Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Third Year Question Bank POWER ELECTRONICS
Încărcat de
venkatesh_paboluDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Third Year Question Bank POWER ELECTRONICS
Încărcat de
venkatesh_paboluDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
EE2301-Power Electronics
Easwari Engineering College
Chennai
Department of EEE
Question Bank
EE2301-Power Electronics
Unit I
Power semiconductor devices
Part A
1. Why IGBT is very popular nowadays?
2. What is the difference between power diode and signal diode?
3. What are the different methods to turn on the thyristor?
4. What is the difference between power diode and signal diode?
5. IGBT is a voltage controlled device. Why?
6. Power MOSFET is a voltage controlled device. Why?
7. What are the different types of power MOSFET?
8. What is the relation between a and ?
9. Define latching current.
10.Define holding current.
11.What is a snubber circuit?
12.What losses occur in a thyristor during working conditions?
13.Define hard-driving or over-drivin gate
14.Define circuit turn off time of SCR.
15.Why circuit turn off time should be greater than the thyristor turn -off time
16.Why is the current gain low at high current level in a power transistor?
17.What are the main advantages of a MOSFET in switching applications?
18.How SCR differ from TRIAC?
19.State the advantages of IGBT over MOSFET?
20.Draw the turn on characteristics of SCR and mark the timings td,tr,ton?
21.State the condition to be satisfied for Load commutation of SCR?
22.In TRIAC which of the mode the sensitivity of the gate is higher?
23.State the advantages of BJT over MOSFET?
24.Define the term pinch off voltage of MOSFET
25.Why MOSFETs are not preferred for low frequency applications?
EASWARI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
EE2301-Power Electronics
26.Why are IGBT becoming popular in their application to controlled
converters?
27.What are the factors that influence the turn-off time of a thyristor?
28.What is reverse recovery time?
Part B
1. Discuss the different modes of operation of thyristor with the help of its
V-I Characteristics.
2. Explain why triac is rarely operated in I quadrant with -ve gate current
and in III quadrant with +ve gate current.
3. Explain the transfer, output, Switching Characteristics of power
MOSFET.
4. Draw the basic structure of an IGBT and explain its operation.
5. Explain the Switching performance of BJT with relevant waveforms
indicating clearly the turn on, turn off times and their components. Also
define the term SOA?
6. Compare the performance Characteristics of power MOSFET and BJT?
7. Briefly discuss the RC triggering of SCR.
8. Differentiate Natural commutation and Forced commutation. Explain the
methods for achieving forced commutation in chopper circuits.
9. Explain the structure, different modes of operation and Characteristics of
TRIAC.
10.Explain the turn ON and turn OFF Characteristics of IGBT with neat
waveforms.
11.Draw the dynamic Characteristics of Unidirectional device during turn
ON and turn OFF and explain.
12.Draw the simplified model of a MOSFET to show the inter electrode
capacitance. Discuss the importance of this capacitance.
13.Calculate the switching losses of an IGBT for the following condition
both for resistance and clamped inductive load.Vcc =200 volt,
tf1=0.5secs, Icm=50 Amps, tr=0.5 secs, F=50 Hz, tf2=25 secs.
14.Explain the forward conduction characteristics of Bidirectional device.
15.Explain the current commutation technique to turn off the SCR with neat
sketch and waveforms.
16.Describe the any two methods of turn-on mechanism of SCR.
17.Draw and explain the forward characteristics of SCR using two transistor
model of SCR
18.Explain the operation of driver and snubber circuits for power MOSFET.
EASWARI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
EE2301-Power Electronics
Unit II
PHASE CONTROLLEDCOERTERS
PART A
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
What is meant by phase controlled rectifier?
What is the function of freewheeling diodes in controlled rectifier?
What are the advantages of freewheeling diodes in a controlled rectifier?
What is meant by delay angle?
Define: firing angle
What are the advantages of single phase bridge converter over single
phase mid-point converter?
7. What is commutation angle or overlap angle?
8. What are the different methods of firing circuits for line commutated
converter?
9. What is meant by input power factor in controlled rectifier?
10.What are the types of commutation?
