Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
C210 WML 614
Încărcat de
Efrén SantínTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
C210 WML 614
Încărcat de
Efrén SantínDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
4610-00
14-3
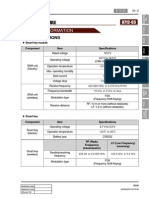
1. SPECIFICATION
Unit
Description
Specification
System operation
Operating type
Motor driven power steering system
Operating temperature
- 40C to 80C
Rated voltage
12 V
Rated current
85 A
Network
8 to 16 V
C-EPS ECU
8 to 16 V
Full Performance
10 to 16 V
Type
3-Phase BLAC (Brushless AC)
Rated current/voltage
85 A / 12 V (at idle 0.5 A)
Position sensor type
Hall sensor type
Torque & angle sensor
Type
Non-contact type
Steering column
Operating type
Manual tilting & telescoping
Lower shaft
Type
Sliding (Ball slip) type
Steering gear
Gear ratio
50.7 mm/rev
Rack stroke
145 mm
Inner wheel
38.62
Outer wheel
31.07
Operating voltage
Motor
Maximum steering angle
14-4
2. TIGHTENING TORQUE
4610-00
3. DIFFERENCES BETWEEN HPS AND EPS
HPS (Hydraulic Power Steering)
HPS
1
Crankshaft pulley (DDU)
Auto tensioner
Tensioner pulley
Vacuum pump
A/C compressor pulley
Alternator pulley
Water pump pulley
No.1 idle pulley
No.2 idle pulley
10
Power steering pump
EPS (Electric Power Steering)
EPS
14-5
14-6
1. OVERVIEW
The electric power steering, EPS, does not have any belt-driven steering pump constantly running, so it
is lightweight and the motor consumes energy only when the steering wheel is turned by the driver, and
this leads to improvement in fuel efficiency. Also, the elimination of a belt-driven pump and its
accessories greatly simplifies manufacturing and maintenance. While offering these benefits, as it does
not contain any steering oil, the environment is not polluted both when the steering system is produced
and discarded.
In other words, the electric power steering (EPS) system uses the electric motor to assist the steering
force. It functions independently regardless of whether the engine is running or not, unlike the existing
hydraulic power steering.
The EPS system generates an assist steering force variably depending on the driving conditions by
controlling the motor's operation, based on the input signals from the sensors such as torque sensor and
angle sensor. In turn, the EPS receives the torque signal by the driver's movements of the steering
wheel, as well as the vehicle speed, and uses the motor to determine the assist torque. The EPS
controls the motor for this. Another features of EPS are fail-safe function, diagnosis function,
communication function between units and interface function for external diagnostic device.
The EPS system components such as the torque sensor, steering angle sensor, fail-safe relay, etc. are
located in the steering column and EPS unit assembly.
Advantages:
(1) Assurance of improved steering
- Provides optimal steering force according to the
vehicle speed
- Enhanced steering stability while driving at high
speed
(2) Reduced fuel consumption
- Consumes energy only when steering wheel
is turned (improved by 3 to 5%)
- Energy saving (reduced by 85% compared
with hydraulic power steering)
- Reduced number of parts: Elimination of
steering pump, hydraulic hose, pump pulley,
oil reservoir, belt, bracket, etc.
