Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Vasculitis - Student Notes Tabulated2
Încărcat de
Kirstie de LunaDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Vasculitis - Student Notes Tabulated2
Încărcat de
Kirstie de LunaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
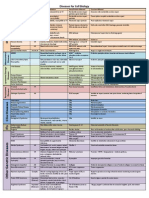
Wegners Granulomatosis
Type of
Vasculature
Epidemiology
Pathology &
Pathogenesis
Clinical
Manifestation
Small arteries & veins
Granulomatosis vasculitis of
upper & lower Respiratory tract
3:100,000 cases
1 M : 1 F w/ mean age of 40 yrs
Necrotizing vasculitis
Intra/extra-vascular granuloma
Lung: multiple, bilateral,nodular
cavitary infiltrates
Sinuses & Nasopharynx:
inflammation, granuloma, &
necrosis w/ or w/o vasculitis
Renal: focal or segmental GN or
RPGN
aberrant cell-mediated immune
response
Chronic S. aureus nasal carriage
associated replase
Inc. secretion of IFN-g, TNF-a,
CD4+
Nose: Nasal ulceration -> saddle
nose
Ear: Serous otitis media
Pulmo: asymptomatic infiltrate or
cough, hemoptysis, dyspnea,
chest discomfort
Eye: sore eyes/red eyes,
dacryosystitis, ciliary vessel
vasculitis, retro-orbital mass
lesion
Skin: papules, palpable purpura,
subcutaneous nodules, ulcers
Cardio: pericarditis, coronary
vasculitis, cardiomyopathy,
mimics MI @ <40 y/o
CNS: wrist-drop (mononeuritis
multiplex), cerebral vasculitis
mimics CVA (stroke), cranial
neuritis
Renal: mild GN protienuria,
hematuria, rbc cast
Churg-Strauss Syndrome
Small & medium muscular
arteries, capillaries, veins &
venules
Allergic Angitis &
granulomatosis
1-3: million cases
1.2 M : 1 F mean age of 48 yrs
Necrotizing vasculitis w/
eosinophilic infiltration in any
organ w/ pulmonary
predominance
Strongly associated w/ Asthma
Other organs: skin, CVS, kidneys,
PNS, GI
3 Phases:
st
1 : Prodromal allergic rhinitis,
nasal polyps, asthma attacks
nd
2 : Eosinophilic (+) eosinophilia
in PBS, manifesting w/ Leoffler
syndrome
rd
3 : Vasculitis
Nonspecific manifestations: fever,
malaise, anorexia, wt loss
Severe asthmatic attack w/
pulmonary infiltrates
wrist-drop (mononeuritis
multiplex) first sign purpura
and subcutaneous nodules
along radial nerve destruction
Allergic rhinitis & sinusitis
PAN
(Polyarteritis nodosa)
Small & medium sized muscular
arteries
(renal & visceral arteries)
Mutlisystem necrotizing vasculitis
Inflammation of entire wall
Uncommon dse
th th
2 M : 1 F @ 4 -5 decade
classic PAN
Segmental & bifurcations &
branches of arteries
Polymorphonuclear
neutrophilic infiltrates in all
layers of vessel wall
Intimal proliferation &
degeneration of entire vessel
wall
Compromises lumen ->
thrombos formation -> infarct
Assoc. w/ Hairy Cell leukemia
MPA
(Microscopic Polyangitis)
Small vessels esp. capillaries &
venules
Necrotizing vasculitis w/ no or
few immune complexes
GN & pulmonary capillaritis
M>F w/ mean age of 57 yrs
Histologically similar to PAN w/
predilection for capillaries and
venules
Minimal immuglobin deposition
Classification Criteria:
Wt loss of >4kg since onset
Livedo reticularis
Testicular pain/tenderness
Myalgias, weakness, leg
tenderness
Mono/polyneuropathies
Development of HPN
Takayasus Artertis
(Aortic Arch Syndrome)
Medium & large arteries
Medium & large artery
Cranial/Temporal arteritis
F>M @ >50 y/o
Involved one or more branches of
carotid artery ( temporal, aorta
& its branches)
Closely assoc. w/ PMR
Panarteritis w/ inflammatory
mononuclear infiltrates w/ giant
cell formation
Ag driven disease (t-cell,
macrophage, dendritic cells)
CD4 activated @ adventitia
leading to macrophage
differentiation
IL2 & IFN-g progressive arterities
Renal: arteritis w/o GN, renal HPN
Liver: assoc. w/ HBV (10-30%)
Constitional: fever, malaise, wt
loss depending on organ
involved
Skin: purpura, Livedo reticularis
(mottled appearance),
gangrene
HPN
Chronic Kidney Dse
GCA & PMR
(Giant Cell Arteritis &
Polymyalgia Rheumatica)
5 most common:
1. Kidney Inflammation (80%)
2. Wt Loss (>70%)