11.List the merits of phase control.
12. What is meant by forced commutation?
13. It is required to operate a 1 phase full converter in the inverter mode
with RLE load. Should the average O/P voltage be more or less than E
during inverter operation? Why?
14. What are the advantages of three phase converter over three phase
converter?
15. Write any four performance parameters of a phase controlled rectifiers?
16. What is a dual converter?
17. What is the inversion mode of a rectifier?
18. When fully controlled converter operates in inverting modes?
19. Define displacement factor, total harmonic distortion.
20. Give any differences between single phase full converter and
semiconverter.
21. What is meant by Line commutated inerter.
22. Define the term voltage ripple factor, current ripple factor.
23. What is static VAR compensator?
24. What is static synchrous compensator?
25. What is meant by reactive power compensation?
26. Define real power and reactive power.
27. Define power factor.
28. List any two devices for reactive power compensation.
29. List the parameters for controlling power in a transmission line.
30. Draw the output voltage of a converter as function of firing angle.
31.Why the power factor of semiconverter better than full Converter?
32.What are the effects of source impedance in the controlled rectifiers?
EASWARI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
EE2301-Power Electronics
33. Is the input power factor of fully controlled converter is less than that of
half controlled converter? Justify your answer.
34.For the single phase fully controlled bridge converter having load of R,
determine the average output voltage if the supply is 230V, 50 Hz, single
phase AC and the firing angle is 60.
Part B
1. Describe briefly the principle of operation of 1 phase bridge using 4
SCRs with relevant waveforms.
2. Discuss the working of above converter in the inverter mode with RLE
load.
3. A single phase two pulse bridge converter feeds power to RLE load with
R=6, L= 6 mH, E=60 V, AC source voltage is 230 V, 50 Hz for
continuous conduction. Find the average value of load current for a firing
angle of 50. In case one of the 4 SCRs gets open circuited. Find the
new value of average load current assuming the output current as
continuous.
4. Write short notes on:
a. Facts devices
b. Static VAR compensator
5. A single phase two pulse bridge converter feeds power to RLE load.
Source voltage is 230 V, 50 Hz. Average load current of 10 Amps is
continuous over the conduction. Find the average value of load current
for a firing angle of 50. In case one of the 4 SCRs gets open circuited.
Find the new value of average load current assuming the output current
as continuous. For R=0.4 , L= 2 mH. Compute
i. Firing angle delay for E=120 V
ii. Firing angle delay for E= -120 V
6. Indicate which source is delivering power to load in parts (i) and (ii)
7. Discuss the operation of single phase half controlled rectifier with
inductive load. Also derive the average output voltage equation.
8. Explain the operation of three phase half controlled rectifier with resistive
load. Also derive the average output voltage equation.
9. Discuss the operation of three phase full controlled rectifier with
inductive load. Also derive the average output voltage equation.
10.With necessary circuit and waveforms, explain the principle of operation
of 6 pulse converter. Also derive the average output voltage equation.
11.Discuss the effect of source inductance on the performance of single
phase full converter.
EASWARI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
EE2301-Power Electronics
12.Describe the operation of single phase two pulse bridge converter using 4
SCRs with relevant waveforms. Discuss the working of above converter
mode with RLE load.
13.Describe the effect of source inductance on the performance of a single
phase full converter indicating clearly the conduction of various thyristors
during one cycle. Derive the expression for its output voltage.
14.Explain the operation of single phase dual converter taking into the effect
of source inductance with neat power circuit diagram for the firing angle
=30.
15.Discuss the operation of three phase full controlled rectifier with resistive
load for the firing angle 60, 90 and150.
16.A single phase semi converter is operated from 120 V, 50 Hz ac suppy.
The load current with average value Idc is continuous and ripple free
firing angle a=p. Determine
i. (1)Displacement factor
ii. (2)Harmonic factor of input current
iii. (3)Input power factor
17.Discuss the operation of single phase full controlled rectifier with
inductive load for continuous and discontinuous. Also derive the average
output voltage equation.
18.A single phase full converter is connected to R load. The source voltage
is 230V, 50 Hz. The average load current is 10 A. For R=20, find the
firing angle.
