Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Dielectric Strength ASTM D149, IEC 60243
Încărcat de
Pugel YeremiasDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Dielectric Strength ASTM D149, IEC 60243
Încărcat de
Pugel YeremiasDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
10/12/2014
Dielectric Strength ASTM D149, IEC 60243
You are here: Home > Services > Polymers and
Plastics > Testlopedia > Dielectric Strength ASTM D149, IEC 60243
Services
Dielectric Strength ASTM D149, IEC
60243
Polymer and Plastic
Services
Send us a request
E-mail Us
web.cp-a pa c@i ntertek.com
Polymer Testing Laboratory
Call Us
Testlopedia - The Plastics
Testing Encyclopedia
+65 6322 8228
Analytical Testing of Polymers
Composites Testing
Show other conta cts
Tensile Testing
Scope:
Shear Testing
Dielectric Strength is a measure of the electrical
Adhesive Testing
strength of a material as an insulator. Dielectric strength is defined as the
Weathering Ageing Testing
maximum voltage required to produce a dielectric breakdown through the material
Automotive Plastics Testing
and is expressed as Volts per unit thickness. A higher dielectric strength represents
Packaging Services
a better quality of insulator.
Chemical Analysis
Materials Analysis
Test Procedure:
Food Contact Services
Dielectric Strength ASTM D149, IEC
60243
Polymer, Plastic Services
A-Z
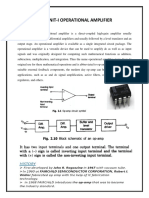
There are three basic procedures that can be used to determine the dielectric
strength of an insulator. These procedures are the short-time method, the slow
rate-of-rise method and the step-by-step method. Each of these three methods has
the same basic set-up, which consists of the test specimen placed between two
electrodes in air or oil.
Resources:
Reference Gui de to
Eva l ua ti ng As s embl y
Fa i l ure of Compos i tes a nd
Pl a s ti cs
Polymers and Plastics
Gl oba l Pol ymers a nd
Pl a s ti cs Tes ti ng
Pol ymer a nd Pl a s ti c
Servi ces A-Z
For the most common test, the short-time method, voltage is applied across the two electrodes and raised
from zero to dielectric breakdown at a uniform rate. Breakdown is when an electrical burn-through punctures
the sample, or decomposition occurs in the specimen. The rate of voltage rise is determined by the time it
takes the sample to reach dielectric breakdown.
The slow-rate-of rise method starts at 50% of the breakdown voltage as determined by the short-time-method
and is increased at a uniform rate.
The step-by-step method starts at 50% of the short-time-test then voltage is increased at equal increments for
a specified time period until breakdown. The test is sometimes performed in oil to prevent arcing from the
electrode to the ground.
Specimen size:
The recommended specimen type for this test is a 4 inch plaque or larger. Any specimen thickness can be
used; however the most common thickness is between 0.8 to 3.2 mm (0.032 to 0.125 inch). Specimens over 2
mm thick are typically tested in oil to decrease the chance of flashover before breakdown.
Data:
Dielectric strength is calculated by dividing the breakdown voltage by the thickness of the sample. The data is
expressed in Volts/mil. The location of the failure is also recorded. A higher dielectric strength represents a
better quality of insulator.
**Please note that this test description is intentionally generic in nature and aimed at providing a descriptive
summary to enhance test understanding. Due to copyright restrictions, we are not able to provide copies of
standards. Standards can be obtained from appropriate standards authorities.
Testlopedia - The Plastics Testing Encyclopedia
Dielectric Constant and Dissipation Factor
Surface Resistivity, Volume Resistivity, ASTM D257, IEC 60093
Request more information to see how Intertek can help your organization with Dielectric Strength ASTM D149,
IEC 60243.
Intertek Group plc.
