Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
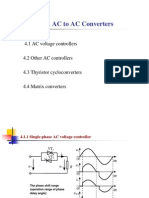
Unit V: AC Voltage Controller and Cycloconverter
Încărcat de
TapasRoutDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Unit V: AC Voltage Controller and Cycloconverter
Încărcat de
TapasRoutDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
www.Vidyarthiplus.
com
UNIT V
AC voltage controller and
cycloconverter
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
4.1.1 Single-phase AC voltage controller
VT1
VT2
u1
u1
io
O
uo
R uo
O
io
The phase shift range
(operation range of phase
delay angle):
O
u VT
O
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
Resistive load, quantitative analysis
RMS value of output voltage
Uo =
(
2U sint) d(t) =U
1
sin2 +
2
(4-1)
RMS value of output current
Uo
R
RMS value of thyristor current
Io =
(4-2)
U1 1 sin2
1 2U1 sint
(
)
d
t
=
(1 +
)
IT =
2
R
R
2
Power factor of the circuit
=
P UoIo Uo
=
=
=
S U1I o U1
1
sin 2 +
2
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
(4-3)
(4-4)
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
Inductive (Inductor- resistor) load , operation principle
u1
VT 1
O
io
uG1
VT2
R
u1
uo
L
O
uG2
O
uo
O
io
The phase shift range:
O
uVT
O
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
t
t
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
4.2 Other AC controllers
4.2.1 Integral cycle controlAC power controller
VT1
VT2
u1
io
Conduction 2N
uo angle = M
2U1
uo
R O
M
2
M
u1
uo,io
3
M
4
M
Line period
Control period = M *Line period
=2
Circuit topologies are the same as AC voltage controllers.
Only the control method is different.
Load voltage and current are both sinusoidal when thyristors are conducting.
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
4.3 Thyristor cycloconverters
4.3.1 Single- phase thyristor-cycloconverter
Circuit configuration and operation principle
P
N
Z
uo
a p=
Output
voltage
Average
a p=0
output voltage
a p=
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
Single- phase thyristor-cycloconverter
Modes of operation
uo
uo,io
O t1
iP
uP
t4
t3
t5
uN
iN
uo
t2
uo
uP
io
io
uN
t
uo
O
iP
P
N
O
iN
Rectifi
Inver
cation
sion
blocking
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
blocking
Rectifi
Inver
cation
sion
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
Typical waveforms
uo
O
io
O
t
1
3
2
6
5
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
Modulation methods for firing delay angle
Calculation method
For the rectifier circuit
u o = U d0 cos
(4-15)
u2 u3 u4 u5 u6 u1
t
For the cycloconverter
ap3 ap4
output
uo =Uom sinot
(4-16)
Equating (4- 15) and (4-16)
us2 us3 us4 us5 us6 us1
uo
Uom
cos =
sinot = sinot
Ud0
therefore
(4-17)
= cos1 ( sinot)
(4-18)
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
Principle of cosine
wave-crossing method
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
Output voltage ratio
(Modulation factor)
1.0
0.9
0.8
0.3
0.2
0.1
150
Uom
120
=
(0 1)
Ud 0
/( )
90
=0
=0.1
0.2
0.3
0.8
0.9
1.0
60
30
0
3 2 t
2
2
Output voltage phase angle
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
The configuration with common input line
4.3.2 Three- phase thyristor-cyclo converter
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
The configuration with star-connected output
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
Typical waveforms
Output voltage
200t/ms
Input current with
Single-phase output
200 t/ms
Input current with
3-phase output
200 t/ms
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
Input and output characteristics
The maximum output frequency and the harmonics in the output voltage
are the same as in single-phase circuit. Input power factor is a little
higher than single-phase circuit. Harmonics in the input current is a
little lower thanthe single- phase circuit due to the cancellation of some
harmonics among the 3 phases.
To improve the input power factor:
Use DC bias or 3k order component bias on each of the 3 output
phase voltages
Features and applications
Features:
Direct frequency conversionhigh efficiency
Bidirectional energy flow, easy to realize 4- quadrant operation
Very complicatedtoo many power semiconductor devices
Low output frequency
Low input power factor and bad input current waveform
Applications:
High power low speed AC motor drive
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
4.4 Matrix converter
Circuit configuration
input
b
c
u
S1
S1
S1
S2
S2
S2
Sij
v
output
w
S3
S3
S3
a)
b)
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
Usable input voltage
U1m
1 Um
2
Um
a)
3
U1m
2
b)
c)
a) Single-phase input b) Use 3 phase voltages c) Use 3 line-line voltages
voltage
to construct output
to construct output
voltage
voltage
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
Features
Direct frequency conversionhigh efficiency can realize good input and
output waveforms, low harmonics, and nearly unity displacement
factor
Bidirectional energy flow, easy to realize 4- quadrant operation
Output frequency is not limited by input frequency
No need for bulk capacitor (as compared to indirect frequency converter)
Very complicatedtoo many power semiconductor devices
Output voltage magnitude is a little lower as compared to indirect
frequency converter.
