Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Appendix1 Glossary
Încărcat de
Marius HustiuDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Appendix1 Glossary
Încărcat de
Marius HustiuDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
A Ap pp pe en nd di ix x 1 1
Glossary of Terms
Agitator
A type of mechanical mixing device; used in copiers in the toner supply to keep toner
particles separated; also used in the development unit to combine toner and carrier,
creating twocomponent developer.
AI Short Protocol
Artificial Intelligence Short Protocol reduces the time required for the protocol
exchange with a particular terminal by saving the communication parameters and the
modem rate used to send the last page of a transmission. These parameters are used
for the start of the next transmission to that terminal.
Air Knife (or Air
Separation)
The air knife paper separation process uses jets of air to separate sheets of paper for
paper feed.
Attenuation
After the modem converts data to serial and modulates it, the data passes through an
attenuator, which adjusts the TX level.
Auger
A screw-like mechanical transport device used to move bulk materials in many
different applications. It relies on a large screw with deep, wide-pitched threads turning
inside a close-fitting cylinder. The threads act like an endless scoop or wedge to lift
material from one end of the cylinder to the other.
Automatic Document
Feeder (ADF)
A motorized device that allows automatic feeding, alignment and stacking of multiple
originals, greatly improving the overall efficiency of photocopying.
10 March 2004 1
Appendix 1 Glossary of Terms
Automatic Document
Handler (ADH)
An advanced type of document feeder that can recycle and reverse originals.
Autorouting
When a G3 fax message with a SUB code is received, the machine compares it with
the personal codes stored in the machine with e-mail addresses. If there is a match,
the machine automatically routes the message to that e-mail address.
Baud Rate
The Baud Rate is the number of bits per second divided by the number of bits per
Baud.
Bias Roller
A bias roller is a roller that has a constant electric voltage applied to it. Such rollers are
used at various places in copiers and printers. A typical use is in a copiers cleaning
system, where a bias roller is often used to attract toner removed by a cleaning blade
or brush.
Bipolar Junction
Transistor
A bipolar junction transistor contains two junctions between p and n type
semiconductor, and three electrodes (the collector, the base, and the emitter). See
Transistors.
Block Diagram
A kind of electronic map that divides a system into a number of functional blocks; it
shows all the interconnections among the blocks, but generally does not show detail
inside them.
Bond
A category of papers, consisting of many individual types. Most bond papers are
suitable for use in plain-paper copiers.
Breakdown Voltage
The voltage at which current will flow in reverse through a diode. Regular diodes will
generally be destroyed if a reverse voltage greater than the breakdown voltage is
applied; however, zener diodes are designed to operate at the breakdown voltage.
See Zener Diode.
10 March 2004 2
Appendix 1 Glossary of Terms
Brushless DC Motor
In standard DC motors, the magnet is stationary while the coil rotates, and brushes
complete the electrical contact to the rotor. However, In a brushless DC motor, the coil
is stationary and the magnet moves.
Call Collision
Prevention
After the scanning the document, the machine checks whether there is an incoming
fax message. The machine cannot dial if there is an incoming message. This differs
between North American, and European and Asian models. See North American
models and European and Asian models.
Carrier (copiers)
Carrier is one of the components of a two-component developer. Carrier consists of
tiny iron-based beads that attract toner particles through a triboelectric charge and
transport them to the photoconductor during the development process. See
Triboelectric Charge.
Carrier (facsimile)
The carrier is the base frequency wave that fax machines use for communication. To
transmit data, fax machines superimpose a modulating signal onto the carrier wave by
varying the frequency, amplitude, or phase (or a combination of these) in a standard
manner. See Modulation Techniques.
Central Processing Unit
(CPU)
A microprocessor chip that is used as the primary control and information processing
device in a sophisticated electronic system.
Charge
The first step in the copy process; during the charge process, an even electrical
charge is applied to the photoconductor, preparing it to receive the image of an original
during exposure.
Charge Corona Unit
A corona unit used for the first step in the copy process, to apply an even high
voltage charge to the photoconductor; usually ventilated by a blower to help distribute
ions during charging.
10 March 2004 3
Appendix 1 Glossary of Terms
Charge Coupled
Device (CCD)
A solid-state component made from a number of very small light-sensitive elements;
the amount of light falling on each element produces an electrical signal of
corresponding strength. CCDs are used in laser-based copiers, fax machines and
some television cameras.
Cleaning
That step in the copy process during which residual toner particlesthose left behind
after image transferare removed from the photoconductor. Cleaning relies mainly on
mechanical systems but electrostatic forces may also be used.
Cleaning Blade
An element in a copiers cleaning system. After a copy has been made, the cleaning
blade acts like a windshield wiper, riding along the surface of the photoconductor to
wipe off all remaining toner particles.
Cleaning Brush
An element in a copiers cleaning system. After a copy has been made, the cleaning
brush removes the residual toner from the surface of the photoconductor. See Bias
Roller.
Clutch
A control device for rotational movement; a clutch will either be engaged, locking its
components together and transferring rotation, or disengaged, letting its components
turn separately and preventing the transfer of rotation.
Clutch, Magnetic
See Magnetic Clutch.
Clutch, Magnetic
Spring
See Magnetic Spring Clutch
Clutch, Slip
See Torque Limiter Clutches. See Slip Clutch.
Clutch, Spring
See Spring Clutch.
