Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Plant Transport Ans PDF
Încărcat de
Pa GesDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Plant Transport Ans PDF
Încărcat de
Pa GesDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
AS 5
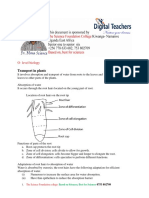
TRANSPORT IN PLANTS
ANSWERS & MARK SCHEMES
QUESTIONSHEET 1
(a) (i)
(ii)
increased solute pressure;
lowers their water potential;
thus water enters by osmosis;
max 2
inner wall has extra thickening/uneven wall thickening;
causes differential expansion when cytoplasm presses on it (opening stoma);
(b) process which returns system to the norm/equilibrium;
drying of cells leads to stomatal closure/converse;
fall in CO2 concentration leads to stomatal opening/converse;
max 3
(c) loss of water kills plants/reduces leaf surface area/reduces light absorption;
but stomata must be open for entry/exit of CO2 /O2;
also transpiration stream enables transport of salts /transpiration has a cooling function;
max 2
TOTAL 9
QUESTIONSHEET 2
(a) obtain epidermal strip/impression using nail varnish or similar;
observe under low power light microscope with eyepiece/slide grid/micrometer;
count number of stomata in stated area;
repeat to obtain mean;
(b) (i)
(ii)
B;
similar stomatal density on both surfaces in B;
A;
has lowest stomata density/least stomata;
thus less chance of water loss occurring too quickly/less chance of wilting;
TOTAL 8
QUESTIONSHEET 3
(a) X = tracheid;
Y = vessel;
(b) large leaf surface area and many stomata;
result in much water loss by transpiration;
this must be replaced from transpiration stream;
vessels can transport greater volumes/faster than tracheids;
(c) (i)
(ii)
phloem;
sieve tube;
companion cell;
the bulk transport of materials from one point to another;
as a result of pressure difference between the two points;
TOTAL 11
Page 1
AS 5
TRANSPORT IN PLANTS
ANSWERS & MARK SCHEMES
QUESTIONSHEET 4
(a) (i) potometer;
(ii) the rate of water uptake by the shoot;
(iii) movement of bubble indicates volume of water taken up by the shoot;
(b) (i)
(ii)
1
1
1
cut shoot underwater;
keeping leaves dry;
set up complete apparatus underwater;
keep all joints air tight/prevent unwanted bubbles entering;
max 3
use a fan at different speeds for air currents;
allow at least 15 minutes to acclimatise;
set air bubble to start of scale using water in reservoir (and tap);
measure distance air bubble moves in a specific time;
repeat 3 times at each air speed and calculate means;
max 4
TOTAL 10
QUESTIONSHEET 5
(a) (i)
(ii)
A = vessel/vessel unit;
B = tracheid;
xylem;
(iii) parenchyma;
fibre/sclerenchymatous fibre;
(iv) lignin;
to allow elongation during stem growth/if it was solid it would not stretch;
(b) (i)
(ii)
conduction of water and salts;
mechanical support;
cell contents have died so it is hollow allowing water flow;
end cell walls have broken down forming a continuous tube giving unimpeded water passage;
lignin gives rigidity giving some mechanical strength/keeping tube open;
3
TOTAL 12
QUESTIONSHEET 6
(a) (i)
(ii)
A = guard cells;
B = accessory cells of stoma;
C = epidermal cells;
to allow stomata to close to reduce water/transpiration loss/preventing wilting;
to allow stomata to open to enable transpiration for cooling;
to enable oxygen entry through stomata for respiration;
to enable carbon dioxide entry through stomata for photosynthesis;
(to allow transpiration = 1)
(to allow gas exchange = 1)
(iii) cells A can photosynthesise and thus accumulate sugars/use up CO2 ;
which initiates the mechanism for stomatal opening;
(b) (i)
(ii)
4
2
4 1.000
; = 381 (stomata mm2) ; (units in the question so not essential in the answer)
0.0105
assumption that the stomata are randomly distributed (and they may not be);
1
TOTAL 12
Page 2
AS 5
TRANSPORT IN PLANTS
ANSWERS & MARK SCHEMES
QUESTIONSHEET 7
(a) (i)
in angiosperms main xylem conducting tissue is vessels;
where as in gymnosperms it is tracheids;
angiosperms have broader leaves/more stomata than gymnosperms;
(ii) removal of bark removes phloem;
responsible for transport of sugars to fruit;
to enable fuit development/formation of food store in fruit;
(iii) movement/uptake/loading of sucrose from mesophyll cells to phloem is active/requires ATP;
metabolic inhibitors stop respiration/prevent ATP manufacture;
max 2
max 2
TOTAL 6
QUESTIONSHEET 8
(a) for storage;
to provide energy for fruit/tomato development;
to make fruits/tomatoes attractive to animals;
for animal dispersal;
max 3
(b) end walls of sieve tube elements are perforated/ref to sieve plates;