Disclaimer Terms Privacy Cookies | Services About Us Contact Us | Follow us:
http://www.intertek.com/polymers/testlopedia/dielectric-strength-astm-d149/
1/1
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Dieter Kind, Hermann Kärner (Auth.) - High-Voltage Insulation Technology - Textbook For Electrical Engineers-Vieweg+Teubner Verlag (1985)Document202 paginiDieter Kind, Hermann Kärner (Auth.) - High-Voltage Insulation Technology - Textbook For Electrical Engineers-Vieweg+Teubner Verlag (1985)I'am Phil100% (3)
- QA QC PLAN For CNG..Document21 paginiQA QC PLAN For CNG..Pugel Yeremias100% (1)
- Clearance Creepage Distance in Electrical EquipmentDocument5 paginiClearance Creepage Distance in Electrical EquipmentNghiemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ik Rating Iec 62262 PDFDocument1 paginăIk Rating Iec 62262 PDFSENTHAMIL SELVANÎncă nu există evaluări
- s1446 - 6 Rev Thru 3-21-16Document57 paginis1446 - 6 Rev Thru 3-21-16Russell ShacklefordÎncă nu există evaluări
- Weidmann Paper PresentationDocument54 paginiWeidmann Paper PresentationSharad Garg100% (1)
- 06 Krempel CelluloseBaseInsulationMaterials PDFDocument29 pagini06 Krempel CelluloseBaseInsulationMaterials PDFreza515heiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brochure - Electrical Insulating PapersDocument28 paginiBrochure - Electrical Insulating Papersbpd21Încă nu există evaluări
- Ageing Phenomena of CelluloseDocument9 paginiAgeing Phenomena of CellulosedchyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To ABB Digital Transformers - ThomasDocument39 paginiIntroduction To ABB Digital Transformers - Thomassajeevi piumikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- BIOTEMP Technical Data - Updated February 2008Document23 paginiBIOTEMP Technical Data - Updated February 2008Elena Dobre100% (1)
- Iec 60243-1Document58 paginiIec 60243-1Michel Bouquet100% (1)
- 13 Ed Gulski PraesentationDocument45 pagini13 Ed Gulski Praesentationcarlos vidalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interface A PDFDocument28 paginiInterface A PDFHoangÎncă nu există evaluări
- IEC-614391-1 &2 - For Switchgears - GMA-US - LRDocument12 paginiIEC-614391-1 &2 - For Switchgears - GMA-US - LRKapil GalwaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- DC Resistance or Conductance of Insulating Materials: Standard Test Methods ForDocument18 paginiDC Resistance or Conductance of Insulating Materials: Standard Test Methods ForShaikh KamaluddinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brochure - Electrical Insulating PapersDocument28 paginiBrochure - Electrical Insulating PapersEko SusantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- D202-08 Standard Test Methods For Sampling and Testing Untreated Paper Used For Electrical InsulationDocument35 paginiD202-08 Standard Test Methods For Sampling and Testing Untreated Paper Used For Electrical InsulationSalma Farooq100% (1)
- 1.000 Scope: DVC, Electricity Dept., Spec. No. EDCON/EHV/L37 & 38Document13 pagini1.000 Scope: DVC, Electricity Dept., Spec. No. EDCON/EHV/L37 & 38abhijit0% (1)
- InsulationDocument2 paginiInsulationKumar ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- TYPICAL Defects and Failure Modes in 110-750 KV Bushings - V. Sokolov 1997Document19 paginiTYPICAL Defects and Failure Modes in 110-750 KV Bushings - V. Sokolov 1997Весна РадинÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermoplastic Insulations and Jackets For Wire and Cable: Standard Test Methods ForDocument15 paginiThermoplastic Insulations and Jackets For Wire and Cable: Standard Test Methods Forastewayb_964354182Încă nu există evaluări
- Water TreeDocument94 paginiWater TreekeyurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Low-Noise Power Transformer With The Noise Effect SurveyDocument5 paginiDesign of Low-Noise Power Transformer With The Noise Effect SurveyKannan Veeran100% (1)
- HV Insulations Comp.190310Document24 paginiHV Insulations Comp.190310M V Ravindra MutyalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Astm d1533Document5 paginiAstm d1533Kevin Carmona ToralÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hi PotDocument20 paginiHi PotPrabhudoss Thandavan0% (1)
- Tan Delta Test On 6KV HT MotorDocument6 paginiTan Delta Test On 6KV HT MotorhafezasadÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2016-2 HVTT-IEEE STD 4 PresentationDocument63 pagini2016-2 HVTT-IEEE STD 4 PresentationKarthikeyan NarayananÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water Tree Cable JointsDocument151 paginiWater Tree Cable JointsSellappan MuthusamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paper DuvalDocument10 paginiPaper Duvaljoaquin65Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4. Breakdown in Solid DielektrikDocument40 paginiChapter 4. Breakdown in Solid DielektrikLal100% (3)
