Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
CKD causes, symptoms, stages & treatment
Încărcat de
KarenLópezAragónDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
CKD causes, symptoms, stages & treatment
Încărcat de
KarenLópezAragónDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
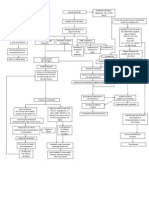
Chronic kidney disease
Chronic kidney disease is the slow loss of kidney function over time. The main
function of the kidneys is to remove wastes and excess water from the body.
Causes
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) slowly gets worse over time. In the early stages,
there may be no symptoms. The loss of function usually takes months or years
to occur. It may be so slow that symptoms do not appear until kidney function
is less than one-tenth of normal.
The final stage of chronic kidney disease is called end-stage renal
disease (ESRD). At this stage, the kidneys are no longer able to remove enough
wastes and excess fluids from the body. The patient needs dialysis or a kidney
transplant.
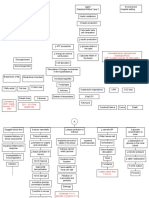
Many other diseases and conditions can damage the kidneys, including:
Autoimmune disorders (such as systemic lupus
erythematosus and scleroderma)
Birth defects of the kidneys (such as polycystic kidney disease)
Certain toxic chemicals
Injury or trauma
Kidney stones and infection
Problems with the arteries leading to or inside the kidneys
Some pain medications and other drugs (such as cancer drugs)
Reflux nephropathy (in which the kidneys are damaged by the backward
flow of urine into the kidneys)
Other kidney diseases
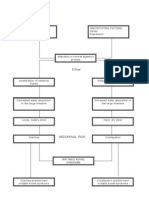
Chronic kidney disease leads to a buildup of fluid and waste products in the
body. This condition affects most body systems and functions, including:
Blood pressure control
Red blood cell production
Vitamin D and bone health
Symptoms
The early symptoms of chronic kidney disease are also symptoms of other
illnesses. These symptoms may be the only signs of kidney disease until the
condition is more advanced.
Symptoms may include:
Appetite loss
General ill feeling and fatigue
Headaches
Itching (pruritus) and dry skin
Nausea
Weight loss without trying to lose weight
Other symptoms that may develop, especially when kidney function has gotten
worse, include:
Abnormally dark or light skin
Bone pain
Brain and nervous system symptoms:
Drowsiness and confusion
Problems concentrating or thinking
Numbness in the hands, feet, or other areas
Muscle twitching or cramps
Breath odor
Easy bruising, bleeding, or blood in the stool
Excessive thirst
Frequent hiccups
Low level of sexual interest and impotence
Menstrual periods stop (amenorrhea)
Shortness of breath
Sleep
problems,
such
as insomnia, restless
and obstructive sleep apnea
Swelling of the feet and hands (edema)
Vomiting, typically in the morning
leg
syndrome,
Many people are not diagnosed with chronic kidney disease until they have lost
most of their kidney function.
There is no cure for chronic kidney disease. Untreated, it usually worsens
to end-stage renal disease. Lifelong treatment may control the symptoms of
chronic kidney disease.
