Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Physics I Problems PDF
Încărcat de
BOSS BOSS0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
662 vizualizări1 paginăA horseshoe's center of gravity is along the line behind the string. A water skier moving with constant velocity must lean backward. The mighty Zimbo claims to have leg muscles so strong he can stand flat on his feet. What determines how far back she must lean? Draw a free-body diagram for the water skier.
Descriere originală:
Titlu original
Physics I Problems (113).pdf
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentA horseshoe's center of gravity is along the line behind the string. A water skier moving with constant velocity must lean backward. The mighty Zimbo claims to have leg muscles so strong he can stand flat on his feet. What determines how far back she must lean? Draw a free-body diagram for the water skier.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
662 vizualizări1 paginăPhysics I Problems PDF
Încărcat de
BOSS BOSSA horseshoe's center of gravity is along the line behind the string. A water skier moving with constant velocity must lean backward. The mighty Zimbo claims to have leg muscles so strong he can stand flat on his feet. What determines how far back she must lean? Draw a free-body diagram for the water skier.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 1
361
Exercises
the horseshoes center of gravity is along the line behind the
string? How can you locate the center of gravity by repeating the
process at another nail hole? Will the center of gravity be within
the solid material of the horseshoe?
Q11.9 An object consists of a ball of weight W glued to the end of
a uniform bar also of weight W. If you release it from rest, with the
bar horizontal, what will its behavior be as it falls if air resistance
is negligible? Will it (a) remain horizontal; (b) rotate about its center of gravity; (c) rotate about the ball; or (d) rotate so that the ball
swings downward? Explain your reasoning.
Q11.10 Suppose that the object in Question 11.9 is released from
rest with the bar tilted at 60 above the horizontal with the ball at
the upper end. As it is falling, will it (a) rotate about its center of
gravity until it is horizontal; (b) rotate about its center of gravity
until it is vertical with the ball at the bottom; (c) rotate about the
ball until it is vertical with the ball at the bottom; or (d) remain at
60 above the horizontal?
Q11.11 Why must a water skier moving with constant velocity lean
backward? What determines how far back she must lean? Draw a
free-body diagram for the water skier to justify your answers.
Q11.12 In pioneer days, when a Conestoga wagon was stuck in the
mud, people would grasp the wheel spokes and try to turn the
wheels, rather than simply pushing the wagon. Why?
Q11.13 The mighty Zimbo claims to have leg muscles so strong
that he can stand at on his feet and lean forward to pick up an
apple on the oor with his teeth. Should you pay to see him perform, or do you have any suspicions about his claim? Why?
Q11.14 Why is it easier to hold a 10-kg dumbbell in your hand
at your side than it is to hold it with your arm extended
horizontally?
Q11.15 Certain features of a person, such as height and mass, are
xed (at least over relatively long periods of time). Are the following features also xed? (a) location of the center of gravity of the
body; (b) moment of inertia of the body about an axis through the
persons center of mass. Explain your reasoning.
Q11.16 During pregnancy, women often develop back pains from
leaning backward while walking. Why do they have to walk this
way?
Q11.17 Why is a tapered water glass with a narrow base easier to
tip over than a glass with straight sides? Does it matter whether the
glass is full or empty?
Q11.18 When a tall, heavy refrigerator is pushed across a rough
oor, what factors determine whether it slides or tips?
Q11.19 If a metal wire has its length doubled and its diameter
tripled, by what factor does its Youngs modulus change?
Q11.20 Why is concrete with steel reinforcing rods embedded in it
stronger than plain concrete?
Q11.21 A metal wire of diameter D stretches by 0.100 mm when
supporting a weight W. If the same-length wire is used to support a
weight three times as heavy, what would its diameter have to be (in
terms of D) so it still stretches only 0.100 mm?
Q11.22 Compare the mechanical properties of a steel cable, made
by twisting many thin wires together, with the properties of a
solid steel rod of the same diameter. What advantages does each
have?
Q11.23 The material in human bones and elephant bones is essentially the same, but an elephant has much thicker legs. Explain
why, in terms of breaking stress.