Clutch, Torque Limiter
See Torque Limiter Clutches.
10 March 2004 4
Appendix 1 Glossary of Terms
Coefficient of Friction
(of paper)
The coefficient of friction directly affects the efficiency of paper feeding. It must be high
enough that the feed and transport rollers can get a good grip. However, it must be low
enough that the sheets of paper slip over each other.
Cold Cathode
Fluorescent Lamp
A variation of the fluorescent lamp. See Fluorescent Lamps, Applications.
Contact Image Sensor
(CIS)
The contact image sensor (CIS) is a compact image reading assembly containing an
LED array, an array of self-focusing optic fibers (SELFOC), and a strip of light
detectors, such as phototransistors. The CIS is used instead of the CCD in the most
compact of fax machines.
Corona Unit
A copier component that uses a high electrical voltage to create a localized electrical
field of charged ions; various kinds of corona units are used at different points in the
copy process. See Pre-Cleaning, Quenching, Transfer And Separation Corona Units.
Corona Wire
A thin wire usually made from tungsten and coated with carbon. Mounted inside a
corona unit, it carries the high voltage needed to generate an electrical field for a
specific copier application.
Cross Mixing
The process by which toner and carrier are mixed together inside a copier; also
creates and distributes the triboelectric charge that binds the toner to the carrier
particles.
Current
The rate of flow of electricity through a conductor; current is measured in Amperes or
Amps.
Data Compressor and
Reconstructor - DCR
Part of a fax circuit; it compresses the data before sending it out over the telephone
line. It also reconstructs compressed data coming in from the telephone line.
DC Motor
A motor that operates on direct current.
10 March 2004 5
Appendix 1 Glossary of Terms
DC motor, Brushless
See Brushless DC motor.
Developer,
Mono-component
See Mono-component Developer.
Developer,
Two-component
Also called dual-component developer. See Two-component Developer.
Development
That step in the copy process which first produces a visible image on the
photoconductor. During development, toner is applied to the photoconductor, where it
is electrically attracted to the latent image formed during exposure.
Development Roller
Part of a copiers development system. Development rollers use some combination of
magnetism, triboelectric charge and/or bias voltage to apply toner to the latent image
on the photoconductor.
Diode
A p-type semiconductor joined to an n-type semiconductor. A diode allows current to
move in only one direction. See Diodes.
Diode, Zener
See Zener Diode.
DNS
Domain Name System is a service that enables the IP address to be obtained from the
host under the TCP/IP network environment.
Doctor Blade
Part of a copiers development system. It limits the thickness of developer picked up
by the development roller by scraping off the excess as the roller turns. It determines
the height of the magnetic brush.
Dual Component Toner
Toner designed to work in a dual-component development system. This toner is
similar to the non-magnetic type monocomponent toner. It works with a separate
particle known as a carrier. The mixture of toner and carrier is known as developer.
10 March 2004 6
Appendix 1 Glossary of Terms
Duplex Unit
A paper handling device that permits the making of two-sided copies without manual
intervention by the user. Available through the installation of a peripheral duplex unit
on mid-size copiers, duplexing is a standard feature on most high-volume machines.
Duplexing
Making two-sided copies.
ECM Memory
Error Correction Mode memory, an optional extension to Group 3 protocol, is a
countermeasure for the frequent data errors that occur in areas that suffer from noisy
telephone lines. See ECM.
Electromagnetic Clutch
A type of clutch which contains its own electromagnetic actuator. When the clutchs
coil is energized, two metal plates are pulled together and transmit rotation to a given
component. When not energized, the two plates are separated by a spring, and no
rotation is transmitted.
E-mail
Electronic mail is a system in which messages in the form of digital data are sent and
received between computers.
Erase Lamp
A component which removes certain parts of the latent image after exposure. After
considering reproduction ratio and paper size, the main control board turns on specific
sections of the erase lamp to remove the charge from the photoconductor outside the
desired image area.
Estimated Fillbit
Control-EFC
This process was developed by Ricoh to improve the efficiency of MH, MR, and MMR
coding.
Ethernet
This is the most commonly used LAN. See Ethernet Frame Structure.
Exposure
A process where light is applied to a photoconductor to create a latent reverse image
in the form of a charge pattern on the surface of the photoconductive material. See
Photocopying Processes.
10 March 2004 7
Appendix 1 Glossary of Terms
Exposure Lamp
Part of a copiers exposure and optical systems; provides the necessary illumination to
create a reflected image from an original, which in turn creates an electrical latent
image on the photoconductor.
Fax On Demand-FOD
A polling application with pre-recorded voice assistance.
FRR Paper Feed
One of the standard paper feeding systems; the FRR (feed and reverse roller) feed
mechanism consists of a pick-up roller, a feed roller, and a reverse roller.
Feed Roller
The first roller to handle paper a copiers paper feed system; pulls individual sheets
from a paper supply, feeding them into the copier where they are passed to other
rollers in the paper path.
FIFO Memory
First-In First-Out Memory synchronizes the transfer of video data to (transmission) or
from (reception) the modem.
Fluorescent Lamp
A lamp consisting of a gas-filled, closed glass tube that has electrodes at each end
and an internal coated surface of a phosphorous material.
Frequency Shift Keying
Frequency shift keying (FSK) is s type of frequency modulation that is used for
transmitting digital signals.
