Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Chris Hoffman Explains Linux File System Conventions - How-To Geek
Încărcat de
Ron GonzalesTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Chris Hoffman Explains Linux File System Conventions - How-To Geek
Încărcat de
Ron GonzalesDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
HTG Explains: The Linux Directory Structure Explained
http://www.howtogeek.com/117435/htg-explains-the-linux-directory-structureexplained/
If youre coming from Windows, the Linux file system structure can seem
particularly alien. The C:\ drive and drive letters are gone, replaced by a /
and cryptic-sounding directories, most of which have three letter names.
The Filesystem Hierarchy Standard (FHS) defines the structure of file systems on
Linux and other UNIX-like operating systems. However, Linux file systems also
contain some directories that arent yet defined by the standard.
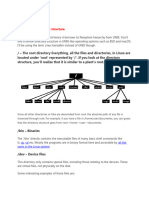
/ The Root Directory
Everything on your Linux system is located under the / directory, known as the
root directory. You can think of the / directory as being similar to the C:\
directory on Windows but this isnt strictly true, as Linux doesnt have drive
letters. While another partition would be located at D:\ on Windows, this other
partition would appear in another folder under / on Linux.
/bin Essential User Binaries
The /bin directory contains the essential user binaries (programs) that must be
present when the system is mounted in single-user mode. Applications such as
Firefox are stored in /usr/bin, while important system programs and utilities
such as the bash shell are located in /bin. The /usr directory may be stored on
another partition placing these files in the /bin directory ensures the system
will have these important utilities even if no other file systems are mounted.
The /sbin directory is similar it contains essential system administration
binaries.
/boot Static Boot Files
The /boot directory contains the files needed to boot the system for example,
the GRUB boot loaders files and your Linux kernels are stored here. The boot
loaders configuration files arent located here, though theyre in /etc with
the other configuration files.
/cdrom Historical Mount Point for CD-ROMs
The /cdrom directory isnt part of the FHS standard, but youll still find it on
Ubuntu and other operating systems. Its a temporary location for CD-ROMs
inserted in the system. However, the standard location for temporary media is
inside the /media directory.
/dev Device Files
Linux exposes devices as files, and the /dev directory contains a number of
special files that represent devices. These are not actual files as we know
them, but they appear as files for example, /dev/sda represents the first SATA
drive in the system. If you wanted to partition it, you could start a partition
editor and tell it to edit /dev/sda.
This directory also contains pseudo-devices, which are virtual devices that
dont actually correspond to hardware. For example, /dev/random produces random
numbers. /dev/null is a special device that produces no output and automatically
discards all input when you pipe the output of a command to /dev/null, you
discard it.
/etc Configuration Files
The /etc directory contains configuration files, which can generally be edited
by hand in a text editor. Note that the /etc/ directory contains system-wide
configuration files user-specific configuration files are located in each
users home directory.
/home Home Folders
The /home directory contains a home folder for each user. For example, if your
user name is bob, you have a home folder located at /home/bob. This home folder
contains the users data files and user-specific configuration files. Each user
only has write access to their own home folder and must obtain elevated
permissions (become the root user) to modify other files on the system.
/lib Essential Shared Libraries
The /lib directory contains libraries needed by the essential binaries in the
/bin and /sbin folder. Libraries needed by the binaries in the /usr/bin folder
are located in /usr/lib.
/lost+found Recovered Files
Each Linux file system has a lost+found directory. If the file system crashes, a
file system check will be performed at next boot. Any corrupted files found will
be placed in the lost+found directory, so you can attempt to recover as much
data as possible.
/media Removable Media
The /media directory contains subdirectories where removable media devices
inserted into the computer are mounted. For example, when you insert a CD into
your Linux system, a directory will automatically be created inside the /media
directory. You can access the contents of the CD inside this directory.
/mnt Temporary Mount Points
Historically speaking, the /mnt directory is where system administrators mounted
temporary file systems while using them. For example, if youre mounting a
Windows partition to perform some file recovery operations, you might mount it
at /mnt/windows. However, you can mount other file systems anywhere on the
system.
