Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Demographics
Încărcat de
cbellsnlDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Demographics
Încărcat de
cbellsnlDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Sudan
DEMOGRAPHICS MATERNAL AND NEWBORN HEALTH
Total population (000) 37,707 (2006) Under-five mortality rate Causes of under-five deaths Causes of maternal deaths Coverage along the continuum of care
Deaths per 1000 live births Globally more than one third of child deaths are attributable to Regional estimates for Africa, 1997-2002
Total under-five population (000) 5,483 (2006) undernutrition
Causes of neonatal
Unmet need for family planning (%) 26 (1992-1993)
Births (000) 1,225 (2006) Measles Injuries Obstructed labor Contraceptive
150 5% 5% deaths Abortion 7 Pre-pregnancy
Birth registration (%) 64 (2006) Other HIV/AIDS Diarrhoea 1% Antenatal visits for woman (4 or more visits, %) --- Anaemia 4% 4% prevalence rate
120 6% 3% Tetanus 3%
4% Antenatal visit
Under-five mortality rate (per 1000 live births) 89 (2006) 120 Other 5% (1 or more) 60 Pregnancy
Diarrhoea Congenital 8% Intermittent preventive treatment for malaria (%) ---
89 Hypertensive Skilled attendant
Infant mortality rate (per 1000 live births) 61 (2006) 13% Infection 14%
disorders Haemorrhage 87 Birth
90 C-section rate (total, urban, rural; %) 34%
at birth
29 (2000) 9%
Neonatal mortality rate (per 1000 live births) Neonatal Asphyxia 19% (Minimum target is 5% and maximum target is 15%) 20,19,24 (1992-1993)
HIV/AIDS *Postnatal care Neonatal period
Total under-five deaths (000) 109 (2006) 60 40
31%
Sepsis/Infections,
57%
Early initiation of breastfeeding (within 1 hr of birth, %) --- including AIDS Exclusive
16 Infancy
Maternal mortality ratio (per 100,000 live births) 450 (2005) 30 Pneumonia breastfeeding
16%
MDG Target 16% Preterm 50%
Postnatal visit for baby (within 2 days for home births, %) ---
Lifetime risk of maternal death (1 in N) 53 (2005) Measles 73
0 Malaria Other causes
Total maternal deaths 5,300 (2005) 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 2015 21% 30%
Source: Lawn JE, Cousens SN
0 20 40 60 80 100
Source: UNICEF, 2006 Source: WHO, 2006 for CHERG (Nov 2006) Source: Khan, Khalid S., et al, Lancet 2006:367:1066-74 Source: DHS, MICS, Other NS
*See Annex for indicator definition
Antenatal care Skilled attendant at delivery Neonatal tetanus protection
INTERVENTION COVERAGE FOR MOTHERS, NEWBORNS AND CHILDREN Percent women aged 15-49 years attended at least once by a Percent live births attended by skilled health personnel Percent of newborns protected against tetanus
NUTRITION skilled health provider during pregnancy
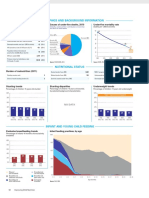
Stunting prevalence (moderate and severe, %) 48 (2000) Complementary feeding rate (6-9 months, %) 47 (2000) 100 100 100
86 87
Wasting prevalence (moderate and severe, %) 18 (2000) Low birthweight incidence (%) 31 (1999) 80 75 80 80
70 72
60
Underweight prevalence Exclusive breastfeeding Vitamin A supplementation 60 60 60
Percent
Percent
Percent
Percent children < 5 years underweight for age* Percent infants < 6 months exclusively breastfed Percent children 6-59 months receiving vitamin A doses
40 40 40
At least one dose Two doses
100 100 100 92 93 90 20 20 20
79 99 90
93
80 80 80 88 70 0 0
1989-1990 1992-1993 2000 1988-1993 2000 1981 1986 1991 1996 2001 2006
60 60 60 DHS Other NS MICS Other NS MICS
Percent
Percent
Percent
Source: WHO/UNICEF
34
38
40 31 40 40
20 17 20 13 16 20
31 WATER AND SANITATION EQUITY
15 0 0
0 0 0
1986 1992 2000 1990 2000 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 Water Sanitation Coverage gap by wealth quintile
Other NS Other NS MICS DHS MICS
Source: UNICEF
Percent population using improved drinking water sources Percent population using improved sanitation facilities
*Based on 2006 WHO reference population Rural Urban Total Rural Urban Total
100 100
CHILD HEALTH 85
78
80 70 80
64 64
Immunization Malaria prevention Prevention of mother to child 60 57 60 53 50
Percent
Percent
Percent of children immunised against measles No data
Percent of children immunised with 3 doses DPT
Percent children < 5 years sleeping under ITNs transmission of HIV 34
Percent HIV+ pregnant women receiving ARVs for PMTCT
40 40 33
Percent of children immunised with 3 doses Hib 26 24
20 20
100 100
0 0
78 1990 2004 1990 2004
80 80
73 Source: WHO/UNICEF JMP, 2006 Source: WHO/UNICEF JMP, 2006
60 60
Percent
Percent
No data
40 40 POLICIES SYSTEMS
20 20
Coverage gap (%) No data
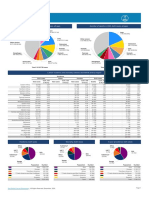
0.4 International Code of Marketing of Breastmilk Financial Flows and Human Resources
0 0 Substitutes Partial Ratio
1990 1995 2000 2005 2006 2000 Per capita total expenditure on health (US$) 54 (2007) poorest/wealthiest
Source: WHO/UNICEF MICS
New ORS formula and zinc for management of Difference
General government expenditure on health as
diarrhoea Yes poorest-wealthiest (%)
% of total government expenditure (%) 7 (2007)
Diarrhoeal disease treatment Malaria treatment Pneumonia treatment
Percent children < 5 years with diarrhoea receiving oral rehydration Percent febrile children < 5 years using antimalarials Percent children < 5 years with suspected pneumonia taken to Community treatment of pneumonia with antibiotics Yes Out-of-pocket expenditure as % of total