Treating the condition that is causing the problem may help prevent or delay
chronic kidney disease. People who have diabetes should control their blood
sugar and blood pressure levels and should not smoke.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Predisposing Conditions, Management and Prevention of Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument52 paginiPredisposing Conditions, Management and Prevention of Chronic Kidney DiseaseSaad MotawéaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Age Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat IntakeDocument3 paginiAge Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat Intakenursing concept mapsÎncă nu există evaluări
- CKD Guide: Risks, Stages, and Management of Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument54 paginiCKD Guide: Risks, Stages, and Management of Chronic Kidney DiseaseJosh Matthew RosalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assaz Predisposing Factors: Advanced Age Gender Ileal Resection/Disease RaceDocument3 paginiAssaz Predisposing Factors: Advanced Age Gender Ileal Resection/Disease RaceryanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chronic Kidney Disease: A. Pathophysiology A. Schematic DiagramDocument3 paginiChronic Kidney Disease: A. Pathophysiology A. Schematic DiagramDaniel GeduquioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hepatic EncephalopathyDocument3 paginiHepatic EncephalopathyAnonymous GIGXKjfLÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of ESRD: Organ Dysfunctions & Associated AbnormalitiesDocument5 paginiPathophysiology of ESRD: Organ Dysfunctions & Associated AbnormalitiesCarl JardelezaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Schematic Diagram of CKD Sec. To DM Nephropathy, DM Type 2, DM FootDocument8 paginiSchematic Diagram of CKD Sec. To DM Nephropathy, DM Type 2, DM Footbeuwolfagate50% (2)
- Liver Cirrhosis: (Alterations in Metabolic and Endocrine Functions)Document8 paginiLiver Cirrhosis: (Alterations in Metabolic and Endocrine Functions)Jorie RocoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Osteosarcoma-Ana and PhysiologyDocument4 paginiOsteosarcoma-Ana and PhysiologyNeirfla WassabiÎncă nu există evaluări
- "Acute Coronary Syndrome Non ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction, Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes Mellitus Type 2, and Community Acquired Pneumonia" Client Centered PathophysiologyDocument3 pagini"Acute Coronary Syndrome Non ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction, Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes Mellitus Type 2, and Community Acquired Pneumonia" Client Centered PathophysiologyCarl Elexer Cuyugan Ano50% (2)
- Annotated Group 2 Impetigo Concept Mapping 1Document30 paginiAnnotated Group 2 Impetigo Concept Mapping 1DHANE ANN CAMPOSANOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of DiarrheaDocument3 paginiPathophysiology of DiarrheaFathur RahmatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bladder Cancer Types, Symptoms, Tests & TreatmentDocument1 paginăBladder Cancer Types, Symptoms, Tests & TreatmentCarmina AguilarÎncă nu există evaluări
- End Stage Renal Disease: A. Pathophysiology A. Schematic DiagramDocument2 paginiEnd Stage Renal Disease: A. Pathophysiology A. Schematic DiagramSharmaine Camille de LeonÎncă nu există evaluări
- NF DR Concept Map Week 12Document4 paginiNF DR Concept Map Week 12Kyra Bianca R. FamacionÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP 2 MiDocument16 paginiNCP 2 MiWendy EscalanteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding Addison's Disease: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument10 paginiUnderstanding Addison's Disease: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentAnn KelseaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of Chronic Renal Failure PDFDocument4 paginiPathophysiology of Chronic Renal Failure PDFDewa Made Rendy SanjayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of DMDocument4 paginiPathophysiology of DMNicole Louise N. VillanuevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hypertension Obstruction: Chronic Renal FailureDocument3 paginiHypertension Obstruction: Chronic Renal FailureDiane-Richie PezLo100% (1)
- NCP 1Document3 paginiNCP 1kat2111993Încă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of Portal HYPERTENSION PDFDocument11 paginiPathophysiology of Portal HYPERTENSION PDFCamilo VidalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Buerger DiseaseDocument3 paginiBuerger DiseaseElmer DizonÎncă nu există evaluări
