Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
PS21 FinalsReviewer
Încărcat de
Ian De La Cruz0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
416 vizualizări2 paginiPhysics Reviewer
Titlu original
PS21_FinalsReviewer
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentPhysics Reviewer
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
416 vizualizări2 paginiPS21 FinalsReviewer
Încărcat de
Ian De La CruzPhysics Reviewer
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 2
PHYSICS 21 REVIEWER
1.
2.
Suppose you are hiking down the Grand Canyon. At the
top, the temperature early in the morning is a cool 3C. By
late afternoon, the temperature at the bottom of the canyon
has warmed to a sweltering 34C. What is the difference
between the higher and lower temperatures in (a)
Fahrenheit degrees and (b) kelvins?
Dermatologists often remove small precancerous skin
lesions by freezing them quickly with liquid nitrogen,
which has a temperature of 77 K. What is this temperature
on the (a) Celsius and (b) Fahrenheit scales?
3.
On the Rankine temperature scale, which is sometimes
used in engineering applications, the ice point is at 491.67
degrees R and the steam point is at 671.67 degrees R.
Determine a relationship (analogous to Equation 12.1)
between the Rankine and Fahrenheit temperature scales.
4.
A steel aircraft carrier is 370 m long when moving through
the icy North Atlantic at a temperature of 2.0C. By how
much does the carrier lengthen when it is traveling in the
warm Mediterranean Sea at a temperature of 21C?
5.
When the temperature of a coin is raised by 75 C, the
coins diameter increases by 2.3 x10 -5 m. If the original
diameter of the coin is 1.8 x 10-2 m, find the coefficient of
linear expansion.
6.
A steel ruler is calibrated to read true at 20.0 C. A
draftsman uses the ruler at 40.0 C to draw a line on a 40.0
C copper plate. As indicated on the warm ruler, the length
of the line is 0.50 m. To what temperature should the plate
be cooled, such that the length of the line truly becomes
0.50 m?
7.
8.
9.
A copper kettle contains water at 24 C. When the water is
heated to its boiling point of 100.0 C, the volume of the
kettle expands by 1.2 x10 -5 m3. Determine the volume of
the kettle at 24 C.
Suppose that the steel gas tank in your car is completely
filled when the temperature is 17 C. How many gallons
will spill out of the twenty-gallon tank when the
temperature rises to 35 C?
The bulk modulus of water is B = 2.2 x 10 9 N/m 2. What
change in pressure P (in atmospheres) is required to keep
water from expanding when it is heated from 15 to 25 C?
10. Two identical thermometers made of Pyrex glass contain,
respectively, identical volumes of mercury and methyl
alcohol. If the expansion of the glass is taken into account,
how many times greater is the distance between the degree
marks on the methyl alcohol thermometer than the distance
on the mercury thermometer?
11. Ideally, when a thermometer is used to measure the
temperature of an object, the temperature of the object itself
should not change. However, if a significant amount of heat
flows from the object to the thermometer, the temperature
will change. A thermometer has a mass of 31.0 g, a specific
heat capacity of c = 815 J/(kgC), and a temperature of
12.0C. It is immersed in 119 g of water, and the final
temperature of the water and thermometer is 41.5C. What
was the temperature of the water before the insertion of the
thermometer?
12. A rock of mass 0.20 kg falls from rest from a height of 15
m into a pail containing 0.35 kg of water. The rock and
water have the same initial temperature. The specific heat
capacity of the rock is 1840 J/(kgC). Ignore the heat
absorbed by the pail itself, and determine the rise in the
temperature of the rock and water.
13. How much heat must be added to 0.45 kg of aluminum to
change it from a solid at 130 C to a liquid at 660 C (its
melting point)? The latent heat of fusion for aluminum is
4.0 x105 J/kg.
14. Find the mass of water that vaporizes when 2.10 kg of
mercury at 205 C is added to 0.110 kg of water at 80.0 C.
15. A 42-kg block of ice at 0 C is sliding on a horizontal
surface. The initial speed of the ice is 7.3 m/s and the final
speed is 3.5 m/s. Assume that the part of the block that
melts has a very small mass and that all the heat generated
by kinetic friction goes into the block of ice. Determine the
mass of ice that melts into water at 0C.
