Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Unit 2 Handouts
Încărcat de
Víctor BLDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Unit 2 Handouts
Încărcat de
Víctor BLDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
INGLS I, 2
GTI 1
UNIT 2
LANGUAGE REFERENCE
Reflexive pronouns
We often use reflexive pronouns when the subject and object of the action is the same person. They dont
always have to refer to the subject of the clause: He sees himself as the same as everyone else.
We can also use reflexive pronouns after prepositions to refer back to a previous noun to make the
meaning clear: I bought a coat for myself / I bought myself a coat.
But we use a personal pronoun not a reflexive pronoun when the reflexive meaning is clear from the
context: They took their trainers with them (not *themselves).
We can say by oneself to mean without company or to mean without help: Old people often spend a lot of
time by themselves.
Sometimes we use a reflexive pronoun to add emphasis: The company director himself greeted us at the
door.
Reflexive verbs
Common reflexive verbs:
ENJOY ONESELF: Divertirse. -It seems to me that you are not sure whether or not one should enjoy
oneself.
HELP ONESELF: Autoayudarse. The better one understands this, the better one can help oneself.
CONVINCE ONESELF: Convencerse. To convince oneself that these criteria are important in and of
themselves is not easy, given that, on the contrary, what results is arbitrary action by everyone.
HURT ONESELF: hacerse dao a s mismo. It may be done to try to hurt oneself or to "get high" or
intoxicate.
MARKET ONESELF: autopromocionarse. How to market oneself at a job fair.
PAY ONESELF: ahorrar (colloquial). The phrase "pay yourself first" has become increasingly
popular in personal finance and investing circles.
BEHAVE ONESELF: comportarse bien. Learn how to behave oneself.
PRIDE ONESELF: enorgullecerse de algo. He prides himself on his loyalty to his friends.
DEVOTE ONESELF: consagrarse a algo. To "cultivate" or look after, and hence to devote oneself
to something which deserves special attention and care.
Verbs that are often reflexive in Spanish but not in English:
OFFER: I offered to cook for all my friends.
REFUSE: He refused to sit down.
CONCENTRATE: Relax and concentrate on what youre.
GET UP: Do you get up early on Saturdays?
INGLS I, 2
GTI 1
Collocations with reflexive verbs
Just be yourself s t mismo.
Enjoy yourselves! Disfrutad!
Behave yourselves! - Comportaos!
Help yourself! Srvete!
Make yourself at home! - Sintete como en casa!
I couldnt make myself understood. No pude hacerme entender.
We had the whole place to ourselves. Tenamos el lugar para nosotros solos.
Suit yourself! Haz lo que quieras.
VERB TENSES IN NARRATION
When relating events in the past, we often use these verb tenses:
a) Past Simple: to relate the main events of a story. In 1990 we moved to London and I gota job in an
engineering company.
b) Past Continuous: to give the background to events: At that time I was living in London and
working in an engineering company. One day
a. (!) If we use state verbs such as know, be, have; they will be in the simple form. It was
the weekend and I had a free afternoon, so I decided to
c) Past Perfect Simple: to go back from the past and relate events that happened earlier. It was
already 8.30 and I was still 10 Km from the airport. I had left the house in good time, but
d) Past Perfect Continuous: to go back from the past and describe earlier activities. I felt very
relieved when we finally found a flat. We had been looking for months, but there hadnt been
anything suitable.
e) Future in the past: to express a future idea which is set in the past (would / was going to):
When she joined Sony, she was 22 and had only a years experience. It would be an enormous
challenge for her.
LANGUAGE NOTES
TALENT, SKILL AND ABILITY
These words are followed by the structures below:
HAVE A TALENT FOR + NOUN/-ING: You have a talent for learning English. She has a talent
for music and she shows it.
ACQUIRE/DEVELOP SKILLS IN / NOUN/-ING: The government supported a number of
programmes designed to help them acquire skills in business. He must acquire skills
in employing the scientific method before he starts to work.
