Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Belt Feeder Calc. Pns Line 1
Încărcat de
Waris La Joi WakatobiDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Belt Feeder Calc. Pns Line 1
Încărcat de
Waris La Joi WakatobiDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Project
Client
Location
Unit
:
:
:
:
Assesment Jhon lin Group
PT. Pandu Nusantara Sakti (PNS)
Line 1
Belt Feeder
BELT FEEDER CALCULATION
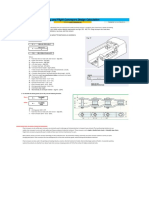
1. PROFILE BELT FEEDER
Hh
Wh
Lh
L
Cc
TOP VIEW
1. MODEL
SIDE
2. INPUT DATA
Material Type
Bulk Density
Surchage Angle
Angle Repose
Lump Size
Belt Width
Belt Feeder Length
Lifting
Friction Coefficient Coal-steel
7 ROM
Coal, Bituminous
()
()
()
600
(B)
(Cc)
(H)
(C)
1400
850
20
37
12
7
9,1
0,79
0,65
kg/m
Deg.
Deg.
mm
mm
m
m
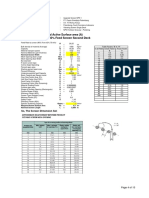
3. BELT and Idler Data
Belt Width
Belt Type
Rating
Carcass Weight
Carcass Gauge
Top Cover Gauge
Bottom Cover Gauge
Belt Weight
Carry Idler spacing
Carry Idler Weight
Unitary Carry Idler Weight
Return Idler spacing
Return Idler Weight
Unitary Return Idler Weight
Total Unitary Weight
Length of the Belt Conveyor
Material Loading on Belt
Length of Surcharge material
(B)
RMBT
Md
dGk
TGk
BGk
(Mb )
(Sc)
(Mc)
(Wc)
(Sr)
(Mr)
(Wr)
(M)
(Cc)
(Wh)
(Lh)
1400
FABRIC - EP / 23
315 / 3
31
mm
N/mm
3,75
kg/m^2
2,7
5
2
16,98
300
25
83
1,1
35
32
132,13
9,1
933
1800
mm
mm
mm
kg/m
mm
kg
kg/m
m
kg
kg/m
kg/m
m
mm
mm
5,25 kg/m
8,3804 m^2
3,35216 m^2
4. SPEED AND CAPACITY OF BELT FEEDER
Actual Ratio Drive Unit
Driver Teeth
Driven Teeth
Angular Speed of Drive Unit
Controlling Gate
Actual Angular Speed
Belt Speed
Actual Capacity
Mass Material
5.
BELT FEEDER LOAD
Numerical co-efficient, being a
function of Conveyor length
Conveyor inclination
Artificial co-efficient of friction
Total primary resistance
Slope Resistance
Resistance beyond feed zone
Resistance at Loading Material
Resistance bulk and belt
Resistance Internal Bulk
Total Seconcadary Resistance
Length of wall Palte
Throughing Factor
Co-efficient of friction idler and belt
Co-efficient of friction belt-belt cleaner
Tilting angle
Drag resistance
Resistance between Skirt Plate-material
Internal Belt Cleaner
External Belt Cleaner
Area Contact belt cleaner-Belt
Pressure Between Belt-Belt Cleaner
Resistance between Belt-Belt Cleaner
Volume of the surcharge material
Volume of unload Material
Specific Weight of Material
Internal Friction on Bulk
Shearing Resistance Vertical Load
Special main Resistance
6. POWER AND BELT TENSIONS
Effective Tension On Belt
Belt Power
Power loss due to drive pulley
Absorbed power at gear box output
Gearbox Efficiency
Required power at motor shaft
Actual Drive in Use
(i)
(Z1)
(Z2)
(n)
(h)
(n1)
(v)
(C)
(Mg)
350
20
15
31
1485
7
35,93
0,752
752,161
0,2458
(n)
()
(f)
(FH)
(FN)
(Fa)
(Fska)
(Fb)
(Fw)
(Fs)
(L)
(Ci)
(0)
(1)
(i)
(Fi)
(Fsk)
(bi)
(be)
(Ai)
(P)
(Fbc)
(Vfs)
(Vu)
(Q)
(1)
(TQ)
(Fsp)
5
0,03
398,49
1,905
208,934
547,319
100
315
1171,25
3900
0,4
0,35
0,65
0
0
5178,83
0
0
0
0
0
1,08
0,69
1,50
0,75
11077,90
16256,73
(Te)
(Pb)
(Pl)
(Pa)
()
17826,48
13,41
0,21
13,62
94,00
14,5
15
(Ptotal)
(PActual)
rpm
mm
rpm
m/s
t/h
m/s
350
Deg.