16. An unknown material has a normal melting/freezing point
of -25.0 C, and the liquid phase has a specific heat
capacity of 160 J/(kgC). One-tenth of a kilogram of the
solid at -25.0 C is put into a 0.150-kg aluminum
calorimeter cup that contains 0.100 kg of glycerin. The
temperature of the cup and the glycerin is initially 27.0 C.
All the unknown material melts, and the final temperature
at equilibrium is 20.0 C. The calorimeter neither loses
energy to nor gains energy from the external environment.
What is the latent heat of fusion of the unknown material?
17. It is claimed that if a lead bullet goes fast enough, it can
melt completely when it comes to a halt suddenly, and all
its kinetic energy is converted into heat via friction. Find
the minimum speed of a lead bullet (initial temperature is
30.0 C) for such an event to happen.
18. A woman has been outdoors where the temperature is 10
C. She walks into a 25 C house, and her glasses steam
up. Using the vapor pressure curve for water that
accompanies Problem 75, find the smallest possible value
for the relative humidity of the room.
19. Liquid nitrogen boils at a chilly -195.8 C when the
pressure is one atmosphere. A silver coin of mass 1.5 x10 -2
kg and temperature 25 C is dropped into the boiling liquid.
What mass of nitrogen boils off as the coin cools to
-195.8 C?
20. A lead object and a quartz object each have the same initial
volume. The volume of each increases by the same amount,
because the temperature increases. If the temperature of the
lead object increases by 4.0 C, by how much does the
temperature of the quartz object increase?
21. Ice at -10.0 C and steam at 130 C are brought together at
atmospheric pressure in a perfectly insulated container.
After thermal equilibrium is reached, the liquid phase at
50.0 C is present. Ignoring the container and the
equilibrium vapor pressure of the liquid at 50.0 C, find the
ratio of the mass of steam to the mass of ice. The specific
heat capacity of steam is 2020 J/(kgC).
22. Multiple-Concept Example 11 uses the same physics
principles as those employed in this problem. A block of
material has a mass of 130 kg and a volume of 4.6 x10 -2
m3. The material has a specific heat capacity and
coefficient of volume expansion, respectively, of 750 J/(kg
C) and 6.4 x10-5 (C)-1. How much heat must be added
to the block in order to increase its volume by 1.2 x10 -5 m3?
23. A gas is enclosed within a chamber that is fitted with a
frictionless piston. The piston is then pushed in, thereby
compressing the gas. Which statement below regarding this
process is consistent with the first law of thermodynamics?
a.
b.
c.
d.
The internal energy of the gas will increase.
The internal energy of the gas will decrease.
The internal energy of the gas will not change.
The internal energy of the gas may increase, decrease, or
remain the same, depending on the amount of heat that
the gas gains or loses.
24. Is it possible for the temperature of a substance to rise
without heat flowing into the substance?
a.
b.
c.
Yes, provided that the volume of the substance does not
change.
Yes, provided that the substance expands and does
positive work.
Yes, provided that work is done on the substance and it
contracts.
25. The first law of thermodynamics states that the change U
in the internal energy of a system is given by U Q W,
where Q is the heat and W is the work. Both Q and W can
be positive or negative numbers. Q is a positive number if
________, and W is a positive number if ________.
a.
b.
c.
d.
the system loses heat; work is done by the system
the system loses heat; work is done on the system
the system gains heat; work is done by the system
the system gains heat; work is done on the system
26. A system does 164 J of work on its environment and gains
77 J of heat in the process. Find the change in the internal
energy of (a) the system and (b) the environment.
27. In exercising, a weight lifter loses 0.150 kg of water
through evaporation, the heat required to evaporate the
water coming from the weight lifters body. The work done
in lifting weights is 1.40 x105 J. (a) Assuming that the latent
heat of vaporization of perspiration is 2.42 x10 6 J/ kg, find
the change in the internal energy of the weight lifter. (b)
Determine the minimum number of nutritional Calories of
food (1 nutritional Calorie = 4186 J) that must be
consumed to replace the loss of internal energy.
