Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Particular Nature of Matter, Diffusion
Încărcat de
ChaudhryAbdullahDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Particular Nature of Matter, Diffusion
Încărcat de
ChaudhryAbdullahDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
O LEVEL PAST PAER QUESTIONS.
______________________________________________________________________________
TOPIC 1: PARTICULAR NATURE OF MATTER, DIFFUSION.
Paper 1- Multiple choice Questions.
1- By which process does all the smell of cooking spread to all rooms in a house?
A- decomposition
[J00/Q1]
B-diffusion
C-displacement
D-distillation
2- What can be deduced about two gases that have the same molecular mass?
A-They have the same solubility in water at room temperature.
B- They have the same boiling point.
C-They have the same number of atoms in one molecule.
D-They have the same rate of diffusion at room temperature.
[D00/Q2]
3- Which property of a gas affects the rate at which it spreads throughout a
laboratory?
A boiling point
B molecular mass
C reactivity
D solubility in water
[Nov2002/Q1]
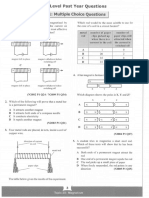
4- The graph gives the melting points of mixtures of lead and tin.
The graph shows that any mixture of lead and tin must have a melting point
A above that of tin.
B below that of lead.
C below that of both tin and lead.
D between that of tin and lead.
[Nov2002/Q2]
O LEVEL PAST PAER QUESTIONS.
______________________________________________________________________________
TOPIC 1: PARTICULAR NATURE OF MATTER, DIFFUSION.
5- The apparatus shown in the diagram was set up.
Over a period of time how will the water level at X change?
A It will fall, then rise and return to X.
B It will fall and remain at a lower level.
C It will rise, then fall then return to X.
D It will rise and remain at a higher level.
[Nov 2003/Q3]
6- A gas, X, is less dense than air and insoluble in water.
Which method cannot be used to collect the gas?
O LEVEL PAST PAER QUESTIONS.
______________________________________________________________________________
TOPIC 1: PARTICULAR NATURE OF MATTER, DIFFUSION.
[Nov 2003/Q2]
7- Methylamine, CH3NH2 (Mr = 31), and hydrogen chloride, HC l (Mr = 36.5) are both gases
which are soluble in water.
The gases react together to form a white solid, methylammonium chloride.
In an experiment to demonstrate rates of diffusion the following apparatus is set up.
Where will the white solid form?
8-A liquid boils at a temperature of 100 oC.
Which other property of the liquid proves that it is pure water?
A It does not leave a residue when boiled.
B It freezes at 0 oC.
C It is neither acidic nor alkaline.
D It turns white anhydrous copper(II) sulphate blue.
[Nov -2004/Q3]
9- In which conversion do H2O molecules lose speed?
A ice water
B ice steam
C steam ice
D water steam A ice water
[Nov-2004/Q5]
O LEVEL PAST PAER QUESTIONS.
______________________________________________________________________________
TOPIC 1: PARTICULAR NATURE OF MATTER, DIFFUSION.
10-The experiment is set up as shown and left until there is no further change.
What is observed?
A a colourless layer below a purple layer
B a colourless liquid with the purple crystal unchanged
C a purple layer below a colourless layer
D a uniformly purple solution
[May-2005/Q1]
11- A sample of a pure compound is heated until it is completely molten and the
compound is then
allowed to cool until it is completely solid again.
The graph shows how the temperature of the compound changes with time.
When are liquid and solid
both present?
A
B
C
D
P to Q and R to S
P to Q
Q to R
R to S
[May
-2005/Q3]
12- A beaker of nitrogen is inverted over a porous pot containing carbon monoxide
as shown.
The water level does not change.
What is the reason for this?
A Both gases are diatomic.
B Nitrogen is an unreactive gas.
C The gas particles are too large to pass
through the porous pot.
D The two gases have the same relative
molecular mass.
O LEVEL PAST PAER QUESTIONS.
______________________________________________________________________________
TOPIC 1: PARTICULAR NATURE OF MATTER, DIFFUSION.
[May-2005/Q4]
13- Which of the following is a pure compound?
A ethanol
B petrol
C steel
D tap water
[Nov-2005/Q1]
14- The coverplate is removed from the gas jars shown in the diagram. After
several days, the colour
of the gas is the same in both jars.