therapy or increased fluids, with continued feeding appropriate health provider
Percent children < 5 years with suspected pneumonia receiving expenditure on health (%) 63 (2007)
IMCI adapted to cover newborns 0-1 week of age No
antibiotics
Density of health workers (per 1000 population) 1.1 (2004)
100 100 100 Costed implementation plan(s) for maternal,
newborn and child health available Yes Official Development Assistance to child health
80 80 80 per child (US$) 9 (2005)
Midwives be authorised to administer a core set of
60 60 50 60 57 life saving interventions --- Official Development Assistance to maternal and
Sudan
Percent
Percent
Percent
neonatal health per live birth (US$) 15 (2005)
40 38
40 40 Maternity protection in accordance with ILO
Convention 183 No National availability of Emergency Obstetric Care
20 20 20 services (% of recommended minimum) 35 (2005)
Specific notification of maternal deaths ---
0 0 0
2000
MICS
2000
MICS
2000
MICS
Countdown to 2015
2008 Report
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- An Go LaDocument1 paginăAn Go LacbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- DemographicsDocument1 paginăDemographicscbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- DemographicsDocument1 paginăDemographicscbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- DemographicsDocument1 paginăDemographicscbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- DemographicsDocument1 paginăDemographicscbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- DemographicsDocument1 paginăDemographicscbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- DemographicsDocument1 paginăDemographicscbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- DemographicsDocument1 paginăDemographicscbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- DemographicsDocument1 paginăDemographicscbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guinea BissauDocument1 paginăGuinea BissaucbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- DemographicsDocument1 paginăDemographicscbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- DemographicsDocument1 paginăDemographicscbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- DemographicsDocument1 paginăDemographicscbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- DemographicsDocument1 paginăDemographicscbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- DemographicsDocument1 paginăDemographicscbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- DemographicsDocument1 paginăDemographicscbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- DemographicsDocument1 paginăDemographicscbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- DemographicsDocument1 paginăDemographicscbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- DemographicsDocument1 paginăDemographicscbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ben inDocument1 paginăBen incbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- DemographicsDocument1 paginăDemographicscbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Burkina FasoDocument1 paginăBurkina FasocbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ye MenDocument1 paginăYe MencbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Country Health Profile: Maternal, Newborn & Child Survival in FijiDocument4 paginiCountry Health Profile: Maternal, Newborn & Child Survival in Fijipaperpin27Încă nu există evaluări
- Liberia: Country ProfileDocument4 paginiLiberia: Country Profilegeorgeloto12Încă nu există evaluări
- Reporting On Reproductive Health in Africa (Ayorinde Ajayi)Document35 paginiReporting On Reproductive Health in Africa (Ayorinde Ajayi)National Press FoundationÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maternal CZEDocument4 paginiMaternal CZEYajie LuoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Major causes of death in children under five globally in 2008Document1 paginăMajor causes of death in children under five globally in 2008raissa leeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutrition IDN PDFDocument2 paginiNutrition IDN PDFdini mutia KhairunnisaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutrition LCADocument2 paginiNutrition LCAShernia EliboxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cervix Uteri: Source: Globocan 2020Document2 paginiCervix Uteri: Source: Globocan 2020nour abdallaÎncă nu există evaluări
- On Epidemological Aspects of Maternal and Child HealthDocument30 paginiOn Epidemological Aspects of Maternal and Child HealthBisma Maqbool67% (3)