N
N
N
N
N
N
N
mm
deg
N
N
m
N/m
N
m
m
Ton
Assuming
N
N
N
kW
kW
kW
%
kW
Kw
230
Pulley Surface type
Coefficient of friction
Take-up Type
Wrap angel
Tension on tight side
Tension on slack side
Belt sag
Minimum Tension
Tail Tension
length of Take-up Pulley from Head
Lift of Take-up Pulley from Head
Take-up Tension
Belt Selection
Maximum Belt Running Tension = (T1)/B
Belt Selection -----> FABRIC - EP / 315 / 3
Running Tension / Rating.
7. PULLEY DIAMETER SELECTION
Recommended Min. Pulley Diameter
- Drive Pulley Diameter
- Tail Pulley Diameter
Assuming Mass of Pulley
- Head Pulley Mass
- Tail Pulley Mass
8. DRIVE PULLEY SHAFT DESIGN
Dia. Shaft at Coupling
Weight of Head Pulley
Horizontal Force
Vertical Force
Resultant Force
Pulley Bearing Center
arm Length
Bending Moment
Torque
Combined Shock and Fatique Factor (Bending)
Combined Shock and Fatique Factor (Torsion)
Equivalent Torque
Allowable Shear Stress
Case:1 Based on Equivalent torque
Shaft Diameter at Hub
Case:2 Based on Linear deflection.
Pulley Bearing Center
Max Deflection
Allowable Deflection
Shaft Diameter Required at Hub.
(T1)
(T2)
(S)
(Tmin)
(Tt)
(L1)
(H1)
(Ttu)
(Tmax)
Rubber Lagging Pulley
0,4
Manual
180
27501,79
9675,31
0,02
316,89
9557,89
0
0
9675,3
19,64
31
63%
1,65
Deg.
N
N
N
N
m
m
N/mm
N/mm
Ok, but check the Accel. & drift condition
(DTr1)
(DTr2)
400
315
mm
mm
(Mh)
(Mt)
490
450
kg
kg
(Dc)
(Whp)
(Fhh)
(Fhv)
(Fhr)
(Lbc)
(al)
(MB)
(MT)
(Kb)
(Kt)
(Teq)
(fs)
120
4806,9
33801,1
-4752,6
34133,60642
2
0,225
3840,03
1929,15
2
1,5
8207,1
45
mm
N
N
N
N
m
m
N.m
N.m
N.m
MPa
(Dh)
97,57
mm
(Lbc)
2
1200
0,00167
102,82
mts
mm
68,23
mm
(a)
(Dr)
Case:3 Based on Equivalent torque at coupling end.
Shaft Diameter at Hub
(Dc)
Assuming
Assuming
9. TAIL PULLEY SHAFT DESIGN
Weight of Head Pulley
Horizontal Force
Vertical Force
Resultant Force
Bending Moment
Allowable Bending Stress
(Wtp)
(Fth)
(Ftv)
(Ftr)
(MtB)
(fb)
6376,5
19115,78
6376,5
20151,25
2267,02
90
N
N
N
N
N.m
MPa
Case:1 Based on Bending moment.