19.Write notes on battery Charger.
20. Discuss with the aid of schematic diagram and waveforms, the principle
of operation of a two quadrant two pulse converter in the rectifying and
inverting mode of operation.
21. The full wave controlled bridge rectifier has an ac Input of 120V rms at
60Hz and a 20 load resistor. The delay angle is 40. Determine 1)
Average load voltage 2) Average load current and 3) RMS load voltage.
22.Drive the expressions for average output voltage and rms output voltage
of single phase semiconductor.
23.A 220V ,1 KW resistive load is supplied by 220 VG,50 Hz source
through single phase fully controlled rectifier. Determine the following
for 800 W output.
(i)
Output oltage
(ii) Rms alue of input current
(iii) Fundamental component of input current
(iv) Displacement factor
EASWARI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
EE2301-Power Electronics
Unit III
DC DC CONVERTERS
1.
2.
3.
4.
What is meant by dc chopper?
What are the applications of dc chopper?
What is meant by step-up and step-down chopper?
Write down the expression for average output voltage for step
up chopper
5. What is meant by duty- cycle?
6. What are the two types of control strategies?
7. What are the two types of TRC?
8. What is meant by TRC?
9. What is meant by FM control in a dc chopper?
10.What is meant by PWM control in dc chopper?
11.What are the methods of controlling the output voltage of a chopper?
12.What is the principle of current limit control for chopper?
13.Give the uses of resonant switching.
14.What is meant by buck converter?
15.What are the advantages of ZVS when compared to ZCS?
16.What is meant by SMPS and its two adantage?
17.Give the application of SMPS?
18.What are the classification of dc to dc converter depending upon the
directions of current and voltage?
Part B
1. Describe the principle of step-up chopper. Derive an expression for its
average output voltage in terms of input dc voltage & duty cycle.Derive
an expression for its average output voltage.
2. Discuss the principle of operation of buck converter with suitable
waveform. Derive an expression for its average DC O/P voltage.
3. A step down DC chopper has input voltage of 230 V with 10 load
resistor connected, voltage drop across chopper is 2 V when it is ON. For
a duty cycle of .5, calculate the average and r.m.s value of output voltage
and Power delivered to the load.
4. Explain the operation and need for resonant switching in SMPS.
5. Describe briefly the principle of operation of buck-boost converter with
a neat circuit diagram and waveform.
6. A step up chopper has input voltage of 220V and the output voltage of
660V. If the non conducting time of chopper is 100secs. Compute the
pulse width of output voltage. In case the pulse width is halved for
constant frequency operation. Find the new output voltage.
EASWARI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
EE2301-Power Electronics
7. Classify the basic topologies of switching regulators and explain the
operation of buck converter with continuous load current using suitable
waveforms.
8. Explain about Type E Chopper.
9. Prove the output voltage of step down chopper is Vo=D Vs
10.Explain the operation of Boost and buck boost converter with neat circuit
diagram and explain its equivalent circuit for different modes with
necessary waveforms.
11.Compare linear and switched mode power supplies.
12.With a neat sketch an output voltage waveforms, explain the working of
full bridge SMPS.
13.For a type A chopper ( first quadrant ), express the following variable as a
function of VS, R and duty cycle in case the load is resistive.
14.Design the filter components for a buck converter which has an input
voltage of 12 V and output voltage of 5 V. the peak to peak output ripple
voltage is 20 mV and peak to peak ripple current of inductor is limited to
0.8 A. the switching frequency is 25 KHz.
15. A dc chopper has an input voltage of 200 V and a load of 20
resistances. When chopper is on, its voltage drop is 1.5 V and the
chopping frequency is 10 KHz. If the duty cycle is 80%, find. 1) Average
output voltage 2) RMS output voltage 3) Chopper on time
UNIT IV
INVERTERS
PART A
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
What is meant by inverter?
What are the applications of an inverter?
What are the main classifications of inverter?
Why thyristors are not preferred for inverter?
How output frequency is varied in case of a thyristor?
Give two advantages of CSI.
What is the main drawback of a single phase half bridge inverter?
