Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Exp1 EED3012 WRIMMotor Experiments EM3000
Încărcat de
EnesVSDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Exp1 EED3012 WRIMMotor Experiments EM3000
Încărcat de
EnesVSDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
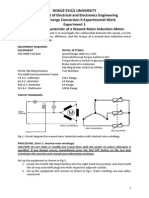
DOKUZ EYLL UNIVERSITY
Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering
EED3012 Energy Conversion II Experimental Work
Experiment 1
Torque-Speed Characteristic of a Wound-Rotor Induction Motor
The object of this experiment is to investigate the relationship between the speed/torque
characteristic of wound rotor induction motor with shorted rotor windings and block rotor
test.
EQUIPMENT REQUIRED:
Three-phase Rotor Winding Motor
Magnetic Powder Brake Unit
Brake Control Unit
Three-phase AC/DC Power Supply
Three-phase Power Supply Module
Three-pole Current Limit Protection Switch Module
Digital Power Analysis Meter
Coupling
Coupling Guard
Shaft End Guard
Connecting Leads Set
Safety Bridging Plugs Set
EM-3330-3B
EM-3320-1A
EM-3320-1N
EM-3310-1D
EM-3310-1B
EM-3310-2A
EM-3310-3H
EM-3390-2A
EM-3390-2B
EM-3390-2C
EM-3390-3A
EM-3390-4A
CIRCUIT DIAGRAMS:
Fig-1. Circuit diagram for wound-rotor induction motor
DOKUZ EYLL UNIVERSITY
Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering
EE323 Armature Windings and Induction Machines
Experimental Work
Fig-2. Connection diagram for wound-rotor induction motor
Fig-3. Connection diagram for wound-rotor induction motor for blocked-rotor test
PROCEDURE: (Part-1: shorted rotor windings)
Set up the equipment as shown in Fig-1 and Fig-2.
1. Mechanically couple the wound-rotor induction machine to magnetic powder brake
unit using a coupling. Install the coupling guard and shaft end guard. Electrically
connect the brake controller to the magnetic powder brake using the RS232 cable.
Before using the brake controller and magnetic powder brake unit, you must first
calibrate the torque display of the brake controller to 0 kg.m by adjusting the zero adj
knob located on the rear panel of magnetic powder brake unit with power on.
DOKUZ EYLL UNIVERSITY
Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering
EE323 Armature Windings and Induction Machines
Experimental Work
2. Install the required modules in the experimental frame. Construct the circuit in
accordance with the circuit diagram in Fig-1 and the connection diagram in
Fig-2. Note: The thermal switches of the wound-rotor induction machine and
magnetic powder brake unit must be connected together. The stator windings
of the motor are connected in delta.
3. Sequentially turn on the Brake Controller, Magnetic Power Brake Unit, 3-P
current limit protection switch, and three-phase power supply.
4. Manipulate the brake controller to operate in Mode\Closed Loop\Constant
Torque mode and set the output torque to 0.0 kg.m. If the controller does not
operate normally, reboot it by pressing RESET button.
5. Manipulate the brake controller such that output torque is adjusted to the
values given in Table-1 by operating the unit in Mode\Closed Loop\Constant
Torque mode. Complete Table-1.
6. Sequentially turn off the three-phase power supply, 3-P current limit protection
switch modules, magnetic powder brake unit, and brake controller.
7. Using the results of Table-1, plot the graphs of speed, current, and efficiency
vs torque.
Calculate the input power, output power and efficiency using the following formulas:
Input Power:
V I
Pin
1 , ll
Pout
Output Power:
Efficiency:
P
2 n (rpm ) T ( Nm )
out
60
100%
in
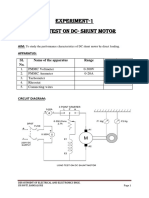
PROCEDURE: (Part-2: blocked rotor test)
Set up the equipment as shown in Fig-3.
1. Install the required modules in the experimental frame. Construct the circuit in
accordance with the connection diagram in Fig-3.
2. Sequentially turn on the Brake Controller, Magnetic Power Brake Unit, 3-P current
limit protection switch, three-phase power supply, and 3-phase AC/DC power supply.
3. Manipulate brake controller to operate in mode\open loop\manual mode and
set the output voltage to7 volt.
4. Press the on pushbutton on three-phase power supply module. Set the on-off
switch on fourpole switch module to on position for starting the motor in delta.
5. On the 3 phase AC/DC power supply, slowly turn the voltage control knob
clockwise so that the motor current I is equal to the rated value of 2.0 A.