Q11.24 There is a small but appreciable amount of elastic hysteresis in the large tendon at the back of a horses leg. Explain how this
can cause damage to the tendon if a horse runs too hard for too
long a time.
Q11.25 When rubber mounting blocks are used to absorb machine
vibrations through elastic hysteresis, as mentioned in Section 11.5,
what becomes of the energy associated with the vibrations?
EXERCISES
Section 11.2 Center of Gravity
11.1 .. A 0.120-kg, 50.0-cm-long uniform bar has a small 0.055-kg
mass glued to its left end and a small 0.110-kg mass glued to the
other end. The two small masses can each be treated as point
masses. You want to balance this system horizontally on a fulcrum
placed just under its center of gravity. How far from the left end
should the fulcrum be placed?
11.2 .. The center of gravity Figure E11.2
of a 5.00-kg irregular object is
Center of
shown in Fig. E11.2. You need
gravity
to move the center of gravity
2.20 cm to the left by gluing on
x
a 1.50-kg mass, which will
then be considered as part of
the object. Where should the
center of gravity of this additional mass be located?
11.3 . A uniform rod is 2.00 m long and has mass 1.80 kg. A
2.40-kg clamp is attached to the rod. How far should the center of
gravity of the clamp be from the left-hand end of the rod in order
for the center of gravity of the composite object to be 1.20 m from
the left-hand end of the rod?
Section 11.3 Solving Rigid-Body Equilibrium Problems
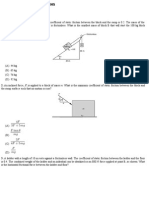
11.4 . A uniform 300-N trapdoor in a oor is hinged at one side.
Find the net upward force needed to begin to open it and the total
force exerted on the door by the hinges (a) if the upward force is
applied at the center and (b) if the upward force is applied at the
center of the edge opposite the hinges.
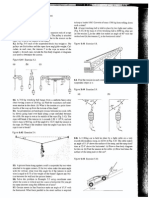
11.5 .. Raising a Ladder. A ladder carried by a re truck is
20.0 m long. The ladder weighs 2800 N and its center of gravity is
at its center. The ladder is pivoted at one end (A) about a pin
(Fig. E11.5); you can ignore the friction torque at the pin. The ladder is raised into position by a force appliedS by a hydraulic piston
at C. Point C is 8.0 m from A, and the force F exerted by the piston
S
makes an angle of 40 with the ladder. What magnitude must F
have to just lift the ladder off the support bracket at B? Start with a
free-body diagram of the ladder.
Figure E11.5
S
F
12.0 m
8.0 m
40
11.6 .. Two people are carrying a uniform wooden board that is
3.00 m long and weighs 160 N. If one person applies an upward
force equal to 60 N at one end, at what point does the other person
lift? Begin with a free-body diagram of the board.
11.7 .. Two people carry a heavy electric motor by placing it on a
light board 2.00 m long. One person lifts at one end with a force of
400 N, and the other lifts the opposite end with a force of 600 N.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- DYNA6 Manual With ExamplesDocument227 paginiDYNA6 Manual With ExamplesDeepmalaJayesh100% (1)
- GP1 S 14 Chap 5 ProblemsDocument14 paginiGP1 S 14 Chap 5 ProblemsUmbina Gescery100% (1)
- College Physics A Strategic Approach 3rd Edition Knight Test BankDocument23 paginiCollege Physics A Strategic Approach 3rd Edition Knight Test Bankpaullanb7nch100% (32)
- 507 Mechanical Movements: Mechanisms and DevicesDe la Everand507 Mechanical Movements: Mechanisms and DevicesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (28)
- 1 2 3 A CentergravityDocument3 pagini1 2 3 A Centergravityapi-325609547100% (1)
- SolidWize CSWA Practice ExamDocument24 paginiSolidWize CSWA Practice ExamAntonio Jambrešić100% (4)
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 paginăPhysics I Problems PDFBOSS BOSSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rec ch10Document5 paginiRec ch10tivakholisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 paginăPhysics I Problems PDFBOSS BOSSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Particle Dynamics (QB)Document28 paginiParticle Dynamics (QB)Raju SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 paginăPhysics I Problems PDFBOSS BOSSÎncă nu există evaluări