/opt Optional Packages
The /opt directory contains subdirectories for optional software packages. Its
commonly used by proprietary software that doesnt obey the standard file system
hierarchy for example, a proprietary program might dump its files in
/opt/application when you install it.
/proc Kernel & Process Files
The /proc directory similar to the /dev directory because it doesnt contain
standard files. It contains special files that represent system and process
information.
/root Root Home Directory
The /root directory is the home directory of the root user. Instead of being
located at /home/root, its located at /root. This is distinct from /, which is
the system root directory.
/run Application State Files
The /run directory is fairly new, and gives applications a standard place to
store transient files they require like sockets and process IDs. These files
cant be stored in /tmp because files in /tmp may be deleted.
/sbin System Administration Binaries
The /sbin directory is similar to the /bin directory. It contains essential
binaries that are generally intended to be run by the root user for system
administration.
/selinux SELinux Virtual File System
If your Linux distribution uses SELinux for security (Fedora and Red Hat, for
example), the /selinux directory contains special files used by SELinux. Its
similar to /proc. Ubuntu doesnt use SELinux, so the presence of this folder on
Ubuntu appears to be a bug.
/srv Service Data
The /srv directory contains data for services provided by the system. If you
were using the Apache HTTP server to serve a website, youd likely store your
websites files in a directory inside the /srv directory.
/tmp Temporary Files
Applications store temporary files in the /tmp directory. These files are
generally deleted whenever your system is restarted and may be deleted at any
time by utilities such as tmpwatch.
/usr User Binaries & Read-Only Data
The /usr directory contains applications and files used by users, as opposed to
applications and files used by the system. For example, non-essential
applications are located inside the /usr/bin directory instead of the /bin
directory and non-essential system administration binaries are located in the
/usr/sbin directory instead of the /sbin directory. Libraries for each are
located inside the /usr/lib directory. The /usr directory also contains other
directories for example, architecture-independent files like graphics are
located in /usr/share.
The /usr/local directory is where locally compiled applications install to by
default this prevents them from mucking up the rest of the system.
/var Variable Data Files
The /var directory is the writable counterpart to the /usr directory, which must
be read-only in normal operation. Log files and everything else that would
normally be written to /usr during normal operation are written to the /var
directory. For example, youll find log files in /var/log.
For more detailed technical information about the Linux file system hierarchy,
consult the Filesystem Hierarchy Standard documentation.
Chris Hoffman is a technology writer and all-around computer geek. He's as at
home using the Linux terminal as he is digging into the Windows registry.
Connect with him on Google+.
Published 06/25/12
Copyright 2006-2015 How-To Geek, LLC
All Rights Reserved
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Comenzi LinuxDocument7 paginiComenzi LinuxleulgeorgeÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Root DirectoryDocument5 paginiThe Root DirectoryInbaSaaharanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linux File System Structure and Key DirectoriesDocument2 paginiLinux File System Structure and Key DirectoriesAshfaq AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- LinuxDocument3 paginiLinuxAlexander Paul MusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 5: # Touch File1.txt # LN - S File1.txt /home/tecmint/file1.txt (Create Symbolic Link)Document9 paginiExperiment 5: # Touch File1.txt # LN - S File1.txt /home/tecmint/file1.txt (Create Symbolic Link)gshreyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- File System HierarchyDocument21 paginiFile System Hierarchykrushna khatalÎncă nu există evaluări
- W$ - Linuxcommand - Org-File System A Guided Tour (2206)Document3 paginiW$ - Linuxcommand - Org-File System A Guided Tour (2206)rodger69Încă nu există evaluări