3. Skin Lesion (>60%)
4. Nerve Damage (60%)
5. Fever (55%)
Gradual onset
Constitional: fever, wt loss,
musculoskeletal pain
Hemoptysis alveolar damage
Mononeuritis multiplex wristdrop
GI & cutanteous vasculitis
Splinter Hemorrhage
Muscle wasting
PMR: stiffness, muscular pain in
neck, shoulder, lower back, hip
& thighs w/ 40-50% w/ GCA or
10-20% of PMR progressing to
GCA
Both GCA & PMR:
Fever, Anemia, headache >50y/o
Malaise, fatigue, anorexia, wt
loss, sweat arthralgia
Temporal Artery: thickened &
nodular, pulsates early in dse
Scalp pain, jaw claudication &
tongue
Ischemic optic neuropathy
MI, Extemety claudication, stroke,
visceral Infarct
Inflammation & stenosis
1.2-2.6: million cases
Common among adolescent girls
& women Asians
Panarteritis
Aortic arches & branches usually
at origin
Intimal proliferation & fibrosis
Scarring & vascularization
Distruption & degeneration of
internal elastic lamina
Constitution S/Sx depending on
organ involved
HPN
Absent of pulse on branch
affected
Presence of bruit
Labratory
Wegners Granulomatosis
Churg-Strauss Syndrome
PAN
(Polyarteritis nodosa)
MPA
(Microscopic Polyangitis)
(+) c-ANCA
(antiproteinase-3)
(+) p-ANCA
(antimyeloperoxidase)
(-) ANCA
(+) p-ANCA
(antimyeloperoxidase)
(+) p-ANCA (myeloperoxidase)
Elevated ESR
Mild anemia & leukocytosis
Thrombocytosis
Mild hypergammaglobinemia
(+) RF
Diagnosic
Basis
Management
& Prognosis
CXR: nodular
densities/granulomas
predominately on lung base
Tissue Biopsy:
Pulmo. wedge biopsy
(highest yield)
Renal biopsy showing pauciimmune GN
3 Major Patho. Findings:
1. Parencymal necrosis
2. Vasculitis
3. Granulomatous
inflammation w/ mixed
cellular infiltrates
Education, vocational counseling
Physiotherapy
Supportive therapy
Prednisone improves
symptoms not course
(1mg/kgBW/day) Prednisone
to hydrocortisone @ 1:5
Cyclophosphamide
(2mg/kgBW)
Azathioprine (2mg/kg)
Methothrexate (start @
7.5mg/wk to 20-25mg/wk)
Mycophenolate mofetil (1g
BID)
Rituximab - biologic therapy
Eosinophilia >1,000 cell/ul
Elevated ESR, fibrinogen, aglobulin
Sputum smear: crushmann
spirals
Tissue Biopsy:
1. Eosinophilic infiltrates
2. Peri/extra vascular small
necrotizing granulomas
3. Nectrotizing vasculitis
4. Lung necrosis
Untreated 25% (5yr remission)
Treated favorable
o
Mortality 2 cardiovascular causes
Medications:
Prednisone
Cyclophosphamide for
unresponsive to Predinose
High ESR
Leukocytosis w/ PMN dominance
Hypergammaglobinemia
(inverted A:G ratio)
Elevated BUN/Crea unrelated to
dehydration or obstruction
Elevated ESR
Leukocytosis
Anemia
Thrombocytosis
Biopsy of nodular skin, testis,
nerve & muscle lesions
containing granulocytes
GCA & PMR
(Giant Cell Arteritis &
Polymyalgia Rheumatica)
(-) ANCA
Medication:
Prednisone &
cyclophosphamide - same as
Wegners
Antivirals for HBV
Anti-HPN
74% 5 yr survival rate
34% relapse rate
Mortality 2o to:
Pulmonary
GI
Cardiac
Renal
Medication:
Prednisone &
cyclophosphamide - same as
Wegners
(-) ANCA
Elevated ESR
Normocytic Hypochromic Anemia
Elevated Alk PO4
Elevated IgG
Creatine Kinase normal
High ESR
Mild Anemia
High immune globulin
Biopsy of Temporal artery (3-5cm
diameter)
Ultrasound helpful
Biopsy of tissue
Arteriography (contrast MRA):
showing corkscrew appearance
of affected artery & aneurismal
dilation of aorta
Medication:
Prednisone (40-60 mg/day or
1mg/kgBW) gradually
tapered to control symptom
Aspirin reduce ischemic
complications
Methotrexate reduce
steroid dose
Spontaneous remission
94% 5yr survival rate
o
Mortality 2 to:
CHF
CVA
Renal
Aneurysm rupture
Angiography: aneurysm of small
& medium sized arteries of
kidney, liver and visceral organs
Poor prognosis if untreated
o
Mortality 2 to GI or
Cardiovascular
10% replase rate
Takayasus Artertis
(Aortic Arch Syndrome)
Medication:
Prednisone (40-60 mg/day)
for acute S/Sx
Methotrexate (up to 25mg)
for refractory cases
Surgical & angiographic approach
