Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Engineering Instructions On RF
Încărcat de
baneshTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Engineering Instructions On RF
Încărcat de
baneshDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
ENGINEERING INSTRUCTION
BENCHMARKING OF RF NETWORK, PROCEDURE AND FIELD SURVEY
: / / & 075
(No.: GSM/RF/O&M-075)
,
( )
,
(... 9001:2008 )
,
, ,
482001
BHARAT SANCHAR NIGAM
LIMITED
(A Govt. of India Enterprise)
INSPECTION CIRCLE,
(ISO 9001:2008 Certified)
SANCHAR VIKAS BHAWAN,
RESIDENCY ROAD,
JABALPUR,
MP-482001
(No of Pages) : 16
(Issue Number) : 01
(Issued By) : Inspection Circle
(Approved By) : CGM Inspection Circle
(Date of Issue) : Draft
( )(Amendment No. If Any): Nil
(Page Nos. Amended) :
(Issued By) :
(Approved By) :
(Date of Issue) :
All efforts have been made to incorporate all relevant up to date information available, any discrepancies or
need for addition or deletion is felt necessarily may please be intimated to this office for further improvement,
on E-Mail Id agmtechnical@gmail.com.
(Restricted use by BSNL Employees only)
ENGINEERING INSTRUCTIONS GSM
RF
O&M - 075
INDEX
BENCHMARKING OF RF NETWORK PROCEDURE AND FIELD SURVEY
Sl. TOPIC PAGE
1 Scope 3
2 Introduction 3
3 Channels in GSM 3
4 Call Origination process 5
5 Call Scenario MS To Landline 5
6 Network Performance and Quality of Service (QOS) 9
7 DRIVE TEST 12
7.1 Types of Drive Tests 13
7.2 Equipments used in Drive Test 14
7.3 Calling methods used in drive tests 14
8 Defining the routes 15
9 Analysis of Data 15
10 Procedure 15
11 Conclusion 16
Reference 16
Abbreviation 16
BHARAT SANCHAR NIGAM LIMITED
(A Govt. Of India Enterprise)
Restricted to BSNL Staff only
Issue No. 01
Page 2 of 16
Issue Date: Draft
ENGINEERING INSTRUCTIONS GSM
RF
O&M - 075
BENCHMARKING OF RF NETWORK PROCEDURE AND FIELD SURVEY
1. Scope
This Engineering Instruction describes in detail the parameters used in RF network
Benchmarking and the procedure mainly in relation to Voice in GSM Technology.
2. Introduction
Various technologies used in wireless communication are
Global System for mobile communication (GSM)
Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA)
Universal Mobile Telecommunication Systems(UMTS)
Long Term Evaluation(LTE)
Voice, Video and Data Tests are carried out for Indoor Locations , Strategic locations
and Mobility. In the fiercely competitive Telecom Market high quality of service gives a
competitive advantage for a service provider and so all operators carry out the network
testing activity to judge and improve its RF Network against its competitors. Various areas
and associated benchmarking parameters are as under:
1) Accessibility: Parameters are Call Setup Time (CST) CCR (Call completion ratio),
CSSR etc.
2) Retain ability: Call drop rates
3) Mobility: HOSR, HO Failures
4) Data: Throughput rates
In GSM entire coverage area is divided into a lot number of cells and so is called a
cellular network. A cell consists of Mobile Station (MS) and which is connected to Base
Transceiver Station (BTS) via Air Interface. BTS also has Transreceiver which does
transmission and reception of several radiofrequency signals from /to MS.Abis interface
connects BTS to Base Station Controller (BSC) which does radio resource management and
call handovers between BTS.
3. Channels in GSM:
1. Physical Channel on Um Interface:
In GSM the frequency spectrum of 75 Mhz is divided into 124 carrier frequencies
spaced 200Khz(FDMA). One or more carrier frequencies are assigned to each BTS.
Each of these carrier frequencies is then divided in time using TDMA to increase
number of channel per carrier frequency . Each carrier frequency channel carries
eight time divisioned multiplexed physical channel. Thus a physical channel is
determind by carrier frequency and a time slot number.
2. Logical Channel on Um Interface:
One or more logical channel can be transmitted over one physical channel..
