExams Dec2017Document29 paginiTechnicalExams Dec2017ming_zhu10Încă nu există evaluări
- Astm A689 PDFDocument4 paginiAstm A689 PDFpradellesÎncă nu există evaluări
- InsulationDocument63 paginiInsulationSH1961Încă nu există evaluări
- K-Tron Premier Rep Catalog Dec 2010 PDFDocument429 paginiK-Tron Premier Rep Catalog Dec 2010 PDFGerardo González33% (3)
- Carregadeira LiebherrDocument17 paginiCarregadeira Liebherrsanches pita100% (5)
- DDC SVC Man 0189Document180 paginiDDC SVC Man 0189gicuÎncă nu există evaluări
- PHY 103 Equations of StateDocument37 paginiPHY 103 Equations of Statebishal alamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gas Laws HandoutDocument10 paginiGas Laws HandoutVenu ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 2 The Gas LawsDocument7 paginiLecture 2 The Gas LawsScrappy WellÎncă nu există evaluări
- CP Ch5Document33 paginiCP Ch5Ahmad RaghebÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHM 221Document12 paginiCHM 221Necherem MissionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry QuizDocument3 paginiChemistry QuizCielo PulmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Equations of StateDocument33 paginiEquations of StateDevika BharathanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1Document30 paginiChapter 1Siti Hajar Mohd PodziÎncă nu există evaluări
- C4-State of MatterDocument171 paginiC4-State of MatterLan FazlanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phy Chem AssignmentDocument14 paginiPhy Chem AssignmentApril Joy HaroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zero LawDocument10 paginiZero Lawalaa anwarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chap 1 The Properties of Gases SP23Document56 paginiChap 1 The Properties of Gases SP23iB13eÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter - 5 State of MatterDocument5 paginiChapter - 5 State of MatterManan TyagiÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Gas LawDocument30 paginiThe Gas LawDevs FusatoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5.0 States of MatterDocument106 pagini5.0 States of MatterTasya KassimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch.1,214-FOU 5Document84 paginiCh.1,214-FOU 5Ahmed YounisÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11 State of Matter Study NotesDocument15 pagini11 State of Matter Study NotesVivek KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 3a - Non-Ideal Thermal Equations of StateDocument6 paginiLecture 3a - Non-Ideal Thermal Equations of StateMuhammad Usman Saifullah KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Gas Laws: Equations of StateDocument32 paginiThe Gas Laws: Equations of Stateyiye rubyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Real Gases - AnnotatedDocument43 paginiReal Gases - Annotatedrahulinder1234Încă nu există evaluări
- Physical Chemistry 01 2015 1stDocument33 paginiPhysical Chemistry 01 2015 1stAzkha AvicenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry Notes Ideal Gas LawsDocument19 paginiChemistry Notes Ideal Gas LawsAbhishek MasneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 02Document9 paginiLecture 02Putu IndraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vapor Pressure: Pº Pressure of A Substance in Equilibrium With Its Pure Condensed (Liquid or Solid) PhaseDocument32 paginiVapor Pressure: Pº Pressure of A Substance in Equilibrium With Its Pure Condensed (Liquid or Solid) Phaseashoku2Încă nu există evaluări
- Real Gases: Sections 1.4-1.6 (Atkins 6th Ed.), 1.3-1.5 (Atkins 7th, 8th Eds.)Document15 paginiReal Gases: Sections 1.4-1.6 (Atkins 6th Ed.), 1.3-1.5 (Atkins 7th, 8th Eds.)Jefriyanto BudikafaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SCH 103 NotesDocument50 paginiSCH 103 NotesJacqueseÎncă nu există evaluări
- ps1 QuestionsDocument2 paginips1 QuestionsdjambulazizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry Xi Term 2 All ChaptersDocument60 paginiChemistry Xi Term 2 All ChaptersKalpesh BishnoiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gas Laws: M. L. WatsonDocument25 paginiGas Laws: M. L. WatsonAbhishek ChakrabartiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical ChemDocument57 paginiPhysical ChemDENISE COLEÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH5 States of MatterDocument26 paginiCH5 States of Mattersi qi wangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gaseous StateDocument14 paginiGaseous StatemayankÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class Note-6 - Real Gases-1Document9 paginiClass Note-6 - Real Gases-1Sukanya PhukonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture #10 Ideal Gas LawDocument28 paginiLecture #10 Ideal Gas LawShamim khanÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHM131 - Chapter 6 - The Gaseous StateDocument37 paginiCHM131 - Chapter 6 - The Gaseous StateNotes NotesÎncă nu există evaluări
