Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Uts Pemodelan
Încărcat de
shaburoDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Uts Pemodelan
Încărcat de
shaburoDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
a.
Approach that exist in travel-demand models :
- Trip based approach (4 step method)
- Integrated trip based approach
- Tour based approach
- Activity based approach
- Emerging based approach
b. The represents between activity and travel behavior in space - time diagram for
trip based approach, tour based approach, and activity schedule based approach.
c. The change of analysis that directing the trends in transportation modeling
Data : Massive OD Surveys Small Scale Detailed Surveys
Modelling methods : Aggregate Models Disaggregate Models, Static
Dynamic,
Canned Statistical Procedures Flexible Estimation of Models
Application/Forecasting : Mainframe User friendly GIS, powerful PC
Systems,
Aggregate Forecasting Disaggregate Forecasting (micro simulation)
Behavioral Representation : Homogeneous Heterogeneous (including
demographics, attitudes and perceptions). Trips Activity Schedules
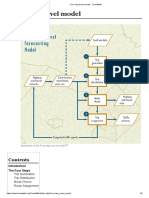
Model of Interaction of Land Use and Transportation
Growth Model
Land Use Model
Location, land-use, and rents
Access
Acci, atti
Land Use and Transport
Interaction
Transport Model
Frequencies
Destination Choice
Mode Choice
Route Assignment
Impacts :
1. The location pattern of activities induces a trip pattern, as the required cost of
performing activities.
Location
Hi
2. The location of each activity is dependent on the transport system, as it defines
the travel cost associated with all activities performed in the future.
Basic assumptions :
1. The basic behavioral position defining this interaction is centered on the activities
that individuals wish to participate in
2. Most activities are spatially dispersed in a way described by the land use pattern,
to reach them individuals travel
Concept of Four Steps Model
The sequence of four stage model :
Major steps in 4 steps method :
Trip Generation: estimation the number of home-based and non-home based
person-trips produced from, and attracted to, each zone in the study area.
Trip Distribution: Determining the trip-interchanges (i.e., number of trips from
each zone to each other zone)
Mode Choice: splitting the person-trips between each pair of zones by travel
mode obtaining both the number of vehicle trips and number of transit trips
between zones.
Assignment: Assigning the vehicle trips to the roadway network to obtain link
volumes and travel times and the person trips to the transit network.
The limitations of the four stage model :
Demand for trip making rather than for activities
Person trips as the unit of analysis
Aggregation errors :
Spatial aggregation
Demographic aggregation
Temporal aggregation
Sequential nature of the four step process
Behavior modeled in earlier steps unaffected by choices modeled in later steps
(e.g. no induced travel)
Limited types of polices that can be analyzed
x
y
300
150
350
200
400
250
250
200
n
1
Xi
300
Yi
150
XiYi
45000
350
200
70000
400
250
250
200
1300
800
Xi
90000
12250
0
16000
0
62500
4350
00
n=
=
=
4
325
B=
200
A=
Maka
X
300
350
400
250
Y
190
210
230
170
0.4
70
10000
0
50000
2650
00
Yi
22500
40000
62500
40000
1650
00
400
300
210
f(x) 190
= 0.4x + 70 230
170
200
100
0
0
R=
2
R =
0.6324
56
0.4
100
R=
200
300
n ( X i Y i ) ( X i ) ( Y i)
[ n X ( ( X )) ][ n Y ( ( Y )) ]
2
i
2
i
Zona
oi
Oi
190
130
130
190
640
700
130
200
200
130
660
720
200
70
270
140
680
760
190
130
60
260
640
690
dd
710
530
660
720
2620
Dd
820
1.154
93
580
1.094
34
750
1.1363
64
720
1
207.81
25
141.81
82
223.52
94
204.84
38
778.00
38
2
142.18
75
218.18
18
78.235
29
140.15
63
578.76
09
Ed
400
Ei
1.0937
5
1.0909
09
1.1176
47
1.0781
25
2870
1.10
Iterasi 1
Zona
1
2
3
4
dd
3
142.18
75
218.18
18
301.76
47
64.687
5
726.82
15
4
207.81
25
141.81
82
156.47
06
280.31
25
786.41
38
oi
Oi
Ei
700
700
720
720
760
760
690
690
2870
500
Dd
820
1.0539
79
580
1.0021
41
750
1.0318
9
720
0.9155
49
dd
1
219.0
301
149.4
734
235.5
954
215.9
011
820
2
142.4
919
218.6
489
78.40
28
140.4
563
580
3
146.7
219
225.1
397
311.3
88
66.75
04
750
4
190.2
624
129.8
414
143.2
564
256.6
397
720
Dd
820
580
750
720
Ed
1
219.49
85
148.83
19
232.94
63
219.15
75
820.43
42
820
0.9994
71
2
142.79
66
217.71
05
77.521
23
142.57
48
580.60
32
580
0.9989
61
3
147.03
56
224.17
34
307.88
68
67.757
18
746.85
3
750
1.0042
14
4
190.66
93
129.28
42
141.64