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
www.Vidyarthiplus.com
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Chapter 4 AC To AC Converters: OutlineDocument25 paginiChapter 4 AC To AC Converters: OutlinesambitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4 AC To AC Converters: OutlineDocument25 paginiChapter 4 AC To AC Converters: Outlinet1m0thyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inside The Power SupplyDocument41 paginiInside The Power SupplyBright UzzalÎncă nu există evaluări
- APEC 2011 Seminar ACDC ACAC Final Inclusive Swiss Rectifier As Sent 010211Document268 paginiAPEC 2011 Seminar ACDC ACAC Final Inclusive Swiss Rectifier As Sent 010211Cristian BandilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Datasheet PDFDocument12 paginiDatasheet PDFmhenley8059Încă nu există evaluări
- C324G Low Power Quad OpAmpDocument12 paginiC324G Low Power Quad OpAmpwhynot05Încă nu există evaluări
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2De la EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4 AC To AC Converters: OutlineDocument25 paginiChapter 4 AC To AC Converters: OutlineprofmnsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mc44608 Fewexternal Components Reliable and Flexible Greenline Very High Voltage PWM ControllerDocument16 paginiMc44608 Fewexternal Components Reliable and Flexible Greenline Very High Voltage PWM ControllerMary ReevesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uc3842b 3843BDocument10 paginiUc3842b 3843Bbob75Încă nu există evaluări
- Datasheet PJ494Document11 paginiDatasheet PJ494Achmad Rifdatul HisanÎncă nu există evaluări
- STRW6252Document15 paginiSTRW6252miltoncgÎncă nu există evaluări
- L2. Single Phase Ac Voltage ControllersDocument104 paginiL2. Single Phase Ac Voltage ControllersShivaram Vadla100% (2)
- Low-Power Quad Operational Amplifier: FeaturesDocument21 paginiLow-Power Quad Operational Amplifier: FeaturesAbbas AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 DC Drives Part2Document75 paginiChapter 1 DC Drives Part2Mohammad MunzirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data SheetDocument9 paginiData SheetLesseigne Marie-ClaireÎncă nu există evaluări
- Panasonic OptoTriac FormulaDocument2 paginiPanasonic OptoTriac Formulaajisetyo1990Încă nu există evaluări
- KA7500 DatasheetDocument6 paginiKA7500 DatasheetSergio Daniel BarretoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4Document41 paginiChapter 4Anil ParmarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 78 S 40Document9 pagini78 S 40Luis AlbertoÎncă nu există evaluări
- XX3842 Series FunctionDocument7 paginiXX3842 Series FunctionbernabethÎncă nu există evaluări
- RISH Master 3430: Digital Multifunction InstrumentDocument5 paginiRISH Master 3430: Digital Multifunction InstrumentShatrughna SamalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power Electronics: Prof. Shete Omkar M. SRCOE, Pune Department of Electrical Engineering University of PuneDocument84 paginiPower Electronics: Prof. Shete Omkar M. SRCOE, Pune Department of Electrical Engineering University of PuneOmkar SheteÎncă nu există evaluări
- UC2842A/3A/4A/5A UC3842A/3A/4A/5A: High Performance Current Mode PWM ControllerDocument16 paginiUC2842A/3A/4A/5A UC3842A/3A/4A/5A: High Performance Current Mode PWM ControllerCortés BernaÎncă nu există evaluări
- UC3845ANDocument15 paginiUC3845ANMiloud ChouguiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Welcome: Electrical Machines Testing DepartmentDocument58 paginiWelcome: Electrical Machines Testing DepartmentMani KandanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power Electronics LectureDocument84 paginiPower Electronics LecturevisaguyÎncă nu există evaluări
- IC-ON-LINE - CN sm34063 3672826Document8 paginiIC-ON-LINE - CN sm34063 3672826Anonymous KuTQvYTuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Datasheet PDFDocument15 paginiDatasheet PDFperro sÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4460 P 40Document16 pagini4460 P 40Mircea PanzariuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Three Phase Induction MotorDocument7 paginiThree Phase Induction MotorPradeep Kumar S SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ca3140, Ca3140A: 4.5Mhz, Bimos Operational Amplifier With Mosfet Input/Bipolar Output FeaturesDocument22 paginiCa3140, Ca3140A: 4.5Mhz, Bimos Operational Amplifier With Mosfet Input/Bipolar Output FeaturesfcabreraibanezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1De la EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Evaluare: 2.5 din 5 stele2.5/5 (3)