- Linux File Structure Cheat SheetDocument4 paginiLinux File Structure Cheat SheettrigerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linux Directory StructureDocument5 paginiLinux Directory StructurebomoarebunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linux File Structure Cheat SheetDocument4 paginiLinux File Structure Cheat Sheeth1tmaxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linux File System ExplainedDocument21 paginiLinux File System ExplainedFake AndroidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Directory Structure (A00127469)Document13 paginiDirectory Structure (A00127469)Mehak preet KaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linux Directory StructureDocument15 paginiLinux Directory StructureG.R.THIYAGU ; Oracle DBAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linux Directory Structure ExplainedDocument3 paginiLinux Directory Structure ExplainedAnonymous vcdqCTtS9Încă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 2 Linux Standard File SystemDocument7 paginiLecture 2 Linux Standard File Systemsherkoasan5Încă nu există evaluări
- Unix Directory StructureDocument6 paginiUnix Directory StructuregobinathÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linux Directory StructureDocument28 paginiLinux Directory StructurefdsaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- File System LinuxDocument3 paginiFile System LinuxVishal ParkashÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linux File Structure Hierarchy ExplainedDocument20 paginiLinux File Structure Hierarchy Explained188W1A1242-Sec-A PUNEET VALLURUPALLIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Q6. Explain File System in LinuxDocument9 paginiQ6. Explain File System in LinuxAkshit AroraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 - Linux Unix Filesystem Hierarchy and StructureDocument2 pagini1 - Linux Unix Filesystem Hierarchy and StructureArshal AzeemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Directory Navigation CommandsDocument9 paginiBasic Directory Navigation CommandsManmeet Kaur100% (1)
- Lecture 03 Linux File System Hierarchy StandardDocument4 paginiLecture 03 Linux File System Hierarchy StandardJohn DuboisÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Beginner's Guide To Disks and Disk Partitions in LinuxDocument7 paginiA Beginner's Guide To Disks and Disk Partitions in LinuxSalimÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Linux File System Structure ExplainedDocument5 paginiThe Linux File System Structure ExplainedTajria SultanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linux Directory StructureDocument2 paginiLinux Directory StructureErnesto ColchadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linux FileSystem PDFDocument8 paginiLinux FileSystem PDFnlly4uÎncă nu există evaluări
- Learning The Shell - Lesson 4 - A Guided TourDocument4 paginiLearning The Shell - Lesson 4 - A Guided TourCatalinUrsuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linux Directory StructureDocument7 paginiLinux Directory StructureAjay KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linux File System StructureDocument3 paginiLinux File System Structuredonald_fÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hier (7) - Linux Man Page: MknodDocument6 paginiHier (7) - Linux Man Page: MknodMidhun Raj SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Managing The Linux File SystemDocument100 paginiManaging The Linux File SystemQuân Nguyễn Trần AnhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linux Directory Structure and Top Level DirectoriesDocument3 paginiLinux Directory Structure and Top Level DirectoriesZain Ul AbedinÎncă nu există evaluări
- File Management in LinuxDocument16 paginiFile Management in Linuxmasterone1Încă nu există evaluări
- System Directories - RHELDocument2 paginiSystem Directories - RHELsalmanpkplusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linux File SystemDocument1 paginăLinux File SystemMam AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linux Directory StructureDocument12 paginiLinux Directory Structuretry75115Încă nu există evaluări
- Unix Filesystem: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument5 paginiUnix Filesystem: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaHari CÎncă nu există evaluări
- Essential Linux Commands Home DictionaryDocument11 paginiEssential Linux Commands Home DictionarySafina FatimaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linux File SystemDocument24 paginiLinux File SystemRaj ShekarÎncă nu există evaluări
- DocumentDocument7 paginiDocumentAndrew XÎncă nu există evaluări
- Techno of AWSVDocument1 paginăTechno of AWSVAnanda ShresthaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fhs in LinuxDocument3 paginiFhs in LinuxBianca PetrescuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ux FSDocument10 paginiUx FSliuylÎncă nu există evaluări
