Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Outriggers
Încărcat de
Humberto EstevezDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Outriggers
Încărcat de
Humberto EstevezDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
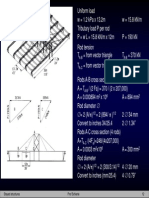
Dimensi Teknik Sipil, Vol. 3, No.
1, Maret 2001, 36-41
ISSN 1410-9530
THE USE OF OUTRIGGER AND BELT TRUSS SYSTEM
FOR HIGH-RISE CONCRETE BUILDINGS
Po Seng Kian
Lecturer, Department of Civil Engineering, Petra Christian University
Frits Torang Siahaan
Alumnus, Department of Building Science, National University of Singapore
ABSTRACT
The outrigger and belt truss system is commonly used as one of the structural system to effectively
control the excessive drift due to lateral load, so that, during small or medium lateral load due to
either wind or earthquake load, the risk of structural and non-structural damage can be minimized.
For high-rise buildings, particularly in seismic active zone or wind load dominant, this system can be
chosen as an appropriate structure.
This paper studies the use of outrigger and belt truss system for high-rise concrete building
subjected to wind or earthquake load. Eight 40storey two dimensional models of outrigger and belt
truss system are subjected to wind load; and five 60storey three dimensional models are subjected
to earthquake load, analyzed and compared to find the lateral displacement reduction related to the
outrigger and belt system location. For the two dimensional 40storey model, 65% maximum
displacement reduction can be achieved by providing first outrigger at the top and second outrigger
at the middle of the structure height. For the three dimensional 60storey structural model
subjected to the earthquake load, about 18 % reduction in maximum displacement can be achieved
with optimum location of the outrigger truss placed at the top and the 33rd level.
Keywords: outriggers, high-rise buildings, wind load, earthquake load, optimum outrigger location.
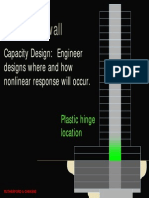
INTRODUCTION
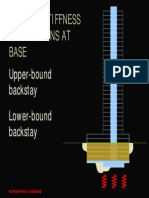
The outrigger and belt truss system is one of the
lateral load resisting system in which the
external columns are tied to the central core
wall with very stiff outriggers and belt truss at
one or more levels (Figure 1). When the lateral
load acts on the building, the bending of the core
rotates the stiff outrigger arms, which is
connected to the core and induces tension and
compression in the columns (Figure 2).
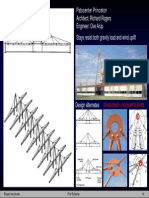
One example of building which uses the
outrigger and belt system is Chifley Tower, 53
storey with 4 levels of basements, located in
Sydney, Australia (constructed 1992). The
building is made of composite floor on steel
decking, steel columns and central steel braced
frame core structure. The building was designed
for wind speed of 50 m/s on 1000-year return
period with a maximum lateral deflection of
0.565 m for a 50-year return. The outriggers are
placed at two levels of the building (Figure 3).
Figure 1. The belt truss system [4]
Note: Discussion is expected before June, 1st 2001. The
proper discussion will be published in Dimensi Teknik
Sipil volume 3 number 2 September 2001.
36
Dimensi Teknik Sipil
ISSN 1410-9530 print 2001 Universitas Kristen Petra
http://puslit.petra.ac.id/journals/civil
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- 08+Updates+to+the+Seismic+Provisions+in+ASCE+7 16+Document20 pagini08+Updates+to+the+Seismic+Provisions+in+ASCE+7 16+Humberto EstevezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Canam Steel Deck PDFDocument168 paginiCanam Steel Deck PDFAnonymous 8hx6hKN3Încă nu există evaluări
- SDVI 2019 Gs FR Tutorial and Exercise 1552485157Document81 paginiSDVI 2019 Gs FR Tutorial and Exercise 1552485157Humberto EstevezÎncă nu există evaluări
- ARCH 614 Note Set 26.1 S2012abn: Foundation DesignDocument1 paginăARCH 614 Note Set 26.1 S2012abn: Foundation DesignHumberto EstevezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hilti-Hy 200-RDocument74 paginiHilti-Hy 200-RHumberto EstevezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Footings Limit StatesDocument1 paginăFootings Limit StatesHumberto EstevezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gaps in Bearing and SC ConexDocument1 paginăGaps in Bearing and SC ConexHumberto EstevezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pages From R.C.hibbbending in Composite Eler-Mechanics of Materials 8th EditionDocument2 paginiPages From R.C.hibbbending in Composite Eler-Mechanics of Materials 8th EditionHumberto EstevezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prestressed Compression MembersDocument1 paginăPrestressed Compression MembersHumberto EstevezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Proportionate and Nonproportionate Shear WallsDocument5 paginiProportionate and Nonproportionate Shear WallsHumberto Estevez100% (1)
- Prestressed Compression MembersDocument1 paginăPrestressed Compression MembersHumberto EstevezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spread Footing CalcsDocument1 paginăSpread Footing CalcsHumberto EstevezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stayed RoofDocument1 paginăStayed RoofHumberto EstevezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lower Bound Theory High RiseDocument1 paginăLower Bound Theory High RiseHumberto EstevezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tolerances: Table 2 Surface Finish ClassDocument1 paginăTolerances: Table 2 Surface Finish ClassHumberto EstevezÎncă nu există evaluări