BHARAT SANCHAR NIGAM LIMITED
(A Govt. Of India Enterprise)
Restricted to BSNL Staff only
Issue No. 01
Page 3 of 16
Issue Date: Draft
ENGINEERING INSTRUCTIONS GSM
RF
O&M - 075
Types of Logical Channel:
SN Typeof Logical
channel
Subtype Use
1 Traffic Channel
TCH,
i)TCH/H
ii)TCH/F
Carry voice and data
These are used for sending
information.
2
Broadcast
Channel
Carry Signalling information
i)BCCH Broadcast Control
Channle
Used in D/L and MS is informed
about LAI, CI etc.
ii)FCCH Frequency
Correction Channel
Used to tune MS with BTS in
U/Ll,D/L direction.
iii)SCH Synchronisation
Channel
Used for time synchronization
of MS and BTS in D/L Direction.
iv)CBCH Cell Broadcast
Channel
Used in D/L Direction.
3 Common
control Channel
Used for control information
i)PCH Paging Channel Used for paging to MS in D/L
Direction.
ii)RACH Random Access
Channel
MS sends channel requests on
this in D/L direction.
iii) AGCH Access Grant
Channel
In response to RACH , channel
id is send on AGCH.
4 Dedicated
Control Channel
Point to Point full duplex
channels used for signaling.
i)SACCHSlow Associated Chl Always associated with TCH or
SDCCH and is used in non
urgent procedures.
ii)FACCH Fast Associated
Channel
It is a main signalingchl used in
call setup and release phase.
iii)SDCCH Standalone
Dedicated Channel
Carries all signaling inf between
MS and BTS when no TCH chl is
allocated.Sigannling inf carried
is like location
update,subscriber
authentication,ciphering &
assignment of TCH
BHARAT SANCHAR NIGAM LIMITED
(A Govt. Of India Enterprise)
Restricted to BSNL Staff only
Issue No. 01
Page 4 of 16
Issue Date: Draft
ENGINEERING INSTRUCTIONS GSM
RF
O&M - 075
4. Call Origination process:
1) MS sends channel request or demands to BTS, BTS forwards this request to BSC, BSC
activates a counter upon receiving channel request from MS in cell/BTS
2) BTS sends channel activation and to MS through BTS and another CT is activated in
order to count channel allocation in cell/BTS
3) Authentication is done by MSC and a call is initiated, after call connection another
counter is started to watch and count abnormal call failure or drop due to BSS or radio
link problem
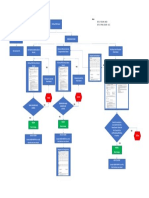
5. CALL Scenario MS to Landline:
STEPS IN REQUEST FOR SERVICE PHASE:
The following is an example of a scenario of a mobile-to-land call. It is assumed that the MS
is already registered with the system and has been allocated a Temporary Mobile subscriber
Identity Number (TMSI).
MS BSS
MSC/
Channel Request
SDCCH Assignment
Service Request
Authentication Ciphering
Equipment Validation Call
set up
Handover(s)
Um A
RACH
AGCH
SDCCH
BHARAT SANCHAR NIGAM LIMITED
(A Govt. Of India Enterprise)
Restricted to BSNL Staff only
Issue No. 01
Page 5 of 16
Issue Date: Draft
ENGINEERING INSTRUCTIONS GSM
RF
O&M - 075
Request for service
Authentication
Ciphering
MS BSS
MSC/
IME I Request
Um A
SDCCH
SDCCH
IMEI Response (IMEI)
EIR
F
IMEI Check Results
Check IMEI
Call setup
Handover(s)
7
BHARAT SANCHAR NIGAM LIMITED
(A Govt. Of India Enterprise)
Restricted to BSNL Staff only
Issue No. 01
Page 6 of 16
Issue Date: Draft
ENGINEERING INSTRUCTIONS GSM
RF
O&M - 075
MS BSS
MSC/
Call Setup Request
Request for service
Authentication Ciphering
Equipment Validation
Um
A
SDCCH
SDCCH
Call Proceeding
Request for Service
Authentication
Ciphering
M
BSS
MSC
/
PST
N
Um A
Network
t
Network
Connect
Start Billing
Alerting
FACCH
Connect
FACCH
Connect
Acknowledgement
10
1
10
1
FACCH
Handover(s)
Call releae
10
11
12
13
14
14
15
BHARAT SANCHAR NIGAM LIMITED
(A Govt. Of India Enterprise)
Restricted to BSNL Staff only
Issue No. 01
Page 7 of 16
Issue Date: Draft
ENGINEERING INSTRUCTIONS GSM
RF
O&M - 075
1 MS transmits a channel request message over the Random Access Channel (RACH)
2 Once the BSS receives the Channel Request message, it allocated a Stand-alone
Dedicated Control Channel (SDCCH) and forwards this channel assignment information
to the MS over the Access Grant channel (AGCH). It is over the SDCCH that the MS will
communicate with the BSS and MSC until a traffic channel is assigned.