Why diodes should be connected in antiparallel with the thyristors in
inverter circuits?
9. What types of inverters require feedback diodes?
10.What is meant a series inverter?
11.What is the condition to be satisfied in the selection of L and C in a series
inverter?
12.What are the applications of a series inverter?
13.What are the applications of a series inverter?
EASWARI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
EE2301-Power Electronics
14.How is the inverter circuit classified based on commutation circuitry?
15.What are the applications of a CSI?
16.What is meant by PWM control?
17.What are the advantages of PWM control?
18.What are the disadvantages of the harmonics present in the inverter
system?
19.What are the methods of reduction of harmonic content?
20.Compare CSI and VSI
21.What are the disadvantages of PWM control?
22.Why PWM inerter is superior to the square wave inverter?
23.Compare between 120 and 180 mode of inverter operation?
24.List the advantages of multiple PWM over single PWM inverter?
25.Define the term Inverter gain.
26.List the methods of controlling the output voltage of inverters?
27.Mention the differences between sinusoidal PWM and modified
sinusoidal PWM techniques.
28.A single phase full bridge inverter has a resistive load of R = 10 and
the input voltage Vdc of 100 V. Find the rms output voltage at
fundamental frequency.
29.Define modulation index of PWM. What is its use?
PART B
1. Describe the operation of series inverter with aid of diagrams. Describe an
expression for output frequency, current and voltages. What are the
disadvantages of basic series inverter?
2. With a neat diagram discuss the operation of an ideal single phase CSI.
3. Draw the three phase inverter for 180 mode operation and explain its
working.
4. State different methods of voltage control in inverters. Describe about
PWM control in inverter.
5. Describe the working of a 1 phase full bridge inverter supplying R, RL
loads with relevant circuit and waveforms.
6. What is the need for controlling the output voltage of inverters? Classify
the various techniques adopted to vary the inverter gain and brief on
sinusoidal PWM.
7. Discuss the functioning of three phase voltage source inverter supplying a
balanced star connected load in 120 degree operating mode.
8. Explain how inverter can be controlled using multiple and sine PWM
techniques.
9. Explain the working principle of single phase current source inverter.
10. Draw the power circuit diagram of a three phase transistorized invertr and
explain its function.
EASWARI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
EE2301-Power Electronics
11. What is PWM? List the various PWM techniques and explain any one of
them?
12. Explain the harmonic reduction by transformer corner lines and stepped
wave inverters.
13. Describe the operation of single phase auto sequential commutated current
source inverter with power circuit and waveforms.
14. Explain the principle of operation of single phase half bridge inverter.
The single phase half bridge inverter has a resistive load of 2.4 and the
dc input voltage is 48 V. determine the r.m.s output voltage at the
fundamentaL frequency, output power and the total harmonic distortion.
15. Describe with a neat sketch and waveform the operation of a single phase
half bridge inverter supplying RL load.
16. Describe the working of a single phase full bridge inverter supplying R,
RL loads with relevant circuit and waveforms.
17. With a neat circuit and relevant waveforms discuss the operation of an
ideal single phase CSI.
UNIT V
AC TO AC CONVERTER
PART A
1. What does ac voltage controller mean?
2. What are the applications of ac voltage controllers?
3. What are the advantages of ac voltage controllers?
4. What are the disadvantages of ac voltage controllers?
5. What are the two methods of control in ac voltage controllers?
6. What is the difference between ON-OFF control and phase control?
7. What is the advantage of ON-OFF control?
8. What is the disadvantage of ON-OFF control?
9. What is the duty cycle in ON-OFF control method?
10.What are the disadvantages of unidirectional or half-wave ac voltage
controller?
11. What type of gating signal is used in single phase ac voltage controller
with RL load?
12.What are the disadvantages of continuous gating signal?
13.What is meant by sequence control of ac voltage regulators?
14.What are the adv antages of sequence control of ac voltage regulators?
15.What is meant by cyclo-converter?
16.What are the two types of cyclo-converters?
17.What are the applications of cyclo-converter?
18.What is meant by step-down cyclo-con verters?