Shaft diameter required at hub
(Dth1)
80,06
mm
Case:2 Based on Linear deflection
Shaft diameter reqd. at hub
(Dth2)
90,13
mm
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- BELT FEEDER Preliminary Dimension IngDocument29 paginiBELT FEEDER Preliminary Dimension Ingshani5573100% (1)
- Belt Feeder Calculation CEMADocument7 paginiBelt Feeder Calculation CEMANAITIK100% (4)
- Apron Feeder Power Calculations PDFDocument4 paginiApron Feeder Power Calculations PDFtuba25% (4)
- Conveyor design parameters for slag ash materialDocument33 paginiConveyor design parameters for slag ash materialMustafa AkbarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sidewinder ManualDocument162 paginiSidewinder Manualoscarjofk0% (1)
- Analisis Drag Scrapper Chain Feeder (FB01 & FB02) EPIDocument10 paginiAnalisis Drag Scrapper Chain Feeder (FB01 & FB02) EPIWaris La Joi WakatobiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Belt Catalog #2 Bridge StoneDocument55 paginiBelt Catalog #2 Bridge Stonetinyfalse100% (3)
- Chapter 13 D1 CEMA Bucket Elevator HP and CalculationsDocument4 paginiChapter 13 D1 CEMA Bucket Elevator HP and Calculationshafidh naufaldiÎncă nu există evaluări
- BELT CONVEYOR - Discharge TrajectoryDocument1 paginăBELT CONVEYOR - Discharge TrajectoryEslam FaroukÎncă nu există evaluări
- BELT CONVEYOR - Discharge TrajectoryDocument3 paginiBELT CONVEYOR - Discharge TrajectorySergio Diaz DuarteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Belt Conveyor CalculationDocument8 paginiBelt Conveyor CalculationFarrahxviiiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transfer Chute Design ManualDocument4 paginiTransfer Chute Design ManualluiasnadradeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manual Helix Delta t6Document309 paginiManual Helix Delta t6Ricardo Garay Reinoso100% (2)
- Bucket Elevator Excel Calculations Bucket Elevator ApplicationsDocument22 paginiBucket Elevator Excel Calculations Bucket Elevator ApplicationsThaigroup CementÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sidewinder Manual (001-155)Document150 paginiSidewinder Manual (001-155)NighWolfÎncă nu există evaluări
- Apron Feeder 7Document1 paginăApron Feeder 7cumpio425428100% (1)
- Telescopic ChuteDocument2 paginiTelescopic Chutebiswajit sabuiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rubber Belt Conveyor Calculations (ISO 5048: 1989 E) : BC 2304 NDDocument8 paginiRubber Belt Conveyor Calculations (ISO 5048: 1989 E) : BC 2304 NDmah moudÎncă nu există evaluări
- Travelling Trippers PDFDocument4 paginiTravelling Trippers PDFPinakesh GhoshÎncă nu există evaluări
- FeederDocument13 paginiFeedernileshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Belt Conveyor Pulley Design - Why The FailuresDocument16 paginiBelt Conveyor Pulley Design - Why The FailuresenrimauryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Belt Conveyor Take Up DesignDocument4 paginiBelt Conveyor Take Up DesignKroya HunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Belt ConveyorDocument3 paginiBelt ConveyorJawed AnsariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bucket Elevators for Powder and Granular MaterialsDocument20 paginiBucket Elevators for Powder and Granular MaterialsCORDOVA DAVILA HECTOR ALONSOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Apron FeederDocument2 paginiApron FeederRaji Suri100% (1)
- Pipe ConveyorDocument4 paginiPipe ConveyorDIBYENDU MONDALÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chute Calculation ExampleDocument1 paginăChute Calculation ExampleBimal DeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cema 576Document9 paginiCema 576Edwin MariacaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chain Conveyor Design Calculation for 400 TPH Drag ConveyorDocument3 paginiChain Conveyor Design Calculation for 400 TPH Drag Conveyorsudip giriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sturt Air ClassifierDocument6 paginiSturt Air ClassifierHenry Vladimir VianchaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 Drag Conveyor Section VIIDocument11 pagini10 Drag Conveyor Section VIIBUDAPESÎncă nu există evaluări