3 The MS transmits a service request message to the BSS over the SDCCH. Included in this
message are the MS TMSI and Location Area Identification (LAI). The BSS forwards the
service request message to the MSC/ VLR.
4 The MSC transmits a request to the MS requesting it to respond with its International
Mobile Equipment Identity (IMEI)
5 The MS upon receiving this request, reads its equipment serial number and returns this
value to the MSC
MS BSS
MSC/
PSTN
Um A
Disconnect
Network Release
Stop Billing
Release
Release complete
Clear Complete
FACCH
FACCH
Channel Release
FACCH
16
17
18
19
20
21
FACCH
22
BHARAT SANCHAR NIGAM LIMITED
(A Govt. Of India Enterprise)
Restricted to BSNL Staff only
Issue No. 01
Page 8 of 16
Issue Date: Draft
ENGINEERING INSTRUCTIONS GSM
RF
O&M - 075
6 The MSC then requests the EIR to check the IMEI for validity. The EIR will first check to
see if the IMEI value is within a valid range. If, so it then checks to see if the IMEI is on a
suspect or know list of invalid equipment.
7 The EIR returns to the MSC the results of the IMEI validation. If the results are negative,
the MSC might abort the call or possibly let the call continue but inform the network
service provider of the event. In this scenario, well assume that the IMEI is valid.
8 The MS transmits a call setup request message to the MSC/ VLR after it has ciphered the
radio channel. Included in this request message are the dialed digits. The MSC, upon
receiving the call setup request message, will request the VLR to supply subscriber
parameters necessary for handling the call. The VLR will check for call barring conditions,
such as the MS being barred from making specific outgoing call (e.g. international calls),
or possibly if some supplementary services are active which prevent the call from being
granted. If the VLR determines that the call cannot be processed, the VLR will provide
the reason to the MSC. In this scenario, well assume that his procedure is successful.
The VLR returns a message to the MSC containing the service parameters for the
particular subscriber.
9 The MSC allocates a trunk to the BSS currently serving the MS. The MSC sends a
message to the BSS supplying it with the trunk number allocated (TN), and requests the
BSS to allocate a radio traffic channel (TCH) for the MS
The BSS allocates a radio traffic channel and transmits this assignments to the MS over
the SDCCH
The MS tunes to the assigned radio traffic channel and transmits an acknowledgment to
the BSS.
The BSS connects the radio traffic channel to the assigned trunk of the MSC. Since a
small portion of a radio traffic channel is available for out-of-band signaling, the SDCCH
is no longer used for signaling between the BSS and MS. The BSS de-allocates the SDCCH.
The BSS then transmits a trunk and radio assignment complete message to the MSC.
10 The MSC sends a network setup message to the PSTN requesting that a call be setup.
Included in the message are the MS dialed digits (DD) and details specifying which trunk
should be used for the call.
6. Network Performance and Quality of Service (QOS):
Network performance and Quality of service (QOS) decide the customer satisfaction
and so are of commercial importance for every operator. Network performance evaluation
is done by deciding certain Key performance Indicators KPIs. Every network event Call
initiator, Traffic channel demand, Channel assignment etc are reported by BTS to BSC and
these events trigger different counters (CT). These counters are either incremented or
decremented by and are measured over a period of time generally one hour and are stored
in Operation and Maintenance Center (OMC), the OMC is used to configure and control BTS.
