Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Lab 3 Proportionality & Superposition: in Out
Încărcat de
Frances NoviDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Lab 3 Proportionality & Superposition: in Out
Încărcat de
Frances NoviDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Francesca Novelli
ENGR 2405
10/07/14
Lab 3 Proportionality & Superposition
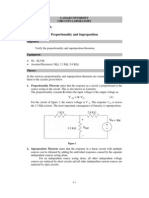
Objective: For students to verify the proportionality and superposition theorems
Background: The Proportionality Theorem (a.k.a Linearity) says that the response in a circuit is
proportional to the source acting in the circuit. The following equation, Vout = K Vin , describes
the relationship between the proportionality constant K and the input and output voltages.
In Figure 1, Vin = 10V is the voltage source and Vout is the 5.1 k resistor.
The Superposition Theorem states that the response in a linear circuit with many sources can be
found by adding the individual responses caused by the separate independent sources acting
alone. When an independent sources acts alone, all of the other voltage sources are replaced by
short circuits and all other independent current sources are replaced by open circuits.
Materials & Equipment:
Assorted Resistors (1 k, 2 k, 5.1 k)
Breadboard
Variable Power Supply
Digital Multi Meter
Assorted jumpers, cables and wires
Paper & Pencil
Procedure:
Part 1: Proportionality Theorem
Measure Vout for the 4 input voltages
Calculate K in each case.
Plot a Graph with Vin on x-axis & Vout on the y-axis using Excel
Francesca Novelli
ENGR 2405
10/07/14
Part 2: Superposition Theorem
Measure and record the voltage across the 5.1 k resistor
Construct Figure 3. Measure and record the voltage across the 5.1 k resistor.
Fill out Table 2 and verify Vout in the 3rd circuit equals to the sum of Vout in the 1st
and 2nd circuits.
Calculations & Results:
Task 1: Measure Vout & Calculate K
Vout (V)
0.589
1.177
2.354
2.943
Vin (V)
2
4
8
10
Vout = K Vin
K = (0.589)/(2)
K = 0.2945
K
0.2945
0.29425
0.29425
0.2943
K = Vout
Vin
K = (1.177)/(4)
K = (2.354)/(8)
K = (2.943)/(10)
K = 0.29425
K= 0.29425
K = 0.2943
Proportionality Constant K
3.5
3
2.5
2
Proportionality
Constant K
1.5
1
0.5
0
2
10
Francesca Novelli
ENGR 2405
10/07/14
Task 2: Measure Vout for each of the three circuits
Power Source
Vout (V)
With only 10 V source
2.95
With only 5 V Source
2.95
With both 5V and 10V sources
5.9
Caluclated K value: K = 2.95V / 10V = 0.295
Discussion Questions & Answers:
Q1: Is the graph obtained in a straight line? A: No, but it is very close to a straight line.
The slope of the graph is about 0.294 if you round. The calculated value of K is 0.295.
The slight difference of 0.001 in K values could have occurred due to a defect in the
resistors, circuit or imprecise measurement. The graph would have had a straight line if I
rounded the values to 0.294 instead of keeping the exact value.
Q2: For each of the 3 circuits you built for the superposition experiment, how well did
the calculated and measured outputs compare? Explain any differences.
A: The 10 Vin has a calculated V out value of 2.943 using proportionality and a value of
2.95 using superposition. The difference is by 0.007 and this error could have occurred
due to change in temperature, defect in resistors or inaccurate measurements made by
me or the multi meter.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Self-Coached Climber - The Guide To Movem - Dan M (1) HagueDocument376 paginiSelf-Coached Climber - The Guide To Movem - Dan M (1) HagueBill Frisch100% (1)
- EE4001 Assigment 2Document4 paginiEE4001 Assigment 2Octav EnachiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Engineering Principles for Technicians: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering DivisionDe la EverandElectrical Engineering Principles for Technicians: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering DivisionEvaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (4)
- Matrix Structural Analysis of BeamsDocument28 paginiMatrix Structural Analysis of BeamsKristine May Maturan0% (1)
- Module 2Document46 paginiModule 2Marc Aljhon Cruzata BhoteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Overhead Line Insulators: Example 4.1Document11 paginiOverhead Line Insulators: Example 4.1e TalalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Overhead Line and Substation InsulationDocument11 paginiOverhead Line and Substation InsulationAnkat Rao RaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 11 - Tests On TransformersDocument27 paginiLesson 11 - Tests On TransformersKaelel Bilang100% (1)
- Verify Proportionality and Superposition Theorems in Circuits LabDocument5 paginiVerify Proportionality and Superposition Theorems in Circuits LabShruti VazeÎncă nu există evaluări
- EEE 202 Lab Experiment SheetDocument3 paginiEEE 202 Lab Experiment SheetAlamgir Kabir ShuvoÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECV211Document103 paginiECV211Daniel KariukiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECD Lab 7 BobDocument15 paginiECD Lab 7 Bobfolkbunny1Încă nu există evaluări
- Physics 2 Revision BookletDocument19 paginiPhysics 2 Revision BookletkhadhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- PhysicsDocument3 paginiPhysicspaguio.iieecscÎncă nu există evaluări