- UNIX File Hierarchy ExplainedDocument3 paginiUNIX File Hierarchy ExplainedJose PlanchartÎncă nu există evaluări
- End Term Question Paper Linux For Devices 2021 SolutionsDocument19 paginiEnd Term Question Paper Linux For Devices 2021 SolutionsKeshavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linux Directory Structure Explained in 16 PointsDocument4 paginiLinux Directory Structure Explained in 16 PointsDavid YavriantzÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Linux Terminal Survival Guide: Mastering Bash Commands and Directory StructureDocument34 paginiThe Linux Terminal Survival Guide: Mastering Bash Commands and Directory StructurezakagiÎncă nu există evaluări
- File System HierarchyDocument11 paginiFile System HierarchymanhtienÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Linux: Nos Text 2.wpd NTC Feb 22, 2006Document17 paginiIntroduction To Linux: Nos Text 2.wpd NTC Feb 22, 2006Pradeep BediÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linux Fundamentals - File System and Partitioning.20121021.183143Document2 paginiLinux Fundamentals - File System and Partitioning.20121021.183143anon_909694178Încă nu există evaluări
- Linux Unix ConceptsDocument18 paginiLinux Unix ConceptsOm Prakash SutharÎncă nu există evaluări
- UNIX Administration Course: Tel: (+44) (0) 1772 893297 Fax: (+44) (0) 1772 892913 WWW: HTTP://WWW - Futuretech.vuurwerk - NLDocument21 paginiUNIX Administration Course: Tel: (+44) (0) 1772 893297 Fax: (+44) (0) 1772 892913 WWW: HTTP://WWW - Futuretech.vuurwerk - NLhariprasadreddy008Încă nu există evaluări
- Manage Directories and Files in Linux: ObjectivesDocument11 paginiManage Directories and Files in Linux: ObjectivesAziz ZouhirÎncă nu există evaluări
- FileSystemHierarchy LinuxDocument3 paginiFileSystemHierarchy LinuxVinay KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Log Files: Log Files Are Files That Contain Messages About The System, Including The KernelDocument21 paginiLog Files: Log Files Are Files That Contain Messages About The System, Including The KernelSougata Roy ChowdhuryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Path DescriptionDocument1 paginăPath Descriptionhasan alaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit-V (Operating System)Document4 paginiUnit-V (Operating System)zakir hussainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Longwood Gardens Certificate of Course CompletionDocument1 paginăLongwood Gardens Certificate of Course CompletionRon GonzalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Basque Language: History and OriginDocument17 paginiThe Basque Language: History and OriginRon Gonzales100% (1)
- Kleffman v. Vonage, No. S169195 (Cal. Sup. CT.) (June 21, 2010)Document23 paginiKleffman v. Vonage, No. S169195 (Cal. Sup. CT.) (June 21, 2010)Venkat BalasubramaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- TPS ReportDocument1 paginăTPS ReportRon GonzalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Game TheoryDocument21 paginiGame TheoryJoan Albet SerraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Love Is A FallacyDocument8 paginiLove Is A FallacyRon GonzalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Ten Commandments of LogicDocument1 paginăThe Ten Commandments of LogicRon GonzalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kleffman v. Vonage, No. S169195 (Cal. Sup. CT.) (June 21, 2010)Document23 paginiKleffman v. Vonage, No. S169195 (Cal. Sup. CT.) (June 21, 2010)Venkat BalasubramaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- 'The Day The Sands Caught Fire' by Jeffrey C. Wynn and Eugene M. ShoemakerDocument8 pagini'The Day The Sands Caught Fire' by Jeffrey C. Wynn and Eugene M. ShoemakerRon GonzalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Agresividad Neurobiología Review AJP 429Document14 paginiAgresividad Neurobiología Review AJP 429jluisalÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Cambridge Declaration On ConsciousnessDocument2 paginiThe Cambridge Declaration On ConsciousnessPatrik NazarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- English-Speaking Children's Interpretation of Disjunction in The Scope of 'Not Every' (Anna Notley, Rosalind Thornton, Stephen Crain) PDFDocument38 paginiEnglish-Speaking Children's Interpretation of Disjunction in The Scope of 'Not Every' (Anna Notley, Rosalind Thornton, Stephen Crain) PDFRon GonzalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Peter Sandman - Responding To Community Outrage PDFDocument155 paginiPeter Sandman - Responding To Community Outrage PDFRon GonzalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Weight Problem - Vowel Length in Classical Latin (Jon Brennan) PDFDocument12 paginiA Weight Problem - Vowel Length in Classical Latin (Jon Brennan) PDFRon GonzalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Rise of Ergativity in Hindi - Assessing The Role of Grammaticalization (Verbeke, de Cuypere) PDFDocument24 paginiThe Rise of Ergativity in Hindi - Assessing The Role of Grammaticalization (Verbeke, de Cuypere) PDFRon GonzalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- OpenStack Install GuideDocument131 paginiOpenStack Install Guiderajagopalan19Încă nu există evaluări