Which statement explains this change?
A Oxygen and bromine gases have equal densities.
B Oxygen and bromine molecules are in random motion.
C Oxygen and bromine molecules diffuse at the same rate.
D Equal volumes of oxygen and bromine contain equal numbers
of molecules.
[NO5/Q3][J01/Q1]
15-The table gives data about four substances.
Which substance has particles in a disorderly arrangement at room temperature? A
[May-2006/Q1]
16-Which gas has the slowest rate of diffusion?
A ammonia, NH3
B methane, CH4
C oxygen, O2
O LEVEL PAST PAER QUESTIONS.
______________________________________________________________________________
TOPIC 1: PARTICULAR NATURE OF MATTER, DIFFUSION.
D nitrogen, N2
[June 2006/Q2]
17-At which temperature does a concentrated aqueous solution of sodium chloride
begin to boil?
A 96 oC
B 99 oC
C 100 oC
D 104 oC
[Nov-2006/Q1]
18- Which property of a gas affects the rate at which it spreads throughout a
laboratory?
A boiling point
B molecular mass
C reactivity
D solubility in water
[June 2007/Q2]
19- Solid ammonium chloride decomposes on heating according to the following
equation.
Which change occurs to the damp red litmus paper in the experiment above?
A remains red
B turns blue and is then bleached
C turns blue and remains blue
D turns blue and then turns red
[June
2007/Q1]
20-What correctly describes the molecules in very dilute sugar solution at room
temperature?A
21- Nitrogen dioxide is a dark brown gas and is more dense than air.
A gas jar containing nitrogen dioxide is sealed with a glass plate and is then
O LEVEL PAST PAER QUESTIONS.
______________________________________________________________________________
TOPIC 1: PARTICULAR NATURE OF MATTER, DIFFUSION.
inverted on top of a
gas jar containing air.
The glass plate is removed.
Which one of the following correctly describes the colours inside the gas jars after a
long period
of time?
A
[May 2008/Q3]
22-Which property shows that a liquid is pure?
A It turns anhydrous copper(II) sulphate blue.
B It is colourless and odourless.
C It has no effect on red or blue litmus paper.
D It boils at a fixed temperature at a given pressure.
[Nov-2008/Q5]
23-Which diagram represents the arrangement of particles in a gas?
2008/Q7]
A [Nov-
O LEVEL PAST PAER QUESTIONS.
______________________________________________________________________________
TOPIC 1: PARTICULAR NATURE OF MATTER, DIFFUSION.
24-Which gas diffuses at the same rate as nitrogen gas?
A carbon dioxide
B carbon monoxide
C neon
D sulphur dioxide
[Nov-2008/Q8]
25- An inflated balloon goes down because gas molecules can diffuse through the
rubber.
Four balloons are filled with different gases at the same temperature and pressure.
Which balloon would go down quickest? B
26-Why does neon gas, Ne, diffuse faster than carbon dioxide gas, CO 2?
A Neon atoms have the lower mass.
B Neon does not form molecules.
C Neon is a noble gas.
D Neon is less dense than air.
[May-2009/Q2]
27- What correctly describes the molecules in very dilute sugar solution at room
temperature? B
[May 2010/ Q2]
28- The diagram shows a diffusion experiment.
O LEVEL PAST PAER QUESTIONS.
______________________________________________________________________________
TOPIC 1: PARTICULAR NATURE OF MATTER, DIFFUSION.
Which gas, when present in the beaker over the porous pot, will cause the water
level at Y to rise?
A carbon dioxide, CO2
B chlorine, Cl2
C methane, CH4
D nitrogen dioxide, NO2
[Nov-2010/Q4]
29- A drop of liquid bromine is placed in the bottom of a gas jar. Brown fumes of
bromine vapour
slowly spread through the covered gas jar.
Why does this happen?
A Bromine vapour is less dense than air.
B Bromine molecules and the molecules in air are always moving around.
C Bromine molecules are smaller than the molecules in air.
D Bromine molecules move faster than the molecules in air.
[J11/Q1]
30-In which pair is each substance a mixture?
A air and water
B limewater and water
C quicklime and limewater
D sea water and air
31-The diagram shows some of the changes of state.