- Superposition and Equivalent Circuit ExperimentDocument6 paginiSuperposition and Equivalent Circuit ExperimentSarem AlemuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electric Circuit Fundamentals: Essential QuestionDocument15 paginiElectric Circuit Fundamentals: Essential QuestionMOBILEE CANCERERÎncă nu există evaluări
- Determination of Plancks Constant From P PDFDocument10 paginiDetermination of Plancks Constant From P PDFFelipe CeregattiÎncă nu există evaluări
- E-Portfolio On Elec and MagnetismDocument20 paginiE-Portfolio On Elec and MagnetismJanine CammagayÎncă nu există evaluări
- BE Lab ReportDocument63 paginiBE Lab ReportArenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electronics Study Material For MSCDocument23 paginiElectronics Study Material For MSCiswaleha100% (1)
- Measuenent of Inductance and Mutual Inductance PDFDocument9 paginiMeasuenent of Inductance and Mutual Inductance PDFAnonymous icxmJmRP6EÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electricity GuideDocument62 paginiElectricity GuideJatin PathakÎncă nu există evaluări
- 12 Physics Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Current Test 01 Answer 7y9dDocument2 pagini12 Physics Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Current Test 01 Answer 7y9dPratik MohlaÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE 369 Power Systems Analysis Transformers Per UnitDocument31 paginiEE 369 Power Systems Analysis Transformers Per UnitSahib Ur RehmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Half Wave RectifierDocument5 paginiHalf Wave RectifierSeski TomabiaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Verifying KVL and KCL Circuit Laws (39Document8 paginiVerifying KVL and KCL Circuit Laws (39TOP 5 GHOSTÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 08 - Superposition TheoremDocument3 paginiLab 08 - Superposition TheoremAamir KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bjte2023 WK02Document36 paginiBjte2023 WK02Hafiz khalidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Me 005Document25 paginiMe 005Pratheesh S KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- ELE 110 Introduction To Electrical Engineering: SemiconductorsDocument19 paginiELE 110 Introduction To Electrical Engineering: SemiconductorspurseyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Units of ElectricityDocument36 paginiUnits of ElectricityMSM7865Încă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Unit Base Units in S. IDocument19 paginiElectrical Unit Base Units in S. IEllen Kay CacatianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electronics II Lab ManualDocument28 paginiElectronics II Lab ManualArafat HossainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 5Document4 paginiExperiment 5Jay LopezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ohm's LawDocument32 paginiOhm's LawPortia A. EgkenÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECE 207: Lab Report #2 Title:: Kirchhoff's Voltage and Current Laws (KVL and KCL) (DC)Document8 paginiECE 207: Lab Report #2 Title:: Kirchhoff's Voltage and Current Laws (KVL and KCL) (DC)Sajid HussainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Measurement BDocument10 paginiElectrical Measurement BAhmed Yousef SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 3 - Metric PrefixesDocument14 paginiLesson 3 - Metric PrefixesMhelier FranciscoÎncă nu există evaluări
- WWW Learncbse in Lakhmir Singh Physics Class 10 Solutions Chapter 1 ElectricityDocument83 paginiWWW Learncbse in Lakhmir Singh Physics Class 10 Solutions Chapter 1 ElectricityakritiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics MarathonDocument130 paginiPhysics MarathonSantosh TiwariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Answers ofAQP PhysicsDocument17 paginiAnswers ofAQP PhysicsApSWgxmwÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fundamentals of Electric Circuits (EE1CPEDocument106 paginiFundamentals of Electric Circuits (EE1CPEDark AngelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1: DC Circuits: Summary and Learning OutcomesDocument12 paginiUnit 1: DC Circuits: Summary and Learning OutcomesKevin CheeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Cl10 Assign16Document2 paginiPhysics Cl10 Assign16Tapas Banerjee100% (1)
- DC Lab Exp 1 (Familiarizing With The Basic DC Circuit Terms & Concepts. Introduction To Laboratory Equipment.) - ACSDocument8 paginiDC Lab Exp 1 (Familiarizing With The Basic DC Circuit Terms & Concepts. Introduction To Laboratory Equipment.) - ACSSujoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- LIU Fall (23-24) Template ReportDocument15 paginiLIU Fall (23-24) Template Report32230951Încă nu există evaluări
- EENG223 Final SolutionsDocument6 paginiEENG223 Final Solutionsercan952Încă nu există evaluări
- A. Basic ConceptsDocument40 paginiA. Basic ConceptsBarkley VelezÎncă nu există evaluări