- AJC TutorialDocument4 paginiAJC TutorialYong Ming HengÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 paginăPhysics I Problems PDFBOSS BOSSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conceptest Clicker Questions: Physics, 4 EditionDocument29 paginiConceptest Clicker Questions: Physics, 4 EditionstephensreenivasulutÎncă nu există evaluări
- Worksheet 09Document2 paginiWorksheet 09Sabine MohamadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 Newton - S Laws of Motion - Problem SetsDocument5 paginiChapter 3 Newton - S Laws of Motion - Problem SetsSimon ManansalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics I ProblemsDocument1 paginăPhysics I ProblemsbosschellenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 paginăPhysics I Problems PDFBOSS BOSSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Extra Problem Phys 1 CH 2Document2 paginiExtra Problem Phys 1 CH 2Quỳnh NguyễnÎncă nu există evaluări
- FINAL EXAMINATION in Dynamics of Rigid BodiesDocument1 paginăFINAL EXAMINATION in Dynamics of Rigid BodiesRochelle TugadeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 paginăPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics MechanicsDocument44 paginiPhysics MechanicsAnkit SwainÎncă nu există evaluări
- PHYA10 - Physics I (Physical Sciences) Practical Worksheet #04Document2 paginiPHYA10 - Physics I (Physical Sciences) Practical Worksheet #04Sabine MohamadÎncă nu există evaluări
- PH600 CH 11 Problems PDFDocument2 paginiPH600 CH 11 Problems PDFMike GaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Exercise For Grade 11Document2 paginiPhysics Exercise For Grade 11Daniel GtsadkanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample Problems Newton's Laws and Applications PDFDocument3 paginiSample Problems Newton's Laws and Applications PDFrussell valino100% (1)
- Sample Problems Newton's Laws and Applications PDFDocument3 paginiSample Problems Newton's Laws and Applications PDFrussell valinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- MHS Physics Problems Chapter 9Document31 paginiMHS Physics Problems Chapter 9Klaus Danjolli100% (1)
- Problems Vibrations and Waves - Physics - 7 - Ed Serway-2 PDFDocument7 paginiProblems Vibrations and Waves - Physics - 7 - Ed Serway-2 PDFNathalia AcevedoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 paginăPhysics I Problems PDFBOSS BOSSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 paginăPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Physics I-5-1Document12 paginiGeneral Physics I-5-1tawhidalahi12345Încă nu există evaluări
- Conceptual Questions: Newton'S First LawDocument4 paginiConceptual Questions: Newton'S First Lawapi-368883407Încă nu există evaluări
- Physics I ProblemsDocument1 paginăPhysics I ProblemsbosschellenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Icse X Force Question BankDocument7 paginiIcse X Force Question BankgpfphysicsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 10Document11 paginiChapter 10kiaunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hapter: Conceptual ProblemsDocument22 paginiHapter: Conceptual ProblemsAbdullah ArabiyatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 ReviewDocument3 paginiChapter 2 ReviewFlora DongÎncă nu există evaluări
- PH600 CH 10 Problems PDFDocument5 paginiPH600 CH 10 Problems PDFMike GaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sheet Two Chapter Three The Laws of MotionDocument24 paginiSheet Two Chapter Three The Laws of MotionTony AtefÎncă nu există evaluări
- FE Statics PDFDocument6 paginiFE Statics PDFMiguel Analuisa0% (1)
- 0304 Special Topics in ForcesDocument5 pagini0304 Special Topics in ForcesimfizicsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class - 9 Concise Physics Solutions Chapter-Laws of Motion Exercise 3 (A) 1Document17 paginiClass - 9 Concise Physics Solutions Chapter-Laws of Motion Exercise 3 (A) 1Sudipt SenguptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 paginăPhysics I Problems PDFBOSS BOSSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit-Two INSTRUCTION - Work Out The Following ProblemsDocument3 paginiUnit-Two INSTRUCTION - Work Out The Following ProblemsKhalid A.Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit-Two INSTRUCTION - Work Out The Following ProblemsDocument3 paginiUnit-Two INSTRUCTION - Work Out The Following ProblemsKhalid A.Încă nu există evaluări