Comparison between hydraulic power steering and electric power steering (EPS)
Hydraulic power steering
Electric power steering
4610-00
14-7
2. OPERATION
Output torque = 1) Steering force (manual torque) + 2) Assist torque
When the driver turns the steering wheel, a torque is generated and the torque sensor and the steering
angle sensor in the EPS system detect the rotation of the steering column to run the electric motor. At
this time, the worm gear connected to the motor drives the helical gear mounted to the steering column
to generate the assist torque for the steering column. This allows the driver to operate the steering wheel
easier.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Oferta Red LIneDocument10 paginiOferta Red LIneEfrén SantínÎncă nu există evaluări
- C210 WML 202Document30 paginiC210 WML 202Efrén SantínÎncă nu există evaluări
- Major Dimension: Top ViewDocument16 paginiMajor Dimension: Top ViewEfrén SantínÎncă nu există evaluări
- C210 WML 102Document1 paginăC210 WML 102Efrén SantínÎncă nu există evaluări
- C210 WML 201Document13 paginiC210 WML 201Efrén SantínÎncă nu există evaluări
- C210 WML 203Document30 paginiC210 WML 203Efrén SantínÎncă nu există evaluări
- C210 WML 103Document1 paginăC210 WML 103Efrén SantínÎncă nu există evaluări
- C210 WML 104Document1 paginăC210 WML 104Efrén SantínÎncă nu există evaluări
- C210 WML 207Document7 paginiC210 WML 207Efrén SantínÎncă nu există evaluări
- C210 WML 206Document20 paginiC210 WML 206Efrén SantínÎncă nu există evaluări
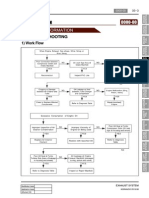
- Troubleshooting: 1) Work FlowDocument4 paginiTroubleshooting: 1) Work FlowEfrén SantínÎncă nu există evaluări
- C210 WML 204Document10 paginiC210 WML 204Efrén SantínÎncă nu există evaluări
- C210 WML 209Document13 paginiC210 WML 209Efrén SantínÎncă nu există evaluări
- C210 WML 208Document9 paginiC210 WML 208Efrén SantínÎncă nu există evaluări
- C210 WML 214Document15 paginiC210 WML 214Efrén SantínÎncă nu există evaluări
- C210 WML 215Document48 paginiC210 WML 215Efrén SantínÎncă nu există evaluări
- C210 WML 212Document11 paginiC210 WML 212Efrén Santín0% (1)
- C210 WML 210Document12 paginiC210 WML 210Efrén SantínÎncă nu există evaluări
- C210 WML 211Document11 paginiC210 WML 211Efrén SantínÎncă nu există evaluări
- C210 WML 213Document5 paginiC210 WML 213Efrén SantínÎncă nu există evaluări
- Specifications: Smart Key Module Component Item SpecificationsDocument32 paginiSpecifications: Smart Key Module Component Item SpecificationsEfrén SantínÎncă nu există evaluări
- C210 WML 501Document14 paginiC210 WML 501Efrén SantínÎncă nu există evaluări
- C210 WML 502Document6 paginiC210 WML 502Efrén SantínÎncă nu există evaluări
- C210 WML 505Document49 paginiC210 WML 505Efrén SantínÎncă nu există evaluări
- C210 WML 508Document24 paginiC210 WML 508Efrén SantínÎncă nu există evaluări
- C210 WML 503Document120 paginiC210 WML 503Efrén SantínÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lamp Specifications: 1) Exterior LampsDocument41 paginiLamp Specifications: 1) Exterior LampsEfrén SantínÎncă nu există evaluări
- C210 WML 506Document50 paginiC210 WML 506Efrén SantínÎncă nu există evaluări
- Specification: Pin No. Specification Pin No. SpecificationDocument8 paginiSpecification: Pin No. Specification Pin No. SpecificationEfrén SantínÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit Item SpecificationDocument22 paginiUnit Item SpecificationEfrén SantínÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- T630 7277035 enUS Om (OPERACIÓN Y MANTENIMIENTO) PDFDocument246 paginiT630 7277035 enUS Om (OPERACIÓN Y MANTENIMIENTO) PDFRamiro Alexis Garcia LópezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Azores, Aljon V.: Children International (Bicol) IncDocument2 paginiAzores, Aljon V.: Children International (Bicol) IncNikko BorborÎncă nu există evaluări
- RINXs Info SessionDocument21 paginiRINXs Info SessionCherry ChoiÎncă nu există evaluări