Fusing
The step in the copy process that bonds toner to a sheet of paper. Heat and pressure
melt toner and force it into the paper surface, creating a copy that meets or exceeds
the durability of the original.
Fusing Lubrication
System
Part of a copiers fusing system, needed to keep toner from sticking to the fusing
rollers. Uses an absorbent pad and/or a blade to coat the rollers with silicone oil.
Gray Scale
A row of small test patches showing a full range of image density, from solid black to
paper white, usually in five to ten steps. Printed on a copier test chart. It is a gauge for
the side-to-side and overall image density of the machine.
10 March 2004 8
Appendix 1 Glossary of Terms
Grid Plate
Part of the charging system in copiers that use an Organic Photoconductor (OPC).
OPCs are more sensitive to high voltage charges, so the grid plate acts as a regulator
between the OPC surface and the charge corona.
Hall Effect Sensors
Hall effect sensors are used in some network control units (NCU) of fax machines to
detect line current.
Halogen Lamp
An incandescent lamp filled with halogen gas.
Hot Roller
The part of a copiers fusing system that contains the fusing heat source, usually a
halogen lamp. The hot roller is usually coated with Teflon, and works with the pressure
roller. See Pressure Roller.
I/O Rate
In fax machines this refers to the amount of time necessary for the scanner or printer
to process one scan line of image data. Modulation and demodulation are not included
in this time measurement.
ID Sensor
A photosensor that measures the image density (reflectivity) of the drum and of a test
pattern (ID sensor pattern). The output of this sensor is used to control toner supply.
ID Sensor Pattern
A standard pattern that is exposed and developed for sensing by the ID sensor.
Image Density
The quality of an original or copy that describes its relative lightness or darkness; high
image density refers to a very dark copy, low image density refers to a very light copy
Image Density Control
The system in a copier that compensates for the variation in reflectivity among
different originals. Some adjust the brightness of the exposure lamp. Others regulate
toner transfer during development, by adjusting a bias circuit. In either case, image
density controls can be manual, automatic or both.
10 March 2004 9
Appendix 1 Glossary of Terms
Interleave Duplexing
A duplexing method used by some digital machines that speeds up duplexing by
storing original images in memory. Sheets continually feed and reverse without
stopping and the correct image for each sheet and side is selected from memory.
ITU-T Standards
International standards for data communication.
JBIG Compression
The JBIG compression method consists of four processes: conversion to bi-level data,
progressive coding, division into strips, and coding.
LAN
Local Area Network. See LAN Fax, LAN Basics.
Large Capacity Paper
Tray
A copier peripheral that holds a much greater amount of paper than a standard tray,
thereby enabling the copier to run for longer periods without the supply being refilled,
typically holds between 500 and 3000 sheets.
Laser Diode
An LED that outputs laser light.
Latent Image
A photographic term which refers to an undeveloped image on a piece of film; in
xerography, it refers to the invisible, electrostatic image formed on the photoconductor
during exposure.
LCD
LCD is an abbreviation for Liquid Crystal Display. An LCD is a digital display that
consists of two sheets of glass separated by hermetically sealed liquid crystal material.
The liquid crystal is normally transparent.
LCT
See Large Capacity Tray.
Lead Edge
The first paper edge to contact the latent image on the photoconductor. The front
edge of a copy as it travels through the paper path.
10 March 2004 10
Appendix 1 Glossary of Terms
Lead Edge Erase
The removal of that portion of a latent image which corresponds to a narrow strip
along the lead edge of the copy, usually no more than 5 mm wide. This prevents a
dark line from the edge of the original document from appearing on the copy. Achieved
through the action of an erase lamp immediately after the exposure process.
Light Emitting Diode
A kind of diode that emits photons. Usually shortened to LED.
LED Array
LEDs mounted together in an array as a light source.
Line Buffer
A memory buffer that ensures synchronization of video data transfer between different
components of the circuit.
Magnetic Brush
A localized concentration of two-component developer formed on the surface of a
development roller by magnetic fields. It brushes developer over the photoconductor
during the development process. This allows toner particles in the brush to be
attracted to the latent image.
Magnetic Clutch
See Electromagnetic Clutch.
Magnetic
Monocomponent Toner
Similar to the non-magnetic monocomponent toner, this type has iron oxide particles
encapsulated in the resin matrix of each individual particle of toner. The toner isnt
actually magnetic itself, but it can be attracted by a magnet.
Magnetic Spring Clutch
The magnetic spring clutch is a hybrid of the electromagnetic and spring clutches.
Unlike the normal spring clutch, the spring is loose when idling.
Magnification Lines
Two lines of an identical specified length, one vertical and one horizontal, printed on a
copier test chart. Used to check the vertical and horizontal magnification of a copiers
optical system.
10 March 2004 11
Appendix 1 Glossary of Terms
Main Control Board
A printed circuit board containing the most important components in a copiers
electronic control system, including the Central Processing Unit (CPU), and factory-
programmed instructions stored on Read Only Memory (ROM) chips. The main board
is linked to other parts of the control system with a number of multi-wire connectors.
Master Belt
A wide, flexible loop of plastic with an organic photoconductor surface.
Modified Huffman
Compression
This compression method has one-dimensional coding scheme codes scan line data
without reference to data on adjacent lines.
Microswitch
Microswitches are electromechanical switching devices containing two contacts.