- Ch12 ISMDocument74 paginiCh12 ISMAlberto RamirezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Laws of Motion 3 (B)Document4 paginiLaws of Motion 3 (B)Samrudh MysoreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uniform Circular Motion Self Test 2Document7 paginiUniform Circular Motion Self Test 2pauljkt1Încă nu există evaluări
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 paginăPhysics I Problems PDFBOSS BOSSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aben - Ex No.3Document11 paginiAben - Ex No.3Regina Grace OficiarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch.5lawsofmotionDocument4 paginiCh.5lawsofmotionsamahadadilkhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ebook College Physics A Strategic Approach Technology Update 3Rd Edition Knight Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument39 paginiEbook College Physics A Strategic Approach Technology Update 3Rd Edition Knight Test Bank Full Chapter PDFStevenMillersqpe100% (11)
- FE StaticsDocument6 paginiFE StaticsJaime CorralesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circular Motion and Energy Review QuestionsDocument6 paginiCircular Motion and Energy Review QuestionsUnzal FatehullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analysis of Vertical Vessels Supported On Legs By: Ray DelaforceDocument6 paginiAnalysis of Vertical Vessels Supported On Legs By: Ray Delaforcesonali panditÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics 1 Sample Multiple Choice ProblemsDocument4 paginiPhysics 1 Sample Multiple Choice ProblemsXinhua WangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Untitled Note - Oct 16, 2023 9.52 PMDocument8 paginiUntitled Note - Oct 16, 2023 9.52 PMyenworkssÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 paginăPhysics I Problems PDFBOSS BOSSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ebook College Physics A Strategic Approach 3Rd Edition Knight Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument44 paginiEbook College Physics A Strategic Approach 3Rd Edition Knight Test Bank Full Chapter PDFkennethalandlj1f100% (13)
- Newton's Laws ExamplesDocument5 paginiNewton's Laws Exampleshola0987Încă nu există evaluări
- CBSE Class 1 English WorksheetsDocument1 paginăCBSE Class 1 English WorksheetsBOSS BOSSÎncă nu există evaluări
- CBSE Class 1 English WorksheetDocument1 paginăCBSE Class 1 English WorksheetBOSS BOSSÎncă nu există evaluări
- CBSE Class 1 English WorksheetDocument2 paginiCBSE Class 1 English WorksheetBOSS BOSSÎncă nu există evaluări
- CBSE Class 1 English WorksheetDocument1 paginăCBSE Class 1 English WorksheetBOSS BOSSÎncă nu există evaluări
- CBSE Class 1 English WorksheetDocument1 paginăCBSE Class 1 English WorksheetBOSS BOSSÎncă nu există evaluări
- CBSE Class 1 English WorksheetDocument1 paginăCBSE Class 1 English WorksheetBOSS BOSSÎncă nu există evaluări
- CBSE Class 1 English WorksheetsDocument1 paginăCBSE Class 1 English WorksheetsBOSS BOSSÎncă nu există evaluări
- CBSE Class 1 English WorksheetDocument1 paginăCBSE Class 1 English WorksheetBOSS BOSSÎncă nu există evaluări
- CBSE Class 1 English Worksheets (17) - After A BathDocument1 paginăCBSE Class 1 English Worksheets (17) - After A BathBOSS BOSSÎncă nu există evaluări
- CBSE Class 1 English Worksheets (16) - A Happy ChildDocument1 paginăCBSE Class 1 English Worksheets (16) - A Happy ChildBOSS BOSSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Albert EinsteinDocument2 paginiAlbert EinsteinBOSS BOSSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Additional One Marks Question Paper 1Document1 paginăAdditional One Marks Question Paper 1BOSS BOSSÎncă nu există evaluări
- CBSE Class 1 English Worksheets (19) - Bubble, Straw and ShoeDocument2 paginiCBSE Class 1 English Worksheets (19) - Bubble, Straw and ShoeBOSS BOSSÎncă nu există evaluări