- Unisonic Technologies Co., LTD: Voltage Mode PWM Control CircuitDocument7 paginiUnisonic Technologies Co., LTD: Voltage Mode PWM Control CircuitEnica LiviaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch9 Intro To Power SuppliesDocument55 paginiCh9 Intro To Power SuppliesfamtaluÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manual OmbiraDocument16 paginiManual Ombirazz2nktÎncă nu există evaluări
- High Voltage Fast-Switching NPN Power Transistor: ApplicationsDocument6 paginiHigh Voltage Fast-Switching NPN Power Transistor: ApplicationsBogdan GrigoreÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECET411 Lecture 4 SCRs PDFDocument68 paginiECET411 Lecture 4 SCRs PDFJM GironellaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Danfoss MCD3000 BrosuraDocument2 paginiDanfoss MCD3000 BrosurazvekoslavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uc284xa Uc384xaDocument16 paginiUc284xa Uc384xayusufwpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Function GeneratorDocument78 paginiFunction GeneratorVishali Chowdary100% (1)
- 3744Document33 pagini3744Imran AbdullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Datasheet tl494Document6 paginiDatasheet tl494london335Încă nu există evaluări
- ZXSC410 420Document12 paginiZXSC410 420Catalin TirtanÎncă nu există evaluări
- InverterDocument26 paginiInverterGs SuÎncă nu există evaluări
- IPEMC 2012 Seminar 3ph PFC Rectifiers FINAL As Sent 310512Document178 paginiIPEMC 2012 Seminar 3ph PFC Rectifiers FINAL As Sent 310512Saidah BaisaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A4989 DatasheetDocument17 paginiA4989 DatasheetGopalkrishnan Nadar100% (1)
- Exciter Basics BeDocument35 paginiExciter Basics Bemauriceblanco1100% (4)
- Chapter Two Literature ReviewDocument18 paginiChapter Two Literature ReviewAhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Static SwitchesDocument55 paginiTypes of Static SwitchesSubhash MurkuteÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1Document43 pagini1Adithya ChandrasekaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lectures Synchronous MachinesDocument47 paginiLectures Synchronous MachinesSaddy CoolÎncă nu există evaluări
- ETPETQENDocument5 paginiETPETQENDiego CordovaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorDe la Everand110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlDe la EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1De la EverandNewnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (3)
- Citra Emulator (CPU JIT) - Pokemon X (In-Game, But Issues) (1080p HD) - Nintendo 3DS - YouTubeDocument4 paginiCitra Emulator (CPU JIT) - Pokemon X (In-Game, But Issues) (1080p HD) - Nintendo 3DS - YouTubeTapasRoutÎncă nu există evaluări
- Short Course Lecture 1 EM Waves and Eikonal EquationsDocument23 paginiShort Course Lecture 1 EM Waves and Eikonal EquationsTapasRoutÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 1423723637Document121 paginiLecture 1423723637TapasRout100% (1)
- Mechanism and Statistic Theory of Multiple Exciton Generation in Quantum DotsDocument4 paginiMechanism and Statistic Theory of Multiple Exciton Generation in Quantum DotsTapasRoutÎncă nu există evaluări
- CSE - Soft ComputingDocument70 paginiCSE - Soft ComputingTapasRoutÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Are The Points To Be Covered in A Statement of Purpose For Applying For Graduate School - QuoraDocument13 paginiWhat Are The Points To Be Covered in A Statement of Purpose For Applying For Graduate School - QuoraTapasRoutÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ece-V-Information Theory & Coding (10ec55) - NotesDocument199 paginiEce-V-Information Theory & Coding (10ec55) - NotesTapasRoutÎncă nu există evaluări
- GATE 2009 Jenna'S Digitals NotesDocument20 paginiGATE 2009 Jenna'S Digitals NotesTapasRoutÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tapas Rout: Course College/University Year AggregateDocument3 paginiTapas Rout: Course College/University Year AggregateTapasRoutÎncă nu există evaluări
- Line Follower RobotDocument5 paginiLine Follower RobotTapasRoutÎncă nu există evaluări