HAVE AN ABILITY TO + INF.: She has the ability to achieve good grades at university .
TALENT can be used as:
a) An uncountable noun to talk about general ability: He has considerable talent as a musician.
b) A countable noun + for: He has a natural talent for playing the piano.
SKILL can be used as:
a) A singular noun: She negotiated the deal with great skill.
b) A plural noun: She has very good negotiating skills.
INGLS I, 2
GTI 1
Other expressions related with talent:
AN APTITUDE FOR + -ING: He shows an aptitude for working with figures and is destined to
become an accountant.
ACCUSTOMED TO + -ING: My father is accustomed to staying up late.
FAMILIAR WITH + NOUN: This module is very useful for visitors who are not familiar with your
region, particularly foreign visitors.
LIE IN SBS (ABILITY) TO + INF.: Power lies in your ability to prevent wars, not in igniting them.
AVALIABLE FOR (NOUN): Such tickets are not available for purchase online.
PHRASAL AND PREPOSITIONAL VERBS
Prepositional verbs follow this structure: VERB + PREP. + NOUN/-ING. I have worked in the marketing
area.
Phrasal verbs have a verb and a particle, but the particle can come before the noun or after it. Please, fill
out this questionnaire. / Please, fill this questionnaire out. / Please, fill it out. Whenever there is a
pronoun, the particle must come after it.
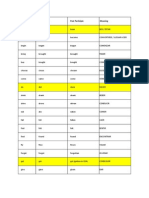
List of some phrasal and prepositional verbs:
Verb
Fill in
Translation
Completar,
rellenar,
suplantar,
sustituir, poner
al da
Hospedar,
colgar,
subir,
levantar
Example
250 Facebook users who filled in a personality questionnaire.
Interact with
Interactuar con
It gives you the chance to interact with other cell-phone users.
Aim at
Apuntar, enfilar,
pretender
Aimed at professionals, these are a great way to find likeminded people
Work in
I have worked in the marketing area for many years.
Take on
Trabajar
en,
introducer
Hacerse cargo de
Succeed in
Lack in
Look up
Benefit from
Rely on
Appeal to
Make out
Opt for
Lograr
Carecer de
Buscar
Beneficiarse de
Confiar en
Gustar
No distinguir
Optar por
Immerse in
Sumergirse en
I didnt succeed in passing the test.
Im lacking in practical experience.
I decided to look up avatar on Wikipedia.
I would benefit from living abroad for a year.
I relied on bluffing to get through the interview.
What really appealed to me was working in a new field.
I cant quite make out what hes saying.
Given the choice, Id opt for both work and study at the same
time.
You need to immerse yourself in the culture in order to learn a
new language.
Put up
When putting up a profile, it would be reasonable for them to
present flattering images.
I am able to take on the demands of a full-time Masters degree.
INGLS I, 2
GTI 1
VOCABULARY
Word formation: SELFHere is a list of some words made with the prefix self.
Word
Translation
Example
self-aware
consciente de
s mismo
egocntrico
It is a self-aware sector and is perfectly capable of standing on its
own two feet.
Any decision promoted through self-centred initiatives, artificial
deadlines and pre-emptive vetoes will be divisive and likely to be
stillborn.
On stage, the band's lead singer was full of self confidence.
self-centred
self-confidence
self-conscious
confianza en
uno mismo
cohibido
self-contained
autnomo
self-critical
autocrtico
self-defence
defensa propia
self-discipline
autodisciplina
self-disciplined
disciplinado
self-doubt
desconfianza
de s mismo
self-esteem
autoestima
self-evident
obvio
self-fulfilling
autorrealizado
r
egosmo
self-interest
self-made
artfice de su
xito
self-pity
autocompasi
n
satisfecho de
s mismo
autosuficiente
self-satisfied
self-sufficient
self-sustaining
self-taught
sense of self
autosustentabl
e
autodidacta
conciencia de
uno mismo
Knowing that everyone was watching made me feel very selfconscious.
