Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
LÍMITES DE FUNCIONES
Încărcat de
PabloCerdaTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
LÍMITES DE FUNCIONES
Încărcat de
PabloCerdaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
CALCULO I
_____________________________________________________________________
UNIDAD I: LIMITE DE FUNCIONES
Consideremos la funcin f ( x) =
x2 x 6
x3
El dominio de f(x) son todos los reales menos el 3. Domf ( x) = {3} , es decir f est
definida en todo excepto en x = 3
Investiguemos que valores toma la funcin f(x) en valores de x cercanos a 3. Tomemos
valores de x menores y mayores a 3.
x
f (x)
2
4
2,5
4,5
2,9
4,9
2,99
4,99
2,999
4,999
x
f (x)
4
6
3,5
5,5
3,1
5,1
3,01
5,01
3,001
5,001
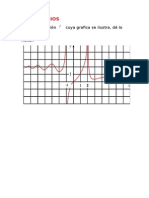
En las tablas podemos ver que si x se aproxima a 3 la funcin f(x) se aproxima a 5
Grficamente:
Luego decimos que si x se aproxima a 3 la funcin f(x) tiende a 5.
DEFINICION: Lmite de una funcin
Sea f(x) una funcin definida en todo n de algn intervalo abierto I, que contenga a a
excepto posiblemente en el nmero a mismo.
El lmite de f(x) cuando x tiende a a es L y se escribe:
Si el siguiente enunciado es verdadero
UNIVERSIDAD AUTONOMA
lim f ( x) = L
xa
CALCULO I
_____________________________________________________________________
Dado cualquier > 0 , sin importar cuan pequeo sea, existe un > 0 tal que s:
0 < x a < f ( x) L <
Lo podemos escribir: > 0, > 0 tal que 0 < x a < f ( x) L <
Nota: El lmite de una funcin cuando x a no siempre existe y si existe es nico.
TEOREMA DE UNICIDAD
Sea A R, f : A R funcin. Si existe el lmite de f cuando x tiende a b entonces
lim f ( x ) es nico. Es decir:
x b
lim f ( x) = L1 y
lim f ( x) = L2
x b
Ejemplo: Sea f ( x) =
x b+
entonces L1 = L2
1
x
Dom f ( x) = {0} Analicemos el lim f ( x) = lim
x 0
x
-1
-0,5
-0,1
-0,01
-0,001
-0,0001
f(x)
-1
-2
-10
-100
-1000
-10000
UNIVERSIDAD AUTONOMA
x 0
1
x
Si x se aproxima a 0 por valores menores, f ( x )
CALCULO I
_____________________________________________________________________
x
1
0,5
0,1
0,01
0,001
0,0001
f(x)
1
2
10
100
1000
10000
Si x se aproxima a 0 por valores mayores, f ( x )
1
=
x 0 x
En este caso no existe el lmite. Lo escribimos lim
Grficamente:
Ejemplos
Tres funciones para las que lim f ( x) = L
xc
UNIVERSIDAD AUTONOMA
CALCULO I
_____________________________________________________________________
Ejemplos
Dos funciones para las que lim f ( x) no existe
x c
PROPIEDADES
1.- lim k = k, k es una constante
x c
2.- lim x = c
x c
3.- lim [ f ( x ) + g( x )] = lim f ( x ) + lim g( x )
xb
xb
xb
4.- lim [ k f ( x ) ] = k lim f ( x )
xb
xb
5.- lim [ f ( x ) * g( x )] = lim f ( x ) * lim g( x )
xb
6.- lim
xb
7.-
xb
xb
f(x)
f ( x ) lim
x b
=
si lim g( x ) 0
x b
g( x ) lim g( x )
x b
lim [ f ( x ) ] = lim f ( x ) n
x b
x b
Ejemplos: Calcular los siguientes lmites:
lim ( 3x + 5) = 3 . 2 + 5 =11
x2
lim ( 4 x + 2 ) = 4 .3 + 2 = 10
x3
UNIVERSIDAD AUTONOMA
lim 3( 2 z + 5 ) = 3 lim( 2 z + 5 ) = 3 ( 2 . 2 + 5) = 27
z 2
z2
lim ( 3x 2 2 x ) = lim 3x 2 lim 2 x = 3 + 2 = 5
x 1
x 1
x 1
CALCULO I
_____________________________________________________________________
lim x = 5
lim x 2 x + x = lim x lim 2 x + x = 9 * (18 + 3) = 189
7 7
lim =
x 1 2
2
lim 3 x + 1)
7
7
3x + 1 x 2 (
lim
=
=
=
x2 2x 6
( 2 x 6 ) 2 2
lim
x2
x 5
x 9
x 9
x 9
FORMAS INDETERMINADAS
En algunos lmites no es posible aplicar directamente los teoremas sobre lmites,
especialmente el lmite de un cuociente de funciones, ya que se presenta la forma
0
indeterminada .