6. Record the motor current motor voltage E motor power P and power factor
cos values displayed by digital power analysis meter and complete Table-2.
DOKUZ EYLL UNIVERSITY
Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering
EE323 Armature Windings and Induction Machines
Experimental Work
7. Sequentially turn off the 3-phase AC/DC power supply, three-phase power
supply, 3-P current limit protection switch modules, magnetic powder brake
unit, and brake controller.
RESULTS:
Explain the main features you have learned from the experiments. Discuss on the
graphics obtained from the tests and comment on the results in your report, also
equivalent circuit parameters must be calculated.
Table-1. Measured values with wound-rotor induction motor with shorted rotor windings
Measured
values
Torque (T, Speed
kg.m)
(n,rpm)
0.00
0.10
0.15
0.20
0.25
0.30
Voltage
(V1, V)
Current
(I1,A)
Input Power
Factor
Calculated
values
Input Power
(Pin,W)
Output Power
(Pout, W)
Efficiency
(%)
Table-2. Measured values with wound-rotor induction motor with blocked rotor test
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- SINGLE PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR - Part2Document6 paginiSINGLE PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR - Part2NUR SYAFIQAH BINTI MOHD SHAHIR STUDENTÎncă nu există evaluări
- DL 30130 - Extract From The ManualDocument6 paginiDL 30130 - Extract From The ManuallpestanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Induction Motor Lab ManualDocument11 paginiInduction Motor Lab ManualRabah ZaimeddineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 5 and 6 No WatermarkDocument44 paginiExperiment 5 and 6 No Watermarkomgeeeeee8Încă nu există evaluări
- SINGLE PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR - Part1Document6 paginiSINGLE PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR - Part1NUR SYAFIQAH BINTI MOHD SHAHIR STUDENTÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3locked Rotor TestDocument5 pagini3locked Rotor TestAlpagut Sencer KaracaÎncă nu există evaluări
- unit14三相同步M 100709Document22 paginiunit14三相同步M 100709rastgonikoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 15 Unit14Document22 pagini15 Unit14Marlon AnchetaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Objectives: Experiment No. 1 Jog ControlDocument19 paginiObjectives: Experiment No. 1 Jog ControlDanica AquinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 3Document7 paginiExperiment 3NUR SYAFIQAH BINTI MOHD SHAHIR STUDENTÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exp2 EED3012 WRIMMotor Experiments FH2MK3Document3 paginiExp2 EED3012 WRIMMotor Experiments FH2MK3EnesVSÎncă nu există evaluări
- EEE363 (Exp 9) Study of The Torque Speed Relationship of Wound Rotor Induction Motor With Variable ResistanceDocument7 paginiEEE363 (Exp 9) Study of The Torque Speed Relationship of Wound Rotor Induction Motor With Variable Resistancesalad.ass420420Încă nu există evaluări
- Research On Velocity Control Methods For Driving Motor of 126l V High Voltage Circuit Breal ErDocument4 paginiResearch On Velocity Control Methods For Driving Motor of 126l V High Voltage Circuit Breal ErBeema ThangarajanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control System Lab EE-324-FDocument45 paginiControl System Lab EE-324-FBalraj SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample Expt Foward-Reverse-StarterDocument5 paginiSample Expt Foward-Reverse-StarterDanica AquinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Star DeltaDocument6 paginiStar DeltaNurain XuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exp1 EED3012 WRIMMotor Experiments FH2MK3Document3 paginiExp1 EED3012 WRIMMotor Experiments FH2MK3EnesVSÎncă nu există evaluări
- American International University-Bangladesh: Title: Study of Wound-Rotor Induction Motor - Part IIDocument5 paginiAmerican International University-Bangladesh: Title: Study of Wound-Rotor Induction Motor - Part IIS M AkashÎncă nu există evaluări
- SMD Lab - 5th Sem Complete ManualDocument59 paginiSMD Lab - 5th Sem Complete ManualPARKHI KAMBOJÎncă nu există evaluări
- EM2 - Lab - 10 - Synchronous Motor Part I - STD PDFDocument7 paginiEM2 - Lab - 10 - Synchronous Motor Part I - STD PDFneonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application On Three Phase Induction Motor: ObjectivesDocument5 paginiApplication On Three Phase Induction Motor: ObjectivesAdnan AltafÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 2 - Iduction Motor Drive Using Slip Power RecoveryDocument6 paginiExperiment 2 - Iduction Motor Drive Using Slip Power RecoveryDeepak BansalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control System Lab EE-324-FDocument45 paginiControl System Lab EE-324-FDheeraj KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment Laboratory Report No.3 DraftDocument8 paginiExperiment Laboratory Report No.3 DraftSherwin CaringalÎncă nu există evaluări