MIME
Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions is a specification for the inclusion of various
types of data in e-mail.
Modified MR
Compression
The Modified MR method uses the same algorithm as the MR method, but has 6 main
differences.
Modulating Signal
The data signal from the fax machine. See Modulation Techniques.
Moisture Content
(of paper)
Moisture content directly affects paper transport, copy quality, and curl. The generally
acceptable range is 4 ~ 6 percent moisture. See Paper Characteristics.
Monocomponent Toner
A special toner formulation that has both magnetic and electrical properties; functions
without carrier. See Monocomponent Developer.
Motor, Stepper
See Stepper Motor.
Moving Platen
A type of scanning optical system in which originals are placed on a glass document
surface (the platen) which moves across a fixed exposure slit and lamp during an
exposure; found only on relatively small, low-speed copiers.
10 March 2004 12
Appendix 1 Glossary of Terms
Moving Scanner
A type of scanning optical system in which originals are placed on a fixed glass
document surface, under which is a moving lamp and mirror assembly (the scanner).
This scanner moves under the original during an exposure. Found on most medium-
to-high speed copiers; this design is also known as fixed platen scanning
Modified Read
Compression
This is the Modified Read compression method. It is an expanded form of the one-
dimensional run length encoding method. While the MH method encodes pixels in the
pixel scanning direction, the MR also takes notice of the pixels in the feed direction.
Neon Lamp
Similar to the cold cathode fluorescent lamp, but light emission is from the neon gas
rather than the phosphorous inside coating.
Network Control Unit
(NCU)
Interfaces a fax machine with the telephone network.
Network Interface
Circuits
The filters, relays, attenuators and other components in these circuits interface the
machine with the public telephone network.
New Estimated Fillbit
Control
Fill bits are never added to the data and the receiver uses the SAF memory or hard
disk instead of the FIFO memory. If the receiver's memory is full, it sends PIN to the
transmitter and the line is disconnected.
Non-magnetic
Monocomponent Toner
All-in-One toner that contains pigments for printing in a matrix of resin. This kind of
toner usually comes in a cartridge and is used with non-magnetic rollers.
Offset Image
A partial image that remains on the photoconductor or fusing rollers due to incomplete
cleaning and is transferred to subsequent copies.
Opacity of Paper
Paper must be sufficiently opaque to prevent image show through. This is especially
important in paper used for duplexing. Most brands of paper use some kind of filler to
enhance opacity. See Paper Characteristics.
10 March 2004 13
Appendix 1 Glossary of Terms
Organic
Photoconductor (OPC)
A type of photoconductor based on certain organic chemicals, rather than metallic
elements like selenium or silicon. An OPC requires negative charging before
exposure. It is generally non-toxic, enabling it to be handled and disposed of more
easily than selenium types.
Over-toning
A condition that occurs when a copiers toner supply system is delivering too much
toner to the development unit; the excess toner builds up inside the copier, especially
around the photoconductor and paper path.
Paddle Roller
Part of the development unit of many copiers. It pushes charged developer (a mix of
toner and carrier) against the development roller, which picks up the developer
through magnetic attraction and brushes it over the latent image.
Paper Brightness
The brightness of a paper is a measure of its light reflectivity. See Paper
Characteristics.
Paper Curl
Curl in paper is a major cause of transport problems resulting in misfeeds. See Paper
Characteristics.
Paper Feed System
The various rollers, belts, sensors and control devices that are responsible for moving
sheets of paper through the copier; begins with the paper supply, and ends with the
exit tray or sorter that holds the finished copies. See Paper Feed
Paper Size
There are several standard systems for measuring paper size. The most commonly
used is the ISO (International Organization for Standardization) series of paper sizes.
In the United States, paper sizes are usually measured in inches.
Paper Stiffness
Paper stiffness is a result of the orientation of the fibers within the paper. Stiffness
affects paper feeding and transport in copiers and laser printers. Paper is generally
two or three times stiffer in the with grain direction than in the cross grain direction.
See Paper Characteristics.
10 March 2004 14
Appendix 1 Glossary of Terms
Paper Weight
There are three systems for classifying paper weight. These are the ISO system
(g/m2), the USA system (lb), and the Japanese system (Kg).
Parallel Circuit
A type of electrical connection in which components each have a direct, independent
path to a power source.
Phosphor
A chemical coating on the inside of a fluorescent tube that produces visible light when
struck by ultraviolet radiation. See Fluorescent Lamp.
Photoconductor
A special material that acts as an insulator in darkness and as a conductor when
exposed to light.
Photointerrupter
An electronic sensors that has a photocell and a light emitting diode (LED) on either
side of a small gap. When a tab on a moving component enters the gap, it blocks the
light from the LED, shutting off the photocell and signaling the components position to
the machines Main Control Board.
Phototransistor
A phototransistor works like an ordinary bipolar transistor, except that light shining on
the base of the transistor switches it on.
Pick-off Pawls
Part of a copiers paper separation system that provides a mechanical separation
method. Pick-off pawls ride along the surface of the photoconductor to peel off any
paper not removed electrically.
Point-to-point Diagram
An electronic map, specially designed for troubleshooting equipment with replaceable
circuit boards; combines features of a schematic drawing and a block diagram,
concentrating on connections to and from different components.