0
En estos casos se hace necesario realizar primero algn proceso algebraico, para luego
determinar el valor del lmite.
2 x 2 + 2 x 12
Ejemplo: lim
x 2 3x 2 5x 2
Si evaluamos tanto el numerador como el denominador se obtiene la expresin
tiene sentido. Si factorizamos ambos polinomios obtenemos:
lim
x 2
( x 2) ( 2x + 6)
2 x 2 + 2 x 12
= lim
= lim
2
3 x 5 x 2 x 2 ( x 2 ) ( 3x + 1) x 2
( 2 x + 6 ) 10
=
( 3x + 1) 7
Ejemplo:
lim
x2
x2 4
2 x
= lim
x2
(x
( 2 + x ) = lim ( x + 2 ) ( x 2 ) ( 2 + x ) = 8
( x 2)
x)( 2 + x)
4)
x2
EJERCICIOS PROPUESTOS
a ) lim
x - 1
d ) lim
x 1
x3 + 1
-x 2 + 1
x -1
x- 1
b ) lim
x 5
e ) lim
UNIVERSIDAD AUTONOMA
h 0
x 2 - 5x
x 2 - 25
(x
c ) lim
x2 - 1
x 2 + 3x + 2
f ) lim
2- x-3
x 2 - 49
x - 1
+ h ) - x3
h
3
x 7
0
que no
0
CALCULO I
_____________________________________________________________________
LIMITES LATERALES
Lmite lateral izquierdo. Se escribe
lim f ( x ) = L
x b
(x se aproxima a b por valores
menores).
Lmite lateral derecho. Se escribe lim+ f ( x) = L (x se aproxima a b por valores mayores)
xb
El lmite de f(x) existe y es igual a L si y solo si los limites laterales son iguales.
si x 1
x + 2
Ejemplo: Dada la siguiente funcin: f ( x) = 2
x 1 si x < 1
La grfica de la funcin es la siguiente.
En ella puede observarse que lim+ f ( x ) = 3
x 1
lim f ( x ) = 2
x 1
Observe que el lmite por la derecha (3), es diferente al lmite por la izquierda (2)
Por lo tanto lim f ( x ) NO EXISTE
x 1
Ejemplo: Representemos grficamente la funcin definida por:
x 2 2
f ( x) = x
4 x
si x < 2
si 2 < x < 4
si
UNIVERSIDAD AUTONOMA
x4
CALCULO I
_____________________________________________________________________
Como lim+ f ( x ) = 2 y lim f ( x ) = 2 ,entonces lim f ( x ) = 2
x2
x2
x2
Como lim+ f ( x ) = 0 y lim f ( x ) = 4 ,entonces lim f ( x ) = no existe
x4
x4
x4
Ejercicio
Considere la representacin grfica de la funcin g definida por:
x 1
x + 3
g ( x) =
1
( x 4 )2
si
x 2
si 2 < x < 1
si
si
1 x 3
x>3
Determine si existe cada uno de los siguientes lmites:
a)
lim g ( x)
x 2
b) lim g ( x )
x 1
c) lim g ( x)
x 3
d) lim g ( x)
x4
e) lim g ( x)
x0
UNIVERSIDAD AUTONOMA
CALCULO I
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
LIMITES INFINITOS
Grafique en su cuaderno en la calculadora la funcin f ( x) =
1
y observe hacia donde
x2
tienden las imgenes de f cuando x tiende a cero.