- (EM 2) - Lab Manual 4th SemDocument43 pagini(EM 2) - Lab Manual 4th SemTime LapserÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practical 6 Star Delta StarterDocument4 paginiPractical 6 Star Delta StarterMohammad Nurayzat Johari50% (2)
- Lab Report 09Document5 paginiLab Report 09Shameen MazharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Remote and Automatic ControlDocument11 paginiRemote and Automatic ControldenramrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment No. 09 - Speed ControlDocument6 paginiExperiment No. 09 - Speed Controlabheetpethe.scoe.entcÎncă nu există evaluări
- LAB-VOLT 3-Phase Induction (Squirrel-Cage) MachinesDocument11 paginiLAB-VOLT 3-Phase Induction (Squirrel-Cage) Machinesanyr2Încă nu există evaluări
- 4364 533 IdcDocument3 pagini4364 533 Idcyogesh_b_kÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ecte 323 Labexperiment 3Document13 paginiEcte 323 Labexperiment 3Malik ZaidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment #7: Slip Ring Motor: Alasala CollegesDocument5 paginiExperiment #7: Slip Ring Motor: Alasala CollegesabdullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Total 363 Lab ManualDocument67 paginiTotal 363 Lab ManualBisal Sarker JoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8 Indution MotorDocument4 pagini8 Indution MotorSandrawarman BalasundramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 5 PDFDocument8 paginiExperiment 5 PDFRegar EfendiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Marine and Offshore Power SystemDocument46 paginiMarine and Offshore Power SystemMamta MrjnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Controlled Three Phase DrivesDocument160 paginiControlled Three Phase Drivesakoca23Încă nu există evaluări
- E M L - M: Lectrical Achines AB AnualDocument29 paginiE M L - M: Lectrical Achines AB AnualSuresh Kumar MunnurukapuÎncă nu există evaluări
- C6.6 ENGINE - GENERATOR SET Operation & Maintenance Manuals - PARALLEL OPERATIONDocument4 paginiC6.6 ENGINE - GENERATOR SET Operation & Maintenance Manuals - PARALLEL OPERATIONsuperteffyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brake Load Test of Squirel Cage Induction Motor 3 PhaseDocument7 paginiBrake Load Test of Squirel Cage Induction Motor 3 Phasejassisc100% (1)
- 2011 Implementation and Control of An Acdcac Converter For Electric Vehicle Application1Document6 pagini2011 Implementation and Control of An Acdcac Converter For Electric Vehicle Application1ashikhmd4467Încă nu există evaluări
- Em 30 02 01Document25 paginiEm 30 02 01ChanKamMinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electric Drive Lab Laboratory Manual: Dev Bhoomi Institute Chakrata Road, Navgaoun Manduwala, UttarakhandDocument15 paginiElectric Drive Lab Laboratory Manual: Dev Bhoomi Institute Chakrata Road, Navgaoun Manduwala, Uttarakhandjaya mishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 19 Speed PDFDocument8 pagini19 Speed PDFNur Muhammad DzikriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ee0041l-Finals (Sa) KilakigaDocument85 paginiEe0041l-Finals (Sa) KilakigaKYLE LEIGHZANDER VICENTEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Soft Starting and Braking Application For Squirrel-Cage Induction Motors Operating in Intermittent DutyDocument11 paginiSoft Starting and Braking Application For Squirrel-Cage Induction Motors Operating in Intermittent Dutyni60Încă nu există evaluări
- Eecs 3480 Electrical Energy Conversion Lab Manual Version 4Document54 paginiEecs 3480 Electrical Energy Conversion Lab Manual Version 4mohammed100% (1)
- Experiment No. 1 The Separately Excited DC Shunt Generator: ObjectiveDocument12 paginiExperiment No. 1 The Separately Excited DC Shunt Generator: ObjectiveedwardÎncă nu există evaluări
- IM - Motors To GensDocument4 paginiIM - Motors To Gensmenilanjan89nLÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 Part2-1520417690Document6 pagini5 Part2-1520417690rastgonikoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Emlab 2Document21 paginiEmlab 2hafizrahimmitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Voltage Regulation of alternator-EMF, MMF - ZPF-Expt-7Document7 paginiVoltage Regulation of alternator-EMF, MMF - ZPF-Expt-7Gingka HaganeÎncă nu există evaluări
- EEE363 (Exp 7) Study of The Starting Characteristics and Torque Speed Relationship of Three Phase Synchronous MotorDocument6 paginiEEE363 (Exp 7) Study of The Starting Characteristics and Torque Speed Relationship of Three Phase Synchronous Motorsalad.ass420420Încă nu există evaluări