10 March 2004 15
Appendix 1 Glossary of Terms
Polarity
The quality of electricity that describes its tendency to exist in either a positive or
negative state. In most electrical circuits, polarity determines the direction of current
flow. In electrostatic charges, polarity indicates the charge of ions that make up an
electrical field, and therefore determines the polarity of materials that can be attracted
by that field. A charge of a given polarity always attracts materials with a charge of the
opposite polarity
Polyphase Shift Keying
A type of phase modulation (PM) where data modulation occurs by altering the phase
of the carrier wave and frequency remains constant.
POP
Post Office Protocol servers are computers that receive mail using SMTP. The mail
includes a setting to ensure that it is directed to the POP server. POP servers are used
when the user is not permanently connected to the internet.
Pre-cleaning Corona
Unit
A corona unit used just before cleaning in the copy cycle. It creates an electrical field
that reduces the charge on the photoconductor before mechanical cleaning, making it
easier to remove leftover toner.
Pressure Roller
Part of a copiers fusing system. During fusing, toner is forced into the surface of the
paper by two rollers, the pressure roller and the hot roller. The pressure roller is
usually made of silicon rubber, to help it withstand heat and provide a good grip on the
paper. See Hot Roller.
Pre-transfer Lamp
Used in some copiers to reduce the charge of the latent image after development,
weakening its attraction just enough to assure a clean transfer. It also prevents toner
particles from being attracted back to the photoconductor during separation.
Process Control
Process control is a system that automatically changes machine processes to
compensate for changes in the environment or the machine condition.
10 March 2004 16
Appendix 1 Glossary of Terms
Protocol Signals
Fax machines use two types of signals: Single (short, timed transmitted tones like
CED and CNG) and frame-like HDLC signals that transmit digital information like DIS
and NSF.
PSTN
Public Switched Telephone Network
Quadrature Amplitude
Modulation (QAM)
QAM is a combination of amplitude modulation (AM) and phase modulation (PM).
Quenching
Quenching is the process that eliminates any residual electric charge remaining on the
photoconductor after the cleaning process. Quenching prepares the photoconductor
for the charge step of the next copy or print cycle.
Quenching Corona
A corona used at the end of the copy process; it creates an electrical field to help
remove latent image charge on the photoconductor after mechanical cleaning,
preparing the surface for the next copy cycle; always used in conjunction with a
quenching lamp
Quenching Lamp
Shines light on the surface of the photoconductor to remove the latent image, after the
leftover toner has been removed by the cleaning system. See Quenching.
Reception Modes
There are two types of reception modes: manual (telephone mode) and automatic (fax
mode).
Reed Switch
Reed switches are magnetically operated switches with contacts hermetically sealed in
a glass capsule.
Reflective Photosensor
Reflective photosensors are short-range sensors that have a light emitting element
(usually an LED) and a light sensitive element (usually a phototransistor).
10 March 2004 17
Appendix 1 Glossary of Terms
Registration
The process by which paper is lined up properly with the developed image on the
photoconductor; registration is usually accomplished with a system of rollers,
mechanical guides and electronic sensors.
Registration Marks
These marks are printed at the top and side of a copier test chart as a gauge of paper
alignment and copier erase margins. They consist of thin parallel lines that will show if
the paper is improperly meeting the latent image on the photoconductor.
Registration Rollers
Part of a copiers paper feed system. A pair of rollers that align a sheet of paper to
remove skew, and then feed the sheet toward the photoconductor at the correct time
during the copy cycle to align it with the image on the photoconductor.
Registration Sensor
Part of a copiers paper feed system; an electronic sensor mounted in the paper path
just before the registration rollers. This sensor alerts the copiers control system when
a sheet of paper approaches the registration rollers, so that they can be stopped
before the sheet contacts them.
Relay Devices
Required to expand LANs. These devices do the following: extend the connection
distance, enable connection between networks of different standards, allow control of
high-speed transmission routes and filtering. They include repeaters, bridges,
switches, gateways and routers.
Relay Rollers
Part of a copiers paper feed system; used in machines with long or complex paper
paths simply to move sheets from one area to another. They have no special copy-
related function.
Reproduction Ratio
An optical specification that determines the relationship between original size and copy
image size. A one-to-one reproduction ratio indicates that the original and copy have
the same image size. This ratio can vary in most copiers to produce enlarged and
reduced copies.
10 March 2004 18
Appendix 1 Glossary of Terms
Resolution Bars
Printed on a copier test chart as a gauge of the overall sharpness of a machines
optical system; should be clearly visible on copies as individual lines.
SAF Memory
Store and Forward Memory stores fax messages to send later or for transmission to
more than one location. It also holds the incoming message if, for example, the printer
is out of paper.
Scanner
Part of the exposure system in a moving-scanner copier; these exposure systems
have two scanners. The first consists of a lightweight metal frame containing one
mirror and the exposure lamp. The second has a similar frame and two mirrors. Both
scanners move along guide rails during an exposure, and reflect the image between
them during the scan to maintain a constant optical distance from the original to the
lens.
Schematic Diagram
The most traditional and detailed type of electronic map; shows every circuit, no matter
how complex, and every component, no matter how small.
Selenium Drum
A commonly used photoconductor. It consists of a hollow aluminum cylinder coated
with a layer of selenium-tellurium or selenium-arsenic alloy. The selenium alloy layer
provides the key photoconductive property of having high electrical resistance in the
dark, and low resistance when exposed to light.