My father was a quiet, shy, self-contained man.
As such, each of these pieces could be seen as a self-critical
analysis or a reflection on the practices of the authors' own
governments
It is a strategic deterrent that we would only ever contemplate
using in extreme circumstances of self-defence.
I therefore also ask Members to show an appropriate degree of
self-discipline so that we can finish at a reasonable time.
We must be self-disciplined and make sure that problem does not
arise.
Teenagers experience strong feelings of stress, confusion, selfdoubt, pressure to succeed, financial uncertainty, and other fears
while growing up.
This programme focuses on building self-esteem and providing
life-oriented information and education to improve the socioeconomic situation of poor youths.
But to me, one thing is self-evident: it is our values which must
form the basis of our common legislation.
I believe that this Hamas victory reflects a situation in which
Israeli policy has managed to realise a self-fulfilling prophecy.
The problem lies with too much Western self-interest.
In Chile, self-made businesswomen heading up their own
companies are still few and far between, making Mara Luz Marn
and the vineyard she founded from scratch a rarity indeed
I do not share the self-pity that I rather sense here in this
Chamber, that feeling that we are to blame for so much.
Indeed, they are too amazed and self-satisfied with the
achievements of the last forty years.
I want to be self-sufficient and not rely on help from others.
The danger is that global warming may become self-sustaining, if
it has not done so already.
The responsibility of this task rests on 18-yearold Chinedu, selftaught computer expert who is in charge of training.
Attitudes and behaviors can help a child develop a sense of self, or
cause serious damage to the child's emotional and psychological
health.
INGLS I, 2
GTI 1
GRAMMAR: REPORTED SPEECH
Direct and reported speech
Reporting speech in writing
When we put the reporting verb after direct speech, it can go before the subject, unless the subject is a
pronoun: The operation has been a resounding success, she said.
We use indirect speech for statements, questions and commands.
Reported statements
Common reporting verbs
There are a number of common reporting verbs, often followed by that: say, tell, add, continue, answer,
reply, mention, remark. For the third time that day, the minister replied that it was out of the question.
We can omit that after an introductory verb, except after reply, continue, answer and shout. I told them
they were barred from the club from now on.
There are differences in use between say and tell. We can omit the object or use an indirect object after
say, but we use a direct object after tell.
He said (to us) that his mobile phone had been out of action all day. He told us that his mobile phone
had been out of action all day.
Changes of pronoun and adverb
If the place or time of reporting is significantly different from that in the original speech, we often need to
make changes to adverbs of place and time:
Now > then, here > there, today > that day, tomorrow > the next day; yesterday > the day before;
last Monday > the last/previous Monday.
Alex said, Ill meet you here again tomorrow at 3.30. > Alex said she would meet us there again the next day
at 3.30.
But if the statement is reported on the same day and in the same place, we would say: Alex said she would
meet us here tomorrow at 3.30.
Changes of tense Backshifts
a) Present forms become past forms: Im leaving in ten minutes. She decided she was leaving in ten
minutes.
b) Past forms become past perfect forms: It rained heavily today. Sarah mentioned that it had
rained really heavily that day.
c) Past perfects simple and continuous do not change: Theyd arrived an hour early. I said theyd
arrived an hour early.
When to change the tense
We do not change the tense of the original words in reported speech when:
a) The reporting verb is in a present tense: He says that intelligent life in the universe does not exist.
b) The direct speech includes an unreal past: I wish I were younger. Janice said that she wished
she were younger.
INGLS I, 2
GTI 1
We dont usually change the tense when:
a) The action in the indirect speech is still happening or going to happen: The negotiator said he is
working on the details of a tentative settlement.
b) The reported verb expresses a fact or situation that cannot or is unlikely to change: He explained
that these animals roamed the earth millions of years ago.
c) The verb comes after a time conjunction: Martin replied that he had started the job immediately
after he left school.