56
260.51
05
722.10
96
720
0.9970
79
dd
1
219.3
823
148.7
531
232.8
231
219.0
415
820
2
142.6
483
217.4
843
77.44
07
142.4
267
580
3
147.6
552
225.1
18
309.1
841
68.04
269
750
4
190.1
122
128.9
065
141.2
318
259.7
495
720
Dd
820
580
750
720
Ed
2870
1
Iterasi 2
Zona
1
2
3
4
oi
698.5
063
723.1
035
768.6
426
679.7
475
2870
Oi
700
720
760
690
Ei
1.002
138
0.995
708
0.988
756
1.015
083
2870
1
Iterasi 3
Zona
1
2
3
4
dd
Dd
Ed
oi
700
720
760
690
Oi
700
720
760
690
Ei
1
1
1
1
2870
2870
1
Iterasi 4
Zona
1
2
3
4
oi
699.7
98
720.2
62
760.6
797
689.2
603
2870
Oi
700
720
760
690
2870
Ei
1.000
289
0.999
636
0.999
106
1.001
073
Ed
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Ch.11: Transportation Planning Process (Objectives)Document17 paginiCh.11: Transportation Planning Process (Objectives)Abdulaziz Al-ghamdiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Travel Demand ForecastingDocument54 paginiTravel Demand ForecastingKristelle Ginez100% (1)
- Class Project DiscussionDocument27 paginiClass Project DiscussionHari PÎncă nu există evaluări
- Travel Demand ModelingDocument8 paginiTravel Demand ModelingMarco Jay BalanayÎncă nu există evaluări
- TRANSPODocument30 paginiTRANSPOkkkÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.3 - An Activity-Based Model Template For Cube VoyagerDocument21 pagini2.3 - An Activity-Based Model Template For Cube Voyagercitilabs100% (1)
- Uthm 6 - Note Lecture Mka 2133 - Transportation ForecastingDocument37 paginiUthm 6 - Note Lecture Mka 2133 - Transportation ForecastingazcompÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 2 Transportation PlanningDocument27 paginiLecture 2 Transportation Planninghassan tahirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 3.transportion ModellingDocument7 paginiTopic 3.transportion ModellingCivil EngineeringÎncă nu există evaluări
- Travel Demand ForecastingDocument26 paginiTravel Demand ForecastingKAYE100% (3)
- Transportation Planning and Modelling: Muhammad Zudhy Irawan Zudhyirawan - Staff.ugm - Ac.idDocument15 paginiTransportation Planning and Modelling: Muhammad Zudhy Irawan Zudhyirawan - Staff.ugm - Ac.idMohamed Ali SalemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transportation Planning System ContextDocument14 paginiTransportation Planning System ContextJUVIN SINGH KOYALÎncă nu există evaluări
- Travel Demand Forecasting I. Trip GenerationDocument5 paginiTravel Demand Forecasting I. Trip GenerationJaper WeakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transportaion Demand (4 Methods)Document5 paginiTransportaion Demand (4 Methods)Japer WeakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Travel Demand Forecasting I. Trip GenerationDocument5 paginiTravel Demand Forecasting I. Trip GenerationJaper WeakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Travel Demand Forecasting I. Trip GenerationDocument5 paginiTravel Demand Forecasting I. Trip GenerationJaper WeakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transportation Planning System ContextDocument19 paginiTransportation Planning System ContextJA Ramoneda100% (1)
- Assignment No: 01Document8 paginiAssignment No: 01waqasÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is Travel Demand ModelingDocument2 paginiWhat Is Travel Demand ModelingMahindra DeshmukhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Agent-Based ModelingDocument8 paginiAgent-Based ModelingAsaduzzaman ParishÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transportation Planning - Part 6-10Document33 paginiTransportation Planning - Part 6-10adnan qadirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Travel Demand ForecastingDocument22 paginiTravel Demand ForecastingEngr XsadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Travel Demand Forecasting PDFDocument22 paginiTravel Demand Forecasting PDFEngr XsadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trip DistributionDocument15 paginiTrip DistributionAqeel Younis100% (1)
- Transportation Engineering Introduction To Planning and The Four-Step Model January 12, 2011Document26 paginiTransportation Engineering Introduction To Planning and The Four-Step Model January 12, 2011Abdul Hamid BhattiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Highway NotesDocument111 paginiHighway NotesdzikrydsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case StudyDocument12 paginiCase StudyMikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Travel Demand ForecastingDocument14 paginiTravel Demand Forecastingpilipinas19Încă nu există evaluări
