Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Computer Networks (CS425) : Instructor: Dr. Dheeraj Sanghi
Încărcat de
Anish VeettiyankalTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Computer Networks (CS425) : Instructor: Dr. Dheeraj Sanghi
Încărcat de
Anish VeettiyankalDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
11/8/2014
CS425: Computer Networks: Lecture 02
Computer Networks (CS425)
Instructor: Dr. Dheeraj Sanghi
Prev | Next | Index
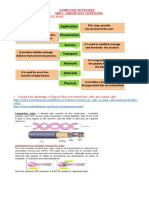
Session Layer
It deals with the concept of Sessions i.e. when a user logins to a remote server he should be
authenticated before getting access to the files and application programs. Another job of session layer is
to establish and maintain sessions. If during the transfer of data between two machines the session breaks
down, it is the session layer which re-establishes the connection. It also ensures that the data transfer
starts from where it breaks keeping it transparent to the end user. e.g. In case of a session with a database
server, this layer introduces check points at various places so that in case the connectoin is broken and
reestablished, the transition running on the database is not lost even if the user has not committed. This
activity is called Synchronization. Another function of this layer is Dialogue Control which determines
whose turn is it to speak in a session. It is useful in video conferencing.
Presentation Layer
This layer is concerned with the syntax and semantics of the information transmitted. In order to make it
possible for computers with different data representations to communicate data structures to be
exchanged can be defined in abstract way alongwith standard encoding. It also manages these abstract
data structres and allows higher level of data structres to be defined an exchange. It encodes the data in
standard agreed way(network format). Suppose there are two machines A and B one follows 'Big Endian'
and other 'Little Endian' for data representation. This layer ensures that the data transmitted by one gets
converted in the form compatibale to othe machine. This layer is concerned with the syntax and
semantics of the information transmitted.In order to make it possible for computers with different data
representations to communicate data structures to be exchanged canbe defined in abstract way alongwith
standard encoding. It also manages these abstract data structres and allows higher level of data structres
to be defined an exchange. Other functions include compression, encryption etc.
Application Layer
The seventh layer contains the application protocols with which the user gains access to the network. The
choice of which specific protocols and their associated functions are to be used at the application level is
up to the individual user. Thus the boundary between the presentation layer and the application layer
represents a separation of the protocols imposed by the network designers from those being selected and
implemented by the network users.For example commonly used protocols are HTTP(for web browsing),
FTP(for file transfer) etc.
Network Layers as in Practice
In most of the networks today, we do not follow the OSI model of seven layers. What is actually
implemented is as follows. The functionality of Application layer and Presentation layer is merged into
one and is called as the Application Layer. Functionalities of Session Layer is not implemented in most
networks today. Also, the Data Link layer is split theoretically into MAC (Medium Access Control)
http://www.cse.iitk.ac.in/users/dheeraj/cs425/lec02.html
1/6
11/8/2014
CS425: Computer Networks: Lecture 02
Layer and LLC (Link Layer Control). But again in practice, the LLC layer is not implemented by most
networks. So as of today, the network architecture is of 5 layers only.
Network Layers in Internet Today
Some Related Links on OSI Model and TCP Model
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/OSI_model
http://www.tcpipguide.com/free/t_OSIReferenceModelLayers.htm
http://www.geocities.com/SiliconValley/Monitor/3131/ne/osimodel.html
http://www.tech-faq.com/osi-model.shtml
http://www.networkdictionary.com/protocols/osimodel.php
Physical Layer
Physical layer is concerned with transmitting raw bits over a communication channel. The design issues
have to do with making sure that when one side sends a 1 bit, it is recieved by the other side as 1 bit and
not as 0 bit. In physical layer we deal with the communication medium used for transmission.
Types of Medium
Medium can be classified into 2 categories.
1. Guided Media : Guided media means that signals is guided by the prescence of physical media
i.e. signals are under control and remains in the physical wire. For eg. copper wire.
2. Unguided Media : Unguided Media means that there is no physical path for the signal to
propogate. Unguided media are essentially electro-magnetic waves. There is no control on flow of
signal. For eg. radio waves.
http://www.cse.iitk.ac.in/users/dheeraj/cs425/lec02.html
2/6
11/8/2014
CS425: Computer Networks: Lecture 02
Communication Links
In a nework nodes are connected through links. The communication through links can be classified as
1. Simplex : Communication can take place only in one direction. eg. T.V broadcasting.
2. Half-duplex : Communication can take place in one direction at a time. Suppose node A and B are
connected then half-duplex communication means that at a time data can flow from A to B or from
B to A but not simultaneously. eg. two persons talking to each other such that when speaks the
other listens and vice versa.