EASWARI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
EE2301-Power Electronics
PART B
1. Draw the possible configuration of a single phase AC voltage controller
and compare them.
2. Explain the operation of multistage control of AC voltage controllers
with neat Diagram.
3. Explain the operation of 1 AC voltage controller feeding R and RL
load.Derive an expression for output voltage.
4. Explain the operation of sequence control of AC voltage controller.
5. Discuss the working of 2 stage sequence control of AC voltage controller.
6. Discuss the working of a three phase to single phase cyclo converter with
neat voltage and current waveforms.
7. Describe the three phase to three phase cyclo converter with relent circuit
arrangement using 18 thyristors.
8. Show that fundamental RMS value of per phase output voltage of low
frequency for an mpulse cycloconverter is given by p pm n E Epn or sin.
9. A resistive load of 5 is fed through a single phase full wave AC voltage
controller from 230 ,50 Hz source. If the firing angle of thyristor is 120,
find the output RMS voltage, input power factor and average current of
thyristor.
10.With necessary circuit and waveforms, explain the principle of operation
of single phase ac voltage controller feeding R load by on-off control and
phase control. Derive the expression for rms value of output voltage in
both cases.
11.Draw the circuit and waeforms of single phase to single phase step up
cycloconverter for output frequency=four times input frequency.Assume
continuous conduction.
12.Explain the working of three phase bidirectional delta connected AC
voltage controller.
Prepared by
HOD/EEE
EASWARI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
EE2301-Power Electronics
EASWARI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Power Electronics: Lecture Notes of Power Electronics CourseDe la EverandPower Electronics: Lecture Notes of Power Electronics CourseÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE2301 Power ElectronicsDocument12 paginiEE2301 Power ElectronicsMuniyasamy BalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2De la EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Încă nu există evaluări
- PE Blueprint SemDocument4 paginiPE Blueprint Semsparkle courageÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 3: Switching Power SuppliesDe la EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 3: Switching Power SuppliesÎncă nu există evaluări
- PE Lesson PlanDocument10 paginiPE Lesson PlanAnbalagan GuruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Powerelectronics in Power System (QB)Document9 paginiPowerelectronics in Power System (QB)T.l. SelvamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power Electronics Question BankDocument6 paginiPower Electronics Question BankDarshan B RÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analysis of Inverter-NEWDocument8 paginiAnalysis of Inverter-NEWMATHANKUMAR.SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pe Course File 9 198Document190 paginiPe Course File 9 198Dr ADITYA VORAÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE6503 Power ElectronicsDocument8 paginiEE6503 Power ElectronicscoolrajeeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mlp-Ee 51Document11 paginiMlp-Ee 51prasad357Încă nu există evaluări
- PE - Vel - 1st EditionDocument5 paginiPE - Vel - 1st Editionnaveen kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- PE Unit Wise Important QuestionsDocument5 paginiPE Unit Wise Important Questionssai krishnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anna UniversityDocument3 paginiAnna UniversitySuryaa KrishnanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power ElectronicsDocument7 paginiPower ElectronicsPrabha KaruppuchamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ee 6503Document2 paginiEe 6503Attagasam ArjunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maharaja Institute of Technology Mysore Department of Electronics and Communication EngineeringDocument2 paginiMaharaja Institute of Technology Mysore Department of Electronics and Communication EngineeringDhanush Gowda D TÎncă nu există evaluări
- WWW Universityquestions inDocument8 paginiWWW Universityquestions inagreykatoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power Electronics - 102409025108 - 1Document7 paginiPower Electronics - 102409025108 - 1Herbert DeepakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power Electronics Important QuestionsDocument4 paginiPower Electronics Important QuestionsShuvamSarkar0% (1)
- Power Electronics 102409025108 1Document7 paginiPower Electronics 102409025108 1sushil4056Încă nu există evaluări