cytoplasm of sieve tube element is thin/peripheral/contains few organelles/has no nucleus;
cellulose cell walls allow exchange of substances across them;
ref to elongated sieve tubes;
max 3
TOTAL 6
QUESTIONSHEET 9
(a) A:
B:
C:
D:
E:
(b) (i)
(ii)
piliferous layer; (reject epidermis)
endodermis;
xylem;
phloem;
root hair;
B Function:
Adaptation:
control entry of water/salts into xylem ;
Casparian strip/ligin deposit in walls/on radial walls (blocks apoplastic path);
E Function:
Adaptation:
absorb water/salts;
large surface area/single cells/extensions of piliferous layer;
2
TOTAL 9
Page 3
AS 5
TRANSPORT IN PLANTS
ANSWERS & MARK SCHEMES
QUESTIONSHEET 10
(a) ensure all apparatus is full of water/contains no air;
cut shoot under water;
use grease/vaseline in all joints to prevent leakage;
keep leaves dry;
distance moved/mm
(b) (i)
max 2
100
80
60
40
20
0
1
number of leaves
one for correct scale;
one for correct labelled axes; (no. of leaves on X-axis)
one for correct plot;
one for joining points with a ruled straight line; (IOB recommendations)
(ii)
distance moved by bubble decreases as number of leaves decreases;
as less water is lost from leaves by transpiration;
less water is drawn up the stem/xylem;
less water absorbed by shoot;
(iii) that water uptake equals water lost from leaves;
max 3
1
TOTAL 10
QUESTIONSHEET 11
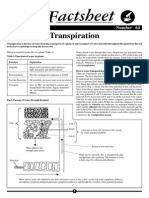
(a) thick epidermis on lower/abaxial/outer surface;
prevents diffusion of water;
no stomata on abaxial/lower/outer surface;
reduces evaporation/transpiration/diffusion loss of water;
leaf is rolled; confines/protects inner tissues/reduces/reduces diffusion gradient;
hairs; reduce air movement;
large epidermal/hinge cells; shrink to roll leaf when transpiration high;
sunken stomata; reduces transpiration;
(any two pairs of mark points)
(b) water evaporates from mesophyll cells into air spaces;
diffuses out of stoma;
loss of water from cells reduces their water potential relative to adjacent cell;
water moves from cell with higher water potential to cell with lower water potential (etc);
water drawn into mesophyll cells from xylem;
water drawn up xylem;
cohesive force between water molecules;
adhesion force between water molecules and xylem cells;
ref to water drawn across root cortex from root hairs to xylem;
ref apoplast/symplast/vacuolar pathways;
max 4
max 6
TOTAL 10
Page 4
AS 5
TRANSPORT IN PLANTS
ANSWERS & MARK SCHEMES
QUESTIONSHEET 12
(a) defoliation causes sugar concentration to fall;
suggests the source is the leaves;
(b) sugars move from sources/leaves to sinks/storage areas/main stems;
sugars actively taken up by phloem companion cells;
and passed to sieve tubes;
water follows osmotically/along water potential gradient;
creates hydrostatic pressure;
sugars removed from phloem at sink and water follows;
hydrostatic pressure difference between source and sink creates mass flow;
max 4
TOTAL 6
Page 5
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Xerophyte AnsDocument4 paginiXerophyte AnsPa GesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effects of increased carbon dioxide concentration on plants and the environmentDocument6 paginiEffects of increased carbon dioxide concentration on plants and the environmentImran MushtaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transport ADocument4 paginiTransport AKhushi ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Taller BiologíaDocument2 paginiTaller BiologíaJuliana PardoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transport in Plants MSDocument5 paginiTransport in Plants MSOtniel Dita NugrohoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Course Answerbook 22 29Document8 paginiBiology Course Answerbook 22 29Reta SahawnehÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transport in Plants O LevelDocument14 paginiTransport in Plants O LevelTatenda ChirobeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plants transport water and mineralsDocument2 paginiPlants transport water and mineralsMoloy GoraiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Leaf Epidermis and Transpiration LabDocument22 paginiLeaf Epidermis and Transpiration LabSTUTI MATHURÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5090 w01 Ms 2Document4 pagini5090 w01 Ms 2Ahmed Kaleem Khan NiaziÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology revision questionsDocument6 paginiBiology revision questionsJ.Chang ChangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transport of Materials in Flowering Plants + Trans LocationDocument71 paginiTransport of Materials in Flowering Plants + Trans LocationCarolyn KhooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transpiration Notes Class 10Document4 paginiTranspiration Notes Class 10proodootÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plant Anatomy and Physiology GuideDocument14 paginiPlant Anatomy and Physiology GuideorangeviewÎncă nu există evaluări