- EE 6351 - Electrical Drives and Controls (EDC) QBDocument160 paginiEE 6351 - Electrical Drives and Controls (EDC) QBkannanchammyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 3 Squirrel Cage Induction Machine-1Document8 paginiLab 3 Squirrel Cage Induction Machine-1max100% (1)
- Lab9 - Shunt and Cumulative Compound DC GeneratorsDocument12 paginiLab9 - Shunt and Cumulative Compound DC GeneratorsMomal ARÎncă nu există evaluări
- 053 Ferreira FinalDocument15 pagini053 Ferreira Finalluis900000Încă nu există evaluări
- Power Electronics: Lecture Notes of Power Electronics CourseDe la EverandPower Electronics: Lecture Notes of Power Electronics CourseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Machines: Lecture Notes for Electrical Machines CourseDe la EverandElectrical Machines: Lecture Notes for Electrical Machines CourseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eed3018 Experiment 7Document1 paginăEed3018 Experiment 7EnesVSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eed3018 Experiment 9Document1 paginăEed3018 Experiment 9EnesVSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Loop Out (01H), A: Eed 3018 Laboratory Experiment 8: Non-Maskable Interrupt and Simple I/O With Z80 PioDocument1 paginăLoop Out (01H), A: Eed 3018 Laboratory Experiment 8: Non-Maskable Interrupt and Simple I/O With Z80 PioEnesVSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eed 3018 Laboratory Experiment 5: Z80 I/O Operations: Preliminary WorkDocument1 paginăEed 3018 Laboratory Experiment 5: Z80 I/O Operations: Preliminary WorkEnesVSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eed 3018 Laboratory Experiment 4: Program Loops: Preliminary WorkDocument1 paginăEed 3018 Laboratory Experiment 4: Program Loops: Preliminary WorkEnesVSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eed3018 Experiment 6Document1 paginăEed3018 Experiment 6EnesVSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eed3018 Experiment 3Document1 paginăEed3018 Experiment 3EnesVSÎncă nu există evaluări
- SBC (Subtract With Borrow)Document36 paginiSBC (Subtract With Borrow)EnesVSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exp1 EED3012 WRIMMotor Experiments FH2MK3Document3 paginiExp1 EED3012 WRIMMotor Experiments FH2MK3EnesVSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Micro Lecture 6Document34 paginiMicro Lecture 6EnesVSÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Input and Output Devices Are Assigned and Identified by 16-Bit AddressesDocument43 paginiThe Input and Output Devices Are Assigned and Identified by 16-Bit AddressesEnesVSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Micro Lecture 7Document26 paginiMicro Lecture 7EnesVSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eed 3018 Laboratory Experiment 1: Basic Operations in Z80: Preliminary WorkDocument1 paginăEed 3018 Laboratory Experiment 1: Basic Operations in Z80: Preliminary WorkEnesVSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Micro Lecture 4Document47 paginiMicro Lecture 4EnesVSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microprocessor Systems: Asst - Prof.Dr. Haldun SarnelDocument82 paginiMicroprocessor Systems: Asst - Prof.Dr. Haldun SarnelEnesVSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Z80 CPU Instruction Description: - 158 Different Instruction Types - Instruction GroupsDocument41 paginiZ80 CPU Instruction Description: - 158 Different Instruction Types - Instruction GroupsEnesVSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eed3018 Experiment 7Document1 paginăEed3018 Experiment 7EnesVSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eed3018 Experiment 3Document1 paginăEed3018 Experiment 3EnesVSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exp2 EED3012 WRIMMotor Experiments FH2MK3Document3 paginiExp2 EED3012 WRIMMotor Experiments FH2MK3EnesVSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eed 3018 Laboratory Experiment 1: Basic Operations in Z80: Preliminary WorkDocument1 paginăEed 3018 Laboratory Experiment 1: Basic Operations in Z80: Preliminary WorkEnesVSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eed 3018 Laboratory Experiment 4: Program Loops: Preliminary WorkDocument1 paginăEed 3018 Laboratory Experiment 4: Program Loops: Preliminary WorkEnesVSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control Systems - Experiment 3Document16 paginiControl Systems - Experiment 3EnesVSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eed 2008 - HW2Document1 paginăEed 2008 - HW2EnesVSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eed 3018 Laboratory Experiment 1: Basic Operations in Z80: Preliminary WorkDocument1 paginăEed 3018 Laboratory Experiment 1: Basic Operations in Z80: Preliminary WorkEnesVSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Slide 2Document89 paginiSlide 2EnesVSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control Systems - Experiment 2Document5 paginiControl Systems - Experiment 2EnesVSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kirloskar MRP Price ListDocument144 paginiKirloskar MRP Price Listengg2012elect85% (26)