DEFINICION
Se dice que f : S R R tiende a ms
ms infinito cuando x tiende a b, y se escribe.
lim f ( x ) = +
xb
Ejercicio: Verifique que:
lim
x 1
( x + 1)
lim
x0
1
=
x2
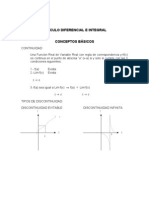
DEFINICION
La recta x = a se llama asntota vertical de la curva y = f ( x) si se cumple cuando menos
una de las siguientes afirmaciones.
lim f ( x) =
xa
lim f ( x) =
xa
UNIVERSIDAD AUTONOMA
lim f ( x) =
x a
lim f ( x) =
x a
lim f ( x) =
x a+
lim f ( x) =
x a+
CALCULO I
_____________________________________________________________________
Ejemplo:
La recta x = 2 es una asntota vertical de la funcin f ( x) =
1
+1
(x 2)
4 y
0
-6
-4
-2
-2
-4
EJERCICIOS PROPUESTOS
3 2x
=
x 4 x 4
a )lim
b ) lim
x
2
3
( x + 3 )2
=
4 9 x2
LIMITES EN EL INFINITO
Ejemplo: Sea la funcin f ( x) =
3x 1
5
. Calcule lim f ( x ) .
, x R, x
x +
2x + 5
2
Al evaluar obtenemos la forma
, en este caso dividimos numerador y denominador por
la mayor potencia de x.
1
3x 1
x =3
lim f ( x ) = lim
= lim
x +
x + 2 x + 5
x +
5 2
2+
x
3
TEOREMA
Si r es cualquier entero positivo, entonces:
lim
x +
UNIVERSIDAD AUTONOMA
1
=0
xr
lim
1
=0
xr
CALCULO I
_____________________________________________________________________
EJERCICIOS PROPUESTOS
Calcular los siguientes limites:
4x 3
=
x + 2 x + 5
2x2 x + 5
=
x
4 x3 1
lim
lim
4 x 3 +5 x 1
=
x +
x+3
lim
4 x 4 x3 + 8 x 2 x
=
x 10 x 4 + 8 x 2 + 8 x
lim
LIMITES ESPECIALES
x
1
1
lim 1 + = e lim (1 + x ) x = e
x
x 0
x
1
lim 1 +
x
f ( x )
f(x)
= e lim (1 + f ( x )) f ( x ) = e
x 0
Ejemplos:
1
1
1
lim 1 + = lim 1 + = e5
x
x
x x
5x
x
2x
1
1
1 2
lim 1 + = lim 1 + = e 2
x
2 x x 2 x
CONTINUIDAD DE FUNCIONES
Consideremos la funcin f ( x) =
x2 x 6
x3
f est definida para todos los nmeros reales excepto el 3,
Observando la grafica podemos ver que f es discontinua en x = 3 (le falta un punto)
UNIVERSIDAD AUTONOMA
CALCULO I
_____________________________________________________________________
DEFINICION
Una funcin f es continua en el nmero a si y solo si se cumplen:
f ( a ) existe
i)
ii)
lim f ( x ) existe
x a
iii) lim f ( x ) = f ( a )
xa
Ejemplo: Analice continuidad de las siguientes funciones:
h ( x)
x2 x 6
= x 3
5
,x 3
,x = 3
-2x + 4 , x < 1
g ( x) =
,x 1
x - 1
DISCONTINUIDAD REPARABLE
Sea f una funcin discontinua en a, tal que:
i)
ii)
lim f ( x ) existe
xa
lim f ( x ) f ( a )
xa
f ( a ) no existe
Tal discontinuidad se llama Discontinuidad Reparable. Si f(x) se redefine en a, es decir;
f ( a ) = lim f ( x ) la funcin cumple las tres condiciones de continuidad.
xa
Ejemplo:
x2 1
x 1 si x 1
Sea f ( x ) =
5 si x = 1
Es continua en x = 1 ?