- HyponatremiaDocument6 paginiHyponatremiaJaymart Saclolo CostillasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case AnalysisDocument12 paginiCase AnalysisFroilan TaracatacÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concept Map para ThyroidDocument7 paginiConcept Map para ThyroidAllene PaderangaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Path o PhysiologyDocument9 paginiPath o PhysiologyKyle Ü D. CunanersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology-Kni Ns PLZZZDocument8 paginiPathophysiology-Kni Ns PLZZZAnna Lira Manluyang MungcalÎncă nu există evaluări
- OUR LADY OF FATIMA UNIVERSITY Case Study on Post Streptococcal GlomerulonephritisDocument20 paginiOUR LADY OF FATIMA UNIVERSITY Case Study on Post Streptococcal GlomerulonephritisMikaCasimiroBalunanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compare and Contrast Two Obstructive Lung Disorders: Asthma vs COPDDocument1 paginăCompare and Contrast Two Obstructive Lung Disorders: Asthma vs COPDAriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Cholecystolithiasis - G4 SB2Document125 paginiAcute Cholecystolithiasis - G4 SB2Jeofy PamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- HemorrhoidsDocument15 paginiHemorrhoidspologroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pleural Effusions: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument20 paginiPleural Effusions: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentSadia GulraizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 Hospital CaseDocument3 paginiDiabetes Mellitus Type 2 Hospital CaseAngel FiloteoÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP CvaDocument7 paginiNCP CvaEmerson SilverioÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Case Study On SchistosomiasisDocument154 paginiA Case Study On SchistosomiasisCarmellaDawn100% (1)
- Glomerulonephritis 10Document5 paginiGlomerulonephritis 10Eden Jay Calija AgoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- PathophysiologyDocument1 paginăPathophysiologyHazel PalomaresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology Diagram of Kawasaki Disease: Precipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorsDocument2 paginiPathophysiology Diagram of Kawasaki Disease: Precipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorsAb Staholic Boii100% (1)
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument33 paginiChronic Kidney DiseasesexiiimammaÎncă nu există evaluări
- annotated-COURSE TASK 2 INCREASED ICPDocument8 paginiannotated-COURSE TASK 2 INCREASED ICPJake AllegoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Addison'sDocument4 paginiAddison'sKoRnflakesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kidney Function and Chronic Renal FailureDocument50 paginiKidney Function and Chronic Renal FailureKevin MontoyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stroke: Hypertensive UrgencyDocument4 paginiStroke: Hypertensive UrgencyMaricar TaboraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pa Tho Irritable Bowel SyndromeDocument1 paginăPa Tho Irritable Bowel Syndromekaye0403Încă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and Physiology PneumoniaDocument4 paginiAnatomy and Physiology PneumoniaJohnson MallibagoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Schistosomiasis (From Anatomy To Pathophysiology)Document10 paginiSchistosomiasis (From Anatomy To Pathophysiology)Tiger Knee100% (1)
- Chapter 27: Fluid and Electrolyte BalanceDocument26 paginiChapter 27: Fluid and Electrolyte BalanceMarwan M.Încă nu există evaluări
- Health TeachingDocument3 paginiHealth TeachingNyj QuiñoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Appendicitis & NPI - Edmalyn GozarDocument78 paginiAcute Appendicitis & NPI - Edmalyn GozarKM100% (1)
- Cs AGNDocument177 paginiCs AGNMa Rafaela Rosales PalomponÎncă nu există evaluări
- Serum ElectrolytesDocument2 paginiSerum ElectrolytesKervin CablaidaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hypothyroidism PathophysiologyDocument1 paginăHypothyroidism PathophysiologyCleo Joyce C. CristalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Complications of Plaster Cast PATIENT LEAFLETDocument6 paginiComplications of Plaster Cast PATIENT LEAFLETRadiyan MeidhiyantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Schematic Diagram: Signs and Symptoms: Headache, Unconsciousness, Nausea and Vomiting, Visual DisturbancesDocument3 paginiSchematic Diagram: Signs and Symptoms: Headache, Unconsciousness, Nausea and Vomiting, Visual DisturbancesJosett RomanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study on Graded Return to Work Program for Carpal Tunnel SyndromeDocument11 paginiCase Study on Graded Return to Work Program for Carpal Tunnel SyndromeMargeaux Deb Bartholomew CarleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Discharge PlanDocument1 paginăDischarge PlanKamille Bianca Macapagal ÜÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human Diseases Case Study 18 ADocument4 paginiHuman Diseases Case Study 18 Aairickann100% (1)