- Belt Feeder Properly DesignedDocument2 paginiBelt Feeder Properly DesignedCarlos Ediver Arias Restrepo100% (1)
- Calculation CEMA 5 - Parte1Document5 paginiCalculation CEMA 5 - Parte1Angel AlvarezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Belt Conveyor PowerDocument10 paginiBelt Conveyor PowerRyukiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conveyor Pulley DesignDocument2 paginiConveyor Pulley DesignZoebair100% (1)
- Travelling Tripper CalculationDocument5 paginiTravelling Tripper CalculationHarshGupta100% (1)
- AUMUND Belt Bucket Elevator Overcomes Coarse Material ChallengesDocument53 paginiAUMUND Belt Bucket Elevator Overcomes Coarse Material Challengesnathaniel villanueva100% (1)
- Vibrating ScreensDocument3 paginiVibrating ScreensvinodsnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Belt Conveyor Belt Feeder Design ProgramDocument147 paginiBelt Conveyor Belt Feeder Design Programmanoj983@gmail.com100% (1)
- Mulani I G (2005) - Belt Feeder Design and Hooper Bin Silo-OCR3Document455 paginiMulani I G (2005) - Belt Feeder Design and Hooper Bin Silo-OCR3Carlos Gallardo LagosÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7155 - 5 Apron Conveyors Apron FeedersDocument5 pagini7155 - 5 Apron Conveyors Apron FeedersMann GurpreetÎncă nu există evaluări
- Apron FeederDocument12 paginiApron FeederMidDeL'OrmeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sidewinder ManualDocument245 paginiSidewinder ManualkukstrongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chute Calculation ExampleDocument1 paginăChute Calculation ExampleRené Mella CidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculation CEMA 5 - Parte3Document5 paginiCalculation CEMA 5 - Parte3Angel AlvarezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yokohama Conveyor BeltsDocument87 paginiYokohama Conveyor BeltsU Thaung Myint100% (12)
- ChuteDesignFormulas Paper43Document11 paginiChuteDesignFormulas Paper43Martin LarochelleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bearing Centre and Face Width in Conveyor PulleyDocument8 paginiBearing Centre and Face Width in Conveyor PulleyPrashant MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Screw ConveyorDocument4 paginiScrew ConveyorRaji SuriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Metso Apron Feeder Application Data SheetDocument2 paginiMetso Apron Feeder Application Data SheetAnonymous 8t0V9SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advances in Mechanical Conveyor Design for Bulk Materials HandlingDocument27 paginiAdvances in Mechanical Conveyor Design for Bulk Materials HandlingJakes100% (1)
- Rex High Performance Chain Bucket Elevator ManualDocument170 paginiRex High Performance Chain Bucket Elevator ManualJohnÎncă nu există evaluări
- C 107 - Pulley Catalog - 04 2014Document46 paginiC 107 - Pulley Catalog - 04 2014kawula alit100% (1)
- Motor Selection CalculatorDocument5 paginiMotor Selection Calculatorjay100% (5)
- Extra Credit 6.6Document7 paginiExtra Credit 6.69thwonder10Încă nu există evaluări
- PT. Bangun Arta Hutama Drum Winch CalculationDocument3 paginiPT. Bangun Arta Hutama Drum Winch CalculationWaris La Joi WakatobiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8.12.01.03 - Technical Data CH890Document8 pagini8.12.01.03 - Technical Data CH890gytoman100% (1)
- Brake CalcDocument4 paginiBrake CalcYash ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Length (FT) Width (FT) Thickness (FT) Structure Description: F1 F2 F3 F4 F5Document44 paginiLength (FT) Width (FT) Thickness (FT) Structure Description: F1 F2 F3 F4 F5FoisulAlamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Komatsu ®: Model Komatsu WA900-3E0 Komatsu WA1200-6 Caterpillar 993 K (T4) GeneralDocument4 paginiKomatsu ®: Model Komatsu WA900-3E0 Komatsu WA1200-6 Caterpillar 993 K (T4) GeneralGaming BebasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technical Data Hino 700 ProfiaDocument5 paginiTechnical Data Hino 700 ProfiaWaris La Joi WakatobiÎncă nu există evaluări