- SRS DOCUMENT (Hospital Management System)Document24 paginiSRS DOCUMENT (Hospital Management System)Aaqib Sultan80% (5)
- AcknowledgementDocument38 paginiAcknowledgementthakurkiranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bosch Voice Alarm Systems: Contributing To A Safer WorldDocument8 paginiBosch Voice Alarm Systems: Contributing To A Safer WorldSaad KhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data Service Plans For All NetworksDocument2 paginiData Service Plans For All NetworksAugustineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Emme Users Group PresentationDocument27 paginiEmme Users Group Presentation69gÎncă nu există evaluări
- Degree Programme Table: Advanced Chemical Engineering (MSC) - 1 Year (Full-Time)Document3 paginiDegree Programme Table: Advanced Chemical Engineering (MSC) - 1 Year (Full-Time)Petra SitanggangÎncă nu există evaluări
- WB 854736Document4 paginiWB 854736Pawan KanuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nitin - Pant Magento - Lead Resume Sep 2022Document2 paginiNitin - Pant Magento - Lead Resume Sep 2022Manisha AswarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test UM Product CatalogDocument28 paginiTest UM Product Catalogdonhacbang100% (1)
- Scott GroverDocument3 paginiScott GroverJoe StephensÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gigaset N870 IP PRO - Multicell System - en - INTDocument122 paginiGigaset N870 IP PRO - Multicell System - en - INTfredon quentinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Later Instagram Analytics Strategy Guide PDFDocument68 paginiLater Instagram Analytics Strategy Guide PDFMuhammad Wisnu WardhanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cost Comparison For Business Decision-Makers: Oracle Exadata Database Machine vs. IBM Power SystemsDocument30 paginiCost Comparison For Business Decision-Makers: Oracle Exadata Database Machine vs. IBM Power SystemsGautham SampathÎncă nu există evaluări
- YANMAR 3TNV-4TNV Series Shop ManualDocument392 paginiYANMAR 3TNV-4TNV Series Shop ManualPHÁT NGUYỄN THẾ91% (22)
- Applications of Thermoelectric Energy: A ReviewDocument5 paginiApplications of Thermoelectric Energy: A ReviewIJRASETPublicationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Career ProfileDocument6 paginiCareer Profileashish gulatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- American Series ManualDocument26 paginiAmerican Series ManualIsael HernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- GSM Frequency Bands - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument5 paginiGSM Frequency Bands - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaSovannarith HoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Samsung E1210S UM IND Eng Rev.1.0 090203Document2 paginiSamsung E1210S UM IND Eng Rev.1.0 090203Ahsan BurhanyÎncă nu există evaluări
- SI3000 Pono Datasheet PDFDocument2 paginiSI3000 Pono Datasheet PDFJose JoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gas Turbine Offline Wash Advisor: Maximum Net Profit AnalysisDocument4 paginiGas Turbine Offline Wash Advisor: Maximum Net Profit AnalysisHBNBILÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bollinger Bands %B (%B) - TradingView DocumentationDocument5 paginiBollinger Bands %B (%B) - TradingView DocumentationFinTÎncă nu există evaluări
- Better Linux Disk Caching & Performance With VM - Dirty - RatioDocument5 paginiBetter Linux Disk Caching & Performance With VM - Dirty - RatioSelçuk GÜLTEKİNÎncă nu există evaluări
- Epsilon 140z DatasheetDocument2 paginiEpsilon 140z DatasheetRiga RingsÎncă nu există evaluări
- ZTE Access Systems Series ZXA10 C300 C300M C350M v1 0 PDFDocument26 paginiZTE Access Systems Series ZXA10 C300 C300M C350M v1 0 PDFRonaldo YoupLoadÎncă nu există evaluări
- LPG For Heavy Duty Engines 2017Document116 paginiLPG For Heavy Duty Engines 2017Neagoie SergiuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Datasheet - HK Pcf7991at 450658Document1 paginăDatasheet - HK Pcf7991at 450658Adrian FernandezÎncă nu există evaluări