Desarrollo:
1. - f (1) = 5
x2 1
( x 1) ( x + 1) = lim x + 1 = 2
2. - lim
= lim
( )
x 1
x 1
( x 1)
x 1 x 1
3. - lim f ( x ) f (1)
x 1
UNIVERSIDAD AUTONOMA
CALCULO I
_____________________________________________________________________
Luego la funcin es discontinua en x = 1 , pero podemos redefinirla del siguiente modo
x2 1
x 1 si x 1
g ( x) =
2 si x = 1
UNIVERSIDAD AUTONOMA
CALCULO I
_____________________________________________________________________
GUIA EJERCICIOS N1: LIMITE Y CONTINUIDAD DE FUNCIONES
CALCULO I
I.- Calcular los siguientes lmites:
1 ) lim 3 x 2 2 x + 1
x 2
2t + 1
4t
t 4
2
x 7 x + 10
3 ) lim
x 5
x 2 25
x2 1
4 ) lim 2
x 1 x + 3 x + 2
2x2 + x 1
5 ) lim
x 1
x3 x
2 x 3 14 x 2 12 x + 24
6 ) lim 3
x 10 x 2 + 27 x 18
x 1
x +1
7 ) lim 3
x 1 x + 1
x2
3x 2 5
2 x + 18
10 ) lim
x +1 2
x3
x 9
2 ) lim
8 ) lim
9 ) lim
4 x3 13 x 2 + 4 x + 12
3 x3 5 x 2 16 x + 28
x 3
11 ) lim
x 7
12 ) lim
x 1
2 x3
x 2 49
x 1
x2 + 3 2
x a
x a
xa
1+ x 1 x
14 ) lim
x 0
x
2
t 49
15 ) lim
t 7
t 2 + 15 ( t + 1 )
13 ) lim
16 ) lim
x 5
2x 1 3
2x + 6 4
II.- Calcular los siguientes limites en el infinito:
2 x2
x + 2 x 2 + 1
5 x3 2 x 2 + 5
lim
x 2 x 2 x + 1
8x4 2 x2 + 1
lim
x + 5 x 5 x 3 + x 2 + 2
2x + 7
lim
x 4 5 x
lim
x2 2x + 5
x + 7 x 3 + x + 1
5 x3 12 x + 7
lim
x
4x2 1
lim
lim
x2 + 4
x+4
lim
w2 2 w + 3
w+5
x +
w+
III.- Calcular los sgtes. limites especiales:
3x
1
lim 1 + =
x
x
lim 1 + =
x
2x
1+ x
lim
=
x
x
x
1
lim 1 =
x
x
lim 1 =
x
2x
1
lim
=
x
x +1
UNIVERSIDAD AUTONOMA
CALCULO I
_____________________________________________________________________
k
lim 1 +
x
x
mx
=
x
a
lim 1 + =
x
x
1
lim 1 +
x
x
x+3
2x + 3
lim
=
x 2 x + 9
IV. Calcular los siguientes lmites laterales:
2 si x < 1
f ( x ) = 1 si x = 1
3 si x > 1
lim f ( x ) =
x 1
x 2 si x 2
F( x ) =
8 2 x si x > 2
lim F( x ) =
x2
3 + t 2 si t < 2
g( t ) = 0 si t = 2
11 t 2 si t > 2
lim g( t ) =
t 2
x + 1 si x < 1
f ( x ) = x 2 si 1 x 1
2 x si x > 1
lim f ( x ) =
x 1
lim f ( x ) =
x 1
3 x si x 0
g( x ) =
3 x si x > 0
lim g( x ) =
x 0
3 x 2 si x < 4
Sea f ( x ) =
5 x + k si x 4
Hallar el valor de k tal que
lim f ( x ) exista
x4
V. Analice continuidad de las siguientes funciones, en caso que la discontinuidad sea
reparable, redefina la funcin:
x2 9
+ 5 si x 3
g( x ) = x 3
11 si x = 3
2 x2 + 3
si x 1
5
f ( x ) = 6 5 x si 1 < x < 3
x 3 si x 3
Determine a y b de modo que la sgte. funcin sea continua en todo
1
si x 3
g( x ) = x 3
5 si x = 3
3 + x si x 1
h( x ) =
3 x si x > 1
ax + bx 2 si x 1
f ( x ) = x 2 si 1 < x 5
a + bx si x > 5
UNIVERSIDAD AUTONOMA
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Limites (General)Document11 paginiLimites (General)Luis Abel Martinez RiquelmeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Límites matemáticos: nociones intuitivas y teoremas fundamentalesDocument4 paginiLímites matemáticos: nociones intuitivas y teoremas fundamentalesSergio Ivan Olvera MartinezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculo DiferencialDocument75 paginiCalculo DiferencialjaanaiyaruroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Límites laterales y continuidad de funcionesDocument17 paginiLímites laterales y continuidad de funcionesJared Ibarra AguileraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Limites Al InfinitoDocument36 paginiLimites Al InfinitoAlexander GuevaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ejercicios Resueltos de LimitesDocument9 paginiEjercicios Resueltos de LimitesAmIn20122Încă nu există evaluări
- Calculo DiferencialDocument10 paginiCalculo DiferencialKaren VasquezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lim Sol 1Document8 paginiLim Sol 1Denis GonzalezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculo Diferencial e Integral Completo para ImprimirDocument43 paginiCalculo Diferencial e Integral Completo para ImprimirJairo Isaí Pacheco PérezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test Mru Mrua Simil Grafica PDFDocument10 paginiTest Mru Mrua Simil Grafica PDFbuhodecadizÎncă nu există evaluări