We make the tense change if we no longer believe the direct speech statement:
Wheres Tom this evening? He said he was going to join us, but I dont think he will.
Modal verbs
Where possible, the present form of the modal verb changes to its past form (will would; may
might):
The new law will be in place soon. She said the new law would be in place soon.
Shall becomes would when it refers to the future, but should when it is a suggestion.
I shall tell them everything. I decided I would tell them everything.
Shall we tell the manager? She suggested that they should tell the manager.
We can both use must and had to in reported speech. : The doctor said that I must/had to lose twenty
kilos.
In the negative, we can use mustnt or wasnt/werent to. She said we mustnt/werent to think badly of
her.
Reported questions
Common reporting verbs
The most common verbs for reporting questions are ask and want to know.
The assistant asked what type of printer we had, but I dont know. / Laura wanted to know if
anybody had reported the missing person.
We also use enquire for formal questions and wonder for ask ourselves.
Patterns
We introduce reported closed questions (Yes/No) with if or whether. Lester wondered if/whether there
was anything better in life.
We can present alternatives in reported questions with whether or not, but we do not use if or not,
except by putting or not at the end of the question. Deborah asked whether or not there was a lift in the
apartment block. / Deborah asked if there was a lift in the apartment block or not.
In reported questions we use a question word: The nurse asked when exactly the pain had started.
We report negative questions which express surprise or criticism with a functional verb like complain:
Isnt that stupid? She complained that it was stupid.
INGLS I, 2
GTI 1
Reported orders and requests
Common reporting verbs
Verbs used to report commands are tell, order, command and forbid: When the vet had finished, he told
them to let the animal sleep.
We use ask for reporting requests, and beg or urge with urgent requests: His secretary asked me to come
back later.
Patterns
In reported commands we use a reporting verb and (not) to + infinitive. Several members of the Royal
Family urged Edward VII not to abdicate.
We can use ask for + passive infinitive if we dont mention the person to whom the command was given:
The cinema manager asked for the culprit to be brought to his office.
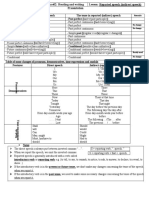
Reporting verbs and their patterns
Pattern
VERB ONLY
VERB + (THAT)+ CLAUSE
Example
She apologised.
He admitted (that) he had hacked
into the companys account
system.
VERB + THAT + CLAUSE
She shouted that she had
murdered the politician.
She reassured me that I would
arrive on time.
They offered to pick up the
children.
VERB + OBJECT + THAT +
CLAUSE
VERB + TO + INFINITIVE
VERB + (OBJECT) + TO +
INFINITIVE
VERB + OBJECT + TO +
INFINITIVE
She begged (us) to let her stay.
VERB + OBJECT + TO +
INFINITIVE + COMPLEMENT
She considers Muhammad Ali to
have been the greatest boxer ever.
VERB + -ING FORM
He denied doing it.
VERB
+
OBJECT
PREPOSITION + -ING FORM
I advised him not to say anything.
They accused me of forging the
cheques.