- 1 The High Risk MotherDocument161 pagini1 The High Risk MotherRaquel M. MendozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- KMC To Reduce Neonatal Mortality Hadi P Unair 29 Sept 2016Document63 paginiKMC To Reduce Neonatal Mortality Hadi P Unair 29 Sept 2016mimimomopipiÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Open Ophthalmology JournalDocument5 paginiThe Open Ophthalmology JournalFenny Duma SariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jamaica Country Profile Highlights Maternal and Child Health StatisticsDocument4 paginiJamaica Country Profile Highlights Maternal and Child Health StatisticsZineil BlackwoodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Essential Newborn Care: From Evidence To Practice: Maria Asuncion Silvestre, MD, FPSNBM, FaapDocument84 paginiEssential Newborn Care: From Evidence To Practice: Maria Asuncion Silvestre, MD, FPSNBM, FaapShane Lim GarciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Child Health Programme: 4.2.2 Causes of Child Mortality in IndiaDocument24 paginiChild Health Programme: 4.2.2 Causes of Child Mortality in IndiaSolomon JosephÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pakistan 2015Document2 paginiPakistan 2015shujahkianiÎncă nu există evaluări
- G Minaccia Parto PretDocument64 paginiG Minaccia Parto PretEleonora Francesco Consalvo DonzelliÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1malnutrition As Health ProblemDocument37 pagini1malnutrition As Health ProblemIntan Sahara BachsinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maternal Mortality in OmanDocument2 paginiMaternal Mortality in OmanmRta03100% (1)
- Globo Can Ecuador 2020Document2 paginiGlobo Can Ecuador 2020Park Triple S Kim HyungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutrition PHL PDFDocument2 paginiNutrition PHL PDFJaiy HingcoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stakeholder Meeting - Revitalizing IudDocument52 paginiStakeholder Meeting - Revitalizing Iudkarun009640Încă nu există evaluări
- 20 Breast Fact SheetDocument2 pagini20 Breast Fact Sheetyuliaindahp18Încă nu există evaluări
- PROBLEM ANALYSIS TREE or Maternal Newborn and Child Mortality in Areas Most Hit by The Anglophone CrisisDocument2 paginiPROBLEM ANALYSIS TREE or Maternal Newborn and Child Mortality in Areas Most Hit by The Anglophone CrisisEpie marcÎncă nu există evaluări
- WOMEN AND CHILD HEALTH GUIDEDocument45 paginiWOMEN AND CHILD HEALTH GUIDEjulianaÎncă nu există evaluări
- nursing research posterDocument1 paginănursing research posterapi-739571998Încă nu există evaluări
- Indicative Target TemplateDocument11 paginiIndicative Target TemplateMulugeta DagneÎncă nu există evaluări
- PRUMan PRULady Leaflet ENGDocument3 paginiPRUMan PRULady Leaflet ENGJessicaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Him & Her: PRU PRUDocument3 paginiHim & Her: PRU PRUshirley lee wenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Codigo RojoDocument32 paginiCodigo RojoradiolafiesteraÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Study of Intrauterine Fetal Death in A Tertiary Care HospitalDocument4 paginiA Study of Intrauterine Fetal Death in A Tertiary Care HospitalintanÎncă nu există evaluări
- MOR Health System Profiles 2018Document2 paginiMOR Health System Profiles 2018Chaymae SahraouiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Infertility Among Productive AgeDocument18 paginiInfertility Among Productive Ageari gunawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Practical Approach To Preventing Child Deaths: What The Pediatrician Can DoDocument44 paginiA Practical Approach To Preventing Child Deaths: What The Pediatrician Can DoSophia Loraine Dorone JesuraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Essential Newborn CareDocument54 paginiEssential Newborn CareBrigitte CovarrubiasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Poster CFRDocument1 paginăPoster CFRIka Rara RositaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DemographicsDocument1 paginăDemographicscbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- DemographicsDocument1 paginăDemographicscbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- DemographicsDocument1 paginăDemographicscbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tanzania, United Republic ofDocument1 paginăTanzania, United Republic ofcbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- DemographicsDocument1 paginăDemographicscbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Burkina FasoDocument1 paginăBurkina FasocbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ye MenDocument1 paginăYe MencbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- DemographicsDocument1 paginăDemographicscbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ye MenDocument1 paginăYe MencbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- DemographicsDocument1 paginăDemographicscbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- The GambiaDocument1 paginăThe GambiacbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ben inDocument1 paginăBen incbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ben inDocument1 paginăBen incbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sierra LeoneDocument1 paginăSierra LeonecbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- DemographicsDocument1 paginăDemographicscbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ben inDocument1 paginăBen incbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- DemographicsDocument1 paginăDemographicscbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- DemographicsDocument1 paginăDemographicscbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ben inDocument1 paginăBen incbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- DemographicsDocument1 paginăDemographicscbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- DemographicsDocument1 paginăDemographicscbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- DemographicsDocument1 paginăDemographicscbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- DemographicsDocument1 paginăDemographicscbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- DemographicsDocument1 paginăDemographicscbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ben inDocument1 paginăBen incbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- DemographicsDocument1 paginăDemographicscbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- DemographicsDocument1 paginăDemographicscbellsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Education Solutions, Edunsol@gmail - Com, 09996522162Document170 paginiEducation Solutions, Edunsol@gmail - Com, 09996522162edphrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solutions For RefugeesDocument24 paginiSolutions For RefugeesjacquelineÎncă nu există evaluări
- 296402-Official ESTA Application Website U.S. Customs and Border Protection PDFDocument5 pagini296402-Official ESTA Application Website U.S. Customs and Border Protection PDFLouise Ann TunstallÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mozart, Beethoven, Yesudas Effect Class 2Document12 paginiMozart, Beethoven, Yesudas Effect Class 2Dr Suvarna NalapatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Challenges and Opportunities in Preventive and Social MedicineDocument3 paginiChallenges and Opportunities in Preventive and Social MedicineIJAR JOURNALÎncă nu există evaluări
- ACIDITY REMEDIESDocument3 paginiACIDITY REMEDIESYasmeen JafferÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calamba Doctors' College: Virborough Subdivision, Parian, Calamba City, LagunaDocument15 paginiCalamba Doctors' College: Virborough Subdivision, Parian, Calamba City, LagunaJasthen Audrey StamboughÎncă nu există evaluări
- Warehouse Center Checklist 2Document5 paginiWarehouse Center Checklist 2Sankar ChinnathambiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Product Name: Clinical Chemistry Alkaline WashDocument11 paginiProduct Name: Clinical Chemistry Alkaline WashАндрей ФедуловÎncă nu există evaluări
- Malang Batu Tour Package Itinerary 2 Days 1 NightDocument3 paginiMalang Batu Tour Package Itinerary 2 Days 1 NightSepta SuryadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Veterans Handbook 2020Document69 paginiVeterans Handbook 2020Senator Cory BookerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acy 087Document14 paginiAcy 087johnsmithdosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pq-Unocal Csms '03Document15 paginiPq-Unocal Csms '03Ismail Hamzah Azmatkhan Al-husainiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Commissioning Federal Facilities Chiller (PQ)Document19 paginiCommissioning Federal Facilities Chiller (PQ)Yu-Chih PuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercise Chart: Warm UpDocument1 paginăExercise Chart: Warm UpJeremy van der MerweÎncă nu există evaluări
- Single/ Exam Zone Centre DetailsDocument5 paginiSingle/ Exam Zone Centre DetailsHarsh AroraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Diverticulitis-GcpDocument85 paginiAcute Diverticulitis-Gcpkuro hanabusaÎncă nu există evaluări
- STERILE PARENTERAL FORMULATIONSDocument85 paginiSTERILE PARENTERAL FORMULATIONSShalimashalu100% (1)
- Two Chinese Food Therapies To Prevent UTIDocument2 paginiTwo Chinese Food Therapies To Prevent UTIvivianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sport Science and Sports Medicine Framework 2017 v1Document31 paginiSport Science and Sports Medicine Framework 2017 v1api-443327549Încă nu există evaluări
- Basic IV Therapy CalculationsDocument35 paginiBasic IV Therapy CalculationsRommel IsraelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydrogen Sulphide Safety Around RigDocument14 paginiHydrogen Sulphide Safety Around RigmohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guideline Mood Australia New Zeland PDFDocument120 paginiGuideline Mood Australia New Zeland PDFFábio C NetoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Annual Report 2013-14Document198 paginiAnnual Report 2013-14shahabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Labor and Delivery QuizDocument7 paginiLabor and Delivery QuizAmy50% (2)
- Fundamentals of EU Regulatory Affairs, Fifth Edition Comparative MatrixDocument42 paginiFundamentals of EU Regulatory Affairs, Fifth Edition Comparative Matrixasifmdzakaria57% (7)
- General Duties and Responsibilities of An Electrical Engineer in Construction IndustryDocument2 paginiGeneral Duties and Responsibilities of An Electrical Engineer in Construction Industryumer100% (1)
- CHN Assignment (Community Health Nursing)Document21 paginiCHN Assignment (Community Health Nursing)binjuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mdbsis09 CA A III 2017Document4 paginiMdbsis09 CA A III 2017Guneyden GuneydenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Breast Feeding Final ProposalDocument16 paginiBreast Feeding Final ProposalDeborah BoahemaaÎncă nu există evaluări