- Deypalubos Case Study 2 PDFDocument7 paginiDeypalubos Case Study 2 PDFMikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity Based Mode Choice ModellingDocument10 paginiActivity Based Mode Choice Modellinghaneena kadeejaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Travel Demand and Traffic ForecastingDocument19 paginiTravel Demand and Traffic ForecastingAli CusainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Town-Planning PPT 2Document45 paginiTown-Planning PPT 2arsabanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Subject: Transport Economics Chapter Title: Travel Demand AnalysisDocument25 paginiSubject: Transport Economics Chapter Title: Travel Demand AnalysisIrfan ShinwariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Four-Step Travel Model - TransitWikiDocument3 paginiFour-Step Travel Model - TransitWikiabacus deeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1998 WCTR MultimodalTransportModelDocument16 pagini1998 WCTR MultimodalTransportModelIrwan DharmawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 2 - Travel Demand Forecasting: Transportation PlanningDocument40 paginiLecture 2 - Travel Demand Forecasting: Transportation PlanningEngr mehraj hameedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Marshall CE 254 Trip-DistributionDocument86 paginiMarshall CE 254 Trip-DistributionVikash AgarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is Subsoil DrainageDocument30 paginiWhat Is Subsoil DrainageRajesh KhadkaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ceg552 - Chapter 6Document116 paginiCeg552 - Chapter 6Anis NabihahÎncă nu există evaluări
- BA Teknik Sipil - s12544-023-00590-5Document20 paginiBA Teknik Sipil - s12544-023-00590-5Ainayya AleenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trip DistributionDocument86 paginiTrip DistributionTaqwa Hadidi100% (1)
- Transport Modelling in The Age of Big Data: Cuauhtémoc Anda Pieter Fourie Alexander ErathDocument45 paginiTransport Modelling in The Age of Big Data: Cuauhtémoc Anda Pieter Fourie Alexander ErathGopika N SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transportation Planning and Engineering: Transportation Planning Process (Data Collection Methods - Cont'd)Document17 paginiTransportation Planning and Engineering: Transportation Planning Process (Data Collection Methods - Cont'd)Fortiter FysproÎncă nu există evaluări
- Planning of Transportation SystemsDocument11 paginiPlanning of Transportation SystemsMike WheazzyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 4Document4 paginiTopic 4VERGIE GALVEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transportation Planning and ForecastingDocument113 paginiTransportation Planning and ForecastingCarles FauzanÎncă nu există evaluări
- L3 Intro Transport PlanningDocument35 paginiL3 Intro Transport PlanningddÎncă nu există evaluări
- Webinar06 AccessibilityandTreatmentOfSpace Slides With Notes2Document126 paginiWebinar06 AccessibilityandTreatmentOfSpace Slides With Notes2UsamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- TRB ID: 01-3271: Polydor@Document17 paginiTRB ID: 01-3271: Polydor@Giora RozmarinÎncă nu există evaluări
- TransportationDocument129 paginiTransportationFaith Rezza Mahalia F. BETORIOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Travel Demand ForecastingDocument51 paginiTravel Demand ForecastingGraciele Sera-RevocalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transport Planning: ISTTT TutorialDocument91 paginiTransport Planning: ISTTT TutorialAluscia76Încă nu există evaluări
- Geography: Year Two (IP) Coursework Traffic CongestionDocument12 paginiGeography: Year Two (IP) Coursework Traffic CongestionLee Xiu Qi ArthurÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Activity-Based System of Models For Student Mobility SimulationDocument12 paginiAn Activity-Based System of Models For Student Mobility SimulationTarek SetifienÎncă nu există evaluări
- TranspoDocument6 paginiTranspoEri EliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Forecasting Travel DemandDocument3 paginiForecasting Travel DemandCarl John GemarinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 5. Transportation Planning SurveysDocument36 paginiLecture 5. Transportation Planning SurveysRespicus RJÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2-7958-Article Text-14318-1-10-20210602Document7 pagini2-7958-Article Text-14318-1-10-20210602Pratik JhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- WK 4 Trip Distribution AnalysisDocument9 paginiWK 4 Trip Distribution AnalysisBryan EweÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fix 1Document34 paginiFix 1shaburoÎncă nu există evaluări