- Japanese & Korean Skincare QuizDocument1 paginăJapanese & Korean Skincare Quizhi143Încă nu există evaluări
- Compiler Lab VivaDocument6 paginiCompiler Lab VivaGaurav SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Documentation Matrix DS QMS 00 R2Document19 paginiDocumentation Matrix DS QMS 00 R2DhinakaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- GPS and GSM Based Vehicle Tracking SystemDocument16 paginiGPS and GSM Based Vehicle Tracking SystemShreyas Sridhar0% (2)
- Baker Campbell FormulaDocument3 paginiBaker Campbell FormulaArkayan LahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Use of Simulation in The Design of Milk-Run Intralogistics SystemsDocument6 paginiThe Use of Simulation in The Design of Milk-Run Intralogistics SystemsSoufiane AbdellaouiÎncă nu există evaluări
- For Any Further Ticket Details Contact or Call 3989 5050: Treat Your Smarticket Like CashDocument2 paginiFor Any Further Ticket Details Contact or Call 3989 5050: Treat Your Smarticket Like CashNirbhay GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Batch Process in SAP Net Weaver GatewayDocument12 paginiBatch Process in SAP Net Weaver GatewayArun Varshney (MULAYAM)Încă nu există evaluări
- Datasheet Axis q1656 Le Box Camera en US 424540Document3 paginiDatasheet Axis q1656 Le Box Camera en US 424540petereriksson.rosenforsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aprilia RSV-Tuono Maintenance ManualDocument120 paginiAprilia RSV-Tuono Maintenance ManualelettronicavicenzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DELL Latitude D420 COMPAL LA-3071P Rev 1.0 SchematicsDocument59 paginiDELL Latitude D420 COMPAL LA-3071P Rev 1.0 SchematicsviniciusvbfÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment Questions For ISMDocument17 paginiAssignment Questions For ISMTeetu TomarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 2 Quiz Section A Chapter 1 - SolutionDocument29 paginiModule 2 Quiz Section A Chapter 1 - SolutionSaad RashidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mba Time Table Updated On 1st Nov 2021Document4 paginiMba Time Table Updated On 1st Nov 2021KNRavi KiranÎncă nu există evaluări
- SGRDocument18 paginiSGRMunimÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11 Linear AlgebraDocument31 pagini11 Linear AlgebraHitesh SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Making A Quick Water Material in 3ds Max.: by Gerardo I. RamirezDocument3 paginiMaking A Quick Water Material in 3ds Max.: by Gerardo I. Ramirezpalanisamy744Încă nu există evaluări
- Ibm Qradar DGDocument7 paginiIbm Qradar DGMuhammad TalhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SWC12Document11 paginiSWC12vikkasÎncă nu există evaluări
- "Water Bottle Tracker": (For Water Refilling Stations)Document3 pagini"Water Bottle Tracker": (For Water Refilling Stations)Rated SpgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wireshark EthernetDocument7 paginiWireshark EthernetCherryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermal Plasma Decomposition of Fluorinated Greenhouse GasesDocument12 paginiThermal Plasma Decomposition of Fluorinated Greenhouse GasesSai Santhosh ManepallyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Remotecontrol: Urc-A6Document47 paginiRemotecontrol: Urc-A6Josue TrochezÎncă nu există evaluări
- QE-2019: Hands-On Session - Day-1: Summer School On Advanced Materials and Molecular ModellingDocument50 paginiQE-2019: Hands-On Session - Day-1: Summer School On Advanced Materials and Molecular ModellingAnonymous rn2qoBPjKyÎncă nu există evaluări
- ME302-Syllabus - ME-302 Mechanical Systems IIDocument2 paginiME302-Syllabus - ME-302 Mechanical Systems IIد.محمد كسابÎncă nu există evaluări
- Telecom CaseStudy TCS Enhances Customer Service Hutchison 3G Austria 06 2011Document4 paginiTelecom CaseStudy TCS Enhances Customer Service Hutchison 3G Austria 06 2011Kazim DafedarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechatronics Systems PDFDocument23 paginiMechatronics Systems PDFRamanathan DuraiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mastery TestDocument5 paginiMastery TestjessicachancoÎncă nu există evaluări
- AvPvT CCG CardlistDocument5 paginiAvPvT CCG CardlistDavid de VisserÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2006-2011 Yaris OEM Cruise Control DIY 20110315Document34 pagini2006-2011 Yaris OEM Cruise Control DIY 20110315juanÎncă nu există evaluări