- GCE Biology O-Level Paper 2 Mark SchemeDocument8 paginiGCE Biology O-Level Paper 2 Mark SchemeJonMortÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transport in Plants AnswersDocument3 paginiTransport in Plants AnswersEncik Amir Kamal20% (5)
- Transpiration Exercise ExDocument8 paginiTranspiration Exercise ExGraciously meÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology STD 8 Question Bank 2020-21Document19 paginiBiology STD 8 Question Bank 2020-21ShreyashÎncă nu există evaluări
- c11 BioDocument2 paginic11 BioNur Anisha Binti Mohd AzmyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 9 TranspirationDocument5 paginiLab 9 TranspirationDeborah LinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transpiration Biology Class X - ICSE (2019-20)Document22 paginiTranspiration Biology Class X - ICSE (2019-20)the lillyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Paper One Form Three Marking SchemeDocument4 paginiBiology Paper One Form Three Marking SchemeEdwin Hazard OyaroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Marking Schemes For Topic 3 Stafford PapersDocument30 paginiMarking Schemes For Topic 3 Stafford Papersrifu91Încă nu există evaluări
- Paper 2 November 2001Document5 paginiPaper 2 November 2001MSHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transport in plant SDADocument5 paginiTransport in plant SDAkmakabe78Încă nu există evaluări
- Bio Unit 2 All Topics AnswersDocument69 paginiBio Unit 2 All Topics Answersareyouthere92100% (2)
- Transpiration LabDocument17 paginiTranspiration Labvinayakjeet03Încă nu există evaluări
- Biology Pp1 Marking Scheme Edited-1Document5 paginiBiology Pp1 Marking Scheme Edited-1Godwin OliechÎncă nu există evaluări
- Xylem and Pholem AnswerDocument6 paginiXylem and Pholem AnswerJames SmithÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3.2 Cell Transport Ans PDFDocument23 pagini3.2 Cell Transport Ans PDFtess_15Încă nu există evaluări
- Marking Guidelines For Teachers - Fourth Top Ten QuestionsDocument4 paginiMarking Guidelines For Teachers - Fourth Top Ten QuestionsAyah Al-AnaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Student Worksheet On StomataDocument2 paginiStudent Worksheet On StomataScribd_is_GreatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology EssaysDocument28 paginiBiology EssaysAmos WafulaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8.0 Transport in PlantsDocument9 pagini8.0 Transport in Plantskhenso sitholeÎncă nu există evaluări
- GCSE Biology RevisionDocument2 paginiGCSE Biology RevisionsannnnnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Absorbtion in PlantsDocument15 paginiAbsorbtion in PlantsHema KamatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transport New BioHack - 5b15f889 13af 4789 85ff 82b7d9482ea5Document11 paginiTransport New BioHack - 5b15f889 13af 4789 85ff 82b7d9482ea5Dadi YateshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Section C: Plant Physiology: Plants and FoodDocument8 paginiSection C: Plant Physiology: Plants and FoodMD MotinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plant Adaptations To Dry EnvironmentsDocument2 paginiPlant Adaptations To Dry EnvironmentsTansra KaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1-Membrane Structure Function AnswersDocument16 paginiUnit 1-Membrane Structure Function Answersareyouthere92Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 8 - Transport in PlantsDocument3 paginiChapter 8 - Transport in PlantsLeann LeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Level Transport FinestDocument25 paginiA Level Transport FinestBaguma alexÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lec. 06Document15 paginiLec. 06Wilson BhutiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guidelines - Fourth Top Ten QuestionsDocument4 paginiGuidelines - Fourth Top Ten QuestionsMeerab ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transport in PlantsDocument11 paginiTransport in PlantsZahra nooraniÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2012.water in MedicineDocument14 pagini2012.water in MedicineWILLIAM ROSALES CLAUDIOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transport in Plants Part 1Document12 paginiTransport in Plants Part 1Andre MorrisonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alternative To First Two Marking Points - Thin WallsDocument2 paginiAlternative To First Two Marking Points - Thin WallsRobert EdwardsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transpiration E - BookDocument18 paginiTranspiration E - BookAkku Tyagi50% (2)