3. Full-duplex : Communication can take place simultaneously in both directions. eg. A discussion in
a group without discipline.
Links can be further classified as
1. Point to Point : In this communication only two nodes are connected to each other. When a node
sends a packet then it can be recieved only by the node on the other side and none else.
2. Multipoint : It is a kind of sharing communication, in which signal can be recieved by all nodes.
This is also called broadcast.
Generally two kind of problems are associated in transmission of signals.
1. Attenuation : When a signal transmitts in a network then the quality of signal degrades as the
signal travels longer distances in the wire. This is called attenuation. To improve quality of signal
amplifiers are used at regular distances.
2. Noise : In a communication channel many signals transmits simultaneously, certain random signals
are also present in the medium. Due to interference of these signals our signal gets disrupted a bit.
Bandwidth
Bandwidth simply means how many bits can be transmitted per second in the communication channel. In
technical terms it indicates the width of frequency spectrum.
Transmission Media
Guided Transmission Media
In Guided transmission media generally two kind of materials are used.
1. Copper
Coaxial Cable
Twisted Pair
2. Optical Fiber
1. Coaxial Cable: Coaxial cable consists of an inner conductor and an outer conductor which are
seperated by an insulator. The inner conductor is usually copper. The outer conductor is covered by
a plastic jacket. It is named coaxial because the two conductors are coaxial. Typical diameter of
coaxial cable lies between 0.4 inch to 1 inch. The most application of coaxial cable is cable T.V.
The coaxial cable has high bandwidth, attenuation is less.
http://www.cse.iitk.ac.in/users/dheeraj/cs425/lec02.html
3/6
11/8/2014
CS425: Computer Networks: Lecture 02
2. Twisted Pair: A Twisted pair consists of two insulated copper wires, typically 1mm thick. The
wires are twisted togather in a helical form the purpose of twisting is to reduce cross talk
interference between several pairs. Twisted Pair is much cheaper then coaxial cable but it is
susceptible to noise and electromagnetic interference and attenuation is large.
Twisted Pair can be further classified in two categories:
Unshielded twisted pair: In this no insulation is provided, hence they are susceptible to
interference.
Shielded twisted pair: In this a protective thick insulation is provided but shielded twisted pair is
expensive and not commonly used.
The most common application of twisted pair is the telephone system. Nearly all telephones are
connected to the telephone company office by a twisted pair. Twisted pair can run several
kilometers without amplification, but for longer distances repeaters are needed. Twisted pairs can
be used for both analog and digital transmission. The bandwidth depends on the thickness of wire
and the distance travelled. Twisted pairs are generally limited in distance, bandwidth and data rate.
3. Optical Fiber: In optical fiber light is used to send data. In general terms prescence of light is
taken as bit 1 and its absence as bit 0. Optical fiber consists of inner core of either glass or plastic.
Core is surrounded by cladding of the same material but of different refrective index. This cladding
is surrounded by a plastic jacket which prevents optical fiber from electromagnetic interferrence
and harshy environments. It uses the principle of total internal reflection to transfer data over
optical fibers. Optical fiber is much better in bandwidth as compared to copper wire, since there is
hardly any attenuation or electromagnetic interference in optical wires. Hence there is less
requirement to improve quality of signal, in long distance transmission. Disadvantage of optical
fiber is that end points are fairly expensive. (eg. switches)
http://www.cse.iitk.ac.in/users/dheeraj/cs425/lec02.html
4/6
11/8/2014
CS425: Computer Networks: Lecture 02
Differences between different kinds of optical fibers:
1. Depending on material
Made of glass
Made of plastic.
2. Depending on radius
Thin optical fiber
Thick optical fiber
3. Depending on light source
LED (for low bandwidth)
Injection lased diode (for high bandwidth)
Wireless Transmission
1. Radio: Radio is a general term that is used for any kind of frequency. But higher frequencies are
usually termed as microwave and the lower frequency band comes under radio frequency. There
are many application of radio. For eg. cordless keyboard, wireless LAN, wireless ethernet. but it is
limited in range to only a few hundred meters. Depending on frequency radio offers different
bandwidths.
