Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
CPG Manage Cholesterol
Încărcat de
Shaoran AuliaDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
CPG Manage Cholesterol
Încărcat de
Shaoran AuliaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Clinical Practice Guidelines for Management of Cholesterol (Lipids)
The cholesterol guidelines are based on the National Cholesterol Education Program
(NCEP) Third Report of the Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of
High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III or ATP III). This CPG is not
intended to replace your clinical medical judgment. A physician's medical decisions
should be based on current medical knowledge and practices, taking into consideration the
clinical circumstances of each individual patient.
Goals
To provide guidelines for:
Screening of cholesterol in asymptomatic adults
Management of primary and secondary prevention of coronary heart disease (CHD),
stroke and peripheral vascular disease in adults
Reduction of risk through lifestyle changes and pharmacotherapy
Identification of risk factors through history and physical, including family history and
laboratory testing/screening
Assessment
Identify risk factors through history and physical, including family history and laboratory
testing/screening
Major Risk Factors
Male > 45 years of age
Female > 55 years of age
Family history of premature coronary heart disease (CHD before 55 years of age in
male first degree relative or before 65 years of age in female first degree relative)
Cigarette smoking
Hypertension confirmed by several blood pressure readings of > 140/90 mmHg or on
antihypertensive medications
Low (< 40 mg/dL) HDL cholesterol
Risk Category
CHD and CHD risk equivalents
Multiple (2+) risk factors*
Zero to one risk factor
LDL Goal (mg/dL)
< 100
< 130
< 160
CHD risk equivalents comprise:
Other clinical forms of atherosclerotic disease (peripheral arterial disease, abdominal aortic
aneurysm, and symptomatic carotid artery disease)
Diabetes - refer to the diabetes clinical practice guideline
Multiple risk factors that confer a 10-year risk~ for CHD > 20%
*Risk factors listed above
~
10 year risk assessment is based on Framingham scores for the probability of having a CHD event
in 10 years based on risk factors.
08/03
A Division of Health Care Service Corporation, a Mutual Legal Reserve Company,
an Independent Licensee of the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association
Clinical Practice Guidelines for Management of Cholesterol (Lipids)
Revised August 2003
Screening
Fasting lipoprotein profile (LDL cholesterol, total cholesterol, HDL cholesterol and
triglycerides) measured in all adults 20 years of age and older at least once every five
years. If testing can only be non-fasting, only total cholesterol and HDL will be
usable. When testing is non-fasting, and total cholesterol is > 200 mg/dL or HDL is <
40 mg/dL, a follow-up fasting lipoprotein profile is needed.
Fasting Lab Values
LDL Cholesterol
< 100
Optimal
100-129
Near optimal/above optimal
130-159
Borderline high
160-189
High
> 190
Very high
Total Cholesterol
< 200
Desirable
200-239
Borderline high
> 240
High
HDL Cholesterol
< 40
Low
> 60
High
Triglycerides
< 150
150-199
200-499
> 500
Therapy*
Normal
Borderline high
High
Very high
Initiate multifaceted lifestyle approach to reduce risk of CHD.
Therapeutic Lifestyle Changes (TLC):
TLC diet:
Saturated fat < 7% of calories, cholesterol < 200 mg/day
Consider increased viscous (soluble) fiber (10-25 g/day) and plant
stanols/sterols (2g/day) as therapeutic options to enhance LDL lowering
Weight management
Increased physical activity
Pharmacotherapy
Initiate drug therapy upon discharge from inpatient care for a major coronary event
with LDL cholesterol level of > 130 mg/dL within 24 hours of admission.
Consider adding plant stanols/sterols following 6 weeks of TLC diet therapy with
goals not achieved. Drug therapy does not replace TLC regimen.
Intensify drug therapy following 6 weeks of plant stanols/sterols and increased fiber
with goals not achieved. Again TLC regimen continues.
LDL > 190 mg/dL often requires combinations of statin and bile acid sequestrant
drug therapy.
*Refer to the ATP lll Guidelines At-A-Glance Quick Desk Reference, National Heart,
Lung and Blood Institute, NIH Publication No. 01-3305, May 2001.