- RENOLD CHAIN DOUBLE PITCH SPROCKET DESIGN SPECIFICATIONSDocument1 paginăRENOLD CHAIN DOUBLE PITCH SPROCKET DESIGN SPECIFICATIONSWaris La Joi Wakatobi0% (1)
- Pulley Weight Calc PDFDocument9 paginiPulley Weight Calc PDFWaris La Joi WakatobiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Recommended Lubricants for Gear UnitsDocument9 paginiRecommended Lubricants for Gear UnitsWaris La Joi WakatobiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ELPEX Flexible CouplingDocument24 paginiELPEX Flexible CouplingWaris La Joi WakatobiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calc - Vibrating Screen Single Deck NPK1Document5 paginiCalc - Vibrating Screen Single Deck NPK1Waris La Joi WakatobiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Operating Instructions: BA K295 EN 06.97Document45 paginiOperating Instructions: BA K295 EN 06.97Waris La Joi WakatobiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Recommended Lubricants for Gear UnitsDocument9 paginiRecommended Lubricants for Gear UnitsWaris La Joi WakatobiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Operating Instructions: BA G298 EN 08.98Document39 paginiOperating Instructions: BA G298 EN 08.98Waris La Joi WakatobiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8702en PDFDocument32 pagini8702en PDFWaris La Joi WakatobiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flender GearboxDocument47 paginiFlender GearboxWaris La Joi Wakatobi100% (2)
- RUPEX Coupling RWNDocument26 paginiRUPEX Coupling RWNWaris La Joi WakatobiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Measuring Bulk Coal Friction on Wear PlatesDocument8 paginiMeasuring Bulk Coal Friction on Wear PlatesWaris La Joi WakatobiÎncă nu există evaluări
- N-EUPEX CouplingDocument24 paginiN-EUPEX CouplingWaris La Joi WakatobiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ZAPEX CouplingDocument22 paginiZAPEX CouplingWaris La Joi WakatobiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Editor User's ManualDocument60 paginiEditor User's ManualWaris La Joi WakatobiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flexible N-EUPEXDocument22 paginiFlexible N-EUPEXWaris La Joi WakatobiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gear CouplingDocument36 paginiGear CouplingWaris La Joi WakatobiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analisis Drag Scrapper Chain Feeder (FB01 & FB02) EPIDocument10 paginiAnalisis Drag Scrapper Chain Feeder (FB01 & FB02) EPIWaris La Joi WakatobiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8703en PDFDocument35 pagini8703en PDFWaris La Joi WakatobiÎncă nu există evaluări
- SdeDocument10 paginiSderefiiiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Arpex CouplingDocument38 paginiArpex CouplingWaris La Joi WakatobiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power LV CopperDocument52 paginiPower LV CopperBeny Indrawan SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lsis Is7 Simple Usermanual PDFDocument255 paginiLsis Is7 Simple Usermanual PDFMichael DavenportÎncă nu există evaluări
- UNCTAD Review of Maritime Transport 2017 2017 10Document130 paginiUNCTAD Review of Maritime Transport 2017 2017 10Mehmet AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- PARAMAX NEW Copy Rev2Document281 paginiPARAMAX NEW Copy Rev2Waris La Joi WakatobiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Survey of Cargo Handling ResearchDocument95 paginiSurvey of Cargo Handling ResearchWaris La Joi WakatobiÎncă nu există evaluări
- AlldocumentsDocument8 paginiAlldocumentsWaris La Joi WakatobiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Editor User's ManualDocument60 paginiEditor User's ManualWaris La Joi WakatobiÎncă nu există evaluări