- Question BankDocument11 paginiQuestion BankRohini MukunthanÎncă nu există evaluări
- PE AssignmentsDocument11 paginiPE AssignmentsVinayaniv YanivÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE2301Document6 paginiEE2301Salim KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ty PeDocument3 paginiTy Pepankaj mobile zoneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power Elecronics: Unit 1:: QuestionsDocument8 paginiPower Elecronics: Unit 1:: QuestionsMonishaahÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9A02504 Power ElectronicsDocument4 pagini9A02504 Power ElectronicssivabharathamurthyÎncă nu există evaluări
- PE LessonPlanDocument4 paginiPE LessonPlanNarasimman DonÎncă nu există evaluări
- PX7103-Analysis and Design of InvertersDocument8 paginiPX7103-Analysis and Design of InvertersGabriel SanthoshkumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- PE-2 - Questions of GTU Last 3 PapersDocument2 paginiPE-2 - Questions of GTU Last 3 PapersAkshit PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Important Questions BEEMDocument5 paginiImportant Questions BEEMVIJAY VIDHYA SAGAR SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kings: Question BankDocument6 paginiKings: Question Bankapi-19951707Încă nu există evaluări
- Important Question Bank: Linear and Non Linear ElementsDocument4 paginiImportant Question Bank: Linear and Non Linear ElementsSAURAV CHAUDHARYÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 8 Single Phase InvertersDocument8 paginiLab 8 Single Phase InvertersM Hassan BashirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Single Phase AC To AC Conversion Without Frequency RestrictionsDocument4 paginiSingle Phase AC To AC Conversion Without Frequency RestrictionsTaniyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Manual 8 Inverters PDFDocument8 paginiLab Manual 8 Inverters PDFMuhammad AbubakarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power Electronics Question BankDocument3 paginiPower Electronics Question BankHarish SudhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power ElectronicsDocument6 paginiPower ElectronicsAvanish NiranjanÎncă nu există evaluări
- FinalDocument2 paginiFinalgobinathÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5ee1a Pe Model PaperDocument2 pagini5ee1a Pe Model PaperKushalgym888 gym888Încă nu există evaluări
- Pe Unit 5 PDFDocument8 paginiPe Unit 5 PDFmjrsudhakarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ece Vii Power Electronics (10ec73) AssignmentDocument6 paginiEce Vii Power Electronics (10ec73) AssignmentThomas PriceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Edc Question BankDocument6 paginiEdc Question BankManoj KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial 2 - Transformer - SolutionDocument5 paginiTutorial 2 - Transformer - SolutionDanang Aji NugrohoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 16 Mark Questions - BEEEDocument5 pagini16 Mark Questions - BEEEVignesh GÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pe 17ec73 AssignmentDocument1 paginăPe 17ec73 Assignmentsureshfm1Încă nu există evaluări
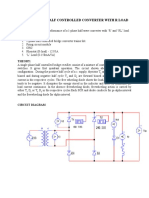
- Single Phase Half Controlled Converter With R LoadDocument3 paginiSingle Phase Half Controlled Converter With R LoadB ANIL KUMARÎncă nu există evaluări
- PE Question BankDocument4 paginiPE Question BankRajesh BhaskarlaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advance Power Electronics - GTU Paper - April2010Document1 paginăAdvance Power Electronics - GTU Paper - April2010be6351Încă nu există evaluări
- 09a50205 PowerelectronicsDocument8 pagini09a50205 PowerelectronicsPaone KalyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 136052104-Mt-Power Electronic Control of DC DrivesDocument2 pagini136052104-Mt-Power Electronic Control of DC DrivesNavneetha PeramoniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sr. No. Name of Experiment: Load Test On 3 Phase Squirrel Cage Induction MotorDocument40 paginiSr. No. Name of Experiment: Load Test On 3 Phase Squirrel Cage Induction MotorSagar G ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nov-Dec 2014 PDFDocument2 paginiNov-Dec 2014 PDFkarthickpjceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Industrial Drives and ControlsDocument4 paginiIndustrial Drives and ControlsMohit SanandiyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ece-Vii-Power Electronics (10ec73) - Assignment PDFDocument6 paginiEce-Vii-Power Electronics (10ec73) - Assignment PDFAdarsh S Shettigar100% (1)