- HV Machines WEBDocument16 paginiHV Machines WEBVassilis DanakasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water BlockingDocument24 paginiWater BlockingramukolakiÎncă nu există evaluări
- VEIKI - 6102 - Pertes Magnétiques Pince de Suspension B7E014AF-1Document9 paginiVEIKI - 6102 - Pertes Magnétiques Pince de Suspension B7E014AF-1Anonymous KqXmitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transformers - App Guide 2015Document6 paginiTransformers - App Guide 2015Florin AdrianÎncă nu există evaluări
- ASTM 877 Standard Test Method For Dielectric Brea PDFDocument6 paginiASTM 877 Standard Test Method For Dielectric Brea PDFAlan Jiménez FernándezÎncă nu există evaluări
- IPC-TM-650 Contact Resistance Test Methods ManualDocument2 paginiIPC-TM-650 Contact Resistance Test Methods ManualMothafukin MorrisseyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gemscab PVC Cables PDFDocument28 paginiGemscab PVC Cables PDFJaved AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- D3755-14 Standard Test Method For Dielectric BreakdowDocument6 paginiD3755-14 Standard Test Method For Dielectric Breakdowjose flores100% (1)
- 3M Cable Termination Installation InstructionDocument8 pagini3M Cable Termination Installation Instructionnixsol75Încă nu există evaluări
- IEEE STD 4000 (DP) PDFDocument46 paginiIEEE STD 4000 (DP) PDFTavo Rodríguez100% (1)
- Polarization IndexDocument1 paginăPolarization Indexfetra_anandhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- TM According To 60354 - GBDocument8 paginiTM According To 60354 - GBbpchimeraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iec 60695 11 10 2013Document15 paginiIec 60695 11 10 2013Jitendra BiswalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transformer Oil AnalysisDocument10 paginiTransformer Oil Analysishemantshah1Încă nu există evaluări
- C57.12.29 Pad-Mounted Equipment-Enclosure Integrity For Coastal EnvironmentsDocument26 paginiC57.12.29 Pad-Mounted Equipment-Enclosure Integrity For Coastal EnvironmentsSureshKumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- TXpert Hub CoreTec4 Leaflet 21-09-2020Document2 paginiTXpert Hub CoreTec4 Leaflet 21-09-2020Ronald QuispeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Standard Test Methods For Crosslinked Insulations and Jackets For Wire and CableDocument25 paginiStandard Test Methods For Crosslinked Insulations and Jackets For Wire and CableLina Rocio Gutierrez BarraganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Silicone Conductor Cover, Overhead Line Cover IndiaDocument6 paginiSilicone Conductor Cover, Overhead Line Cover IndiaNikhil MathewÎncă nu există evaluări
- Temperature RiseDocument31 paginiTemperature Rise2ander100% (3)
- A-Z Cable and Wire TerminologyDocument54 paginiA-Z Cable and Wire Terminologyssingaram1965Încă nu există evaluări
- Dry Type Power TransformersDocument14 paginiDry Type Power TransformersConstantin Dorinel100% (2)
- Partial Discharge-Feb2017 enDocument24 paginiPartial Discharge-Feb2017 enMohamedHussein MohamedHusseinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Partial Discharge Measurement and Monitoring On High Voltage XLPE CablesDocument14 paginiPartial Discharge Measurement and Monitoring On High Voltage XLPE CableskarakoukasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dielectric Strength ASTM D149, IEC 60243 .......Document10 paginiDielectric Strength ASTM D149, IEC 60243 .......Hayat UllahÎncă nu există evaluări
- ASTM D1000 10 Standard Test Methods For Pressure Sensitive Adhesive Coated Tapes Used ForDocument20 paginiASTM D1000 10 Standard Test Methods For Pressure Sensitive Adhesive Coated Tapes Used ForsasikumareÎncă nu există evaluări
- Section - Iii: Polymer Properties AND Single-Point TestingDocument26 paginiSection - Iii: Polymer Properties AND Single-Point TestingaymaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Astm D350.4467-1Document10 paginiAstm D350.4467-1Sundaravaradhan Iyengar100% (1)
- Tensile Testing Composite ASTM D3039Document3 paginiTensile Testing Composite ASTM D3039PaulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dielectric Breakdown Voltage of Insulating Liquids Using VDE ElectrodesDocument5 paginiDielectric Breakdown Voltage of Insulating Liquids Using VDE ElectrodesJavier NegretteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pipe Flexibilty Manual: Check I Design DataDocument5 paginiPipe Flexibilty Manual: Check I Design DataPugel YeremiasÎncă nu există evaluări