These counters are used to different KPI, The KPIs and counters are used to represent QOS
of network. QOS reports are generated by OMC on daily, weekly and monthly basis. KPIs are
generally prepared by considering traffic events of normal day but network performance is
BHARAT SANCHAR NIGAM LIMITED
(A Govt. Of India Enterprise)
Restricted to BSNL Staff only
Issue No. 01
Page 9 of 16
Issue Date: Draft
ENGINEERING INSTRUCTIONS GSM
RF
O&M - 075
generally evaluated by considering typical congestion situation, The important KPIs used to
evaluate n/w performance and benchmarking of RF n/w against to competitors.
1) Call Set up Success Rate ( CSSR)
2) Call Drop Rate (CDR)
3) Handover Success Rate (HSR)
4) Traffic Channel Congestion Rate (TCHCR)
During congestion traffic channel (TCH) and control channel (SDCCH) get blocked and so this
blocking is analysed to improve n/w performance.
A) Call Set up Success Rate (CSSR) :
It is defined as rate of Call attempts until successful assignment of TCH
CSSR = No. of successful regime of SD chl_____
Total no. of request for regime of SD chl
= [ CTO 1 + CTO 2 ]* 100
CTO 3
Let SD denotes Stand alone dedicated control chl
TCH denotes Traffic chl
Where :
1) CTO1 = Counter for SD chl successfully sized for call termination
2) CTO 2 = Counter showing SD chl successfully sized for call origination
3) CTO 3 = It counts SD chl sized request
Reasons for degradation:
1) Faulty BSS Hardware
2) Increase in Inbound traffic,
3) Lack of radio resource allocation.
4) Congestion in radio interface
Remedies:
1) Replace faulty hardware like TRX.
2) Expansion of Transmission network and end hardware.
3) Redefining OMCR parameters like half rate, traffic load sharing etc.
Blocked call complaints from customer is a common flag of CSSR.
B) Call Drop Rate (CDR) :
It is defined as rate of call snot completed successfully.
CDR = Number of TCH Drops after assignment
Total number of TCH Assignment.
CDR= { (CT04+CT05)/ CT06 }*100
BHARAT SANCHAR NIGAM LIMITED
(A Govt. Of India Enterprise)
Restricted to BSNL Staff only
Issue No. 01
Page 10 of 16
Issue Date: Draft
ENGINEERING INSTRUCTIONS GSM
RF
O&M - 075
WHERE:
1) CT04 = Counter value indicating TCH drops due to radio interface problems.
2) CT05= Counter value indicating TCH drops due to BSS Problems.
3) CT06= Counter value indicating number of TCH successfully seized/assigned.
Causes of CDR Degradation:
1) Hardware faults in BSS/BTS.
2) Coverage Limitations.
3) Improper definition of certain parameters defining adjencies.
4) Internal and external interference over Air Interface, Internal interference is due
to in band (900MHZ,1800 MHZ) problems. External Interference is due to other
wireless networks.
Ways of detection of CDR:
1) Customers complaints of blocked calls in a particular area./sector.
2) Adulterated carrier frequencies causing interference can be detected by using
Spectrum Scanners.
3) OMCR Alarms: OMCR Monitors certain counters and does some defined
calculation including uplink interface and raises alarms of CDR.
4) Average of Effective Radiated Power over downlink and Received power over
uplink is used to carry out Path Balance Statistics which helps in finding CDR.