08/03
Clinical Practice Guidelines for Management of Cholesterol (Lipids)
Revised August 2003
Drug classifications
HMG CoA reductase inhibitors (statins)
Bile acid sequestrants
Nicotinic acid
Fibric acids
Goals of pharmacotherapy
Risk Category
CHD or CHD Risk Equivalents
(10-year risk > 20%)
2+ Risk Factors
(10-year risk < 20%)
0-1 Risk Factor
Patient
Instructions
< 130 mg/dL
< 160 mg/dL
Secondary targets of therapy
Metabolic Syndrome
Elevated serum triglycerides
Other Dislipidemias
Incorporate lifestyle modifications and therapies into daily routines
Maintain an active role in care and enlist aid of family members, community resources
and public education programs to achieve goals
Take all medications as prescribed, even if symptom free
Specialist
Involvement
LDL goal
< 100mg/dL
Lipid specialist may be necessary for severe, complex or refractory
lipid disorders
08/03
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Cad Guidelines Secondary 10.04Document2 paginiCad Guidelines Secondary 10.04Wira LinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lipids JBDocument48 paginiLipids JBMuvenn KannanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Screening and Management of Lipids: Patient Population: ObjectiveDocument20 paginiScreening and Management of Lipids: Patient Population: ObjectiveKatie Kroll BradyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Penatalaksanaan HiperkolesterolemiaDocument24 paginiPenatalaksanaan HiperkolesterolemiaQarina Hasyala PutriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hypertension - Detection, Diagnosis and Management: ScopeDocument32 paginiHypertension - Detection, Diagnosis and Management: ScopeRudini Thung TungÎncă nu există evaluări
- HypertensionDocument1 paginăHypertensionDulce PedroÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2018 Aha/Acc/Aacvpr/Aapa/Abc/Acpm/Ada/Ags/ Apha/Aspc/Nla/Pcna Guideline On The Management of Blood Cholesterol: Executive SummaryDocument77 pagini2018 Aha/Acc/Aacvpr/Aapa/Abc/Acpm/Ada/Ags/ Apha/Aspc/Nla/Pcna Guideline On The Management of Blood Cholesterol: Executive SummarydanielÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2013 Acc Aha Guideline On The Treatment of Blood Cholesterol To Reduce Athersclerotic Risk 2Document67 pagini2013 Acc Aha Guideline On The Treatment of Blood Cholesterol To Reduce Athersclerotic Risk 2HidayadÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2018 Aha/Acc/Aacvpr/Aapa/Abc/Acpm/Ada/Ags/Apha/Aspc/Nla/Pcna Guideline On The Management of Blood Cholesterol: Executive SummaryDocument77 pagini2018 Aha/Acc/Aacvpr/Aapa/Abc/Acpm/Ada/Ags/Apha/Aspc/Nla/Pcna Guideline On The Management of Blood Cholesterol: Executive SummaryBetsy Brown ByersmithÎncă nu există evaluări
- LipidsupdateDocument23 paginiLipidsupdatedrshekarforyouÎncă nu există evaluări
- National Cholesterol Education ProgramDocument52 paginiNational Cholesterol Education Programi_top3Încă nu există evaluări
- Europea GuiaDocument12 paginiEuropea GuiaSindy VergaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Metabolic Syndrome - ClinicalKeyDocument7 paginiMetabolic Syndrome - ClinicalKeyJairo Vergara CorenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Management Strategies For Patients/Clients: DyslipidemiaDocument7 paginiManagement Strategies For Patients/Clients: DyslipidemiaminkyaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hyperlipidemia: Revised: October 4, 2019Document7 paginiHyperlipidemia: Revised: October 4, 2019HannaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 14 DyslipidemiaDocument45 pagini14 DyslipidemiaSaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dyslipidemia 2008Document80 paginiDyslipidemia 2008Pucca' JernyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dyslipidemia: Hisham Aljadhey, Pharmd, PHDDocument55 paginiDyslipidemia: Hisham Aljadhey, Pharmd, PHDRany Waisya0% (1)
- National Cholesterol Education Program: Adult Treatment Panel III (ATP III) GuidelinesDocument103 paginiNational Cholesterol Education Program: Adult Treatment Panel III (ATP III) GuidelinesAdil AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guidelines For Adult Diabetes (DM) Care: Abc'SDocument2 paginiGuidelines For Adult Diabetes (DM) Care: Abc'SElizar JarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guía de Práctica Clínica DislipidemiasDocument2 paginiGuía de Práctica Clínica DislipidemiasMelissa MendozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DyslipidemiaDocument20 paginiDyslipidemiaapi-261438047Încă nu există evaluări
- ANNALS DyslipidemiaDocument16 paginiANNALS Dyslipidemiaewb100% (1)