- 05 Gases Without AnswersDocument17 pagini05 Gases Without Answersapi-287405319Încă nu există evaluări
- Zumd 05Document41 paginiZumd 05adsiztayfaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Intro Gases THermodynamics 2022Document15 pagini1 Intro Gases THermodynamics 2022Jey BlaQÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9 - Properties of Gases Boyle's Law (P and V) (1 of 12)Document3 pagini9 - Properties of Gases Boyle's Law (P and V) (1 of 12)Scott AllredÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Van Der Waals Equation Analytical and Approximate SolutionsDocument21 paginiThe Van Der Waals Equation Analytical and Approximate Solutionsvitoribeiro90Încă nu există evaluări
- Gaseous States of Matter (HINTS) 2Document2 paginiGaseous States of Matter (HINTS) 2hchawla421Încă nu există evaluări
- Ideal and Real GasesDocument90 paginiIdeal and Real GasesShubham KanungoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kinetic Theory of GasesDocument66 paginiKinetic Theory of GasesDr. Sushil Kumar SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 PensyarahDocument75 paginiChapter 2 PensyarahAdi BaddÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chem 14 Laboratory Report Van Der Waals Isotherms 5 PDF FreeDocument6 paginiChem 14 Laboratory Report Van Der Waals Isotherms 5 PDF FreePedro Ian QuintanillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Intro Gases THermodynamicsDocument16 pagini1 Intro Gases THermodynamicsThabiso GwijiÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Van Der Waals' Gas (VDW.G.) : NRT RT P V VDocument5 paginiThe Van Der Waals' Gas (VDW.G.) : NRT RT P V VSoji AdimulaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dokumen - Tips - Ideal Gas Law 5584a8a9dcd51Document25 paginiDokumen - Tips - Ideal Gas Law 5584a8a9dcd51Earl CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- WWW Adichemistry ComDocument6 paginiWWW Adichemistry ComElapse Dreammaker KibriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Equation of State PDFDocument84 paginiEquation of State PDFAnubhav SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 Study MaterialDocument33 paginiClass 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 Study MaterialmeghaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gases and Their Properties: Exercises, Examples, and BOLD Numbered ProblemsDocument106 paginiGases and Their Properties: Exercises, Examples, and BOLD Numbered ProblemsMia YukimuraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11) Gas Laws - Second Edition - 1551343848Document9 pagini11) Gas Laws - Second Edition - 1551343848ungaranigundla sachivalayamÎncă nu există evaluări
- States of Matter - Shobhit NirwanDocument20 paginiStates of Matter - Shobhit NirwanANMOL SHREYAM100% (1)
- States of MatterDocument15 paginiStates of MatterShaku JoshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Behaviour of Real GasesDocument7 paginiBehaviour of Real GasesAltaf Rather100% (1)
- Science 10 NotesDocument17 paginiScience 10 NotesDerik Resultay100% (1)
- Unit 1Document26 paginiUnit 1firehywotÎncă nu există evaluări
- Working Guide to Vapor-Liquid Phase Equilibria CalculationsDe la EverandWorking Guide to Vapor-Liquid Phase Equilibria CalculationsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- I'd Been Prepared For Death : - Paul Kalanithi (Page 78)Document4 paginiI'd Been Prepared For Death : - Paul Kalanithi (Page 78)callielizzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- History of NmaDocument6 paginiHistory of NmacallielizzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample Response:: Job Interviewing TutorialDocument7 paginiSample Response:: Job Interviewing TutorialcallielizzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- WS 1Document2 paginiWS 1callielizzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nuclear FissionDocument2 paginiNuclear FissioncallielizzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- This Week's Speaking ChallengeDocument2 paginiThis Week's Speaking ChallengecallielizzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data Gathering ProcedureDocument4 paginiData Gathering ProcedurecallielizzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- BRITTLE Materials BreaksDocument23 paginiBRITTLE Materials BreakscallielizzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- C105 Analysis of Bleach Post-Lab: CalculationsDocument2 paginiC105 Analysis of Bleach Post-Lab: CalculationscallielizzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 6, Lesson 7: Energy Changes in Chemical Reactions: Key ConceptsDocument11 paginiChapter 6, Lesson 7: Energy Changes in Chemical Reactions: Key ConceptscallielizzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Descriptive SentencesDocument5 paginiDescriptive SentencescallielizzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing CurriculumDocument21 paginiNursing CurriculumcallielizzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intro To DistillationDocument33 paginiIntro To Distillationcallielizza100% (1)