- TestDisk Installtion and UsageDocument18 paginiTestDisk Installtion and UsagesamobuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ltib Build Host SetupDocument3 paginiLtib Build Host SetupJohny LaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- HDP To CDP DC In-Place UpgradeDocument76 paginiHDP To CDP DC In-Place UpgradeFaraz AkhtarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Deep Security 12.0 On-Premise Administration GuideDocument1.579 paginiDeep Security 12.0 On-Premise Administration GuiderepotecÎncă nu există evaluări
- FIPA-OS V2.2.0 Distribution NotesDocument39 paginiFIPA-OS V2.2.0 Distribution NotescanahuiriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pmetrics ManualDocument54 paginiPmetrics ManualBaulier CharlesÎncă nu există evaluări
- RNC Log Collection ToolDocument15 paginiRNC Log Collection ToolRookie2Încă nu există evaluări
- Scheduler InstallationDocument49 paginiScheduler InstallationAlys AlysÎncă nu există evaluări
- GU - ST - ZTE UniPOS NDS-GU V13.40 Installation Configuration Acceptance Guide - R1.3Document104 paginiGU - ST - ZTE UniPOS NDS-GU V13.40 Installation Configuration Acceptance Guide - R1.3Varun SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial 122, Introduction To ProModelDocument48 paginiTutorial 122, Introduction To ProModelaaltivegreenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guide to Centralized Installation of Tekla Structures 2016iDocument14 paginiGuide to Centralized Installation of Tekla Structures 2016iRajlić ZoranÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Most Powerful Starter Kit For ArduinoDocument168 paginiThe Most Powerful Starter Kit For ArduinoJohn SmithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application PackagingDocument4 paginiApplication PackagingPradeepan Vimalanathan100% (1)
- Centrify Suite Express Admin GuideDocument62 paginiCentrify Suite Express Admin GuideGora BhattacharjeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- UniproUGENE UserManualDocument296 paginiUniproUGENE UserManualeruditeramanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- TCUADocument43 paginiTCUAkhiladi2Încă nu există evaluări
- SLIDES Intro Embedded Linux 3day ColorDocument180 paginiSLIDES Intro Embedded Linux 3day ColorKhoa PhamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Windows Desktop Search Administration Guide 3 RevbDocument49 paginiWindows Desktop Search Administration Guide 3 RevbDanielD67Încă nu există evaluări
- Otrs Itsm BookDocument86 paginiOtrs Itsm Bookanupgarg123Încă nu există evaluări
- Adobe Reader XI Deployment With Custom SettingsDocument16 paginiAdobe Reader XI Deployment With Custom Settingstristanleboss2Încă nu există evaluări
- ZMC User's Guide 3.3Document105 paginiZMC User's Guide 3.3Kaushal KishorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Name: Purushotham E-Mail: Purushothamthota635 Gmail Com Phone:+91-9705725472 Summary of ExperienceDocument3 paginiName: Purushotham E-Mail: Purushothamthota635 Gmail Com Phone:+91-9705725472 Summary of ExperiencepurushothamÎncă nu există evaluări
- LSWS PHP LSAPI Build Troubleshooting GuideDocument19 paginiLSWS PHP LSAPI Build Troubleshooting GuideKurniawan Setyo NugrohoÎncă nu există evaluări
- WinReducer8. 1 How ToDocument21 paginiWinReducer8. 1 How TojoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Laserdesk Installation Guide and First Steps Scanlab enDocument8 paginiLaserdesk Installation Guide and First Steps Scanlab enprasen10Încă nu există evaluări
- Install Mongodb On Ubuntu 16.04 Lts - Hevo Blog PDFDocument3 paginiInstall Mongodb On Ubuntu 16.04 Lts - Hevo Blog PDFShashin KuroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Configuração Pesquisa OTRSDocument19 paginiConfiguração Pesquisa OTRSfsouzarjÎncă nu există evaluări
- IP Output Plug-In For DataWedge Version 1.1 Release Notes PDFDocument5 paginiIP Output Plug-In For DataWedge Version 1.1 Release Notes PDFEver Jafeht CaballeroÎncă nu există evaluări