SELFOC
An acronym for Self-Focusing Fiber Optic Array. SELFOCs are used for strip exposure
with fixed optics, in contact image sensors, and direct scanning digital systems.
SEP/PWD/SUB/SID
Signals
The ITU-T recommendations were changed in 1996 to allow polling and confidential
communications. At this time, this could only be done between Ricoh-made products.
With the institution of these signals, communication between all fax makers became
possible.
Separation
That step in the copy process during which the paper and toner are separated from
the photoconductor. See Image Transfer And Paper Separation
10 March 2004 19
Appendix 1 Glossary of Terms
Servomotor
Used in many copiers to move scanners in the optical system; servomotors emit a
specific number of electrical pulses with each revolution, allowing a control circuit to
monitor and regulate their speed. Servomotors use feedback to maintain a constant
rotating speed.
Setting Powder
A dry lubricant powder applied to new photoconductors and or cleaning blades
immediately before installation. During initial operation, the powder protects the
surface from scratches that might result from contact with other copier components.
Slip Clutch
Another name for a torque limiter clutch. See Torque Limiter Clutch.
SMR Compression
The Simple Modified Read method is identical to MR coding except that the K
parameter is 8 for Standard and Detail resolution and 16 for Fine.
SMTP
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol is the protocol for communication between internet mail
MTAs (message transfer agents).
Solenoid
A simple electrical control device, consisting of a hollow electromagnet and a metal
plunger. When the magnet is energized, the metal plunger is pulled inside it, triggering
whatever mechanism is attached.
Sorter
A sorter is a paper handling device that feeds finished copies into multiple output bins;
can produce sets of collated copies, matching the order of the original documents, or
count out stacks of single copies.
Spring Clutch
A popular clutch for copier applications; its internal components are normally held
together by a spring connected to an external sleeve, and rotation is transmitted to a
given component. When the sleeve is kept from turning, the spring expands, releasing
one internal component and preventing the transfer of rotation.
Super Speed Coding
(SSC) Method
The Super Speed Coding method combines EFC with Short Preamble and white line
double-speed processing to achieve a further reduction in transmission time.
10 March 2004 20
Appendix 1 Glossary of Terms
Stator
A stationary part of an electric motor in or about which a rotor turns. See DC Motors.
Stepper Motor
A type of electric motor designed to be controlled in individual steps that are portions
of a full rotation, each step as small as one degree of arc. It is often used to adjust
lens position in copiers with variable reproduction ratio. The design of a stepper motor
allows for extremely precise lens placement and easy electronic control. Stepper
motors are used whenever accurate positioning of a component is required.
Stripper Pawls
Part of a copiers fusing system; stripper pawls ride along the surface of the hot roller,
and peel off copies that stick to the roller despite the rollers lubrication.
Subnet
It is difficult for one network to handle 65,534 hosts, therefore the subnet mask creates
subnets to take some of the burden off of the main network. See Subnet and Subnet
Masks.
Subnet Mask
Subnet masks divides the host block into a maximum of 255 subnets within which a
maximum of 255 hosts can exist. This helps to increase the speed with which a user
can access a particular portion of the network. See Subnet and Subnet Masks.
Substitute Reception
Data is stored in memory as it comes in to avoid loss of data if there is a printer
problem. Basically, this means that memory substitutes for the print engine during
reception.
TCP/IP (Transmission
Control Protocol/
Internet Protocol)
A standard internet protocol supported by Windows 95, it allocates 32-bit network
addresses to nodes. The host requires a procedure for passing IP packets to the
desired application. This procedure is filled by the TCP/IP.
Test chart
A specially designed copier original, with printed gauges used to assess many aspects
of copy quality.
10 March 2004 21
Appendix 1 Glossary of Terms
Thermal Head
The thermal head is the central component of the thermal printer. A thermal head
consists of a row of heating elements. If a heating element is turned on, it will heat up.
The heat from the element will make a dot on thermosensitive printer paper.
Thermal Paper
Thermosensitive printer paper. This is the paper used for white-board printers and
thermal fax machines.
Thermistor
A thermistor is a thermally sensitive resistor. It is a heat-sensitive electronic
component, which indicates changes in temperature by varying its electrical
resistance.
Thermoswitch
An electrical control device used for overheat protection in office machines.
Toner
The ink of an electrostatic copier that forms the actual image on finished copies. It is
made from resin and a solid lubricant combined with carbon or a colored pigment. In
dual-component development systems it is bound to carrier particles by a triboelectric
charge, creating two-component developer. See Triboelectric Charge.
Toner Density Sensor
(TD Sensor)
The toner density sensor (or TD sensor) measures the concentration of toner in the
developer.
Toner End Sensor
Part of a copiers development system. The toner end sensor monitors the level of
toner in the toner supply. When the sensor detects a predetermined low-toner
condition, it signals the control system, which then lights a corresponding indicator on
the machines operation panel. It usually detects two different toner levels: Toner
Near End (low) and Toner End (too low to continue operation).
Toner Overflow Sensor
Part of a copiers cleaning system. This sensor monitors the level of toner in the used
toner storage tank. When the sensor detects a predetermined used toner tank full
condition, it signals the control system, which then lights a corresponding indicator on
the operation panel of the machine.