- CIVL402 WorksheetsDocument22 paginiCIVL402 WorksheetsshaburoÎncă nu există evaluări
- S07430010220114023S0743POK p13Document150 paginiS07430010220114023S0743POK p13shaburoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Example of Data From Sieve Analysis Where The Weight Is Equal To The Mass of Soil Retained On A Screen of Particular SizeDocument24 paginiExample of Data From Sieve Analysis Where The Weight Is Equal To The Mass of Soil Retained On A Screen of Particular SizeshaburoÎncă nu există evaluări
- S0793POK p05Document46 paginiS0793POK p05shaburoÎncă nu există evaluări
- CBRDocument4 paginiCBRshaburoÎncă nu există evaluări
- S07430010220114018S0743POK p05 06Document16 paginiS07430010220114018S0743POK p05 06shaburoÎncă nu există evaluări
- S04420000220104002S0442 Session 2 Planning For Earthwork ConstructionDocument24 paginiS04420000220104002S0442 Session 2 Planning For Earthwork ConstructionshaburoÎncă nu există evaluări
- S04420000220104003S0442 Session 3 Heavy Equipment For Earthwork ConstructionDocument25 paginiS04420000220104003S0442 Session 3 Heavy Equipment For Earthwork ConstructionshaburoÎncă nu există evaluări
- S04420000220104008S0442 Session 10-11 Concrete and Concrete EquipmentDocument36 paginiS04420000220104008S0442 Session 10-11 Concrete and Concrete EquipmentshaburoÎncă nu există evaluări
- S04420000220104006S0442 Session 6-7 FoundationDocument39 paginiS04420000220104006S0442 Session 6-7 FoundationshaburoÎncă nu există evaluări
- S08440010220124017S0844 P13-14 Bolt ConnectionDocument34 paginiS08440010220124017S0844 P13-14 Bolt Connectionshaburo100% (1)
- S04420000220104001S0442 Session 1 Introduction To Construction MethodDocument17 paginiS04420000220104001S0442 Session 1 Introduction To Construction MethodshaburoÎncă nu există evaluări
- S04420000220104008S0442 Session 10-11 Concrete and Concrete EquipmentDocument36 paginiS04420000220104008S0442 Session 10-11 Concrete and Concrete EquipmentshaburoÎncă nu există evaluări
- S08440010220124019S0844 P17-18 High Tension Bolt (HTB)Document12 paginiS08440010220124019S0844 P17-18 High Tension Bolt (HTB)shaburoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hot Bin 1: Pemeriksaan Analisa Saringan Agregat Halus Dan KasarDocument8 paginiHot Bin 1: Pemeriksaan Analisa Saringan Agregat Halus Dan KasarshaburoÎncă nu există evaluări
- S07430010220114023S0743POK p13Document150 paginiS07430010220114023S0743POK p13shaburoÎncă nu există evaluări
- S08440010220124012S0844 P23-24 Base PlateDocument23 paginiS08440010220124012S0844 P23-24 Base PlateshaburoÎncă nu există evaluări
- S08440010220124014S0844 P03-04 Design of Tension MembersDocument35 paginiS08440010220124014S0844 P03-04 Design of Tension MembersshaburoÎncă nu există evaluări
- S08440010220124015S0844 P05-06 Design of Compression MemberDocument45 paginiS08440010220124015S0844 P05-06 Design of Compression MembershaburoÎncă nu există evaluări
- S08440010220124020S0844 P19-22 Steel ColumnDocument16 paginiS08440010220124020S0844 P19-22 Steel ColumnshaburoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Klip-Lok 406 271003Document8 paginiKlip-Lok 406 271003kh88hmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- S08440010220124015S0844 P05-06 Design of Compression MemberDocument45 paginiS08440010220124015S0844 P05-06 Design of Compression MembershaburoÎncă nu există evaluări
- S07530010220124009S0753 P01 - 2Document38 paginiS07530010220124009S0753 P01 - 2shaburoÎncă nu există evaluări
- S08440010220124018S0844 P15-16 Weld ConnectionDocument24 paginiS08440010220124018S0844 P15-16 Weld ConnectionshaburoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ethical Aspects of Information Technology: Course Name: CB142 Year: 2011Document10 paginiEthical Aspects of Information Technology: Course Name: CB142 Year: 2011shaburoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hot Bin 1: Pemeriksaan Analisa Saringan Agregat Halus Dan KasarDocument8 paginiHot Bin 1: Pemeriksaan Analisa Saringan Agregat Halus Dan KasarshaburoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ba PalowskiDocument9 paginiBa PalowskishaburoÎncă nu există evaluări
- George J.critsDocument55 paginiGeorge J.critsshaburo100% (1)