2. Terrestrial microwave: In terrestrial microwave two antennas are used for communication. A
focused beam emerges from an antenna and is recieved by the other antenna, provided that
antennas should be facing each other with no obstacle in between. For this reason antennas are
situated on high towers. Due to curvature of earth terristial microwave can be used for long
distance communication with high bandwidth. Telecom department is also using this for long
distance communication. An advantage of wireless communication is that it is not required to lay
down wires in the city hence no permissions are required.
3. Satellite communication: Satellite acts as a switch in sky. On earth VSAT(Very Small Aperture
Terminal) are used to transmit and recieve data from satellite. Generally one station on earth
transmitts signal to satellite and it is recieved by many stations on earth. Satellite communication is
generally used in those places where it is very difficult to obtain line of sight i.e. in highly irregular
terristial regions. In terms of noise wireless media is not as good as the wired media. There are
frequency band in wireless communication and two stations should not be allowed to transmit
simultaneously in a frequency band. The most promising advantage of satellite is broadcasting. If
satellites are used for point to point communication then they are expensive as compared to wired
media.
References of Images
http://ai3.asti.dost.gov.ph/sat/levels.jpg
http://www.ll.mit.edu/Image-Lib/photos/color-Satellite.jpg
http://oldsite.vislab.usyd.edu.au/photonics/revolution/technology/images/twisted_pair.jpg
http://www.cse.iitk.ac.in/users/dheeraj/cs425/lec02.html
5/6
11/8/2014
CS425: Computer Networks: Lecture 02
http://www.radio-electronics.com/info/antennas/coax/cross_section_thro_coax.gif
back to top
Prev | Next | Index
http://www.cse.iitk.ac.in/users/dheeraj/cs425/lec02.html
6/6
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Work Architecture (Contd) and Physical LayerDocument5 paginiWork Architecture (Contd) and Physical Layerde veronÎncă nu există evaluări
- UNIT-3 Osi Reference Model Types of Transmission MediaDocument17 paginiUNIT-3 Osi Reference Model Types of Transmission MediaNandkumar KhachaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- HW1 (Networks)Document10 paginiHW1 (Networks)Sk SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCNA 1 v51 v60 Chapter 4 Exam Answers 2017 100 FullDocument11 paginiCCNA 1 v51 v60 Chapter 4 Exam Answers 2017 100 FullAldo Francisco Resendiz HernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- MI0026 AssignmentDocument8 paginiMI0026 AssignmentAvisekh SarkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Architecture and Structure: OSI Reference ModelDocument5 paginiArchitecture and Structure: OSI Reference ModelMalebogo BabutsiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intro Chapter 3: Network Protocols and CommunicationsDocument5 paginiIntro Chapter 3: Network Protocols and CommunicationsAnonymous d9fyfsmEFÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.ISO-OSI 7-Layer Network ArchitectureDocument5 pagini1.ISO-OSI 7-Layer Network Architecturede veronÎncă nu există evaluări
- Important Questions For MID I CNDocument14 paginiImportant Questions For MID I CN20H51A0540-NAKKA SREEKAR B.Tech CSE (2020-24)Încă nu există evaluări
- Name of The Student: Areeba Shaikh Roll Number: 64 Subject: Computer NetworkDocument5 paginiName of The Student: Areeba Shaikh Roll Number: 64 Subject: Computer NetworkAreeba ShaikhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Network Hardware Activity 1: 1. What Is A Twisted Pair Cable, and Where Do We Usually See Them?Document10 paginiNetwork Hardware Activity 1: 1. What Is A Twisted Pair Cable, and Where Do We Usually See Them?Denver SignabenÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCNADocument14 paginiCCNApraveen murugesanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pass Assignment 1Document27 paginiPass Assignment 1Athl S33% (3)
- Name Kibii Phares REG NO. I231/0861/2017 Unit Network System and Integration Unit Code Ict 3321Document6 paginiName Kibii Phares REG NO. I231/0861/2017 Unit Network System and Integration Unit Code Ict 3321pharesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment-II: Gagandeep KaurDocument12 paginiAssignment-II: Gagandeep KaurYolomanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ieee 802 LansDocument33 paginiIeee 802 LansArvind UpadhyayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 1: Introduction To NetworkingDocument12 paginiModule 1: Introduction To NetworkingKihxan Poi Alonzo PaduaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CT 01Document11 paginiCT 01api-26125777Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter FiveDocument11 paginiChapter Fiveayuba amanÎncă nu există evaluări