- One-Way Joist Part 2Document1 paginăOne-Way Joist Part 2Humberto EstevezÎncă nu există evaluări
- B. Singh, S.K. Kaushik, K.F. Naveen and S. Sharma 470: 5. Design of TiesDocument1 paginăB. Singh, S.K. Kaushik, K.F. Naveen and S. Sharma 470: 5. Design of TiesHumberto EstevezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cable Stays Lecture-PatscenterDocument1 paginăCable Stays Lecture-PatscenterHumberto EstevezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cantilever Wall Tall BuildingDocument1 paginăCantilever Wall Tall BuildingHumberto EstevezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Infineon IRFZ44N DataSheet v01 - 01 ENDocument9 paginiInfineon IRFZ44N DataSheet v01 - 01 ENIkram RidhoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Red Oaks Drive, Frankton, Queenstown-Lakes, Otago PDFDocument1 paginăRed Oaks Drive, Frankton, Queenstown-Lakes, Otago PDFCintiah KenedyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Macedonian KavalDocument1 paginăMacedonian Kavalmikiszekely1362Încă nu există evaluări
- Fill in The Table by Determining The Functions of The Following ItemsDocument6 paginiFill in The Table by Determining The Functions of The Following ItemsJessabel CandidatoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dragons and Winged SerpentsDocument5 paginiDragons and Winged SerpentsYuna Raven100% (1)
- Money, Interest, and Inflation: Answers To CheckpointsDocument16 paginiMoney, Interest, and Inflation: Answers To Checkpointsb96309Încă nu există evaluări
- Catalog Man 1Document116 paginiCatalog Man 1Petrov AndreiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Project ReportDocument83 paginiFinal Project ReportMohit SrivastavaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mold Maintenance StepDocument0 paginiMold Maintenance StepMonica JoynerÎncă nu există evaluări
- DysphagiaDocument4 paginiDysphagiaMicaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pre-Test First QTR 2022-2023Document3 paginiPre-Test First QTR 2022-2023anna marie mangulabnanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ligamentele LargiDocument2 paginiLigamentele LargiIoana IonicaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 13 Managerial AccountingDocument168 paginiChapter 13 Managerial AccountingChandler Schleifs100% (4)
- MPI Report 009 Sub Structure B668Document1 paginăMPI Report 009 Sub Structure B668John DolanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Embedded Systems:: Hacking of Electronic EquipmentsDocument76 paginiEmbedded Systems:: Hacking of Electronic EquipmentsKailashi Chandra SekharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Coronary Syndrome: Diagnosis and Initial Management: Each YearDocument9 paginiAcute Coronary Syndrome: Diagnosis and Initial Management: Each YearGabriela Pacheco0% (1)
- Relatório Final Do Período Experimental - Paulo Manuel Correia Da SilvaDocument56 paginiRelatório Final Do Período Experimental - Paulo Manuel Correia Da SilvaMagda RuanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- WorldShop CatalougeDocument200 paginiWorldShop Catalougee2ashÎncă nu există evaluări
- Recipes G.garvin Copy1 Scribd 5Document7 paginiRecipes G.garvin Copy1 Scribd 5Peggy Bracken StagnoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pocket Book AGDocument67 paginiPocket Book AGsudiraharjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Igc 3 Practical NeboshDocument20 paginiIgc 3 Practical NeboshAbdelkader FattoucheÎncă nu există evaluări
- Consent For Diagnostic And/or Therapeutic ParacentesisDocument2 paginiConsent For Diagnostic And/or Therapeutic ParacentesisnaveenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neoliberalism and Altered State Developmentalism in The Twenty First Century Extractive Regime of IndonesiaDocument26 paginiNeoliberalism and Altered State Developmentalism in The Twenty First Century Extractive Regime of IndonesiaErwin SuryanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 24 - Laminate Modeling - Rev C PDFDocument20 paginiLesson 24 - Laminate Modeling - Rev C PDFraduga_fbÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomia Dezvoltarii PancreasuluiDocument49 paginiAnatomia Dezvoltarii Pancreasuluitarra abuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Product CatalogDocument4 paginiProduct CatalogpeejayjacintoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ingles y Español Unidad 7Document9 paginiIngles y Español Unidad 7Pier Jhoani Ñañez LlanosÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Studies in American Popular History and Culture) Gail Fowler Mohanty - Labor and Laborers of The Loom - Mechanization and Handloom Weavers, 1780-1840 - Routledge (2006)Document292 pagini(Studies in American Popular History and Culture) Gail Fowler Mohanty - Labor and Laborers of The Loom - Mechanization and Handloom Weavers, 1780-1840 - Routledge (2006)Милош Станојловић100% (1)
- Materi B.inggris SMP Kelas 9 Kurikulum 2013Document21 paginiMateri B.inggris SMP Kelas 9 Kurikulum 2013Siti DianurÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPM Chemistry Form 5 - Redox Part 1Document4 paginiSPM Chemistry Form 5 - Redox Part 1ysheng98Încă nu există evaluări