[Nov-2011/Q4]
O LEVEL PAST PAER QUESTIONS.
______________________________________________________________________________
TOPIC 1: PARTICULAR NATURE OF MATTER, DIFFUSION.
Which statement is correct?
A Although the change is not shown on the diagram, a gas can change directly to a
solid.
B The changes 1 and 3 involve particles moving closer together.
C The changes 2 and 4 involve particles moving further apart.
D The changes 3, 4 and 5 all involve the release of energy.
[J12/Q1]
32-Four identical balloons are filled with different gases all at the same temperature
and pressure.
The gases gradually diffuse out of the balloons.
Which pair of balloons will deflate at the same rate?
A P and Q
B Q and R
C R and S
D S and P
[N12/Q2]
33- When drops of bromine are placed on a table-top at one side of a room, the
smell of bromine can
eventually be detected at the other side of the room.
What is not part of the explanation of this?
After evaporation, the bromine particles
A collide with air particles.
B move in a random way.
C spread out to occupy the total available space.
D vibrate from side to side.
Paper -2 Theory
O LEVEL PAST PAER QUESTIONS.
______________________________________________________________________________
TOPIC 1: PARTICULAR NATURE OF MATTER, DIFFUSION.
1- Use the substances named in the table to answer the following questions.
(a) (i) Name a monatomic gas.
...................................................................................................................................
(ii) Name the gas used in the Haber Process to make ammonia.
...................................................................................................................................
(iii) Which substances are liquids at 187 C?
...................................................................................................................................
(iv) Name the substance which is a liquid over the largest range of temperature.
...................................................................................................................................
Box A represents the arrangement of particles in carbon dioxide at 79 C.
(v) Draw a diagram in box B to show the arrangement of particles in carbon dioxide at
77 C.
O LEVEL PAST PAER QUESTIONS.
______________________________________________________________________________
TOPIC 1: PARTICULAR NATURE OF MATTER, DIFFUSION.
The percentage amounts of the same gases were measured in air from a crowded
classroom.
(b) (i) Name one gas whose percentage is higher in air from a crowded classroom.
...................................................................................................................................
(ii) Name one gas whose percentage is lower in air from a crowded classroom.
...................................................................................................................................
[2]
[Nov-2002/Q1]
2- The table shows some information about three gases.
(a) Complete the table by filling in the boxes.
A student heated some solid ammonium chloride, NH4C l, in a test-tube.
Ammonia and one other gas were formed.
He tested the gases coming out of the tube with litmus paper.
The red litmus quickly turned blue.
A few seconds later, both pieces of litmus paper turned red
(b) Name the process which causes the gases to move along the tube.
......................................................................................................................................[1]
(c) Which gas turned the red litmus paper blue?
......................................................................................................................................[1]
(d) Which gas turned the litmus paper red?
......................................................................................................................................[1]
[3]
O LEVEL PAST PAER QUESTIONS.
______________________________________________________________________________
TOPIC 1: PARTICULAR NATURE OF MATTER, DIFFUSION.
(e) Explain why the two gases travelled along the test-tube at different speeds.
Use information from the table.
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................[2]
[Nov-2003/Q2]
3- A student set up the apparatus shown below.
Colourless fumes of hydrogen chloride are given off by the hydrochloric acid.
Colourless fumes of ammonia are given off by the aqueous ammonia.
(a) After a few seconds, white fumes were seen at point X in the tube.
Name the compound formed at point X.
......................................................................................................................................[1]
(b) Use the kinetic particle theory to explain this observation.
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................[3]
(c) The student repeated the experiment using a solution of methylamine, CH3NH2, in place
of ammonia, NH3.
The white fumes were seen at point Y in the tube, rather than at point X.
Explain this difference.
..........................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................[2]
4- Bromine is a halogen. It has two naturally-occurring isotopes.
(a) Define the term isotopes.
..........................................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................... [1]
(b) One isotope of bromine has the symbol
State the number of protons, neutrons and electrons in this isotope of bromine.
protons ............................
O LEVEL PAST PAER QUESTIONS.
______________________________________________________________________________
TOPIC 1: PARTICULAR NATURE OF MATTER, DIFFUSION.
neutrons ..........................
electrons ......................... [2]
(c) Bromine is a liquid at room temperature.