28. When a .22-caliber rifle is fired, the expanding gas from the
burning gunpowder creates a pressure behind the bullet.
This pressure causes the force that pushes the bullet
through the barrel. The barrel has a length of 0.61 m and an
opening whose radius is 2.8 x10 -3 m. A bullet (mass = 2.6
x10-3 kg) has a speed of 370 m/s after passing through this
barrel. Ignore friction and determine the average pressure
of the expanding gas.
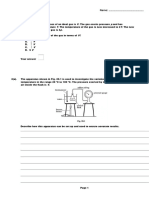
29. (a) Using the data presented in the accompanying pressure
volume graph, estimate the magnitude of the work done
when the system changes from A to B to C along the path
shown. (b) Determine whether the work is done by the
system or on the system and, hence, whether the work is
positive or negative.
30. Refer to Multiple-Concept Example 3 to see how the
concepts pertinent to this problem are used. The pressure of
a gas remains constant while the temperature, volume, and
internal energy of the gas increase by 53.0 C, 1.40 x10 -3
m3, and 939 J, respectively. The mass of the gas is 24.0 g,
and its specific heat capacity is 1080 J/(kgC). Determine
the pressure.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- IDEAL GAS PROCESSESDocument2 paginiIDEAL GAS PROCESSESfitriÎncă nu există evaluări
- IB Thermo (2016)Document7 paginiIB Thermo (2016)Hiroki Nose100% (1)
- Sheet 1Document7 paginiSheet 1Bahaa RaghebÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterDe la EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- PHYSICS 1E Module 9 (Edited)Document54 paginiPHYSICS 1E Module 9 (Edited)Claire G. MagluyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesDe la EverandMechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry Ii Unit 1 Paper 1Document6 paginiChemistry Ii Unit 1 Paper 1maxime namaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Icse X Calorimetry Question BankDocument9 paginiIcse X Calorimetry Question BankanimeshtechnosÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5.1 Prob - Sheet.entropyDocument2 pagini5.1 Prob - Sheet.entropyShrinivas Subhash HulsureÎncă nu există evaluări
- Work sheet.1Document6 paginiWork sheet.1tfkthe46Încă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial 1 - Thermodynamics (2024)Document4 paginiTutorial 1 - Thermodynamics (2024)kkhimatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem set 1 covers energy, heat, gases, and thermodynamicsDocument15 paginiProblem set 1 covers energy, heat, gases, and thermodynamicsFikret BazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heat and Thermodynamics-SubjectiveDocument8 paginiHeat and Thermodynamics-SubjectiveNeeraj KalraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 12 HWDocument9 paginiChapter 12 HWkiaunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problems Chapter 1 Sec BDocument7 paginiProblems Chapter 1 Sec BSana AshfaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2020 - Calorimetry PracticeDocument5 pagini2020 - Calorimetry PracticeAMOS SODJAHINÎncă nu există evaluări
- Determine specific heat capacity from calorimetry experimentsDocument9 paginiDetermine specific heat capacity from calorimetry experimentsR Mathew0% (1)
- ThermoDocument4 paginiThermowong zhi chengÎncă nu există evaluări
- PomeDocument17 paginiPomeAnirudh KaushikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculating Heat Transfer and Temperature ChangesDocument22 paginiCalculating Heat Transfer and Temperature ChangesnallilathaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 11Document14 paginiCH 11UbadahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Midterm Exam ThermodynamicsDocument10 paginiMidterm Exam ThermodynamicsRoselyn BenavidezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analyze math problems instructionsDocument5 paginiAnalyze math problems instructionsJan Ebenezer MorionesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic ThermodynamicsDocument21 paginiBasic ThermodynamicsJess Ryan Olayon100% (1)
- Form 4 Physics Chapter 4 - Teacher'sDocument9 paginiForm 4 Physics Chapter 4 - Teacher'sPavithiran50% (2)
- 2018 - Tutorial - Heat and Heat TransferDocument6 pagini2018 - Tutorial - Heat and Heat TransferShanel100% (1)
- Heat and TemperatureDocument33 paginiHeat and Temperatureapi-3722337100% (1)
- Quiz-1Document1 paginăQuiz-1charltexsatorreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quizz Chapter 2Document6 paginiQuizz Chapter 2torreblancacamilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- UPCS Physics Problem SetDocument13 paginiUPCS Physics Problem SetRicardo Jose BracamonteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Combus Eng'g Homework 1Document5 paginiCombus Eng'g Homework 1Alecsia NuguidÎncă nu există evaluări