- Hyprlipdemia 2020 4th EditionDocument24 paginiHyprlipdemia 2020 4th EditionLillian KrazemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Management of Dyslipidemia and The Prevention of Cardiovascular DiseaseDocument2 paginiManagement of Dyslipidemia and The Prevention of Cardiovascular DiseaseBenny TrisaktyariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clinic Running QuestionsDocument8 paginiClinic Running QuestionsDraykidÎncă nu există evaluări
- ATP-4 Update: Ronald E. Greer II M.DDocument15 paginiATP-4 Update: Ronald E. Greer II M.DReg GreerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clinical Practice Guidelines For Diabetes ManagementDocument5 paginiClinical Practice Guidelines For Diabetes ManagementIqbal Fida MaulanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Management DislipidemiaDocument5 paginiManagement DislipidemiakemalmiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dyslipidemia ATP4 GUIDLINESDocument9 paginiDyslipidemia ATP4 GUIDLINESSandy GunawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- CTC7 Sample Chapter 62014Document26 paginiCTC7 Sample Chapter 62014Enrico S. Rosales50% (4)
- Dyson LineDocument10 paginiDyson LineSharly DwijayantiÎncă nu există evaluări
- LDL WhoDocument12 paginiLDL WhoReza HariansyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Leo Atp IvDocument25 paginiLeo Atp IvLeonardo MedinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dyslipidemia: Dr. Sohail AhmadDocument36 paginiDyslipidemia: Dr. Sohail AhmadChong Zhi LinÎncă nu există evaluări
- HyperlipidemiaDocument38 paginiHyperlipidemiaAadhan ArveeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacological Treatment of HyperlipiedmiaDocument8 paginiPharmacological Treatment of HyperlipiedmiajeffaguilarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dyslipidemia Guidelines Presentation v2Document39 paginiDyslipidemia Guidelines Presentation v2avicennaxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Management of HyperlipidemiaDocument39 paginiManagement of HyperlipidemiaRajgopal100% (2)
- Dyslipidemias in Chronic Kidney Disease: Current Guidelines and Future PerspectivesDocument5 paginiDyslipidemias in Chronic Kidney Disease: Current Guidelines and Future PerspectivesAn-Nisa Khoirun UmmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 23 HyperlipidemiaDocument85 pagini23 HyperlipidemiaIhab MoustafaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clinical Pharmacy Department Clinical Pharmacy and Drug Information PL 504Document61 paginiClinical Pharmacy Department Clinical Pharmacy and Drug Information PL 504Bassant Ahmed Mahmoud Ragab Abdallah AyaadÎncă nu există evaluări
- CPT Group 5 Section DDocument83 paginiCPT Group 5 Section DLinus WerkeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study 2 MNTDocument11 paginiCase Study 2 MNTapi-242547654Încă nu există evaluări
- Metabolic DR - RehabDocument24 paginiMetabolic DR - RehabMohammed Saad NabhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- HyperlipidemiaDocument17 paginiHyperlipidemiabent alfay7a2Încă nu există evaluări
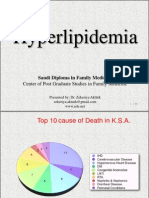
- Hyperlipidemia: Center of Post Graduate Studies in Family MedicineDocument85 paginiHyperlipidemia: Center of Post Graduate Studies in Family MedicineShimelis MekitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Management Dislipidemia PDFDocument5 paginiManagement Dislipidemia PDFkemalmiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Michael O'Riordan: Adult Treatment PanelDocument4 paginiMichael O'Riordan: Adult Treatment PanelwilhuisÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2013 ACC/AHA Guideline On The Treatment of Blood Cholesterol To Reduce Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Risk in AdultsDocument37 pagini2013 ACC/AHA Guideline On The Treatment of Blood Cholesterol To Reduce Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Risk in AdultsIman SaksoukÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diabetes Case PresentationDocument3 paginiDiabetes Case Presentationdeb haart100% (1)
- Nutrition of The Cardiovasculer SystemDocument37 paginiNutrition of The Cardiovasculer SystemAdit KurniadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- IT 9 - Nutrition of CV System - SHPDocument37 paginiIT 9 - Nutrition of CV System - SHPPraditya BriyandiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutrition of The Cardiovasculer System: Syarif Husin Blok 10Document37 paginiNutrition of The Cardiovasculer System: Syarif Husin Blok 10Desi OktarianaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dyslipidemia: Signs and SymptomsDocument24 paginiDyslipidemia: Signs and Symptomschrissanto chandraÎncă nu există evaluări