- Kidney Failure SHORT INFODocument2 paginiKidney Failure SHORT INFOLisa BlackpinkÎncă nu există evaluări
- GastritisDocument1 paginăGastritisKarenLópezAragónÎncă nu există evaluări
- American CultureDocument3 paginiAmerican CultureKarenLópezAragónÎncă nu există evaluări
- Causes, Health Risks and Measures of ObesityDocument2 paginiCauses, Health Risks and Measures of ObesityKarenLópezAragónÎncă nu există evaluări
- CKD causes, symptoms, stages & treatmentDocument2 paginiCKD causes, symptoms, stages & treatmentKarenLópezAragónÎncă nu există evaluări
- 120002677E v02 SD BIOLINE Malaria RDT Series - BrochureDocument4 pagini120002677E v02 SD BIOLINE Malaria RDT Series - BrochureBobbyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kumar Indoor Air Quality Study Summary - Proffer SweepsDocument1 paginăKumar Indoor Air Quality Study Summary - Proffer SweepsAnonymous Pb39klJÎncă nu există evaluări
- Global Infectious Disease Surveillance and DetectionDocument285 paginiGlobal Infectious Disease Surveillance and DetectionAlison CericattoÎncă nu există evaluări
- WHO 2011 Typhoid FeverDocument39 paginiWHO 2011 Typhoid FeverVizzi Alvi Fitrah NasutionÎncă nu există evaluări
- USPSTF RecommendationsDocument3 paginiUSPSTF RecommendationsKevinMathewÎncă nu există evaluări
- UNICEF Guinea COVID-19 Situation Report No.2Document3 paginiUNICEF Guinea COVID-19 Situation Report No.2UNICEFGuineaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Guide To Introducing: Inactivated Polio VaccineDocument48 paginiA Guide To Introducing: Inactivated Polio VaccineJjNoznaugÎncă nu există evaluări
- SSI Guide BookDocument88 paginiSSI Guide Bookutami23Încă nu există evaluări
- Endodontic Surgery: Incision and DrainageDocument8 paginiEndodontic Surgery: Incision and DrainageHadoo OolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guide LymphologyDocument174 paginiGuide LymphologyMaria100% (1)
- How To Write An Abstract UcsbDocument14 paginiHow To Write An Abstract UcsbJohn ReyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uveitis WorkupDocument75 paginiUveitis WorkupGopal RaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 15 - Chapter 7 PDFDocument4 pagini15 - Chapter 7 PDFRamÎncă nu există evaluări
- We Take Pride in Our Denagard InjectionDocument173 paginiWe Take Pride in Our Denagard Injectionnick224100% (1)
- Newborn Physical ExaminationDocument4 paginiNewborn Physical ExaminationastrikusumadewiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Informative Essay For COVID 19Document2 paginiInformative Essay For COVID 19Monaliza Gamposilao100% (3)
- Neurology 5 Ed. Usa: Mcgraw-Hill Inc, 1993:612-616.: Daftar PustakaDocument4 paginiNeurology 5 Ed. Usa: Mcgraw-Hill Inc, 1993:612-616.: Daftar PustakaDwi WaskitoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tuesday, October 21, 2014 EditionDocument12 paginiTuesday, October 21, 2014 EditionFrontPageAfricaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cihm Admission FormDocument7 paginiCihm Admission FormKrishna Gopal DubeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coronavirus ThesisDocument4 paginiCoronavirus Thesisdnr68wp2100% (2)
- Public Health Lab RolesDocument45 paginiPublic Health Lab RolesLarisa Izabela AndronecÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Budget of Dumb Asses 2011Document2 paginiA Budget of Dumb Asses 2011piano1985Încă nu există evaluări
- What Is Bacteria - What Are BacteriaDocument15 paginiWhat Is Bacteria - What Are BacteriaFernando OssÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chest Pain Non TraumaDocument45 paginiChest Pain Non TraumaTita LuthfiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Economics of Conspiracy TheoriesDocument8 paginiThe Economics of Conspiracy Theorieszadanliran100% (1)
- Face To Face ClassesDocument1 paginăFace To Face ClassesRalen Beronilla Odchigue100% (1)
- Dr. Heston Standing Orders LandscapeDocument3 paginiDr. Heston Standing Orders LandscapeJosh Heston100% (1)
- Concept Map Week 4 Ans2 RevisedDocument2 paginiConcept Map Week 4 Ans2 Revisedapi-351433633Încă nu există evaluări
- Nasal Vestibular Furunculosis Presenting As The Rudolph SignDocument2 paginiNasal Vestibular Furunculosis Presenting As The Rudolph Signyeni novi yantiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology and SocietyDocument51 paginiBiology and SocietyVisminda SebastianÎncă nu există evaluări