- KF 1Document19 paginiKF 1Diana Fitriani SurtikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2021 CPC Problem SheetDocument1 pagină2021 CPC Problem SheetHarsh GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Question Bank (Numericals)Document12 paginiQuestion Bank (Numericals)Omid Karimi SadaghianiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practice Problem (Chap # 03)Document4 paginiPractice Problem (Chap # 03)nandlalwarsoorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solution Manual For Chapter 17Document9 paginiSolution Manual For Chapter 17Kenneth LandichoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Engineering Practice Problem 1Document2 paginiBasic Engineering Practice Problem 1neva000Încă nu există evaluări
- GAS LAWS AND THERMODYNAMICS EQUATIONSDocument5 paginiGAS LAWS AND THERMODYNAMICS EQUATIONSSyed Mairaj Ul HaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- TB Chapter11 PDFDocument16 paginiTB Chapter11 PDFsmohanty20Încă nu există evaluări
- TDCE Question Bank - 2018 Unit IDocument11 paginiTDCE Question Bank - 2018 Unit IvinodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Temperature and HeatDocument48 paginiTemperature and Heatalexzandrei.rara937Încă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 1 First Law 2016Document8 paginiAssignment 1 First Law 2016PabitraBadhuk0% (1)
- Mock Test For Chemistry For Engineers 2Document2 paginiMock Test For Chemistry For Engineers 2aramikaelatanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic+2 +1st+Law+Thermodynamics+18+SeptDocument44 paginiTopic+2 +1st+Law+Thermodynamics+18+SeptNOXOLO NOMBULELO WENDY NGXONGOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermodynamics QuestionsDocument4 paginiThermodynamics Questionsprateek vyasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ihw 2Document6 paginiIhw 2LogoÎncă nu există evaluări
- MEG 212 Practise QuestionsdocxDocument11 paginiMEG 212 Practise Questionsdocxoyetunde ridwanÎncă nu există evaluări
- PHYSICS 2 HEAT AND THERMODYNAMICSDocument5 paginiPHYSICS 2 HEAT AND THERMODYNAMICSMohibbullah ShovonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermo SW 1Document3 paginiThermo SW 1TimmyÎncă nu există evaluări
- UP2 HW CH 20 First Law Thermo RevDocument4 paginiUP2 HW CH 20 First Law Thermo Revrameshaarya99Încă nu există evaluări
- Thermodynamics Question Set ADocument4 paginiThermodynamics Question Set AVivek NegiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ChE 122 LE1 Samplex 2Document3 paginiChE 122 LE1 Samplex 2googley71Încă nu există evaluări
- ME214_BTD_Tutorial_QuestionsDocument2 paginiME214_BTD_Tutorial_QuestionsKONDALRAOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermodynamics IntroductionDocument13 paginiThermodynamics IntroductionGissela BTÎncă nu există evaluări
- 16TF603 Entropy AssignmentDocument2 pagini16TF603 Entropy AssignmentMd Sharique AkhtarÎncă nu există evaluări
- TH121 FinalsDocument2 paginiTH121 FinalsIan De La CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Andrew Loomis - Successful DrawingDocument211 paginiAndrew Loomis - Successful DrawingBreana Melvin100% (8)
- HI16 ResearchReflectionsDocument2 paginiHI16 ResearchReflectionsIan De La CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- HI16 4NobleTruthsDocument3 paginiHI16 4NobleTruthsIan De La CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4th Year 3rd QTR Electronics - SymbolsDocument1 pagină4th Year 3rd QTR Electronics - SymbolsIan De La CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cach Ve HoaDocument52 paginiCach Ve HoaBong GheÎncă nu există evaluări
- Created Reality, Shared Reality: "I Am Called To A Dream Greater Than Myself. and I Will Not Dream Anything Less."Document4 paginiCreated Reality, Shared Reality: "I Am Called To A Dream Greater Than Myself. and I Will Not Dream Anything Less."Ian De La CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- AMC124 FinalsReviewerDocument2 paginiAMC124 FinalsReviewerIan De La CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- PE112 FundamentalsofBasketballDocument1 paginăPE112 FundamentalsofBasketballIan De La CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- BNB Teacher's Guide PDFDocument24 paginiBNB Teacher's Guide PDFjosteigerwald100% (1)
- Digital Arts - January 2013Document68 paginiDigital Arts - January 2013KALFERÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fish Scales Glue Final DefenseDocument8 paginiFish Scales Glue Final DefenseIan De La CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- TH121 ReflectionPaper1Document3 paginiTH121 ReflectionPaper1Ian De La CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell - 28 March 2013Document270 paginiCell - 28 March 2013Ian De La CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Draw 50 BirdsDocument58 paginiDraw 50 BirdsIan De La Cruz50% (2)