- DPO 6 0 Enterprise ManualDocument63 paginiDPO 6 0 Enterprise ManualWaris La Joi WakatobiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plate Mill ProcessDocument2 paginiPlate Mill ProcessVinay RajputÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial 5Document6 paginiTutorial 5Mohammad Asri ChristopherÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modified Asphalt Binders: Need of Present PavementsDocument85 paginiModified Asphalt Binders: Need of Present PavementsPalika ChopraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Full Length Test 1 Paper Civil Ki GoliDocument45 paginiFull Length Test 1 Paper Civil Ki GoliPankaj BadiwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- DestrebutionDocument4 paginiDestrebutionYosef AbebeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mccauley Constant Speed Propellers: Threaded Series Threadless Series Retention Nut Split Retainer RingDocument10 paginiMccauley Constant Speed Propellers: Threaded Series Threadless Series Retention Nut Split Retainer Ringcam cotÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modes of Heat Transfer: O Q (Gate, Ies, Ias)Document7 paginiModes of Heat Transfer: O Q (Gate, Ies, Ias)ankitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bolt Tightening TorqueDocument10 paginiBolt Tightening Torquekb7401100% (1)
- Cup 04 HSP Uk Web PDFDocument2 paginiCup 04 HSP Uk Web PDFcasda73Încă nu există evaluări
- Solutions of 8 Online Physics BrawlDocument47 paginiSolutions of 8 Online Physics BrawlDino SelimovicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Daenyx LOGODocument6 paginiDaenyx LOGOamarÎncă nu există evaluări
- B&J Fuel InjectionDocument24 paginiB&J Fuel InjectionZeeshan Ahmad100% (1)
- Z22 DoubleSuctionAxiallysplitSingleStageCentrifugalPump60HzUS E10118 USDocument2 paginiZ22 DoubleSuctionAxiallysplitSingleStageCentrifugalPump60HzUS E10118 USediÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grundfos Catalogue Industry and Water UtilityDocument542 paginiGrundfos Catalogue Industry and Water UtilityAdina Mariana Costache100% (7)
- Investigation of building collapse in AbujaDocument15 paginiInvestigation of building collapse in AbujaEmeso OjoÎncă nu există evaluări
- ExercisesDocument13 paginiExercisesAhmed Magdy BeshrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mcdonnell & Miller Service Parts CatalogDocument76 paginiMcdonnell & Miller Service Parts Catalogkamran shahÎncă nu există evaluări
- CG AlternatorsDocument23 paginiCG AlternatorsHitesh Shinde100% (2)
- Tutorial 2 - Physical OperationsDocument2 paginiTutorial 2 - Physical OperationsnasuhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Directional Controls: Solenoid Operated Directional Control ValvesDocument16 paginiDirectional Controls: Solenoid Operated Directional Control Valvesreincidentesk8Încă nu există evaluări
- Alli 15Document2 paginiAlli 15Robson belchiorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Machine Design Lesson on Buckling of Slender ColumnsDocument10 paginiMachine Design Lesson on Buckling of Slender ColumnsCarl JavierÎncă nu există evaluări
- Valve Vault Connection 2Document50 paginiValve Vault Connection 2Joel LacbayoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering Mechanics Statics 14th Edition Ebook PDFDocument61 paginiEngineering Mechanics Statics 14th Edition Ebook PDFdebra.glisson665100% (42)
- Manual CBR 600fDocument446 paginiManual CBR 600fJavi erÎncă nu există evaluări
- Innovex Lead Seal Casing Patch March2022a-1Document10 paginiInnovex Lead Seal Casing Patch March2022a-1Christian MatteoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Demolition Robot (Brokk 500) (Brochure) - 1Document2 paginiDemolition Robot (Brokk 500) (Brochure) - 1Julius GatchalianÎncă nu există evaluări
- As (One Touch)Document105 paginiAs (One Touch)carlos223344Încă nu există evaluări
- Wire Rope Inspection Checklist FormDocument1 paginăWire Rope Inspection Checklist FormРашад ИбрагимовÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dynapac f1800w En-20220822.134322Document2 paginiDynapac f1800w En-20220822.134322Fredrik ÅkessonÎncă nu există evaluări