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Gyne 2.6 - Benign and Malignant Tumors of The Ovaries and Fallopian TubesDocument8 paginiGyne 2.6 - Benign and Malignant Tumors of The Ovaries and Fallopian TubesVon HippoÎncă nu există evaluări
- DISC, Drugs, Infection, Thick Basal MembraneDocument5 paginiDISC, Drugs, Infection, Thick Basal MembraneHOPEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lec 2 - Blood VesselsDocument12 paginiLec 2 - Blood VesselsJeffrey LübbertÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vasculitis MindnodeDocument1 paginăVasculitis MindnodeToño VargasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cocci Rod 4 Main Classifications: Gram Staph, Strep Bacillus Clostridium Neisseria Pleiomorphic Enterobact-EriceaeDocument2 paginiCocci Rod 4 Main Classifications: Gram Staph, Strep Bacillus Clostridium Neisseria Pleiomorphic Enterobact-EriceaeKimberly KanemitsuÎncă nu există evaluări
- ID Bug chart-DKDocument92 paginiID Bug chart-DKNeil M D'SouzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genetic Disorders-Www - Qworld.co - inDocument13 paginiGenetic Disorders-Www - Qworld.co - inQworld100% (1)
- 7sgdfgf PDFDocument438 pagini7sgdfgf PDFPratik JadhavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Internal Medicine NBME Form 3 ExplanationsDocument11 paginiInternal Medicine NBME Form 3 ExplanationssasghfdgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Internal Medicine Quick TablesDocument276 paginiInternal Medicine Quick Tablesjoey plouffeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Step 1 DrugsDocument46 paginiStep 1 DrugsZebram ZeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diseases - BiochemDocument4 paginiDiseases - BiochemJay FeldmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neurology Musculoskeletal (MedicalBooksVN - Com)Document4 paginiNeurology Musculoskeletal (MedicalBooksVN - Com)Jonathan AiresÎncă nu există evaluări
- All Forms of Shock - Lactic Acid Via Tissue Hypoxia Tubulare Nec Via Coagulation in PT TALDocument10 paginiAll Forms of Shock - Lactic Acid Via Tissue Hypoxia Tubulare Nec Via Coagulation in PT TALlynk787Încă nu există evaluări
- MicrobesDocument12 paginiMicrobesDiMa MarshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathogens of The Vagina-Annie Espinosa - This Is The Revised VersionDocument1 paginăPathogens of The Vagina-Annie Espinosa - This Is The Revised VersionMicroposterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Patho Common Stuff - RobbinsDocument7 paginiPatho Common Stuff - RobbinsMaf BÎncă nu există evaluări
- 45 NOTES To PG (20 Files Merged)Document338 pagini45 NOTES To PG (20 Files Merged)Isak ShatikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mnemonic of Some Rare Genetic Disease PDFDocument9 paginiMnemonic of Some Rare Genetic Disease PDFfaraz100% (1)
- Toxicology USMLE NotesDocument15 paginiToxicology USMLE NotesDuncan JacksonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antivirals, Rubella, Peecorna VIRUSDocument3 paginiAntivirals, Rubella, Peecorna VIRUSErnie G. Bautista II, RN, MDÎncă nu există evaluări
- AtelectasisDocument3 paginiAtelectasisLouis FortunatoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bipolar Disorder Background: Hypomania Has The Same Symptoms of Mania Without Psychotic SymptomsDocument2 paginiBipolar Disorder Background: Hypomania Has The Same Symptoms of Mania Without Psychotic SymptomshumdingerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Poliomyelitis Haemophilus Influenzae Type B VariecellaDocument4 paginiPoliomyelitis Haemophilus Influenzae Type B VariecellaJeanna Chong100% (1)
- Exam 1 DiseasesDocument1 paginăExam 1 DiseasesSolomon Seth SallforsÎncă nu există evaluări