(i) Draw a diagram to show the arrangement of the molecules in liquid bromine.
Show a bromine molecule as
[2]
(ii) A small amount of liquid bromine was placed in the bottom of a sealed flask. After thirty
minutes the brown colour of the bromine had spread throughout the flask.
Use the kinetic particle theory to explain these observations.
..................................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................. [3]
(d) Bromine forms a variety of compounds with other halogens.
(i) Bromine reacts with fluorine to form bromine(I) fluoride, BrF.
Write an equation for this reaction.
............................................................................................................................. [1]
(ii) Another compound of bromine and fluorine is bromine(V) fluoride, BrF5.
Calculate the percentage of bromine by mass in bromine(V) fluoride.
[2]
[Nov-2011/Q5]
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Experimental Techniques (TOPIC 2)Document17 paginiExperimental Techniques (TOPIC 2)ChaudhryAbdullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 - States of MatterDocument9 pagini1 - States of Mattermostafa barakatÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8.acids, Bases and Salts PDFDocument20 pagini8.acids, Bases and Salts PDFHakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heating and Cooling Curve Questions GRD 8Document3 paginiHeating and Cooling Curve Questions GRD 8Melba100% (1)
- IGCSE ChemistryDocument38 paginiIGCSE ChemistryBineta NdiayeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Worksheet 1 - Kinetic Particle TheoryDocument2 paginiWorksheet 1 - Kinetic Particle TheoryFandy ArdyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Redox ReactionsDocument29 paginiRedox ReactionsSoniaAlexÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity 17 (Preparation of Salts)Document4 paginiActivity 17 (Preparation of Salts)Nkemzi Elias NzetengenleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry O Level Notes 1Document12 paginiChemistry O Level Notes 1lubna naz100% (1)
- O Level Pure Physics Topic by Topic 3 109 112Document4 paginiO Level Pure Physics Topic by Topic 3 109 112Kugan KishurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Le Chatelier WorksheetDocument1 paginăLe Chatelier WorksheetRawanఌÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 - States of MatterDocument9 pagini1 - States of Mattermostafa barakat100% (1)
- Diffusion: Kinetic Particle Theory Part 2Document8 paginiDiffusion: Kinetic Particle Theory Part 2izzatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kinetic Particle Theory: Answers To Textbook ExercisesDocument3 paginiKinetic Particle Theory: Answers To Textbook ExercisesariiÎncă nu există evaluări
- S 495160Document4 paginiS 495160Khondokar Tarakky0% (1)
- Some Tips For Chemistry ATPDocument3 paginiSome Tips For Chemistry ATPAbdul HannanÎncă nu există evaluări
- June 2000 - Paper 2Document12 paginiJune 2000 - Paper 2theyaasir67% (3)
- 4.3 Reaction Rates and Reversible ReactionsDocument18 pagini4.3 Reaction Rates and Reversible ReactionsVictor VC100% (5)
- Topic 3Document22 paginiTopic 3ChaudhryAbdullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class XI Redox Reactions NotesDocument5 paginiClass XI Redox Reactions NoteseasaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Igcse Chemistry Section 4 Lesson 4Document48 paginiIgcse Chemistry Section 4 Lesson 4alanoud obeidatÎncă nu există evaluări
- O Level Physics ATP NotesDocument8 paginiO Level Physics ATP NotesAll in one 474728Încă nu există evaluări
- Acids, Bases and Chemical Bonding Challenging QuestionsDocument6 paginiAcids, Bases and Chemical Bonding Challenging Questionschong5650% (2)
- IGCSE Chemistry Section 2 Lesson 1Document66 paginiIGCSE Chemistry Section 2 Lesson 1Antonia Putri Sri Nova YolandhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SA1 Chemistry MCQ PracticeDocument2 paginiSA1 Chemistry MCQ Practicechong56Încă nu există evaluări