- C - Electrical FormulaeDocument1 paginăC - Electrical FormulaeHishamMaeenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 09Document6 paginiExperiment 09Deepan AdakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ideal Diode Circuits AnalysisDocument15 paginiIdeal Diode Circuits AnalysisAravind KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE101 - Quiz #1Document16 paginiEE101 - Quiz #1Rick AlvientoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electric Potential and CurrentDocument62 paginiElectric Potential and CurrentGursharan SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wien Bridge.Document11 paginiWien Bridge.Enock OmariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lakhmir Singh Solutions Class 10 Physics Chapter 1 PDFDocument92 paginiLakhmir Singh Solutions Class 10 Physics Chapter 1 PDFchandranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lebanese International University School of EngineeringDocument12 paginiLebanese International University School of EngineeringHassan RashedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Electrical Lab ReportDocument8 paginiBasic Electrical Lab Reportleon saifullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsDe la EverandModern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (4)
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1De la EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1Încă nu există evaluări
- Differential Forms on Electromagnetic NetworksDe la EverandDifferential Forms on Electromagnetic NetworksEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- Multi-Band Booster With HRLB - In-Band Routed DCN Solution GuideDocument26 paginiMulti-Band Booster With HRLB - In-Band Routed DCN Solution GuideAchintha AluthmanageÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computational Intelligence in Communications and Business AnalyticsDocument369 paginiComputational Intelligence in Communications and Business AnalyticsSourasish NathÎncă nu există evaluări
- Open Hole Logs Introduction GR SP CALDocument21 paginiOpen Hole Logs Introduction GR SP CALmagedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cics Class 05Document18 paginiCics Class 05HarithaÎncă nu există evaluări
- IJETR032052Document6 paginiIJETR032052erpublicationÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCB and ELCB PDFDocument35 paginiMCB and ELCB PDFChris AntoniouÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3-Lecture 03 Translational Mechanical System3-SDocument23 pagini3-Lecture 03 Translational Mechanical System3-SHamza KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Weld CheckDocument6 paginiWeld CheckArnold c ElverÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dental Material Final ReportDocument7 paginiDental Material Final ReportAbdullah Muhammed khaleel HassanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ice o Matic - Cim0436faDocument2 paginiIce o Matic - Cim0436faJean RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unified Modeling Language Class Diagram ..Uml)Document20 paginiUnified Modeling Language Class Diagram ..Uml)Yasmeen AltuwatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 12.6 Perform An Activity - Measuring The Critical Angle For Various MediaDocument2 pagini12.6 Perform An Activity - Measuring The Critical Angle For Various MediaRajeshri SoniÎncă nu există evaluări
- 384 TungaloyDocument32 pagini384 Tungaloyp.designÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mammography View ChapterDocument60 paginiMammography View ChapterSehar GulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Malpresentation and MalpositionDocument33 paginiMalpresentation and MalpositionPeprah Ondiba100% (1)
- Class 9 Sample Paper 2020-21Document3 paginiClass 9 Sample Paper 2020-21sasta jiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Saravel Air Hanling UnitDocument92 paginiSaravel Air Hanling UnitClaire ApapÎncă nu există evaluări
- LAB REPORT-Rock Pore Volume and Porosity Measurement by Vacuum Saturation-GROUP - 5-PETE-2202Document13 paginiLAB REPORT-Rock Pore Volume and Porosity Measurement by Vacuum Saturation-GROUP - 5-PETE-2202Jeremy MacalaladÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mste 3.0 Plane Geometry Hand OutsDocument8 paginiMste 3.0 Plane Geometry Hand OutsJasmine MartinezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermocouple Wire Reference Guide: WWW - Omega.co - Uk +44 (0) 161 777 6611 WWW - Omega.co - Uk +44 (0) 161 777 6611Document1 paginăThermocouple Wire Reference Guide: WWW - Omega.co - Uk +44 (0) 161 777 6611 WWW - Omega.co - Uk +44 (0) 161 777 6611Mohamed MaltiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 13: The Electronic Spectra of ComplexesDocument42 paginiChapter 13: The Electronic Spectra of ComplexesAmalia AnggreiniÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPCU3C14Document20 paginiSPCU3C14ming tsaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- QR Code Attendance Monitoring SystemDocument6 paginiQR Code Attendance Monitoring Systemjenny adlaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 01238-00-AD TY96 Installation ManualDocument42 pagini01238-00-AD TY96 Installation ManualJohan SwanepoelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alkali MetalsDocument12 paginiAlkali MetalsSaki Sultana LizaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Preparation of Gases in LaboratoryDocument7 paginiPreparation of Gases in LaboratoryChu Wai Seng50% (2)
- CFG Grammar: Context Free Grammar BasicsDocument34 paginiCFG Grammar: Context Free Grammar BasicsEd MolloÎncă nu există evaluări
- (It Bus) Computer HistoryDocument6 pagini(It Bus) Computer HistoryRica Elaine LubasanÎncă nu există evaluări