- DNA Viruses: P P P A H H PDocument2 paginiDNA Viruses: P P P A H H PKimberly KanemitsuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Infectious DiseaseDocument28 paginiInfectious DiseaseAnukriti MamgainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiology Arteritis ChartDocument3 paginiCardiology Arteritis ChartM PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zanki (Complete) + R/medicalschoolanki Microbiology ErrataDocument70 paginiZanki (Complete) + R/medicalschoolanki Microbiology ErrataedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nephrotic Nephritic SyndromsDocument4 paginiNephrotic Nephritic SyndromsKimiwari100% (2)
- Part IIDocument64 paginiPart IIhussainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Disease & Def Patho/Mech Clinical S/S DX/ Tests/Labs TX NotesDocument11 paginiDisease & Def Patho/Mech Clinical S/S DX/ Tests/Labs TX NotesSara AshurstÎncă nu există evaluări
- 500 Most Common by Akaas RehmanDocument12 pagini500 Most Common by Akaas RehmanAkas RehmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- USMLE - BRS Pathology - Term ListDocument8 paginiUSMLE - BRS Pathology - Term ListSaeed HasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- IM Part 1 and 2 CombinedDocument100 paginiIM Part 1 and 2 CombinedsasghfdgÎncă nu există evaluări
- ENDOCRINE PATHOLOGY WebpathDocument35 paginiENDOCRINE PATHOLOGY Webpathapi-3766657Încă nu există evaluări
- Microbiology Key WordsDocument5 paginiMicrobiology Key Wordsmoilo86020% (1)
- Bio Chem 1Document5 paginiBio Chem 1Reynaldo RiveraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Renal Buzzword ChartDocument6 pagini2 Renal Buzzword ChartTyler KingÎncă nu există evaluări
- HerniaDocument5 paginiHerniasarguss14100% (5)
- Important Terms - Tropical InfectionDocument8 paginiImportant Terms - Tropical InfectionTimothy JordanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heart Failure - Notes From "Cardiology" (Timmis Et Al) : Main CausesDocument3 paginiHeart Failure - Notes From "Cardiology" (Timmis Et Al) : Main CausesPrarthana Thiagarajan100% (3)
- First Aid PharmacoDocument61 paginiFirst Aid PharmacogirÎncă nu există evaluări
- STEP 1 ChecklistDocument11 paginiSTEP 1 ChecklistHasan Khan RoudbaryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tumor Markers: Blood Group AntigenDocument5 paginiTumor Markers: Blood Group AntigenAngela ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vasculitis: Disorder Vessels Pathology Presentation Test TX OtherDocument3 paginiVasculitis: Disorder Vessels Pathology Presentation Test TX OthermcwnotesÎncă nu există evaluări
- NBME 11 Answers To All Sections 2Document97 paginiNBME 11 Answers To All Sections 2hussainalmusawiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parvo BacteriaDocument2 paginiParvo BacteriaErnie G. Bautista II, RN, MDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Normal Lab Values (USMLE Step 1)Document12 paginiNormal Lab Values (USMLE Step 1)nmp274Încă nu există evaluări
- Post-Strep Infxn Ddressler's Sydrome: Endocarditis Valvular Dse Pericarditis Cardiac TamponadeDocument5 paginiPost-Strep Infxn Ddressler's Sydrome: Endocarditis Valvular Dse Pericarditis Cardiac TamponadeEben Ezar Dela CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardio Block 3Document62 paginiCardio Block 3Maya LaPradeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Internal Medicine - Nephrology: Topic: Cystic Kidney Diseases Lecturer: Dra. Myrna NgoDocument3 paginiInternal Medicine - Nephrology: Topic: Cystic Kidney Diseases Lecturer: Dra. Myrna NgoVon HippoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Midterm Chapter7Document43 paginiMidterm Chapter7Frances FranciscoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final USMLE ScheduleDocument7 paginiFinal USMLE Schedulerobert_bahnsen100% (1)
- 4.1d - Pathology of The Pituitary - Nov.10 - Dr. GalangDocument4 pagini4.1d - Pathology of The Pituitary - Nov.10 - Dr. GalangMiel Raphael AranillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Haematology-Summary My NotesDocument24 paginiHaematology-Summary My NotesToria053Încă nu există evaluări