- DerivadasDocument6 paginiDerivadasErickRojasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guía No 2 - Límites Laterales y Continuidad PDFDocument9 paginiGuía No 2 - Límites Laterales y Continuidad PDFLeo RojasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Taller Sobre LimitesDocument6 paginiTaller Sobre LimitesMiller Leonardo Claros CuellarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guia de Continuidad y Limites LateralesDocument2 paginiGuia de Continuidad y Limites LateralessamitaramirezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Apuntes para El Curso de Cálculo I. MA1001.Vísquez, LeinerDocument85 paginiApuntes para El Curso de Cálculo I. MA1001.Vísquez, Leinergonzalo_ruiz_13100% (1)
- Limites, Cálculo Diferencial e Integral 1Document6 paginiLimites, Cálculo Diferencial e Integral 1Víctor Hernández UreñaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cálculo I guiones clasesDocument122 paginiCálculo I guiones claseschambafloresÎncă nu există evaluări
- CDI Guia09 Ver 12Document22 paginiCDI Guia09 Ver 12Vilma FajardoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduccion A Los Limites 10 y 11032021Document5 paginiIntroduccion A Los Limites 10 y 11032021Gisely A. Lantigua EstévezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Derivada de FuncionesDocument13 paginiDerivada de FuncionesJavier VallenillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Max Tapia Escobar Trabajo Semana 2 CALCULODocument5 paginiMax Tapia Escobar Trabajo Semana 2 CALCULOmax aalejandro tapia escobar100% (1)
- DERIVADAS-TEORÍA Y EJERCICIOS RESUELTOS (NXPowerLite)Document60 paginiDERIVADAS-TEORÍA Y EJERCICIOS RESUELTOS (NXPowerLite)William BenabuenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Matematica I (Limites) (Uss)Document16 paginiMatematica I (Limites) (Uss)Kevin Jordan GuerreroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unidad1 Continuacion Funciones Limites ContinuidadDocument11 paginiUnidad1 Continuacion Funciones Limites ContinuidadcristinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ejercicios Limites IndeterminadosDocument19 paginiEjercicios Limites IndeterminadosDaniel Gacitúa Vásquez83% (12)
- Limit EsDocument13 paginiLimit Es25 Jacob Israel Sanchez GutierrezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ejercicios para Calculo Diferencial 1Document2 paginiEjercicios para Calculo Diferencial 1Aloix KitsuneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Limites y ContinuidadDocument16 paginiLimites y ContinuidadAMYNNXXXXÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trigonometría5to (18 21)Document44 paginiTrigonometría5to (18 21)Luis Carlos Ojeda GarcíaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anã Lisis Matemã Tico I - UTP-2013-IDocument40 paginiAnã Lisis Matemã Tico I - UTP-2013-IDudu RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Operaciones Con LímitesDocument16 paginiOperaciones Con LímitesLuisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Métodos para Calcular LímitesDocument5 paginiMétodos para Calcular LímitesAngel Carrillo33% (3)
- 22 Mod6 Sol 230920 194710Document7 pagini22 Mod6 Sol 230920 194710ramon.carrenoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Preexamen FInalcalculoDocument7 paginiPreexamen FInalcalculoMariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mcdi U2 A2Document5 paginiMcdi U2 A2acinomÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tema5 FuncionesDocument21 paginiTema5 Funcioneslopez1001Încă nu există evaluări