- Andrew Loomis - Drawing The Head and HandsDocument141 paginiAndrew Loomis - Drawing The Head and Handscraciunstef100% (3)
- Fish Scales GlueDocument9 paginiFish Scales GlueIan De La Cruz0% (1)
- 4th Year 2nd QTR Cle PresentationDocument6 pagini4th Year 2nd QTR Cle PresentationIan De La CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4th Year 1st QTR ElectronicsbiomassDocument5 pagini4th Year 1st QTR ElectronicsbiomassIan De La CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Origami BookDocument58 paginiOrigami Bookhuy_nguyen2485% (13)
- 3rd Year Soc Stud 1st QTR PresentationDocument7 pagini3rd Year Soc Stud 1st QTR PresentationIan De La CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2nd Year HE 2nd QTR ReportDocument4 pagini2nd Year HE 2nd QTR ReportIan De La CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- X-Wing (With Cut)Document3 paginiX-Wing (With Cut)Ian De La CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tie InterceptorDocument2 paginiTie InterceptorIan De La CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diagrama - Origami - Caixa Torre (Tower Box)Document4 paginiDiagrama - Origami - Caixa Torre (Tower Box)Ju-XÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tie FighterDocument2 paginiTie FighterIan De La CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Origami Yin-YangDocument2 paginiOrigami Yin-YangMaja PasarićÎncă nu există evaluări
- LillyDocument2 paginiLillyIan De La CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- LillyDocument2 paginiLillyIan De La CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- OCR Gas Laws Revision Questions & MSDocument29 paginiOCR Gas Laws Revision Questions & MS17guoxiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application of Partition Fuction (C)Document2 paginiApplication of Partition Fuction (C)NITISH KUMARÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermodyamics R07Document9 paginiThermodyamics R07hhjjÎncă nu există evaluări
- TM - 114073 - Heat Rate Improvement Reference Manual - Training GuidelinesDocument128 paginiTM - 114073 - Heat Rate Improvement Reference Manual - Training GuidelinesRomi Hamdani SaputraÎncă nu există evaluări
- CLS Aipmt 17 18 XIII Phy Study Package 3 SET 1 Chapter 12Document46 paginiCLS Aipmt 17 18 XIII Phy Study Package 3 SET 1 Chapter 12wjhume33% (3)
- Thermodynamics JEE Advanced Previous Year Questions With Solutions PDFDocument8 paginiThermodynamics JEE Advanced Previous Year Questions With Solutions PDFdpcdglÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2839 PDFDocument326 pagini2839 PDFWilfer Manuel QuicenoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Partition function insights for statistical mechanicsDocument23 paginiPartition function insights for statistical mechanicsRiya MathurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 2Document76 paginiModule 2Raj KamalÎncă nu există evaluări
- CUISON CHAPTER 1 Pt. 2Document53 paginiCUISON CHAPTER 1 Pt. 2Reinzo GallegoÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCTD101B Notes 5 - Internal Energy and EnthalpyDocument5 paginiCCTD101B Notes 5 - Internal Energy and EnthalpyKibwe TrimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermodynamics Multiple Choice ReviewDocument26 paginiThermodynamics Multiple Choice ReviewWillina Marie Chong MableÎncă nu există evaluări
- Essential University Physics 3rd Edition Richard Wolfson Solutions Manual 1Document36 paginiEssential University Physics 3rd Edition Richard Wolfson Solutions Manual 1timothyaliqjtkomaegr100% (21)
- Physics Answers PDFDocument33 paginiPhysics Answers PDFJason LeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4 (Heat and Temperature)Document33 paginiChapter 4 (Heat and Temperature)QaisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Callen Thermodynamics Solution PDFDocument2 paginiCallen Thermodynamics Solution PDFAbrRodriguesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 3 and 4-ThermodynamicsDocument95 paginiTopic 3 and 4-ThermodynamicsNOR AZAM BIN ENDOT / FSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exploring The Thermodynamics of A Rubber Band: Related ArticlesDocument5 paginiExploring The Thermodynamics of A Rubber Band: Related ArticlesNitin rajputÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bme NotesDocument44 paginiBme Notestempoterrace2306Încă nu există evaluări