Methods to improve CDR:
1) Antenna Orientation ( Azimuth) tilts, change in some parameters at OMCR
like Radiated power level improve CDR
2) Timely rectification of hardware faults in BTB/BSC
3) Frequency hopping techniques to reduce interference and use of RF
repeaters also help in reducing CDR
4) Introducing new sites at proper location reduce CDR
5) CDR can also be improved by coverage optimization
C) Handover Success Rate (HSR) :
It is defined as rate of successful handover, It include both inter cell and intra
cell handover mathematically
HSR = { (CTO7 + CTO8)/(CTO9 + CTO10)} * 100
Where
CTO7 = Counter indicating incoming successful handover
CTO8 = Counter indicating no. of successful Outgoing handover
CTO9 = Indicates no. of Outgoing handover requests
CTO10 = Counter value indicating no. of Incoming handover requests
Reasons for HSR degradation :
1) Hardware faults in BTS/BSS
2) Improper planning/definition of Location area code (LAC)
BHARAT SANCHAR NIGAM LIMITED
(A Govt. Of India Enterprise)
Restricted to BSNL Staff only
Issue No. 01
Page 11 of 16
Issue Date: Draft
ENGINEERING INSTRUCTIONS GSM
RF
O&M - 075
3) Coverage limitation and air interface interferences
4) Wrong definition at OMCR for adjencies parameters
Methods to improve HSR :
1) Parameter modification in OMCR such as handover margin, traffic handover, power
budget parameters
2) BSS recourse augmentation such as TRX
3) Coverage improvement and adjacencies audits
D) TCH Congestion rate (TCHCR) :
It is defined as rate of blocked calls due to unavailability of radio resources
TCHCR = No. of calls blocked due to unavailable radio resources
Total no. of requests
= ( CTI 1/CTI 2) * 100
Where :
CTI 1 = Counters indicating no. of assignment failure when TCH is available
CTI 2 = Counter indicating no. of normal assignment request for TCH establishment
Reasons for TCHCR degradation :
1) Media unavailability, Hardware unavailability
2) Increased subscriber density in a particular area
3) TRX hardware fault
Flags pointing TCHCR :
1) Locolised customer complaints
2) OMCR carriers out radio counters mentioned above and raised alarms
Worst cell ratio WCR and CSSR also points to TCH congestion
7. Drive Test:
Drive Test is another tool used by the operator to optimize the mobile radio network
and solve the network- coverage related problems , such as congestion ,limited coverage,
QOS issues. This tool helps in comparing own RF Network with that of other Operators
which helps in subscriber retention and also providing minimum Quality Of Service made
mandatory by Regulatory Authorities of the country.
The RF Drive tool is comprised of Test Mobile Handsets, motor vehicle and a mobile
radio network air interface measurement equipment with software that detects and record
variety of the physical and virtual parameters of the RF network while moving in the field.
BHARAT SANCHAR NIGAM LIMITED
(A Govt. Of India Enterprise)
Restricted to BSNL Staff only
Issue No. 01
Page 12 of 16
Issue Date: Draft
ENGINEERING INSTRUCTIONS GSM
RF
O&M - 075
Data collected by this tool is in the form of log files. These files get stored and are
then assessed to evaluate the important Key Performance Indicators of the network under
study. Following data is collected by the Drive Test Tool:
1) Receive Signal level.
2) Signal Quality Level.
3) Call setup RATES.
4) Service level statics.
5) Interference of signals.
6) Dropped Calls.
7) Handover Information.
8) Neighboring call information.
9) GPS Coordinates.
10) Service Quality.
7.1 Types of Drive Tests:
There are two types of drive tests. They are:
I) Pre swap drive tests:
These are carried out to set reference levels for verification of the Post Swap RF
Network performance .The result of this test are called Network Quality Index
(NQI). NQI s are generally consists of:
a) Received Downlink signal strength.
b) Received Quality
c) Call Setup success rate
d) Handover Success Rate
e) Call Drop Rate.
These tests are carried out in predefined cities on predefined routes.
II) Post Swap DRIVE Tests:
These Drive test is carried out on routes/cities used in Pre swap Tests after Swap
Activity is completed and the result obtained is compared with NQI of pre swap
tests.
The objective of this Radio Network Benchmarking is to compare the actually
achieved radio network performanance parameters with the NQI target from the
Pre Swap Drive Test.
Post Swap drive tests are further classified into :
A) Network Benchmarking Tests:
In this sophisticated multichannel tools are used to measure several network
technologies and service types simultaneously to high degree of accuracy to
provide directly comparable information in respect of signal strength and
weakness. Commonly obtained data from this benchmarking is Comparative
BHARAT SANCHAR NIGAM LIMITED
(A Govt. Of India Enterprise)
Restricted to BSNL Staff only
Issue No. 01
Page 13 of 16
Issue Date: Draft
ENGINEERING INSTRUCTIONS GSM
RF
O&M - 075
Coverage Analysis and Comparative network speed analysis and is generally
used in marketing campaigns. This test is the only way by which the operator
can acquire accurate competitive true level data of its own and competitors
network.