- Lecturio Granulomatosis With PolyangitisDocument6 paginiLecturio Granulomatosis With PolyangitisPranjali WeladiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Systemic VasculitidesDocument124 paginiSystemic VasculitidesshahikamunaferÎncă nu există evaluări
- Request For Message PAFPDocument1 paginăRequest For Message PAFPKirstie de LunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PDS-Work Experience SheetDocument2 paginiPDS-Work Experience SheetCes Camello100% (1)
- ClaimForm2 2018Document2 paginiClaimForm2 2018Geraldine100% (1)
- Manila Central University College of Medicine Department of PediatricsDocument7 paginiManila Central University College of Medicine Department of PediatricsKirstie de LunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hostage Code Purple PolicyProcedure TemplateDocument5 paginiHostage Code Purple PolicyProcedure TemplateKirstie de LunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DR Abhijeet Deshmukh DNB Pediatrics Fellow in PICU & NicuDocument54 paginiDR Abhijeet Deshmukh DNB Pediatrics Fellow in PICU & NicuKirstie de LunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Discharge Summary JAGONOYDocument6 paginiDischarge Summary JAGONOYKirstie de LunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alfonso HX PEDocument5 paginiAlfonso HX PEKirstie de LunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Edited 9th PostGrad Course Day 2 Workshops ParticipantsDocument38 paginiEdited 9th PostGrad Course Day 2 Workshops ParticipantsKirstie de LunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CELESTINODocument4 paginiCELESTINOKirstie de LunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PCAP GuidelinesDocument20 paginiPCAP GuidelinesPatricia Anne Collantes90% (20)
- Vasculitis - Student Notes Tabulated2Document2 paginiVasculitis - Student Notes Tabulated2Kirstie de LunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CELESTINODocument4 paginiCELESTINOKirstie de LunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clinical Abstract 506DDocument1 paginăClinical Abstract 506DKirstie de LunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kirstie Abstract 1Document3 paginiKirstie Abstract 1Kirstie de LunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PD DSM 4 Vs 5Document15 paginiPD DSM 4 Vs 5satish2k3Încă nu există evaluări
- 506D Final HistoryDocument4 pagini506D Final HistoryKirstie de LunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Muni HistoryDocument30 paginiMuni HistoryKirstie de LunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indication Guidelines For TonsillectomyDocument1 paginăIndication Guidelines For TonsillectomyKirstie de LunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lefort FracturefinalDocument15 paginiLefort FracturefinalKirstie de LunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mandras, MichaelDocument16 paginiMandras, MichaelKirstie de LunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clerkship EssentialsDocument14 paginiClerkship EssentialsKirstie de Luna100% (2)
- Clerkship EssentialsDocument14 paginiClerkship EssentialsKirstie de Luna100% (2)
- Borderline Personality DisorderDocument17 paginiBorderline Personality DisorderKirstie de LunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summary CH 12,15,16,17,19,20,22,23,24 PDFDocument4 paginiSummary CH 12,15,16,17,19,20,22,23,24 PDFKirstie de LunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- History 02-17-15Document3 paginiHistory 02-17-15Kirstie de LunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microsoft Word - Some Med Juris Notes (DR Tony Rebosa)Document5 paginiMicrosoft Word - Some Med Juris Notes (DR Tony Rebosa)Maria Sarah LenonÎncă nu există evaluări
- JURIS Answers Dr. BariaDocument2 paginiJURIS Answers Dr. BariaKirstie de LunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nerizon Lina History and PeDocument5 paginiNerizon Lina History and PeKirstie de LunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Presentation PBL 12 (Bipolar Disorder)Document65 paginiCase Presentation PBL 12 (Bipolar Disorder)Rhomizal Mazali83% (6)