- Plant Transport SystemsDocument18 paginiPlant Transport SystemsDanes WaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2015 Wassce - Biology 2 SolutionDocument9 pagini2015 Wassce - Biology 2 SolutionKelvin Yeboah TenkorangÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3.2 Organisms and Substance Exchange - Gas Exchange 2 - MSDocument9 pagini3.2 Organisms and Substance Exchange - Gas Exchange 2 - MSMaymunah HussainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bio Factsheet: TranspirationDocument4 paginiBio Factsheet: Transpirationlastjoe71100% (1)
- Why Do Plants Need So Much WaterDocument20 paginiWhy Do Plants Need So Much WaterCasey MorrisonÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9700 2Document15 pagini9700 2Victoria LoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transport in Plants Ans - 1Document9 paginiTransport in Plants Ans - 1Jathursan GobalakrishnanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 Transpiration LabDocument3 pagini5 Transpiration LabLauren Delgado100% (1)
- Adaptations ExtremeDocument4 paginiAdaptations Extremekikkabuttigieg1466Încă nu există evaluări
- Plant ExcretionDocument25 paginiPlant ExcretionPatrick Tew100% (1)
- Camp's Botany by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.De la EverandCamp's Botany by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.Încă nu există evaluări
- Photosynthesis Ans PDFDocument8 paginiPhotosynthesis Ans PDFPa GesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eco Ans PDFDocument5 paginiEco Ans PDFPa GesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dna Rna Ans PDFDocument8 paginiDna Rna Ans PDFPa GesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mitosis Ans PDFDocument4 paginiMitosis Ans PDFPa GesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiments Ans PDFDocument7 paginiExperiments Ans PDFPa GesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cellular AnsDocument8 paginiCellular AnsPa GesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Repro Flower Ans PDFDocument7 paginiRepro Flower Ans PDFPa GesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tissues Ans PDFDocument8 paginiTissues Ans PDFPa Ges100% (1)
- Mint in ToothpasteDocument3 paginiMint in ToothpastePa GesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human N Envirnment Ans PDFDocument9 paginiHuman N Envirnment Ans PDFPa GesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Repro Flower Ans PDFDocument7 paginiRepro Flower Ans PDFPa GesÎncă nu există evaluări
- AdaptationsDocument7 paginiAdaptationsPa GesÎncă nu există evaluări
- June 2012 Scientific ArticleDocument12 paginiJune 2012 Scientific ArticleJeffry JunusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Natural Selection in ActionDocument3 paginiNatural Selection in ActionPa GesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ecological Niche of A Leaf-Cutter BeeDocument1 paginăEcological Niche of A Leaf-Cutter BeePa GesÎncă nu există evaluări
- mRNA translation and protein synthesisDocument3 paginimRNA translation and protein synthesisPa GesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Natterjack Toads andDocument3 paginiNatterjack Toads andPa GesÎncă nu există evaluări
- New Ideas in BiologyDocument3 paginiNew Ideas in BiologyPa GesÎncă nu există evaluări
- More Than Just Saving SeedsDocument2 paginiMore Than Just Saving SeedsPa GesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exploring BiodiversityDocument4 paginiExploring BiodiversityPa GesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Looking at Plant StemsDocument3 paginiLooking at Plant StemsPa GesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity 4.24 Putting Them Back: Variegata Variegata) Back Into Their Native Forests of Eastern MadagascarDocument3 paginiActivity 4.24 Putting Them Back: Variegata Variegata) Back Into Their Native Forests of Eastern MadagascarPa GesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Extraction of - Fibres - From PlantsDocument3 paginiExtraction of - Fibres - From PlantsPa Ges0% (1)
- Is Your Lifestyle SustainableDocument1 paginăIs Your Lifestyle SustainablePa GesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Check Your Notes For Topic 4Document2 paginiCheck Your Notes For Topic 4my nameÎncă nu există evaluări