B) Optimization and trouble shooting :
These drive tests are used to solve area specific problems such as call drop in
roll out phases of new network and to solve the area specific problems
reported by customers during Operational Phase.
C) Service Quality Monitoring :
In this, automated test calls are made across the network to access the
relative quality of various services using Mean Opinion Score (MOS).It is
focused in finding out the end user experience and helps the operator in
providing technical solutions to problems observed and in maintaining the
QOS standards set by Regulatory Authority of the country.
7.2 Equipments used in Drive Test:
Drive test system consist of
1. Mobile Handset with charger, headset data cable and USB
2. Laptop and adapter
3. GPS
4. Inverter and Terminal
5. Scanner for GSM
7.3 Calling methods used in drive tests: Calling methods used in drive tests are-
i) Idle Mode The MS is on but the call is not in progress.
ii) Dedicated Mode: The MS is ON and call is in progress.
The call made is either a short call or long call.Generally a
combination of calling methods is adopted i.e. Idle+short call,
Idle+Long call etc.
The use of calling methods is as under:
Test Methods Purpose
Idle It is used to record the network condition at idle
state and the level of CI on BCCH
Dedicated- Short Call Used for testing the accessibility and mobility of
network.
Dedicated-Long Call It is used to test retain-ability and sustain-ability.
e.g CDR,HOS
BHARAT SANCHAR NIGAM LIMITED
(A Govt. Of India Enterprise)
Restricted to BSNL Staff only
Issue No. 01
Page 14 of 16
Issue Date: Draft
ENGINEERING INSTRUCTIONS GSM
RF
O&M - 075
8. Defining the routes:
Mainly there are two type of routes depending upon the distribution density of sites and
the surrounding radio environment. They are
1. Urban Area
Here the test route covers the cells are around the BTS and care is taken that the
actual coverage area is covered and handovers can be verified.
Test routes should be so designed that the local customs of traffic are properly
followed so that waiting in traffic is reduced.
2. Suburban area:
The main features of these routes are
i)Route should cover the roads which are covered by different sectors of the site to
be tested.
ii) The overlapping area of surrounding neighbor cells should be covered so that the
handover functions can be verified.
iii) For isolated sites normal coverage area should be covered.
9. Analysis of Data:
The data collecting software like TEMS is used for analysis of data.The data collected
by this software consist of:
1. GSM Radio parameters
2. Current channel
3. Serving +Neighbor Window
4. The data like site name Lat Long Building Height Tower Height, Tower Type, Average
Clutter height, Indoor Rx Level, Seving Cells Max AGL Availability, Azimuth for Max
AGL Availability. LOS Clear, Deviation Of Lat/ Long etc is taken .After collecting this
information the drive test is started. The equipment is set up in a vehicle and long as
well as short calls are generated. A long call is used to measure the handover success
rate and Rx quality while short call is used for CSSR and Rx level.
10. Procedure:
Tool can accommodate two mobiles one for long call and another for short call.
Following parameters are enabled in Route Map
i) Rx Level
ii) Rx Quality
iii) Survey Markers (like CSSR,DCR)
iv) Cell site database.
BHARAT SANCHAR NIGAM LIMITED
(A Govt. Of India Enterprise)
Restricted to BSNL Staff only
Issue No. 01
Page 15 of 16
Issue Date: Draft
ENGINEERING INSTRUCTIONS GSM
RF
O&M - 075
v) Call Statistics.
The drive test is conducted covering all sectors observing Rx Level, Rx Quality,
Interference on BCCH& Hopping Frequencies, Call setup failure reasons etc.
11. Conclusion:
Analysis and performance evaluation of GSM network can be done by drive tests and
by using KPIs .This can also be used for Benchmarking of network of different cellular
operators. It also helps in ensuring a better QOS which satisfies the threshold levels set by
regulatory authorities. Benchmarking activity helps in keeping tight control on Opex
(Operating Expenses), Network parameter setting and stringent QOS desired by customers.