- PV Elite App 1-7Document2 paginiPV Elite App 1-7Pugel YeremiasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Weir Plate or Baffle Plate CalculationDocument6 paginiWeir Plate or Baffle Plate CalculationPugel Yeremias50% (2)
- Specification For Thrust BoringDocument14 paginiSpecification For Thrust BoringPugel Yeremias100% (1)
- Minimum Radius Pipe BendingDocument4 paginiMinimum Radius Pipe BendingPugel YeremiasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guide To Protective Coatings, Inspection, and Maintenance - 2nd Ed - AccessibleDocument132 paginiGuide To Protective Coatings, Inspection, and Maintenance - 2nd Ed - AccessiblePugel Yeremias100% (5)
- Pipeline Stress Analysis With Caesar IIDocument16 paginiPipeline Stress Analysis With Caesar IIPugel YeremiasÎncă nu există evaluări
- B&V Mini LNG PlantDocument84 paginiB&V Mini LNG PlantPugel YeremiasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Have A One Track Mind: Lorna WingDocument4 paginiHave A One Track Mind: Lorna WingsophilauÎncă nu există evaluări
- TI 20220909 SG320HX and SG350HX Short-Circuit Current V1 enDocument5 paginiTI 20220909 SG320HX and SG350HX Short-Circuit Current V1 en2D EngenhariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Assignment 2Document2 pagini12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Assignment 2Mohd UvaisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pte Apeuni 20240408 Global Monthly en Kd54Document321 paginiPte Apeuni 20240408 Global Monthly en Kd54Boyes WorldÎncă nu există evaluări
- FrenchDocument2 paginiFrenchRashid BumarwaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Application in BusinessDocument3 paginiComputer Application in BusinessChegg UserÎncă nu există evaluări
- RealSens Pipetech WorkshopDocument45 paginiRealSens Pipetech Workshopalioo44Încă nu există evaluări
- Additional Instructions For Mailing Your Package: Drop Off LocatorDocument2 paginiAdditional Instructions For Mailing Your Package: Drop Off LocatorEthanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Composite Insulators Profile Optimization Using Particle Swarm Algorithm and Finite Element MethodDocument6 paginiComposite Insulators Profile Optimization Using Particle Swarm Algorithm and Finite Element MethodFernando SantanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Business Ethics PDFDocument16 paginiBusiness Ethics PDFRitika DiwakarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data Sheet 3VA2225-5HL32-0AA0: ModelDocument7 paginiData Sheet 3VA2225-5HL32-0AA0: ModelJENNYÎncă nu există evaluări
- Probability DistributionsDocument167 paginiProbability DistributionslihaiyangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analysis of The Flow Induced by Air-Bubble SystemsDocument16 paginiAnalysis of The Flow Induced by Air-Bubble SystemsStephany CamacaroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circuflow 5200 Operating InstructionsDocument24 paginiCircuflow 5200 Operating InstructionsalexÎncă nu există evaluări
- PMRC Mar Va 115Document11 paginiPMRC Mar Va 115adamsaufimahmud1988Încă nu există evaluări
- Effects of Reservoir Heterogeneity in Laminated ReservoirsDocument3 paginiEffects of Reservoir Heterogeneity in Laminated ReservoirsErik Andres Garcia VillarroelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phillip Hudson: (813) - 334-3337 PSH5017@psu - EduDocument1 paginăPhillip Hudson: (813) - 334-3337 PSH5017@psu - Edupsh5017Încă nu există evaluări
- Python Cheat SheetDocument11 paginiPython Cheat SheetWasswa OpioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project LoveDocument6 paginiProject LoveANAVIC BANDIÎncă nu există evaluări
- ElectrogravimetryDocument5 paginiElectrogravimetryMELISSA VERONICA TUDELANO OSPINAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Edi WowDocument11 paginiEdi WowfantasighÎncă nu există evaluări
- Planer MachineDocument37 paginiPlaner Machinemechfame89% (9)
- Resume Bhairo SINGHwish PhotoDocument2 paginiResume Bhairo SINGHwish PhotoHR BitozzzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ic NotesDocument67 paginiIc NotesVijaya Kumar VadladiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Energy TransportDocument16 paginiEnergy TransportainmnrhÎncă nu există evaluări
- NF EN 10028-3-EnglishDocument17 paginiNF EN 10028-3-Englishhakan gecerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seal Kit Seal KitDocument61 paginiSeal Kit Seal KitМаксим Стратила0% (1)
- Surveying Lab ManualDocument76 paginiSurveying Lab ManualIan Lawrence YupanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- CDI1Document40 paginiCDI1Leonino Angelica Aiko S.Încă nu există evaluări
- Design MatrixDocument1 paginăDesign MatrixThakur Kali DassÎncă nu există evaluări