- CN Experiment 2Document6 paginiCN Experiment 2rudraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bhargav ch-4Document11 paginiBhargav ch-4chandrasekharreddyguduruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wired Communication Media - GeeksforGeeksDocument12 paginiWired Communication Media - GeeksforGeeksLab DasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reference Models in Communication NetworksDocument7 paginiReference Models in Communication NetworksPRODIP DEBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Networking Report For StudentDocument8 paginiNetworking Report For StudentAbhishek DwivediÎncă nu există evaluări
- TUTORIAL SHEET-1 (Solution) : Kcs-603: Computer NetworksDocument8 paginiTUTORIAL SHEET-1 (Solution) : Kcs-603: Computer NetworksANAMIKA SRIVASTAVAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter-1: 1.1 What Is A Virtual Private Network?Document81 paginiChapter-1: 1.1 What Is A Virtual Private Network?Geetha NamavaramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4Document15 paginiChapter 4Okech MableÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digital Control SystemDocument42 paginiDigital Control Systemajas777BÎncă nu există evaluări
- Discuss The Advantages and Disadvantages of Synchronous and Asynchronous TransmissionDocument7 paginiDiscuss The Advantages and Disadvantages of Synchronous and Asynchronous Transmissiondheeru18Încă nu există evaluări
- 4.0.1 Welcome 4.0.1.1 Chapter 4: Network AccessDocument36 pagini4.0.1 Welcome 4.0.1.1 Chapter 4: Network Accesscamys18Încă nu există evaluări
- Layer 6: Presentation LayerDocument9 paginiLayer 6: Presentation Layerriya_1982Încă nu există evaluări
- Computer Networks: Characteristics of Data Communications SystemDocument10 paginiComputer Networks: Characteristics of Data Communications SystemShepherd AndoliniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1 Notes KCS-603 - Computer NetworksDocument50 paginiUnit 1 Notes KCS-603 - Computer Networksmayushbbk18Încă nu există evaluări
- Data Communication S: Lecture - 3Document42 paginiData Communication S: Lecture - 3Fr Sunny100% (1)
- Computer Networks: Characteristics of Data Communications SystemDocument6 paginiComputer Networks: Characteristics of Data Communications SystemShepherd AndoliniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 7 Data Communication NetworkDocument39 paginiUnit 7 Data Communication NetworksimantÎncă nu există evaluări
- Storage Area Network (Black Book)Document65 paginiStorage Area Network (Black Book)Sohail KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.4 Reference Models: Figure 1-20. The OSI Reference ModelDocument3 pagini1.4 Reference Models: Figure 1-20. The OSI Reference ModelDinesh DinuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wa0022.Document15 paginiWa0022.Zam'Ah SirajoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Define Communication, Write The Feature & Component of CommunicationDocument4 paginiDefine Communication, Write The Feature & Component of CommunicationAbu SayedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Define Communication, Write The Feature & Component of CommunicationDocument4 paginiDefine Communication, Write The Feature & Component of CommunicationAbu SayedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computernetwork For InterviewDocument9 paginiComputernetwork For InterviewSangeetha ShankaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- MC0075 Sem3 Smu 2011Document31 paginiMC0075 Sem3 Smu 2011Nitin SivachÎncă nu există evaluări
- Networking Data Comm To StartDocument29 paginiNetworking Data Comm To StartBenson MugaÎncă nu există evaluări
- First Assignment in CnsDocument7 paginiFirst Assignment in CnsAlcala, John Paul P.Încă nu există evaluări
- Five Year SolutionsDocument99 paginiFive Year Solutionsamrita tiwariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Edexcel IAL IT Network Part2 PDFDocument3 paginiEdexcel IAL IT Network Part2 PDFDix BrosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acknowledgement NetDocument57 paginiAcknowledgement NetGihan JayamahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fiber Optic TermsDocument18 paginiFiber Optic TermsRao Wajid Ali KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Answer - Regular CS306 Computer Networks May 2019Document11 paginiAnswer - Regular CS306 Computer Networks May 201911712077 NIVA DILEEP100% (1)