10 March 2004 22
Appendix 1 Glossary of Terms
Toner Shield Glass
A piece of ordinary glass used in copiers as a window in the exposure slit; allows
light to reach the photoconductor, but keeps toner from contaminating the optical
system.
Toner Supply System
A combination of electronic and mechanical components that monitor the density of
toner and add toner to the development unit whenever the density falls too low.
Toner, Dual
Component
See Dual Component Toner.
Toner, Magnetic
monocomponent
See Magnetic Monocomponent Toner.
Toner, Non-magnetic
monocomponent
See Non-magnetic Monocomponent Toner.
Torque limiter clutch
In concept, torque limiter clutches transmit rotation to a drive component (usually a
roller, pulley, or gear mounted on a rotating shaft). As long as the resistance to rotation
is less than the torque (twisting force) limitation of the clutch, the roller turns with the
shaft. If the resistance exceeds the torque limitation, the roller stops turning. It slips
and in fact, may turn in the opposite direction if sufficient counter force is applied.
Transfer
That step in the copy process in which toner, held by the latent image on the
photoconductor, is transferred to a blank sheet of paper, thereby creating a copy.
10 March 2004 23
Appendix 1 Glossary of Terms
Transfer and
Separation (T/S)
Corona Unit
A corona unit used immediately after development. The T/S corona unit creates two
coronas. The first, the transfer corona, is an electrical field that pulls the developed
toner image away from the latent image on the photoconductor, transferring it to a
sheet of paper. The second corona, the separation corona, is an electrical field that
releases the paper, together with the developed toner image, from the
photoconductor.
Transport
The primary job of a copiers paper feed system: moving sheets of paper from the
supply, through the machine, and out into the exit tray; accomplished with a variety of
rubber belts and rollers.
Trapping Layer
The surface layer of a photoconductor. It receives and traps an electrostatic charge on
the surface as long as the photoconductor is in darkness.
Tray Heater
Paper in a copier's paper tray tends to curl as it picks up moisture from the air. Some
machines, especially higher speed models, have heaters in the paper trays to prevent
such curling.
Trellis Code Modulation
(TCM)
TCM uses QAM, but part of the data signal is encoded, using trellis coding, for error
correction purposes.
Triboelectric Charge
A type of static charge that builds up when certain materials are rubbed together.
Triboelectric charges attract toner to carrier in a two-component developer system.
Two-component
Developer
The most popular developer formulation; uses tiny, metallic carrier beads to deliver
much smaller toner particles to the photoconductor during the development process.
Under-toning
A condition that occurs when a copiers toner supply system is delivering too little toner
to the development unit; can lead to carrier abrasion, which may damage the
photoconductor and shorten the useful life of the carrier particles.
10 March 2004 24
Appendix 1 Glossary of Terms
V Sensor
A reflective photosensor similar to the ID sensor that indirectly measures drum
potential. Used before the development of the potential sensor system, it can be found
in earlier models using process control.
Varistor
Acts like two zener diodes connected back to back.
VB or VBB
Development bias.
VD (Dark Potential)
The drum potential in black image areas after exposure. Standard VD is the potential
measured after exposing a black pattern.
VD Pattern
A standard black pattern used for reference.
VG or VGRID
Charge corona grid potential.
VH (Halftone Potential)
A standard halftone drum potential. This value is used for laser power adjustment in
the process control system of some digital products.
Video Processing
The processing that is applied to image data after the machine scans the document.
Both analog and digital video processing steps may be applied to the image data.
VL (Light Potential)
The drum potential in white image areas after exposure. Standard VL is the potential
measured after exposing a white pattern.
VL Pattern
A standard white pattern used for reference. On some machines the VL pattern is
actually a light gray tone rather than pure white.
VLAMP
Exposure lamp voltage.
VO (Original Potential)
The drum potential after the drum is charged.
10 March 2004 25
Appendix 1 Glossary of Terms
Voice Message
Processor
This converts recorded voice messages from analog (audio) to digital for storage in
the memory. It also retrieves the message from memory to send it out over the
telephone line.
VR (Residual Voltage)
The drum potential after the drum has been exposed by the erase lamp.
VREF, VTREF
A targeted control reference for the TD sensor. When VTD becomes too low, toner is
added to the developer to bring VTD back to the VREF value.
VSG
The ID sensor output when checking the erased drum surface.
VSP
The ID sensor output when checking the ID sensor pattern image.
VTD, VT, or VOUT
The output voltage of the TD sensor.
Xenon Flash Lamp
The xenon flash lamps used in office machines are basically the same as the flash
lamps used in photography only much larger.
Xenon Lamp
A xenon lamp is a xenon-filled glass tube with terminals at each end. When a voltage
is applied across the lamp terminals, the xenon gas ionizes and current flows through
the gas, which emits light. The terminals do not have to be preheated, unlike in
fluorescent lamps. Fluorescent xenon lamps also utilize a phosphor coating on the
inside wall of the lamp to generate light.
Xerography
The indirect electrostatic copying system which is the basis of all modern plain paper
copiers; patented in 1939 by Chester Carlson, Xerography comes from the Greek
words for dry writing.
Zener Diode
A diode connected in reverse to a normal diode and is designed to work in excess of
the breakdown voltage.