Verbs following the pattern
Agree, apologise, refuse
Accept, acknowledge, add, admit,
advise, agree, announce, argue,
assert, assume, believe, boast,
confess,
concede,
conclude,
comment, complain, decide,
declare, deny, doubt, exclaim,
expect, explain, foresee, imagine,
imply, insist, know, mention,
notice, observe, point out,
predict,
promise,
protest,
recommend, remark, repeat,
report, respond, reveal, say,
state, suggest, vow, whisper
Answer, continue, reply, shout
Advise, assure, inform, reassure,
remind, tell, warn
Agree, demand, guarantee, offer,
propose, refuse, swear, threaten,
volunteer, vow
Ask (sb), beg (sb), expect (sb),
promise (sb)
Advise,
allow,
challenge,
command, compel, encourage,
expect, forbid, force, implore,
instruct, invite, order, permit,
persuade, remind, request, tell,
urge, warn
Acknowledge, assume, believe,
claim, consider, declare, expect,
feel, find, presume, suppose,
think, understand
Admit, apologise for, decide on,
deny, mention, recommend,
regret, report, suggest
Accuse sb of, blame sb for,
congratulate sb on, thank sb for.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (894)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Text 1 DevavanipravesikaDocument7 paginiText 1 DevavanipravesikaThin Crust Ping Spoofing 14 pizzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cinemas vs StreamingDocument9 paginiCinemas vs StreamingVíctor BLÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cinemas vs StreamingDocument9 paginiCinemas vs StreamingVíctor BLÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present PerfectDocument6 paginiPresent PerfectVíctor BL100% (1)
- Unit 3 HandoutsDocument5 paginiUnit 3 HandoutsVíctor BLÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conditional Sentences GuideDocument7 paginiConditional Sentences GuideVíctor BLÎncă nu există evaluări
- Songs Past SimpleDocument3 paginiSongs Past SimpleVíctor BLÎncă nu există evaluări
- At The British Parliament - Past TensesDocument4 paginiAt The British Parliament - Past TensesVíctor BLÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cinemas vs StreamingDocument9 paginiCinemas vs StreamingVíctor BLÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reading 3 - The Bridges of LondonDocument1 paginăReading 3 - The Bridges of LondonVíctor BLÎncă nu există evaluări
- Real English IIDocument3 paginiReal English IIVíctor BLÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of All Completely Irregular Verbs in EnglishDocument3 paginiList of All Completely Irregular Verbs in EnglishVíctor BLÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1: Talking About EducationDocument4 paginiUnit 1: Talking About EducationVíctor BLÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oral PresentationDocument3 paginiOral PresentationVíctor BLÎncă nu există evaluări
- Infinitive Past Simple Past Participle MeaningDocument3 paginiInfinitive Past Simple Past Participle MeaningVíctor BLÎncă nu există evaluări
- Personal and Critical ResponsesDocument1 paginăPersonal and Critical ResponsesVíctor BLÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oral PresentationDocument3 paginiOral PresentationVíctor BLÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reading Review About FranzenDocument2 paginiReading Review About FranzenVíctor BLÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Irish RevolutionDocument13 paginiThe Irish RevolutionVíctor BLÎncă nu există evaluări
- FRANZEN, Jonathan: Farther AwayDocument6 paginiFRANZEN, Jonathan: Farther AwayVíctor BLÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phra SalsDocument4 paginiPhra SalsVíctor BLÎncă nu există evaluări
- British & American English: 1. Spelling DifferencesDocument12 paginiBritish & American English: 1. Spelling DifferencesVíctor BLÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inversions VictorDocument4 paginiInversions VictorVíctor BLÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1: Talking About EducationDocument4 paginiUnit 1: Talking About EducationVíctor BLÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clefts: 1. It' Cleft SentencesDocument1 paginăClefts: 1. It' Cleft SentencesVíctor BLÎncă nu există evaluări
- Action Verbs With Direct Objects (Grades 5-6) PDFDocument4 paginiAction Verbs With Direct Objects (Grades 5-6) PDFBo Cu BinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atreides (By JVTA, 2017)Document1 paginăAtreides (By JVTA, 2017)Joseph Vintimille Tariki AskarisÎncă nu există evaluări