- Edexcel Igcse ElectrolysisDocument86 paginiEdexcel Igcse ElectrolysisshoshoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrolysis O LevelDocument17 paginiElectrolysis O LevelInnocent EbilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Collated Acids AnswersDocument9 paginiCollated Acids AnswersmadonnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- O Level Physics P1 June 77 - London University Examination BoardDocument10 paginiO Level Physics P1 June 77 - London University Examination Boarddjenner100% (1)
- A-Level Chemistry NotesDocument16 paginiA-Level Chemistry NotesMuradÎncă nu există evaluări
- Moles Workbook Y10Document8 paginiMoles Workbook Y10api-125934329100% (1)
- Chemistry Matters Textbook Full SolutionsDocument46 paginiChemistry Matters Textbook Full SolutionsongjiachengedricÎncă nu există evaluări
- Worksheet Chemistry Electrolysis Ks4Document4 paginiWorksheet Chemistry Electrolysis Ks4Jeffrey PiggottÎncă nu există evaluări
- Identification of Cations, Anions and GasesDocument2 paginiIdentification of Cations, Anions and GasesMustufa FerozÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 Measurement 3E SP WS3 Vernier 2011Document2 paginiChapter 1 Measurement 3E SP WS3 Vernier 2011Chandini JosephÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrolysis of Lead Bromide and BrineDocument13 paginiElectrolysis of Lead Bromide and Brinesondos tawfiqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Preparation of Salts PDFDocument24 paginiPreparation of Salts PDFSoniaAlex50% (2)
- The Particulate Nature of Matter 1 QPDocument10 paginiThe Particulate Nature of Matter 1 QPKHANÎncă nu există evaluări
- IGCSE Chemistry Note (9-1) On States of MatterDocument4 paginiIGCSE Chemistry Note (9-1) On States of MatterMd. Saif Ullah Bari100% (3)
- 1988 1998 Physics Past PapersDocument168 pagini1988 1998 Physics Past PapersAnthony Benson100% (1)
- November 1997 Pure Chemistry PaperDocument11 paginiNovember 1997 Pure Chemistry PaperZeneon100% (1)
- Page 1 of 5Document5 paginiPage 1 of 5Jagdeep PandeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Worksheet On IGCSE Chemical EnergeticsDocument2 paginiWorksheet On IGCSE Chemical EnergeticsSamandarbek Numonov100% (1)
- Valency ChartDocument2 paginiValency ChartRam Krishna SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anglican High School Sec 2 Science Worksheet: Mass, Weight, DensityDocument4 paginiAnglican High School Sec 2 Science Worksheet: Mass, Weight, DensityFrancis Ho HoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Worksheet 2.1Document2 paginiWorksheet 2.1Kelso ZwariyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry Revision Notes For O LevelDocument28 paginiChemistry Revision Notes For O LevelshinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Applications of Solubility Product: (I) Purification of Common SaltDocument6 paginiApplications of Solubility Product: (I) Purification of Common SaltSiddhartha GautamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Homeworks 1 eDocument8 paginiHomeworks 1 eSumi VjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrolysis PDFDocument14 paginiElectrolysis PDFBaryaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Task 1: Group 1 - The Alkali MetalsDocument4 paginiTask 1: Group 1 - The Alkali MetalsNeen NaazÎncă nu există evaluări
- O Levels Cehimstry-Atomic Structure - Chemical BondingDocument16 paginiO Levels Cehimstry-Atomic Structure - Chemical Bondingjave_yeongÎncă nu există evaluări
- E Maths Sec 42011Document267 paginiE Maths Sec 42011Timothy Handoko100% (1)
- Common Chemistry Lab Apparatus (CIE IGCSE)Document12 paginiCommon Chemistry Lab Apparatus (CIE IGCSE)deeyamulla33% (6)
- Fair Test, Variables (P4)Document14 paginiFair Test, Variables (P4)Jegendren TanapalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Qualitative AnalysisDocument3 paginiQualitative AnalysisYukeling TayÎncă nu există evaluări
- O Level Worksheets PHYSICS.Document337 paginiO Level Worksheets PHYSICS.ChaudhryAbdullah85% (61)
- Topic 3Document22 paginiTopic 3ChaudhryAbdullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- MolesDocument16 paginiMolesChaudhryAbdullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- MolesDocument16 paginiMolesChaudhryAbdullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- MetaphysicsDocument20 paginiMetaphysicscrisjava100% (1)