- TN HSC Physics Bookback One MarksDocument1 paginăTN HSC Physics Bookback One MarksBOSS BOSSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design, Analysis of A Multipurpose Survelliance DroneDocument7 paginiDesign, Analysis of A Multipurpose Survelliance DroneManjunath HegdeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4 Static Equilibrium: 4.1 The Important StuffDocument13 paginiChapter 4 Static Equilibrium: 4.1 The Important StuffNoppadol EGATÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 16 Appendix Moment of Inertia of A Spherical ShellDocument6 paginiChapter 16 Appendix Moment of Inertia of A Spherical ShellParmenÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 PDFDocument6 pagini1 PDFMohamed MansourÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 - 9th - E-Techno - PHYSICS - Term-1 - MCS - 2019-20 (AP) - 17-29Document13 pagini2 - 9th - E-Techno - PHYSICS - Term-1 - MCS - 2019-20 (AP) - 17-29lakkysep16Încă nu există evaluări
- System of Particles and Rotational Motion by Rakshita SinghDocument9 paginiSystem of Particles and Rotational Motion by Rakshita SinghRjÎncă nu există evaluări
- PHYS 1120 Centre of Mass & Static Equilibrium SolutionsDocument25 paginiPHYS 1120 Centre of Mass & Static Equilibrium Solutionsbonaabdisa9cÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sae J2292-2016Document13 paginiSae J2292-2016Andris ZaharovÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aerodynamic Center Vs Center of Pressure - Aero CornerDocument5 paginiAerodynamic Center Vs Center of Pressure - Aero CornerDarren-Edward O'NeillÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lois Newton Exercice SDocument6 paginiLois Newton Exercice Ssofyan mziziÎncă nu există evaluări
- Che 2251Document104 paginiChe 2251Alexis Viray100% (1)
- Understanding Center of Mass in Kettlebell TrainingDocument8 paginiUnderstanding Center of Mass in Kettlebell Trainingcamilamorais91Încă nu există evaluări
- 6.6 Moments and Centers of MassDocument8 pagini6.6 Moments and Centers of MassHamed MemarianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ge 6253Document23 paginiGe 6253athishankaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Calculate Center of Gravity: Identify The WeightDocument4 paginiHow To Calculate Center of Gravity: Identify The Weightindrajit sodhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pybullet Quickstart GuideDocument34 paginiPybullet Quickstart GuideJaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dynamics Solns Ch05Document191 paginiDynamics Solns Ch05jbeaubrun93100% (2)
- Airship SimulatorDocument17 paginiAirship SimulatorBrad Rodriguez100% (1)
- CoupleDocument5 paginiCoupleMAHVISH SADAFÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mellman - The Transverse Motion of Solids in Rotating Cylinders-Forms of Motion and Transitions BehaviorDocument20 paginiMellman - The Transverse Motion of Solids in Rotating Cylinders-Forms of Motion and Transitions BehaviorBrenno FerreiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6 Degree of Freedom Splash Pattern Generation ToolDocument57 pagini6 Degree of Freedom Splash Pattern Generation ToolatommotaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Volvo FH 400 4x2 Tractor - Rear Air SuspensionDocument3 paginiVolvo FH 400 4x2 Tractor - Rear Air SuspensionChiheb BEN ABDALLAHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Car Body Design Project ReportDocument43 paginiCar Body Design Project ReportMassimiliano Pezzo0% (1)
- Dynamic and Static Balancing of Rolls - How, Why and WhenDocument2 paginiDynamic and Static Balancing of Rolls - How, Why and WhenAbolfazl KhakiÎncă nu există evaluări
- QUS 103 - Basic Engineering Science (Practicals)Document31 paginiQUS 103 - Basic Engineering Science (Practicals)VietHungCaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Is.12735.1994 0 PDFDocument17 paginiIs.12735.1994 0 PDFshahnawaz ahmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 7 Statics CheckedDocument8 paginiChapter 7 Statics CheckedWan WenÎncă nu există evaluări