- Calculo Del Límite de FuncionesDocument16 paginiCalculo Del Límite de FuncionesGuadalupe HernándezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ma1111 2010 4sd 08Document15 paginiMa1111 2010 4sd 08Vilma FajardoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Teoremas sobre límites de funcionesDocument17 paginiTeoremas sobre límites de funcionesMilagros Accostupa QuispeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guía 1 - Funciones Trigonometricas RDocument13 paginiGuía 1 - Funciones Trigonometricas REdinson GCÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antiderivadas y Calculo de AreasDocument16 paginiAntiderivadas y Calculo de Areasdiegoagram0% (1)
- FIEE (1) Ejercicios de CalculoDocument37 paginiFIEE (1) Ejercicios de CalculoJoab Max Apaza MartinezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tarea de Limites y ContinuidadDocument8 paginiTarea de Limites y ContinuidadAmIn20122Încă nu există evaluări
- Solucion Tarea 2 Limites y ContinuidadDocument13 paginiSolucion Tarea 2 Limites y ContinuidadRicardo Rojas BocanegraÎncă nu există evaluări
- CALCULODocument19 paginiCALCULOMaleny Castillejos MezaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Apunte USM - Matemáticas IIDocument100 paginiApunte USM - Matemáticas IIMacarena Catalán GonzálezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Límites y continuidad de funciones: conceptos básicosDocument22 paginiLímites y continuidad de funciones: conceptos básicosCami DíazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unidad 4 DerivadasDocument27 paginiUnidad 4 Derivadasreynaldo_salas_2Încă nu există evaluări
- Uane - Cd.ejercicios de Repaso.c1.actividad EvaluativaDocument4 paginiUane - Cd.ejercicios de Repaso.c1.actividad EvaluativaGerman MartinezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Límites 240114 084058Document21 paginiLímites 240114 084058Belsi PalaciosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Funciones matemáticas dominio e imagenDocument7 paginiFunciones matemáticas dominio e imagenMariana BalderacchiÎncă nu există evaluări
- David Gonzalez Tarea 3Document12 paginiDavid Gonzalez Tarea 3DAVID FELIPE GONZALEZ SOSAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jhon - Betancurt - Tarea - 3 - Calculo Integral UNADDocument8 paginiJhon - Betancurt - Tarea - 3 - Calculo Integral UNADJhon BetancurtÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculo DiferencialDocument10 paginiCalculo DiferencialTunubalaAlizhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ingeniería energías renovables límites continuidadDocument8 paginiIngeniería energías renovables límites continuidadEdgar PortilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- La ecuación general de segundo grado en dos y tres variablesDe la EverandLa ecuación general de segundo grado en dos y tres variablesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Métodos Matriciales para ingenieros con MATLABDe la EverandMétodos Matriciales para ingenieros con MATLABEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Geometric modeling in computer: Aided geometric designDe la EverandGeometric modeling in computer: Aided geometric designÎncă nu există evaluări
- Crédito EducacionalDocument2 paginiCrédito EducacionalPabloCerdaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Empresa cementera PolpaicoDocument11 paginiEmpresa cementera PolpaicoPabloCerda100% (1)
- Caso AurusDocument1 paginăCaso AurusPabloCerdaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ejercicios de IntegralesDocument23 paginiEjercicios de IntegralesPabloCerdaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Caso AurusDocument1 paginăCaso AurusPabloCerdaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trabajo DesarrolloDocument7 paginiTrabajo DesarrolloPabloCerdaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ejercicio 04 Funcion SI CondicionalDocument9 paginiEjercicio 04 Funcion SI CondicionalPabloCerdaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Triptico Moringa y SabilaDocument2 paginiTriptico Moringa y SabilaJandir Brian Del Carpio CorralesÎncă nu există evaluări