- MS Excel Spreadsheet Add-In For Thermodynamic Properties and Process Simulation of R152aDocument8 paginiMS Excel Spreadsheet Add-In For Thermodynamic Properties and Process Simulation of R152aJuan Fernando Cano LarrotaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Magneto-Fluid MechanicsDocument110 paginiIntroduction To Magneto-Fluid MechanicsCarlos Torres EcheverríaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Capitulo 6 Moran ShapiroDocument59 paginiCapitulo 6 Moran ShapiroGerman GiraudoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 06A - Fuels and Combustion - Fall 2020Document45 paginiLecture 06A - Fuels and Combustion - Fall 2020Huraira TahirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paper 35 Hazards24Document11 paginiPaper 35 Hazards24Sri NivasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phys Theory PDFDocument12 paginiPhys Theory PDFHassan WaqarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heat, Work and the First Law of ThermodynamicsDocument4 paginiHeat, Work and the First Law of ThermodynamicsJerizza ParafinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydrogen Properties PDFDocument536 paginiHydrogen Properties PDFAnonymous 3DHogIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 1.2 - Exergy Evaluation On Engineering ProcessesDocument44 paginiLesson 1.2 - Exergy Evaluation On Engineering ProcessesBilly JhunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 Energy of A System ThermoDocument25 paginiChapter 3 Energy of A System ThermoEmadudin AbdulkaderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermodynamics: Unit 5Document32 paginiThermodynamics: Unit 5Nithin Bharadwaj KummamuruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowDe la EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (48)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessDe la EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (6)
- Quantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishDe la EverandQuantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (18)
- Too Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldDe la EverandToo Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (8)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingDe la EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (5)
- The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismDe la EverandThe Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (500)
- The Beauty of Falling: A Life in Pursuit of GravityDe la EverandThe Beauty of Falling: A Life in Pursuit of GravityÎncă nu există evaluări
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterDe la EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (409)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesDe la EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (2193)
- The Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceDe la EverandThe Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (23)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidDe la EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1395)
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)De la EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (155)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceDe la EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (5)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayDe la EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (125)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeDe la EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsDe la EverandStrange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (94)
- The Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityDe la EverandThe Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (75)
- What is Life?: With Mind and Matter and Autobiographical SketchesDe la EverandWhat is Life?: With Mind and Matter and Autobiographical SketchesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (139)
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldDe la EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (60)
- Starry Messenger: Cosmic Perspectives on CivilizationDe la EverandStarry Messenger: Cosmic Perspectives on CivilizationEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (158)
- Black Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseDe la EverandBlack Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (13)
- The Sounds of Life: How Digital Technology Is Bringing Us Closer to the Worlds of Animals and PlantsDe la EverandThe Sounds of Life: How Digital Technology Is Bringing Us Closer to the Worlds of Animals and PlantsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (5)
- The Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldDe la EverandThe Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (53)