- Being DarwinDocument3 paginiBeing DarwinPa GesÎncă nu există evaluări
- BiodiversityDocument2 paginiBiodiversityPa GesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity 4.21 Superheating Starch: StudentDocument2 paginiActivity 4.21 Superheating Starch: StudentPa GesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transpiration Class 10Document15 paginiTranspiration Class 10shreya morajkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- LeavesDocument26 paginiLeavesRochelle AntigÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phytochemicals and Biological Activities of FagoniDocument4 paginiPhytochemicals and Biological Activities of Fagonirefilda suhailiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tissues - Comprehensive NotesDocument4 paginiTissues - Comprehensive NotesRatheesh HrishikeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Penetrate BarriersDocument6 paginiPenetrate BarriersCatherine TangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unani Pharmacopoeia Part II Vol IDocument156 paginiUnani Pharmacopoeia Part II Vol IHakeem Farhan Tariqi0% (1)
- Plant Tissues: PBOT 111: Lecture 5Document42 paginiPlant Tissues: PBOT 111: Lecture 5Cham RosarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phytochemical and Pharmacological Profile of Ixora Coccinea LinnDocument5 paginiPhytochemical and Pharmacological Profile of Ixora Coccinea LinnFaoezi Ramadhani MuhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: BIOLOGY 9700/33Document16 paginiCambridge International AS & A Level: BIOLOGY 9700/33Sumaya TraoreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Karakter Morfologi Dan Anatomi Pisang Diploid Dan Triploid: A S, A P KDocument6 paginiKarakter Morfologi Dan Anatomi Pisang Diploid Dan Triploid: A S, A P KYusnaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plant Organology Theory PDFDocument24 paginiPlant Organology Theory PDFCaitlin SnymanÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCERT Class 11 Problems BiologyDocument177 paginiNCERT Class 11 Problems BiologyEshwar BoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Quality ControlDocument36 paginiFinal Quality ControlRajeswari Rajarammurthy R100% (1)
- Plus One Botany, Focus Area - FinalDocument35 paginiPlus One Botany, Focus Area - Finalകായംകുളം കൊച്ചുണ്ണിÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paper 3Document3 paginiPaper 3Nur AthirahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parenchyma PDFDocument5 paginiParenchyma PDFmanoj_rkl_07Încă nu există evaluări
- 13.10 Limiting Water Loss in PlantsDocument17 pagini13.10 Limiting Water Loss in PlantsgereseÎncă nu există evaluări
- PlantDocument4 paginiPlant5/1-07 Kornkanokod ChoopongwaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sci Focus 2 HB AnswersDocument38 paginiSci Focus 2 HB Answersal83rt777760% (5)
- Poster FinalDocument1 paginăPoster FinalJulian Manongdo0% (1)
- 9700 s11 QP 31 PDFDocument12 pagini9700 s11 QP 31 PDFTommy WidjayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notes of CH Tissues Class 9Document20 paginiNotes of CH Tissues Class 9PrabhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Differentiated Plant Cell and Tissue TypesDocument22 paginiDifferentiated Plant Cell and Tissue TypesAD-MQÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: BIOLOGY 9700/31Document16 paginiCambridge International AS & A Level: BIOLOGY 9700/31For GamingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evaluation of Crude DrugsDocument7 paginiEvaluation of Crude Drugsoliver senÎncă nu există evaluări
- WARRIER-Some Important Medicinal Plants of The Western Ghats, India, A Profile (2001) PDFDocument408 paginiWARRIER-Some Important Medicinal Plants of The Western Ghats, India, A Profile (2001) PDFJuanManuelAmaroLuisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evaluation of DrugsDocument11 paginiEvaluation of DrugsAnoosha FarooquiÎncă nu există evaluări
- RUBIACEAEDocument24 paginiRUBIACEAEprofptrajasekharanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contributions To The Anatomy of Ruscus Aculeatus L Liliaceaecontributii To The PDFDocument5 paginiContributions To The Anatomy of Ruscus Aculeatus L Liliaceaecontributii To The PDFArdian SyahputraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Preliminary Phytochemical and Pharmacognostical Screening of The Ayurvedic Drug Hygrophila Auriculata (K. Schum) HeineDocument13 paginiPreliminary Phytochemical and Pharmacognostical Screening of The Ayurvedic Drug Hygrophila Auriculata (K. Schum) HeineKicky Chaca100% (1)