- A2.CUASAPAZ - NARANJO.PRADO - QUIMBITA.ICONOGRAFIA - TURISTICA.10291 CompressedDocument15 paginiA2.CUASAPAZ - NARANJO.PRADO - QUIMBITA.ICONOGRAFIA - TURISTICA.10291 CompressedGandhy CZÎncă nu există evaluări
- PLANIMETRIADocument19 paginiPLANIMETRIAJoseLuisCeballosDelVal100% (1)
- Nutricion SenectudDocument25 paginiNutricion SenectudJorge NuñezÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Volumenes y CapacidadesDocument12 pagini2 Volumenes y CapacidadesAlberto AcostaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Produccion de AlfaDocument11 paginiProduccion de Alfamaribel flores OchoaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tarea 2 Psicologia Del DesarrolloDocument3 paginiTarea 2 Psicologia Del DesarrolloWiss Luisa DuranÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4to Grado - Tareas de Matemática. Año Escolar 2016-2017.Document82 pagini4to Grado - Tareas de Matemática. Año Escolar 2016-2017.Alberto Idrogo100% (2)
- Preguntas Examen Arte PrehistóricoDocument5 paginiPreguntas Examen Arte Prehistóricoamparusha100% (2)
- Examen Final EticaDocument7 paginiExamen Final EticaVIVIANA ROJASÎncă nu există evaluări
- Informe Científico.Document8 paginiInforme Científico.steff tatis avendañoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formato de Limpieza y PinturaDocument3 paginiFormato de Limpieza y PinturaJose Miguel GarciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guia y Evaluación de Matemáticas 1Document19 paginiGuia y Evaluación de Matemáticas 1dem00n 666Încă nu există evaluări
- Olericultura Corregida 2021-IIDocument207 paginiOlericultura Corregida 2021-IIRocio Irene Lucano TarrilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Farmacologia 1950 2000Document13 paginiFarmacologia 1950 2000RaulXCastilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- n1.m2 Mariela PianaDocument2 paginin1.m2 Mariela PianapianamarielaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Desarrollo Cognitivo PDFDocument34 paginiDesarrollo Cognitivo PDFJuliana Restrepo BenavidezÎncă nu există evaluări
- El Bautismos Extraño y Los BautistasDocument78 paginiEl Bautismos Extraño y Los Bautistasrudymonzon1239334Încă nu există evaluări
- 08 Diseño de Mezclas PDFDocument18 pagini08 Diseño de Mezclas PDFCristian F Triana0% (1)
- MICRO LABO2 ActualizadoDocument12 paginiMICRO LABO2 ActualizadoAndrésEduardoMartinezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hello Kitty Tsum Tsum PatrónDocument4 paginiHello Kitty Tsum Tsum PatrónEmma Belén Rivas MorenoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Verdad e Interioridad en San AgustínDocument8 paginiVerdad e Interioridad en San AgustínDanielÎncă nu există evaluări
- Orientaciones para El Citado de Textos BibliográficosDocument4 paginiOrientaciones para El Citado de Textos BibliográficosdairalizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tema 2 Agua 2022Document70 paginiTema 2 Agua 2022PaulaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modelo Operativo de Estimación de Recarga y EvapotranspiraciónDocument8 paginiModelo Operativo de Estimación de Recarga y EvapotranspiraciónJuan José Aparicio PorresÎncă nu există evaluări
- II-Actividad 4 Unidad 2Document5 paginiII-Actividad 4 Unidad 2Elizabeth Cintura LadinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Laboratorio Rozamiento Estatico InformeDocument6 paginiLaboratorio Rozamiento Estatico InformeMARIA JOSE MELO CAICEDOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aspectos Biológicos de La Calidad Del AguaDocument15 paginiAspectos Biológicos de La Calidad Del AguaJhordin007Încă nu există evaluări
- Biografía de Los AutoresDocument1 paginăBiografía de Los AutoresGEOVANNY EFRAIN ALVARADO VILLAÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5PARA PLOTEARTodas Las Partes de La Computadora o PCDocument6 pagini5PARA PLOTEARTodas Las Partes de La Computadora o PCIvan BejaranoÎncă nu există evaluări