- DyslipidemiaManagement Continuum 2011Document13 paginiDyslipidemiaManagement Continuum 2011Zuleika DöObsönÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assesment and Management DM HPTDocument49 paginiAssesment and Management DM HPTKehem Pelhem FelhemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cholesterol: 50 Ways to Reduce It NaturallyDe la EverandCholesterol: 50 Ways to Reduce It NaturallyEvaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (1)
- Pathogenesis GallstonesDocument13 paginiPathogenesis Gallstonesسيتي فاطمهÎncă nu există evaluări
- 02p 0244 cp00001 02 Exhibit - A Vol1Document22 pagini02p 0244 cp00001 02 Exhibit - A Vol1Shaoran AuliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ikm UndipDocument3 paginiIkm UndipShaoran AuliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Penelitian Gagal Jantung Abstract Translate Edit 300 WordDocument1 paginăPenelitian Gagal Jantung Abstract Translate Edit 300 WordShaoran AuliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 20-Congestive Heart FailureDocument15 pagini20-Congestive Heart FailureGheavita Chandra DewiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Current Guidelines Asthma PregnancyDocument10 paginiCurrent Guidelines Asthma PregnancyethainkeroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analysis of The Degree of Undertreatment of Hyperlipidemia and Congestive Heart Failure Secondary To Coronary Artery DiseaseDocument5 paginiAnalysis of The Degree of Undertreatment of Hyperlipidemia and Congestive Heart Failure Secondary To Coronary Artery DiseaseShaoran AuliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiac Biomarkers: When To Test? - Physician Perspective: Review ArticleDocument5 paginiCardiac Biomarkers: When To Test? - Physician Perspective: Review ArticleShaoran AuliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercise For Persons With Cardiovascular DiseaseDocument3 paginiExercise For Persons With Cardiovascular Diseasebalab2311Încă nu există evaluări
- 04 146 v13n6 2014 CholesterolCholelithiasisDocument18 pagini04 146 v13n6 2014 CholesterolCholelithiasisShaoran AuliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Specific Igm and Igg Responses in Primary and Secondary Dengue Virus Infections Determined by Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent AssayDocument6 paginiSpecific Igm and Igg Responses in Primary and Secondary Dengue Virus Infections Determined by Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent AssayShaoran AuliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ferdhany Effendi (Malaysia)Document5 paginiFerdhany Effendi (Malaysia)Shaoran AuliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 Gallstone enDocument5 pagini10 Gallstone enFerdian MusthafaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Journal ReadingDocument23 paginiJournal ReadingShaoran AuliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Laporan kASUSDocument1 paginăLaporan kASUSShaoran AuliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reszon PI - Dengue Fever Rapid IgG IgMDocument2 paginiReszon PI - Dengue Fever Rapid IgG IgMShaoran AuliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fareed Kagda (Malaysia)Document1 paginăFareed Kagda (Malaysia)Shaoran AuliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Avthar Singh (Malaysia)Document6 paginiAvthar Singh (Malaysia)Shaoran AuliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ear Nose and Throat Referral GuidelinesDocument10 paginiEar Nose and Throat Referral GuidelinesShaoran AuliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ddtank Play Ddtank Champions and Other Free Games Instantly in Your Favorite Web Browser. Yuk Main DdtankDocument1 paginăDdtank Play Ddtank Champions and Other Free Games Instantly in Your Favorite Web Browser. Yuk Main DdtankShaoran AuliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Avthar Singh (Malaysia)Document6 paginiAvthar Singh (Malaysia)Shaoran AuliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Daftar Pustaka: Liver Physiol 290:G505-G510, 2006Document2 paginiDaftar Pustaka: Liver Physiol 290:G505-G510, 2006Shaoran AuliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Daftar PustakaDocument3 paginiDaftar PustakaShaoran AuliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Consensus Guidelines On The Management of Epilepsy 2010Document94 paginiConsensus Guidelines On The Management of Epilepsy 2010alivestyledÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 