Reference:
1) ITU-T recommendations G.1000, Communication Quality of service : A framework
and definition
2) Halonen T. Romero J. : GSM, GPRS, EDGE performance John Wiley and sons
Abbreviations:
1) WCR : Worst Cell Ratio
2) CSSR : Call Setup Success Rate
3) KPI : Key Performance Indicator
4) TRX : Trans Receiver
5) LAI: Location Area Identity
6) CI: Cell Identity
7) U/L:Uplink
8) D/L: Down link
9) BCCH: Broadcast control channel
10) FCCH: Frequency allocation Channel
11) SCH:Synchronisation Channel
12) CBCH: Cell Broadcast channel
13) PCH: Paging channel
14) RACH: Random access channel
15) AGCH: Access grant channel
16) SACCH:Slow associated control channels
17) FACCH:Fast associated control channels
18) SDCCH:Stand alone dedicated control channel
19) LOS: Line of site
BHARAT SANCHAR NIGAM LIMITED
(A Govt. Of India Enterprise)
Restricted to BSNL Staff only
Issue No. 01
Page 16 of 16
Issue Date: Draft
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Mobile Number Portability (MNP) Implementation in Wire Line SwitchesDocument37 paginiMobile Number Portability (MNP) Implementation in Wire Line SwitchesgrksudÎncă nu există evaluări
- WCS CapacityDocument2 paginiWCS CapacityRajesh PorwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ee Gate 2010Document16 paginiEe Gate 2010Sekhar ChallaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mobile Number Portability in IndiaDocument12 paginiMobile Number Portability in IndiaverarvindÎncă nu există evaluări
- USIM : Mandatory Selection Procedure For INTERNATIONAL ROAMINGDocument1 paginăUSIM : Mandatory Selection Procedure For INTERNATIONAL ROAMINGbaneshÎncă nu există evaluări
- White Paper 1 - LifeCell Transplant Matrix (Ver 002) - 44 Transplants - November 2016Document8 paginiWhite Paper 1 - LifeCell Transplant Matrix (Ver 002) - 44 Transplants - November 2016baneshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asset GuidelinesDocument2 paginiAsset GuidelinesbaneshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intelligent Networks: A Concept For The 21st Century: Capability Set 2: CS-2Document17 paginiIntelligent Networks: A Concept For The 21st Century: Capability Set 2: CS-2baneshÎncă nu există evaluări
- MGMT 7 Energy Conservation and Fire SafetyDocument17 paginiMGMT 7 Energy Conservation and Fire SafetybaneshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Index of Constitutional Provisions and Guidelines for SC/ST CertificatesDocument135 paginiIndex of Constitutional Provisions and Guidelines for SC/ST Certificatessanjay1009Încă nu există evaluări
- RRB Section Engineer Previous PapersDocument8 paginiRRB Section Engineer Previous PapersbaneshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Correct Setting For International RoamingDocument2 paginiCorrect Setting For International RoamingbaneshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter08.Bsnl Cda RulesDocument21 paginiChapter08.Bsnl Cda RulesDheeraj Kumar TambiÎncă nu există evaluări
- PUNE CSC LOCATIONSDocument4 paginiPUNE CSC LOCATIONSbhagwatsagarÎncă nu există evaluări
- GSM Terminating Call FlowDocument4 paginiGSM Terminating Call Flowxxxhere100% (3)
- Performa For Compiling Polling DataDocument2 paginiPerforma For Compiling Polling DatabaneshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Broadband ComponentsDocument31 paginiBroadband Componentsmnarukula100% (1)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (587)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (265)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Modeling of Surge Currents in Lightning Protection System Using ATP-EMTPDocument4 paginiModeling of Surge Currents in Lightning Protection System Using ATP-EMTPMuhammad HaycalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Automation of Diesel Generator Using PLC & ScadaDocument12 paginiAutomation of Diesel Generator Using PLC & ScadaRaghav Mesta50% (2)
- Erection of Transmission Tower and Design of ResidentialDocument40 paginiErection of Transmission Tower and Design of ResidentialBoopathi YoganathanÎncă nu există evaluări