- IT-2205 Lec 05 Guided Transmission MediaDocument31 paginiIT-2205 Lec 05 Guided Transmission MediaIrfan SaminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment Name: Objective:: To Study OSI Reference ModelDocument5 paginiExperiment Name: Objective:: To Study OSI Reference ModelUterus Xbox er f u. RÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hafiz Danish ZahidDocument7 paginiHafiz Danish ZahidShoaib AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- DC Chapter FourDocument21 paginiDC Chapter FourGetnete degemuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2Document7 paginiChapter 2Hrituja HedauÎncă nu există evaluări
- Training On Network: PREPARED BY: Vishal BediDocument141 paginiTraining On Network: PREPARED BY: Vishal BedidsmehlawatÎncă nu există evaluări
- UNIT 1 AKTU Last Five Year Solutions - Computer Networks - (KCS-603)Document15 paginiUNIT 1 AKTU Last Five Year Solutions - Computer Networks - (KCS-603)mayushbbk18Încă nu există evaluări
- Rdso ReportDocument28 paginiRdso ReportLekhraj SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedDe la EverandCCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedÎncă nu există evaluări
- DLO AdminGuide 8.0Document260 paginiDLO AdminGuide 8.0juanmaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Gilliam Autism Rating Scale GARS - 2 A Pilot SDocument2 paginiThe Gilliam Autism Rating Scale GARS - 2 A Pilot SAnish VeettiyankalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interview Evaluation ReportDocument6 paginiInterview Evaluation ReportShankar CoolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Health Care Delivery System in IndiaDocument11 paginiHealth Care Delivery System in IndiaAnish VeettiyankalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Normal MenstruationDocument38 paginiNormal MenstruationAnish VeettiyankalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Networking Interview Question and Answer PDFDocument30 paginiComputer Networking Interview Question and Answer PDFImranRafiqÎncă nu există evaluări
- EconomyDocument3 paginiEconomyAnish VeettiyankalÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8 Standard PrecautionsDocument10 pagini8 Standard PrecautionsAnish VeettiyankalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Networks (CS425) : Transport Layer Protocol (Continued)Document4 paginiComputer Networks (CS425) : Transport Layer Protocol (Continued)Anish VeettiyankalÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Obstetobric History Should IncludeDocument4 paginiAn Obstetobric History Should IncludeAnish VeettiyankalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Staffing in Nursing UnitsDocument13 paginiStaffing in Nursing UnitsAnish Veettiyankal100% (1)
- Post MortemDocument13 paginiPost MortemAnish VeettiyankalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Post MortemDocument13 paginiPost MortemAnish VeettiyankalÎncă nu există evaluări
- LectureDocument3 paginiLectureAnish VeettiyankalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evaluationofeducationalprogramsinnursing 130309043334 Phpapp02Document22 paginiEvaluationofeducationalprogramsinnursing 130309043334 Phpapp02Anish VeettiyankalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jason Dela Cruz Jose": IT Engineer / Systems EngineerDocument3 paginiJason Dela Cruz Jose": IT Engineer / Systems EngineerAnish VeettiyankalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Karnataka: 4 T' Block, Jayanagar, Bangalore - 560 041Document4 paginiRajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Karnataka: 4 T' Block, Jayanagar, Bangalore - 560 041verghese17Încă nu există evaluări
- Computer Networks (CS425) : Transport Layer Protocol-Implementation IssuesDocument5 paginiComputer Networks (CS425) : Transport Layer Protocol-Implementation IssuesAnish VeettiyankalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Networks (CS425) : Unix Socket Programming (Contd..)Document6 paginiComputer Networks (CS425) : Unix Socket Programming (Contd..)Anish VeettiyankalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Networks (CS425) : ARP, RARP, ICMP ProtocolsDocument7 paginiComputer Networks (CS425) : ARP, RARP, ICMP ProtocolsAnish VeettiyankalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Networks (CS425) : Transport Layer Protocol-Implementation IssuesDocument5 paginiComputer Networks (CS425) : Transport Layer Protocol-Implementation IssuesAnish VeettiyankalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Networks (CS425) : Unix Socket ProgrammingDocument4 paginiComputer Networks (CS425) : Unix Socket ProgrammingAnish VeettiyankalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Networks (CS425) : Transport Layer ProtocolDocument3 paginiComputer Networks (CS425) : Transport Layer ProtocolAnish VeettiyankalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Networks (CS425) : Routing AlgorithmsDocument5 paginiComputer Networks (CS425) : Routing AlgorithmsAnish VeettiyankalÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Are PortfoliosDocument3 