- APSPDCL Electrical Technical Question Papers Answers Free Download PDFDocument13 paginiAPSPDCL Electrical Technical Question Papers Answers Free Download PDFmurali4u35100% (2)
- 18EES101J Basic Electrical Engineering EeeDocument122 pagini18EES101J Basic Electrical Engineering EeeShaik RazaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- User'S Manual Synop - Synchronous Generator Optimization Synan - Synchronous Generator AnalysisDocument20 paginiUser'S Manual Synop - Synchronous Generator Optimization Synan - Synchronous Generator AnalysisguestÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 - AC FundamentalsDocument21 paginiChapter 3 - AC FundamentalsNur AfiqahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Performance Testing of AC MotorsDocument3 paginiElectrical Performance Testing of AC Motorsnguyen_huu_duy_hcmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Machines (Induction Motor)Document5 paginiElectrical Machines (Induction Motor)Faizan MateenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Generator RotorDocument84 paginiGenerator RotorVENUÎncă nu există evaluări
- Slipring ManualDocument66 paginiSlipring ManualRobin GhekiereÎncă nu există evaluări
- Motor Protection - Types of Faults and Protection DevicesDocument35 paginiMotor Protection - Types of Faults and Protection Deviceswondu aÎncă nu există evaluări
- Induction Motor Circle Diagrams: GP Technologies LTDDocument5 paginiInduction Motor Circle Diagrams: GP Technologies LTDAmmar Al-KindyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9A02306 Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument4 pagini9A02306 Basic Electrical EngineeringsivabharathamurthyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Generator Testing Project ReportDocument51 paginiGenerator Testing Project Reportsudheer0% (1)
- Lsa 53.2 Lsa 54.2Document40 paginiLsa 53.2 Lsa 54.2محمود المستكاويÎncă nu există evaluări
- Encoder EUCHNER ABSOLUTO PDFDocument80 paginiEncoder EUCHNER ABSOLUTO PDFeletropaulomococa77% (13)
- J14Document10 paginiJ14RifanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power SystemsDocument54 paginiPower SystemsBindu ChipiriÎncă nu există evaluări
- 03 - Thomson Et Al - Current Signature Analysis To Detect Induction Motors FaultsDocument9 pagini03 - Thomson Et Al - Current Signature Analysis To Detect Induction Motors FaultsCar AljaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Caterpillar R448 Voltage Regulator Setup, Troubleshooting, and Correct Part Identification Guide (4450, 4467)Document7 paginiCaterpillar R448 Voltage Regulator Setup, Troubleshooting, and Correct Part Identification Guide (4450, 4467)CEVegaO100% (1)
- A Review of The Design Issues and Techniques For Radial-Flux Brush Surface and Internal Rare Earth PM MotorsDocument17 paginiA Review of The Design Issues and Techniques For Radial-Flux Brush Surface and Internal Rare Earth PM MotorsأسامةبوعزيزÎncă nu există evaluări
- Turbina Kaplan BulboDocument87 paginiTurbina Kaplan BulboJuanRamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Surface Permanent Magnet Motors: How Does A PM Motor Work?Document3 paginiSurface Permanent Magnet Motors: How Does A PM Motor Work?HAMID SULIAMANÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transformer & Speed Voltages PDFDocument41 paginiTransformer & Speed Voltages PDFAbhishek KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3SS-MUMI-00902 - Standard LV Motor SpecDocument17 pagini3SS-MUMI-00902 - Standard LV Motor SpecAshishÎncă nu există evaluări
- Improving Power System Stabilizer & Load Freqencey Control (Challenges and Solutions)Document38 paginiImproving Power System Stabilizer & Load Freqencey Control (Challenges and Solutions)hendroshadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Machine Drives: Dr. Arsalan ArifDocument6 paginiElectrical Machine Drives: Dr. Arsalan ArifFaraz AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 101Document48 paginiWeek 101Raphael SebucÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eletrical Machines (K-Wiki - Synchronous Machines)Document59 paginiEletrical Machines (K-Wiki - Synchronous Machines)qwer100% (1)
- Oral Question Bank For Meo Class IiDocument9 paginiOral Question Bank For Meo Class IiKeshav ShahiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Champion Generator TestDocument2 paginiChampion Generator TestMichael PorterÎncă nu există evaluări