- CM20180320 16121 49538Document5 paginiCM20180320 16121 49538Ignacio LucasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Apt x100Document16 paginiApt x100lbbrhznÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application for EE/Aux/POS entry and work permit flow chartDocument1 paginăApplication for EE/Aux/POS entry and work permit flow chartJose Mari BarrogaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eaton Memshield 2 MCB Distribution Board System TechnicalDocument63 paginiEaton Memshield 2 MCB Distribution Board System TechnicalSameerEkriemÎncă nu există evaluări
- STTH6006W: Turbo 2 Ultrafast - High Voltage RectifierDocument7 paginiSTTH6006W: Turbo 2 Ultrafast - High Voltage RectifierSofyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pioneer Avh-P3400bh p2400bt 2450bt 2490bt PDFDocument152 paginiPioneer Avh-P3400bh p2400bt 2450bt 2490bt PDFCitroen FreireÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH-03 Current Electricity: Lect-13Document26 paginiCH-03 Current Electricity: Lect-13coriniwÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Broadband Low-Reflection Metamaterial AbsorberDocument6 paginiA Broadband Low-Reflection Metamaterial AbsorberRiston SinagaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ED Quiz 2 Questions and AnswersDocument6 paginiED Quiz 2 Questions and AnswersMahi ChapliÎncă nu există evaluări
- PCS 7 Engineering SystemDocument556 paginiPCS 7 Engineering SystemcathyvuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wind Energy Wind Is Generated As The Fluid and Gaseous Parts of The Atmosphere Move Across The Surface of The EarthDocument3 paginiWind Energy Wind Is Generated As The Fluid and Gaseous Parts of The Atmosphere Move Across The Surface of The EarthEphraim TermuloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Longitudinal Induction Voltage Measurement On Communication Cables Running Parallel To Overhead Lines or Power CablesDocument4 paginiLongitudinal Induction Voltage Measurement On Communication Cables Running Parallel To Overhead Lines or Power CablesmojoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Service Manual: Av Receiver Model ModelDocument204 paginiService Manual: Av Receiver Model ModelJJ ChávezÎncă nu există evaluări
- MV Public Distribution Networks Throughout The World: BackDocument28 paginiMV Public Distribution Networks Throughout The World: Backmiksa samuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Condensed Matter Physics Lecture Notes (PDFDrive)Document41 paginiCondensed Matter Physics Lecture Notes (PDFDrive)Dulen BoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- PIC Part5 InterruptsDocument53 paginiPIC Part5 InterruptsJean Profite100% (2)
- Clion-Marine Chiller Specs 2017Document1 paginăClion-Marine Chiller Specs 2017Sandy NugrahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Satellite TelevisionDocument2 paginiSatellite TelevisionDorin LunguÎncă nu există evaluări
- 16EI7201 - Computer Control of Process - IAQBDocument6 pagini16EI7201 - Computer Control of Process - IAQBMadhusudhanan RamaiahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Android Game Programming For DummiesDocument127 paginiAndroid Game Programming For DummiesbillyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 44POSITIONDocument188 pagini44POSITIONstefan corjucÎncă nu există evaluări
- SONY KDL-40EX520 Chassis AZ2G DIAGRAMA SERVICE MANUALDocument154 paginiSONY KDL-40EX520 Chassis AZ2G DIAGRAMA SERVICE MANUALJorge VasquezÎncă nu există evaluări
- CTC-211 Engine SystemsDocument393 paginiCTC-211 Engine SystemsGoutam Saha100% (1)
- Iec 60243-1-2013Document58 paginiIec 60243-1-2013FernandoCrespoMon100% (1)
- CGL - Instruction & Maintenance Manual Voltage TransformerDocument18 paginiCGL - Instruction & Maintenance Manual Voltage TransformerHari Krishna.MÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abs General Description and System OperationDocument2 paginiAbs General Description and System OperationDavid Wise-MannÎncă nu există evaluări
- ICT Class Routine Jan-June 2024 (16.01.24)Document8 paginiICT Class Routine Jan-June 2024 (16.01.24)FardinÎncă nu există evaluări