- Sathyabama University: 414601-614601-614PT501-614PT501 (2007)Document7 paginiSathyabama University: 414601-614601-614PT501-614PT501 (2007)kannan09Încă nu există evaluări
- Beee QbankDocument8 paginiBeee QbankRahul singhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Apec 3Document2 paginiApec 3Sathish Kumar KarneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eln QBDocument3 paginiEln QBbalakrishnak eceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Estimate of The Heat Gain or Loss and The Surface Temperatures of Insulated Flat, Cylindrical, and Spherical Systems by Use of Computer ProgramsDocument19 paginiEstimate of The Heat Gain or Loss and The Surface Temperatures of Insulated Flat, Cylindrical, and Spherical Systems by Use of Computer ProgramsAlessio MiniatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transformer Bushings PDFDocument36 paginiTransformer Bushings PDFhashamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Harmonicguard Series Drive-Applied Harmonic Filter Installation, Operation, and Maintenance ManualDocument67 paginiHarmonicguard Series Drive-Applied Harmonic Filter Installation, Operation, and Maintenance ManualGanesh MurthyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Background: e H 2 MC BDocument7 paginiBackground: e H 2 MC BPranab HazraÎncă nu există evaluări
- CPC 100 CP TD1 CR500 DIRANA MPD 600 Article Ensuring A Reliable Power Supply OMICRON Magazine 2015 ENUDocument3 paginiCPC 100 CP TD1 CR500 DIRANA MPD 600 Article Ensuring A Reliable Power Supply OMICRON Magazine 2015 ENUarnenylundÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7I Energy ResourcesDocument25 pagini7I Energy ResourcesChristineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch2-Properties of Pure Substance PDFDocument58 paginiCh2-Properties of Pure Substance PDFISRAEL HAILUÎncă nu există evaluări
- Astm B267 07Document5 paginiAstm B267 07Srinivasan Krishnamoorthy100% (1)
- Cold Electricity - Amperage Without Voltage Similar To EV Gray TH Moray J BediniDocument13 paginiCold Electricity - Amperage Without Voltage Similar To EV Gray TH Moray J Bediniqqqq100% (2)
- Electric Heaters and AccessoriesDocument10 paginiElectric Heaters and AccessoriesIulian NeaguÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ele Lab ReportDocument42 paginiEle Lab ReportDik Man RyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 78-Sine and Cosine RuleDocument8 pagini78-Sine and Cosine RuleSameh SalahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Emerging Startup StudyDocument5 paginiEmerging Startup StudyAhmed ZaheerÎncă nu există evaluări
- TestDocument361 paginiTestJake Sy100% (1)
- Horsepower LabDocument2 paginiHorsepower LabHiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Report 1Document4 paginiLab Report 1puja sahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diffraction From N Number of SlitsDocument44 paginiDiffraction From N Number of SlitsPiyush BhatnagarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 4 - Kirchhoffs LawsDocument4 paginiLab 4 - Kirchhoffs LawsAnuradha ItwaruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bliss Anand America - Magnetic Level Gauges - NewDocument25 paginiBliss Anand America - Magnetic Level Gauges - NewNikhil WadhwaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Caracteristicas de Bloqueo Del TiristorDocument20 paginiCaracteristicas de Bloqueo Del TiristorJose Alvaro Aquino MamaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture Note - Chapter 1Document30 paginiLecture Note - Chapter 1zamspaceklÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydraulics 2 - Lesson 1 - Example ProblemsDocument9 paginiHydraulics 2 - Lesson 1 - Example ProblemsAngelo RosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analysis of Vertical Axis Wind Turbine: Mini Project Work Report Submitted ToDocument47 paginiAnalysis of Vertical Axis Wind Turbine: Mini Project Work Report Submitted ToSanketÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 2Document58 paginiLecture 2Meej AustriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technical Data Sheet: Procedure API 11A4.1Document2 paginiTechnical Data Sheet: Procedure API 11A4.1Yurika ToledoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Martin de WitDocument200 paginiMartin de WitDimitris Sampatakos100% (1)