paginiWhat Are PortfoliosAnish VeettiyankalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Networks (CS425) : Instructor: Dr. Dheeraj SanghiDocument7 paginiComputer Networks (CS425) : Instructor: Dr. Dheeraj SanghiAnish VeettiyankalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Networks (CS425) : Data EncodingDocument7 paginiComputer Networks (CS425) : Data EncodingAnish VeettiyankalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Networks (CS425) : ISO-OSI 7-Layer Network ArchitectureDocument5 paginiComputer Networks (CS425) : ISO-OSI 7-Layer Network ArchitectureAnish VeettiyankalÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Are PortfoliosDocument3 paginiWhat Are PortfoliosAnish VeettiyankalÎncă nu există evaluări
- VFDBDocument1 paginăVFDBmcdonald212Încă nu există evaluări
- Google Certified Professional Cloud Architect - Part 3: Course FeaturesDocument5 paginiGoogle Certified Professional Cloud Architect - Part 3: Course Featureshuber.mcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Releasenotes 17.02.008 enDocument66 paginiReleasenotes 17.02.008 enamirokhovatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Math Kernel LibraryDocument4 paginiMath Kernel Libraryava939Încă nu există evaluări
- Lora Wan Based Gps Tracking SystemDocument14 paginiLora Wan Based Gps Tracking Systemiot forumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yamaha CS6x Service ManualDocument63 paginiYamaha CS6x Service ManualBao Hoang NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Virtualization and The CloudDocument21 paginiVirtualization and The CloudTrung Kiên NguyễnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alibaba Cloud Products Brochure - enDocument85 paginiAlibaba Cloud Products Brochure - enAnkush AdlakhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MOA For TABLET 2023Document2 paginiMOA For TABLET 2023Phoeza Espinosa VillanuevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Telecom Switching Systems (16TE54)Document75 paginiTelecom Switching Systems (16TE54)Shreya RameshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Automation in Construction: Kai Guo, Limao ZhangDocument22 paginiAutomation in Construction: Kai Guo, Limao ZhangPedro FalkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Audiority EpicPigGuiro ManualDocument8 paginiAudiority EpicPigGuiro ManualJorge VillafañaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anviz VF30Pro Flyer en 08.08.2019Document2 paginiAnviz VF30Pro Flyer en 08.08.2019Hen Drix LevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kerry Brandis Physiology MRXBWDocument3 paginiKerry Brandis Physiology MRXBWTowhidulIslam33% (6)
- MCAlink User's ManualDocument12 paginiMCAlink User's ManualAhmadou Yerima AbbaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Empowerment Technologies: Quarter 1 - Week 2Document14 paginiEmpowerment Technologies: Quarter 1 - Week 2justin simanganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Survey of Cyber Security in SA PDFDocument5 paginiSurvey of Cyber Security in SA PDFAhmad AbdulbasetÎncă nu există evaluări
- Business Intelligence-Final PrintDocument13 paginiBusiness Intelligence-Final PrintsahrÎncă nu există evaluări
- R999000216 09 2015 Automation Media PDFDocument124 paginiR999000216 09 2015 Automation Media PDFJose Manuel Barroso PantojaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MC CDP - Exam GuideDocument5 paginiMC CDP - Exam GuideArunDagarÎncă nu există evaluări
- PX 231 (Series) Operator ManualDocument52 paginiPX 231 (Series) Operator ManualHari Abu Usamah100% (1)
- Robofil 240 SLP 440 SLPDocument11 paginiRobofil 240 SLP 440 SLPJakus JankaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vlsi PT 1st Year SyllabusDocument17 paginiVlsi PT 1st Year SyllabusMANGAL KUMAR MOHAPATRAÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2019 1280 Enterprise 1Document5 pagini2019 1280 Enterprise 1Julio HerreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- PCDRA - Dump - PDF FunalDocument39 paginiPCDRA - Dump - PDF Funalsnowdex88Încă nu există evaluări
- BTS11 User Manual EN00Document143 paginiBTS11 User Manual EN00ชัชวาล เมตตาÎncă nu există evaluări
- NTP 334.009 (2020) Cementos Cementos Portland RequisitosDocument29 paginiNTP 334.009 (2020) Cementos Cementos Portland RequisitosCarmenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Buy Apple Gift Cards - AppleDocument1 paginăBuy Apple Gift Cards - AppleKfmy NannyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Touchstone-2-Workbook-Answers - PDF (PDF - TXT)Document2 paginiTouchstone-2-Workbook-Answers - PDF (PDF - TXT)Karina Marin sosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- KNIME Usage and BenefitsDocument3 paginiKNIME Usage and BenefitsKushal ParekhÎncă nu există evaluări