- Rotes For Mage - The Awakening - Force 3 Matter 2 Prime 2 Time 3Document11 paginiRotes For Mage - The Awakening - Force 3 Matter 2 Prime 2 Time 3Danielle Jones67% (3)
- Natural Science As PhilosophyDocument13 paginiNatural Science As PhilosophyGregorio AlvarezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cat b1.1 Mod 2 Course Note (Dcam Part 66) - Issue 1 Revision 0 Jan 2011Document212 paginiCat b1.1 Mod 2 Course Note (Dcam Part 66) - Issue 1 Revision 0 Jan 2011Tai Hwa Chen0% (1)
- Basic Transurfing PrinciplesDocument16 paginiBasic Transurfing Principlesscot9y59pe94% (16)
- A Dynamic and Substantive Cosmological Ether James Demeo, PH.DDocument7 paginiA Dynamic and Substantive Cosmological Ether James Demeo, PH.DAdhava R R VÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Part II, 2nd Year, MathematicsDocument85 paginiPhysics Part II, 2nd Year, MathematicsMamunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final EssayDocument5 paginiFinal Essayapi-377064153Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 6 Periodic Table Form 1Document12 paginiChapter 6 Periodic Table Form 1nantheni1779% (14)
- CH 13Document12 paginiCH 13يزيد الزهرانيÎncă nu există evaluări
- KSBF Lesson PlanDocument5 paginiKSBF Lesson PlanJACEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Laws of MatterDocument6 paginiLaws of MatterjyclynnnÎncă nu există evaluări
- A List of 240 Physics Topics & Questions To ResearchDocument11 paginiA List of 240 Physics Topics & Questions To ResearchMuhammad TahirÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHAPTER 2:the Structure of The Atom SPM 2004P2S1: Table 1Document10 paginiCHAPTER 2:the Structure of The Atom SPM 2004P2S1: Table 1mia adrinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mcqs in Thermodynamics Part V: What Is Your Iq Score?Document10 paginiMcqs in Thermodynamics Part V: What Is Your Iq Score?Joshua OrlandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- THE SECRET PLUS - THE ULTIMATE LAW OF ATTRACTION Multiply The Power of The Law of Attraction by A Factor of 5-10 by Adding SECRET INGREDIENTS by James F. CoyleDocument60 paginiTHE SECRET PLUS - THE ULTIMATE LAW OF ATTRACTION Multiply The Power of The Law of Attraction by A Factor of 5-10 by Adding SECRET INGREDIENTS by James F. Coyleshila353100% (4)
- SGJVZGNZCKXCDocument70 paginiSGJVZGNZCKXCAnkit KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- TEXT Higher Power2006 - Murdo MacDonald-BayneDocument268 paginiTEXT Higher Power2006 - Murdo MacDonald-BayneLisa Brack100% (17)
- Murdo-MacdonaldDocument80 paginiMurdo-MacdonaldsolomonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit Iii Saqs and AssignmentDocument3 paginiUnit Iii Saqs and AssignmentBeth OdiamanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 MatterDocument8 paginiChapter 3 Matternaza9775100% (2)
- Exam Question URLsDocument1 paginăExam Question URLsDessouki YousefÎncă nu există evaluări
- Melanin Physics by NEB HERUDocument72 paginiMelanin Physics by NEB HERURobert MccrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 1 - EcosystemDocument3 paginiLesson 1 - EcosystemPaul Assie RosarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bio Unit 3 Bioenergetics Unit PlanDocument6 paginiBio Unit 3 Bioenergetics Unit Planapi-376095456100% (1)
- Properties Changes of MaterialsDocument28 paginiProperties Changes of Materialsapi-273214847Încă nu există evaluări
- KS3 Chemistry: Solids, Liquids and GasesDocument25 paginiKS3 Chemistry: Solids, Liquids and GasesAbdul Rahman100% (1)
- Prime Matter - The Explanation For Atoms - Neal AdamsDocument6 paginiPrime Matter - The Explanation For Atoms - Neal AdamsJared BondÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gregory P. Fields Religious Therapeutics Body and Health in Yoga, Ayurveda, and Tantra PDFDocument239 paginiGregory P. Fields Religious Therapeutics Body and Health in Yoga, Ayurveda, and Tantra PDFtridestron100% (1)