- 09 Mathematics Surface Areas and Volume Test 02Document2 pagini09 Mathematics Surface Areas and Volume Test 02Vikas SuryavanshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter - 04Document38 paginiChapter - 04Alfredo Lopez CordovaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power Electronics For Renewable Energy, Smart Grids: - Chunyan An - Pooja ShahDocument23 paginiPower Electronics For Renewable Energy, Smart Grids: - Chunyan An - Pooja ShahaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Report Phy210 Group 9 As1202b Siti Nur Khadijah Farra AlliyahDocument6 paginiLab Report Phy210 Group 9 As1202b Siti Nur Khadijah Farra AlliyahFARRA ALLIYAH MOHD FAIZULÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pressure Vessels: Design, Formulas, Codes, and Interview Questions & Answers ExplainedDe la EverandPressure Vessels: Design, Formulas, Codes, and Interview Questions & Answers ExplainedEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Hyperspace: A Scientific Odyssey Through Parallel Universes, Time Warps, and the 10th DimensionDe la EverandHyperspace: A Scientific Odyssey Through Parallel Universes, Time Warps, and the 10th DimensionEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (3)
- Einstein's Fridge: How the Difference Between Hot and Cold Explains the UniverseDe la EverandEinstein's Fridge: How the Difference Between Hot and Cold Explains the UniverseEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (51)
- Chasing the Demon: A Secret History of the Quest for the Sound Barrier, and the Band of American Aces Who Conquered ItDe la EverandChasing the Demon: A Secret History of the Quest for the Sound Barrier, and the Band of American Aces Who Conquered ItEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (25)
- Vibration Basics and Machine Reliability Simplified : A Practical Guide to Vibration AnalysisDe la EverandVibration Basics and Machine Reliability Simplified : A Practical Guide to Vibration AnalysisEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (2)
- Laminar Flow Forced Convection in Ducts: A Source Book for Compact Heat Exchanger Analytical DataDe la EverandLaminar Flow Forced Convection in Ducts: A Source Book for Compact Heat Exchanger Analytical DataÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pilot's Handbook of Aeronautical Knowledge (2024): FAA-H-8083-25CDe la EverandPilot's Handbook of Aeronautical Knowledge (2024): FAA-H-8083-25CÎncă nu există evaluări
- Post Weld Heat Treatment PWHT: Standards, Procedures, Applications, and Interview Q&ADe la EverandPost Weld Heat Treatment PWHT: Standards, Procedures, Applications, and Interview Q&AÎncă nu există evaluări
- Machinery's Handbook Pocket Companion: Quick Access to Basic Data & More from the 31st EditionDe la EverandMachinery's Handbook Pocket Companion: Quick Access to Basic Data & More from the 31st EditionÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Laws of Thermodynamics: A Very Short IntroductionDe la EverandThe Laws of Thermodynamics: A Very Short IntroductionEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (10)
- Bulk Material Handling: Practical Guidance for Mechanical EngineersDe la EverandBulk Material Handling: Practical Guidance for Mechanical EngineersEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Safety Theory and Control Technology of High-Speed Train OperationDe la EverandSafety Theory and Control Technology of High-Speed Train OperationEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (2)
- Airplane Flying Handbook: FAA-H-8083-3C (2024)De la EverandAirplane Flying Handbook: FAA-H-8083-3C (2024)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (12)
- Cyber-Physical Systems: Foundations, Principles and ApplicationsDe la EverandCyber-Physical Systems: Foundations, Principles and ApplicationsHoubing H. SongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical Vibrations and Condition MonitoringDe la EverandMechanical Vibrations and Condition MonitoringEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Practical Guides to Testing and Commissioning of Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing (Mep) InstallationsDe la EverandPractical Guides to Testing and Commissioning of Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing (Mep) InstallationsEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (3)
- Handbook of Mechanical and Materials EngineeringDe la EverandHandbook of Mechanical and Materials EngineeringEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (4)
- Electrical (Generator and Electrical Plant): Modern Power Station PracticeDe la EverandElectrical (Generator and Electrical Plant): Modern Power Station PracticeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (9)
- Gas Turbines: A Handbook of Air, Land and Sea ApplicationsDe la EverandGas Turbines: A Handbook of Air, Land and Sea ApplicationsEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (9)