- All About Determiners "all1" and "any1Document106 paginiAll About Determiners "all1" and "any1Thoibah SantosoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reported Speech, Teacher SheetDocument2 paginiReported Speech, Teacher SheetDARK SAD QUEENÎncă nu există evaluări
- REPORTED SPEECH Direct Indirect Changes and No ChangesDocument4 paginiREPORTED SPEECH Direct Indirect Changes and No ChangesLeo AramburuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter - 08 - MorphologyDocument17 paginiChapter - 08 - MorphologyCarly AdinataÎncă nu există evaluări
- Glossika Lithuanian Fluency 1 (PDFDrive)Document287 paginiGlossika Lithuanian Fluency 1 (PDFDrive)ErikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- TENSESDocument78 paginiTENSESSatriyo Ibnu0% (1)
- Introduction To Norwegian - Word List Day 1Document5 paginiIntroduction To Norwegian - Word List Day 1AntonioÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Are Correlative Conjunctions?: Conjunction Coordinating Conjunctions Subordinating ConjunctionsDocument2 paginiWhat Are Correlative Conjunctions?: Conjunction Coordinating Conjunctions Subordinating ConjunctionshoneyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Full Blast Plus 4: Student's Book p69-70 Teacher's Book p69-70Document2 paginiFull Blast Plus 4: Student's Book p69-70 Teacher's Book p69-70Siti Athirah0% (1)
- Vocab StrategiesDocument6 paginiVocab StrategieseeepeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kelas 9 - Latihan Soal Passive VoiceDocument3 paginiKelas 9 - Latihan Soal Passive VoiceIkhsan Dinn IslamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Q1 G7 Worksheet Direct and Reported SpeechDocument5 paginiQ1 G7 Worksheet Direct and Reported SpeechQueeny Abiera TolentinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- We Use The Present Continuous Tense To Talk About: Action Happening Now ExampleDocument4 paginiWe Use The Present Continuous Tense To Talk About: Action Happening Now ExampleSawab SchwabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Personal Best A2 - TB Unit4Document16 paginiPersonal Best A2 - TB Unit4BryanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indirect Speech, Relative Clause, Passive VoiceDocument22 paginiIndirect Speech, Relative Clause, Passive VoiceFebby DwiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4.3 Grade 4 English Handout Term 3 2023#Document28 pagini4.3 Grade 4 English Handout Term 3 2023#Jenique BronkhorstÎncă nu există evaluări
- Characteristics of The Modern Korean Language. Phonetics, Morphology and Syntax.Document7 paginiCharacteristics of The Modern Korean Language. Phonetics, Morphology and Syntax.Tania ZazaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Regular Verbs, Verbos Regulares en Inglés.: Inf - Present Past Tense P. Participle Gerund SpanishDocument2 paginiRegular Verbs, Verbos Regulares en Inglés.: Inf - Present Past Tense P. Participle Gerund SpanishNIEVES LOPEZ DIEGO ALEXANDERÎncă nu există evaluări
- Irregular Verbs Day1Document12 paginiIrregular Verbs Day1luis angel peña gómezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Voca-Book (Good Will Hunting)Document25 paginiVoca-Book (Good Will Hunting)Анастасия ВознесенскаяÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group 1: Cesya Claudia Sirait Dwi Alicia Melki Totong Satria PaliluDocument16 paginiGroup 1: Cesya Claudia Sirait Dwi Alicia Melki Totong Satria PaliluGalang RanggaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tugas B.Inggris Comparison ExerciseDocument2 paginiTugas B.Inggris Comparison ExerciseYuda DwigunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Using Commas To Set Off Introductory PhrasesDocument3 paginiUsing Commas To Set Off Introductory PhrasesMelinda SuharaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Four Corners Students Book3 Scope and Sequence PDFDocument4 paginiFour Corners Students Book3 Scope and Sequence PDFAlexander PalenciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- What's The News Today?: Pathway To English For Senior High School Grade XII General ProgramDocument22 paginiWhat's The News Today?: Pathway To English For Senior High School Grade XII General ProgramMaulana Surya NegaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- American English File Book 1 Unit 3 y 4: Answer KeyDocument7 paginiAmerican English File Book 1 Unit 3 y 4: Answer KeyHORUS ORTEGAÎncă nu există evaluări
- LESSON PLAN WeekendingOct.14th, 2022Document17 paginiLESSON PLAN WeekendingOct.14th, 2022Athlyn DurandÎncă nu există evaluări