- Reflections of Feelings - RogersDocument3 paginiReflections of Feelings - RogersUyên TrươngÎncă nu există evaluări
- Desinfectants and AntisepticsDocument14 paginiDesinfectants and AntisepticsAri Sri WulandariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Developmental Activities For AdultsDocument4 paginiDevelopmental Activities For Adultsapi-508703903Încă nu există evaluări
- Pontalis, J. B. (2014) - No, Twice NoDocument19 paginiPontalis, J. B. (2014) - No, Twice NocabaretdadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Presentation:: DR - Amra Farrukh PG.T Su.IDocument75 paginiCase Presentation:: DR - Amra Farrukh PG.T Su.IpeeconÎncă nu există evaluări
- Allergy Test PapersDocument5 paginiAllergy Test PapersDaniel MoncadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7.hematology SummaryDocument91 pagini7.hematology SummaryPeter Shirima100% (1)
- 10 DOH Approved Herbal MedicationsDocument33 pagini10 DOH Approved Herbal MedicationsBeanncaAngelesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antibiotic Guidelines For BONE AND JOINT INFECTIONSDocument3 paginiAntibiotic Guidelines For BONE AND JOINT INFECTIONSKhurram NadeemÎncă nu există evaluări
- C1 Mod 2 - Introduction To Psychoactive Substance UseDocument22 paginiC1 Mod 2 - Introduction To Psychoactive Substance UsePUSAT LATIHAN AADKÎncă nu există evaluări
- EBCPG Acute AppendicitisDocument53 paginiEBCPG Acute AppendicitisKenneth NuñezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Resume Rough DraftDocument1 paginăResume Rough Draftapi-392972673Încă nu există evaluări
- Approach To A Patient With Upper GI BleedDocument42 paginiApproach To A Patient With Upper GI BleedMuhammad Naveed AslamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anemia PPT 3 Nov 2014Document60 paginiAnemia PPT 3 Nov 2014Susi DesmaryaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guidelines TX of HPNDocument3 paginiGuidelines TX of HPNjheyfteeÎncă nu există evaluări
- MushroomDocument36 paginiMushroomthamaraibala9788100% (1)
- Radiology X-Rayfilm ScreensDocument39 paginiRadiology X-Rayfilm ScreensFourthMolar.comÎncă nu există evaluări
- Punjab Drugs Rules 2007Document33 paginiPunjab Drugs Rules 2007RphNaeemMalik75% (12)
- Osma y Barlow 2021 PU en SpainDocument15 paginiOsma y Barlow 2021 PU en Spaingerard sansÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of Surgeries: AbdomenDocument35 paginiList of Surgeries: AbdomenSaurav SaikiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Poster ISCP10 Final Daft CWCDocument1 paginăPoster ISCP10 Final Daft CWCVizaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment and Management of Patients With Vascular Disorders and Problems of Peripheral CirculationDocument45 paginiAssessment and Management of Patients With Vascular Disorders and Problems of Peripheral CirculationCarlos RiosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mephentermine Abuse For Stamina, Resulting in Mania - A Case ReportDocument4 paginiMephentermine Abuse For Stamina, Resulting in Mania - A Case Reportgaurav sharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Post-Partum HemorrhageDocument15 paginiPost-Partum Hemorrhageapi-257029163Încă nu există evaluări
- Cae Open Cloze PhobiasDocument3 paginiCae Open Cloze PhobiasValéria DuczaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Informative Speech OutlineDocument3 paginiInformative Speech Outlineapi-27792479886% (14)
- Author's Overall Organizational PatternDocument6 paginiAuthor's Overall Organizational PatternTashieka GrahamÎncă nu există evaluări
- ASEAN Guideline On Stability of Drug ProductDocument8 paginiASEAN Guideline On Stability of Drug ProductSanjiv MenonÎncă nu există evaluări
- OT and Eating DysfunctionDocument1 paginăOT and Eating DysfunctionMCris EsSemÎncă nu există evaluări