- AMERSHAM Ion Exchange ManualDocument162 paginiAMERSHAM Ion Exchange ManualNguyen Thi Phuong NhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Approved Water Product As of 06092019 FittingsDocument6 paginiApproved Water Product As of 06092019 FittingsHazel Liow HYÎncă nu există evaluări
- Apollo15 Colossus3 CMC Data CardsDocument18 paginiApollo15 Colossus3 CMC Data CardsPablo De LeonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Product Data: 58GP, GS Upflow Natural-Draft Gas-Fired FurnaceDocument8 paginiProduct Data: 58GP, GS Upflow Natural-Draft Gas-Fired FurnaceMichael MartinÎncă nu există evaluări
- 213078Document38 pagini213078Mbade NDONGÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECE 551 Assignment 2: Ajit R Kanale, 200132821 January 25, 2017Document5 paginiECE 551 Assignment 2: Ajit R Kanale, 200132821 January 25, 2017Ajit KanaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3CP.1.3 PaperDocument4 pagini3CP.1.3 PaperAlexander ChekalinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical ComprehensionDocument14 paginiMechanical Comprehensiondanielhealy100% (6)
- SolarDocument4 paginiSolarShweta RawatÎncă nu există evaluări
- SAP Brazil Localization PortfolioDocument31 paginiSAP Brazil Localization Portfoliosatishkr14Încă nu există evaluări
- User Manual: Touch Control LED LampDocument1 paginăUser Manual: Touch Control LED LampHector LuisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab ManualDocument9 paginiLab ManualMohit SinhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Saniaccess Pump Product SheetDocument1 paginăSaniaccess Pump Product SheetArun UdayabhanuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trailler On JettyDocument4 paginiTrailler On JettyFuad Andaru BaskaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 78-00583 Profo Metpoint Ocv Compact 8p Int DisplayDocument8 pagini78-00583 Profo Metpoint Ocv Compact 8p Int DisplayLinh NgoÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Overview of Load Flow Analysis Methods For Electrical Distribution NetworksDocument3 paginiAn Overview of Load Flow Analysis Methods For Electrical Distribution NetworksSantosh Ramana Kumar JogaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Production and Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients 5EEC Group 1Document10 paginiProduction and Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients 5EEC Group 1Derrick RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- BedZED Toolkit Part 1Document44 paginiBedZED Toolkit Part 1Razvan NenciuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Business - 29 Aug 2014Document146 paginiBusiness - 29 Aug 2014Iftikhar AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bank Account StatementDocument1 paginăBank Account StatementsadasdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Building A Reliable Capacitive Sensor Interface by Analog DevicesDocument2 paginiBuilding A Reliable Capacitive Sensor Interface by Analog DevicesShri KulkarniÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCNA 1 v60 Study Material Chapter 9 Transport LayerDocument9 paginiCCNA 1 v60 Study Material Chapter 9 Transport LayerRazaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curriculum Vitae: Contact DetailsDocument3 paginiCurriculum Vitae: Contact DetailsDhileepÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is A Surge TankDocument13 paginiWhat Is A Surge TankAnikateÎncă nu există evaluări
- Degassed Cation Conductivity MeasurementDocument11 paginiDegassed Cation Conductivity MeasurementPhạm Nhật MinhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Astm f1554Document3 paginiAstm f1554ingsabrinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PSM 1-6-7 (Ic) Emma Work Cards R 20 (30-11-18)Document322 paginiPSM 1-6-7 (Ic) Emma Work Cards R 20 (30-11-18)Héctor SánchezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gujarat Technological University: SUBJECT NAME: Computer Aided Manufacturing SUBJECT CODE: 2171903 BE Semester VIIDocument4 paginiGujarat Technological University: SUBJECT NAME: Computer Aided Manufacturing SUBJECT CODE: 2171903 BE Semester VIIKrupal VithlaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- 080Document10 pagini080Luis Adrián ElguézabalÎncă nu există evaluări
- TqemDocument3 paginiTqemJudith D'SouzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- B1 Eurocodes Implementation & UseDocument12 paginiB1 Eurocodes Implementation & UsetyukgombaÎncă nu există evaluări