1 Basile Hypertension OLDocument31 pagini3 1 Basile Hypertension OLShaoran AuliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anemia Heart Failure 2010Document18 paginiAnemia Heart Failure 2010Shaoran AuliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3403.full AnemiaDocument8 pagini3403.full AnemiaShaoran AuliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chest 1971 Argano 4chest43 5Document5 paginiChest 1971 Argano 4chest43 5Shaoran AuliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The World Healthiest Foods Part III - FruitsDocument39 paginiThe World Healthiest Foods Part III - FruitsKyle J. NortonÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Body Matters Fyss - 2010 - English PDFDocument623 paginiThe Body Matters Fyss - 2010 - English PDFClauLopez99100% (1)
- Chronic Adaptations To Training: Liveitup2Document20 paginiChronic Adaptations To Training: Liveitup2dvenumohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lipids and MembranesDocument9 paginiLipids and MembranesPatricia Bianca BunagÎncă nu există evaluări
- C) Accuracy: Alhamdi Bara AspalalDocument6 paginiC) Accuracy: Alhamdi Bara AspalalKervy Jay AgraviadorÎncă nu există evaluări
- GUGGUL (Commiphora Mukul) - DR Pramod Nanda 9437409132Document7 paginiGUGGUL (Commiphora Mukul) - DR Pramod Nanda 9437409132Dr Pramod NandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Disorders of Lipid Metabolism & AtherosclerosisDocument16 paginiDisorders of Lipid Metabolism & AtherosclerosisMuthiaranifsÎncă nu există evaluări
- 21 Days KetoDocument49 pagini21 Days KetoIsmail Magh100% (4)
- Lipid BrochureDocument5 paginiLipid BrochureDharmawan WanawijayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ilyias Mpu3313 v2 Health and WellnessDocument20 paginiIlyias Mpu3313 v2 Health and WellnessjennaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atrovas Dan Feno FibrateDocument9 paginiAtrovas Dan Feno FibrateGalih Antona SinatriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interpretation of Lab TestsDocument29 paginiInterpretation of Lab TestsRitesh Singh100% (6)
- Tam1726834776305969 - RLS 4Document16 paginiTam1726834776305969 - RLS 4Rahul GÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solubility of Nicotinic Acid in Water, Ethanol, Acetone, Diethyl Ether, AcetonitrileDocument10 paginiSolubility of Nicotinic Acid in Water, Ethanol, Acetone, Diethyl Ether, AcetonitrileArini Intan MutiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Synergy Science: The Benefits of Echo WaterDocument9 paginiSynergy Science: The Benefits of Echo WaterSubbaraju GvÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiovascular Diseases: Risk FactorsDocument18 paginiCardiovascular Diseases: Risk FactorsShin QuinnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diagnostic Tests and ProceduresDocument49 paginiDiagnostic Tests and Procedurespmahi8854Încă nu există evaluări
- Fast Facts 2015 PDFDocument28 paginiFast Facts 2015 PDFاِدغارداوغوستوÎncă nu există evaluări
- HDL Precipitant 2Document7 paginiHDL Precipitant 2Nur IndahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phlebotomy Unit 6 Study GuideDocument3 paginiPhlebotomy Unit 6 Study GuidemilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activated Charcoal UseDocument6 paginiActivated Charcoal UseRodney LangleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Preparation of Soybean Milk and Its Comparision With Natural MilkDocument1 paginăPreparation of Soybean Milk and Its Comparision With Natural MilkIshan PaltaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Cholesterol MetabolismDocument18 paginiIntroduction To Cholesterol MetabolismmacapunkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding Healthy EatingDocument20 paginiUnderstanding Healthy EatingBenedict Ray Andhika100% (1)
- Presentation 1Document36 paginiPresentation 1Alice Chews IceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lipids MetabolismDocument11 paginiLipids MetabolismfakhribabikerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pink Panther - Diabetes Management - Chapter 11Document18 paginiPink Panther - Diabetes Management - Chapter 11jennmoyerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Questions: I. Understanding The Disease and PathophysiologyDocument8 paginiCase Questions: I. Understanding The Disease and Pathophysiologyapi-532124328Încă nu există evaluări
- Lipid Profile TestDocument2 paginiLipid Profile TestPrateek KanadeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutrients 11 00655Document20 paginiNutrients 11 00655Ibtidau NiamilahÎncă nu există evaluări