10 March 2004 26
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Final Round: HE FR TR TRDocument2 paginiFinal Round: HE FR TR TRMarius HustiuÎncă nu există evaluări
- C 03 DDDDocument1 paginăC 03 DDDMarius HustiuÎncă nu există evaluări
- PolWor Comprehensive EnglishDocument38 paginiPolWor Comprehensive EnglishLuca DorinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scan 03042020110646Document1 paginăScan 03042020110646Marius HustiuÎncă nu există evaluări
- P D160 - D161 - CHN - V1.00Document91 paginiP D160 - D161 - CHN - V1.00Marius Hustiu0% (1)
- Model Th-c1 Manual FinalDocument433 paginiModel Th-c1 Manual FinalMarius HustiuÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- VTP8 Series Frequency Inverter ManualDocument70 paginiVTP8 Series Frequency Inverter ManualpiernodoyunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jackalope MASK by LapaStudiosDocument23 paginiJackalope MASK by LapaStudiosJorge Luis Valenzuela SalazarÎncă nu există evaluări
- D6K2Document20 paginiD6K2ivanamanticÎncă nu există evaluări
- Muhammad Rafi: EducationDocument3 paginiMuhammad Rafi: Educationabid445875Încă nu există evaluări
- Probus 215rkdlde00 SCB (Euro 4.5)Document343 paginiProbus 215rkdlde00 SCB (Euro 4.5)Manuel RibeiroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drawing or Document Control ListDocument22 paginiDrawing or Document Control ListRsp SrinivasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jansen'S Linkage: by Pavan SrinivasDocument14 paginiJansen'S Linkage: by Pavan SrinivasNELLORE PAVAN SRINIVAS SINGH NIT APÎncă nu există evaluări
- C0008310 CLM PDFDocument588 paginiC0008310 CLM PDFjobyÎncă nu există evaluări
- HX & HY Service Data SheetDocument16 paginiHX & HY Service Data Sheetmauricio olayaÎncă nu există evaluări
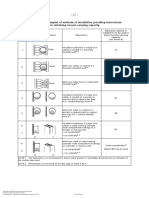
- Table A.52.3 - Examples of Methods of Installation Providing Instructions For Obtaining Current-Carrying CapacityDocument7 paginiTable A.52.3 - Examples of Methods of Installation Providing Instructions For Obtaining Current-Carrying Capacityvasu1984Încă nu există evaluări
- SIMATIC NET PROFIBUS Optical Link Module OLM Operation ManualDocument61 paginiSIMATIC NET PROFIBUS Optical Link Module OLM Operation ManualwiruÎncă nu există evaluări
- DGCK50B07947 EngbDocument3 paginiDGCK50B07947 EngbJustinÎncă nu există evaluări
- MP190E42H: Technical DescriptionsDocument22 paginiMP190E42H: Technical DescriptionsBroCactusÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2001 Hermetic Check Operating InstructionsDocument6 pagini2001 Hermetic Check Operating InstructionsAndres CarmonaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cat314 MCVDocument11 paginiCat314 MCVAimHigh100% (1)
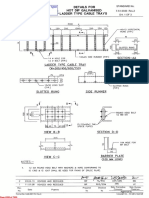
- 7-51-0333 - Details For HOT DIP Galavanised Ladder Type Cable TraysDocument3 pagini7-51-0333 - Details For HOT DIP Galavanised Ladder Type Cable TraysChandrashekharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bobcat 226 yDocument19 paginiBobcat 226 yEduardoÎncă nu există evaluări
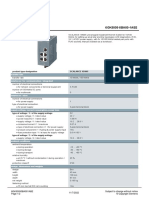
- 6GK50050BA001AB2 Datasheet enDocument2 pagini6GK50050BA001AB2 Datasheet enLuis BritoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Apron Feeder Power Calculations PDFDocument4 paginiApron Feeder Power Calculations PDFtuba25% (4)
- L-33 (SM) (Ia&c) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document18 paginiL-33 (SM) (Ia&c) ( (Ee) Nptel)Marvin BayanayÎncă nu există evaluări
- TAQA Approved Vendor List 30.05.2021Document328 paginiTAQA Approved Vendor List 30.05.2021Bala KrishnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- HB10000 Atlas CopcoDocument32 paginiHB10000 Atlas CopcoCarlos Paz100% (1)
- Manual Cuptor ARISTON PDFDocument56 paginiManual Cuptor ARISTON PDFRamona Cristina VarbanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Service Manual: LCD TVDocument78 paginiService Manual: LCD TVlivinggood58Încă nu există evaluări
- SCI1500A: Crawler Crane 150 Tons Lifting CapacityDocument34 paginiSCI1500A: Crawler Crane 150 Tons Lifting CapacityUpendra KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE102 Lab 1Document12 paginiEE102 Lab 1Romulo TuiqalauÎncă nu există evaluări
- HHOG - PHC-ENG-2022-061 Flowline Construction Schedule of Prices 08022023Document13 paginiHHOG - PHC-ENG-2022-061 Flowline Construction Schedule of Prices 08022023Peter ObueroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Machine Members Bits With AnswersDocument5 paginiDesign of Machine Members Bits With AnswersyeswanthÎncă nu există evaluări
- IGS-NT 4.3.1 New Features ListDocument33 paginiIGS-NT 4.3.1 New Features ListJo RoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Centrifugal Fans GREENHECKDocument10 paginiCentrifugal Fans GREENHECKValentin LupascuÎncă nu există evaluări