- Analytical Chemistry ExercsisesDocument7 paginiAnalytical Chemistry ExercsisescallielizzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coca-Cola 125 Years BookletDocument27 paginiCoca-Cola 125 Years BookletShahid Muhammed TawhidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Equipment Design: Batangas State UniversityDocument1 paginăEquipment Design: Batangas State UniversitycallielizzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Batangas State University: Ojt Form 8 Student-Trainees Feedback FormDocument1 paginăBatangas State University: Ojt Form 8 Student-Trainees Feedback FormcallielizzaÎncă nu există evaluări
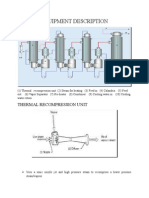
- Equipment Description: Thermal Recompression UnitDocument3 paginiEquipment Description: Thermal Recompression UnitcallielizzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Crossword Puzzle QuizDocument3 paginiCrossword Puzzle QuizcallielizzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Address City State Zipcode: Sheet1Document4 paginiAddress City State Zipcode: Sheet1callielizzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Personal History StatementDocument1 paginăPersonal History StatementcallielizzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- UNF ThreadDocument4 paginiUNF ThreadMUUTHUKRISHNANÎncă nu există evaluări
- Products DatabaseDocument104 paginiProducts DatabaseAlexÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zinc and Tin Alloy Wire Used in Thermal Spraying For Electronic ApplicationsDocument4 paginiZinc and Tin Alloy Wire Used in Thermal Spraying For Electronic ApplicationsBang AnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ueg 36Document2 paginiUeg 36PRADO_COMETA50% (2)
- DPF CeramicDocument11 paginiDPF Ceramicelliott_wolfÎncă nu există evaluări
- Boge Up To 300kw - PDFDocument12 paginiBoge Up To 300kw - PDFparsmessengerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Severn GloconDocument6 paginiSevern GloconAmit Surti0% (1)
- Carbomastic 15 PDS 2013Document2 paginiCarbomastic 15 PDS 20134508366279Încă nu există evaluări
- Pannaipatty - Compound WallDocument38 paginiPannaipatty - Compound WallrkpragadeeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- A560 - Castings Chromium Nickel AlloyDocument3 paginiA560 - Castings Chromium Nickel AlloychemtausifÎncă nu există evaluări
- H-HS-0043 AP Abrasive Cream CleanerDocument1 paginăH-HS-0043 AP Abrasive Cream CleanerDania UzairÎncă nu există evaluări
- Argus General Brochure V8Document20 paginiArgus General Brochure V8danieldayettddÎncă nu există evaluări
- PSA Nitrogen PlantsDocument4 paginiPSA Nitrogen PlantsIdo Aprilian TariganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cryoseal: Liquid Nitrogen Containers (Dewars) : Also Available 340/550 Liters Bulk Storage ContainersDocument2 paginiCryoseal: Liquid Nitrogen Containers (Dewars) : Also Available 340/550 Liters Bulk Storage ContainersDr. Awanish MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cleaning and Sanitizing: Concentration - The Presence of Too Little Sanitizer Will Result in An InadequateDocument3 paginiCleaning and Sanitizing: Concentration - The Presence of Too Little Sanitizer Will Result in An InadequateRhodaCastilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- GRGR 2023-2024 SSR InagalluDocument203 paginiGRGR 2023-2024 SSR InagalluT Venu BabuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interrupts 23Document248 paginiInterrupts 23cmchristoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microcontrollers: Digitally Addressable Lighting Interface (DALI) Unit Using The MC68HC908KX8Document162 paginiMicrocontrollers: Digitally Addressable Lighting Interface (DALI) Unit Using The MC68HC908KX8alexwongks6118Încă nu există evaluări
- General Motion Control: A Complete Range of Motion Products For Efficient Machine AutomationDocument47 paginiGeneral Motion Control: A Complete Range of Motion Products For Efficient Machine AutomationDan PopescuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Steam FlowmeterDocument20 paginiTypes of Steam FlowmeterLidijaSpaseskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Service Manual: CB 18S CB 27S CB 37SDocument85 paginiService Manual: CB 18S CB 27S CB 37SMack DieselÎncă nu există evaluări