Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Electronic Components Symbols Functions
Încărcat de
yamaha355Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Electronic Components Symbols Functions
Încărcat de
yamaha355Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
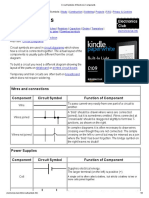
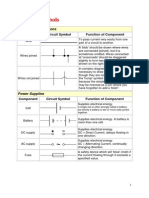
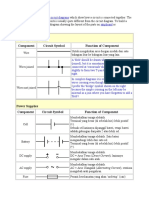
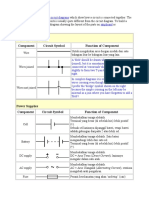
Circuit Symbols
Circuit symbols are used in circuit diagrams which show how a circuit is connected together. The actual layout of the
components is usually quite different from the circuit diagram. To build a circuit you need a different diagram showing the
layout of the parts on strip board or printed circuit board.
Circuit symbols are used in circuit diagrams, which show how a circuit is connected together. The actual layout of the
components is usually quite different from the circuit diagram. To build a circuit you need a different diagram showing the
layout of the parts on the printed circuit board. However understanding electronics circuit give you a better understanding
of how to find faults in an electronic circuit
Wires and connections
Component
Circuit Symbol
Wire
Function of Component
To conduct or pass current from one part of a circuit to another.
wires joined symbol
A 'blob' should be drawn where wires are connected (joined), but it is
sometimes omitted. Wires connected to another wire should be
staggered slightly to form two T-junctions, as shown. Such help to
transmitted current to other paths
Wires joined
wires crossing but not joined symbol
In diagrams it is often necessary to draw wires crossing even though
they are not connected. It is preferred to have the 'hump' symbol as
shown because the simple crossing of the wire may be misread as a
join where you have forgotten to add a 'blob'!
Wires not joined
Power Supplies
Component
Circuit Symbol
Supplies electrical energy.
The larger terminal indicates the positive (+).
A single cell is often interpreted and called a battery, but a battery is two
or more cell joined together.
cell symbol
Cell
battery sy mbol
Supplies electrical energy. A battery is more than one cell.
The larger terminal is the positive (+). And the small terminal is called the
negative (-)
Battery
+
DC supply
AC supply
Fuse
Function of Component
Supplies electrical energy.
DC = Direct Current, always flowing in one direction.
Supplies electrical energy.
AC = Alternating Current, continually changing direction of it currents it is
negative and then Positive which alternates again.
AC power supply sy mbol
A safety device, which will 'blow' or melt if the current flowing through it
exceeds a specified value. Used as a protection for electrical circuits.
fuse sy mbol
transformer symbol
Two coils of wire linked by an iron core. Transformers are used to step up
(increase) and step down (decrease) AC voltages. Energy is transferred
between the coils by the magnetic field in the core. There is no electrical
connection between the coils.
Transformer
earth symbol
Earth
(Ground)
A connection to earth. For many electronic circuits this is the 0V (zero
volts) of the power supply, but for mains electricity and some radio circuits
it really means the earth. It is also known as ground.
Output Devices: Lamps, Heater, Motor, etc.
Component
Circuit Symbol
Function of Component
lamp (lighting) symbol
Lamp (lighting)
A transducer, which converts electrical energy to light. This symbol is
used for a lamp providing illumination, for example a car headlamp.
Lamp (indicator)
A transducer which converts electrical energy to light. This symbol is
used for a lamp which is an indicator, for example a warning light on a
car dashboard.
Heater
A transducer which converts electrical energy to heat.
motor sy mbol
A transducer, which converts electrical energy to kinetic energy
(motion).
Motor
bell symbol
Bell
A transducer, which converts electrical energy to sound.
buzzer symbol
Buzzer
Inductor
(Coil, Solenoid)
A transducer, which converts electrical energy to sound.
A coil of wire, which creates a magnetic field when current, passes
through it. It may have an iron core inside the coil. It can be used as a
transducer converting electrical energy to mechanical energy by pulling
on something.
inductor sy mbol
Switches
Component
Push Switch
(push-to-make)
Push-to-Break
Switch
On-Off Switch
(SPST)
Circuit Symbol
push-to-make switch sy mbol
push-to-break switch sy mbol
SPST on-off switch sy mbol
SPDT switch symbol
2-way Switch
(SPDT)
Function of Component
A push switch allows current to flow only when the button is
pressed. This is the switch used to operate a doorbell. It is a
abbreviated NO for normally open .
This type of push switch is normally closed abbreviated NC for
normally closed (on), it is open (off) only when the button is
pressed.
SPST = Single Pole, Single Throw.
An on-off switch allows current to flow only when it is in the closed
(on) position.
SPDT = Single Pole, Double Throw.
A 2-way changeover switch directs the flow of current to one of two
routes according to its position. Some SPDT switches have a
central off position and are described as 'on-off-on'.
DPST switch sy mbol
Dual On-Off
Switch
(DPST)
DPST = Double Pole, Single Throw.
A dual on-off switch, which is often used to switch mains electricity
because it can isolate both the live and neutral connections.
DPDT switch symbol
Reversing
Switch
(DPDT)
DPDT = Double Pole, Double Throw.
This switch can be wired up as a reversing switch for a motor. Some
DPDT switches have a central off position.
relay sy mbol
An electrically operated switch, for example a 9V battery circuit
connected to the coil can switch a 230V AC mains circuit.
NO = Normally Open, COM = Common, NC = Normally Closed.
Relay
Resistors
Component
Resistor
Circuit Symbol
Function of Component
A resistor restricts the flow of current, for example to limit the current
passing through an LED. A resistor is used with a capacitor in a timing
circuit.
resistor symbol
This type of variable resistor with 2 contacts (a rheostat) is usually
used to control current. Examples include: adjusting lamp brightness,
adjusting motor speed, and adjusting the rate of flow of charge into a
capacitor in a timing circuit.
rheostat sy mbol
Variable Resistor
(Rheostat)
Variable Resistor
(Potentiometer)
This type of variable resistor with 3 contacts (a potentiometer) is
usually used to control voltage. It can be used like this as a transducer
converting position (angle of the control spindle) to an electrical signal.
Variable Resistor
(Preset)
This type of variable resistor (a preset) is operated with a small
screwdriver or similar tool. It is designed to be set when the circuit is
made and then left without further adjustment. Presets are cheaper
than normal variable resistors so they are often used in projects to
reduce the cost.
po tentiometer symbol
Capacitors
Component
Circuit Symbol
capacitor symbol
Function of Component
A capacitor stores electric charge. A capacitor is used with a resistor
in a timing circuit. It can also be used as a filter, to block DC signals
but pass AC signals.
Capacitor
A capacitor stores electric charge. This type must be connected the
correct way round. A capacitor is used with a resistor in a timing
circuit. It can also be used as a filter, to block DC signals but pass
AC signals.
po larised capacitor sy mbol
Capacitor,
polarized
v ariable capacitor symbol
Variable Capacitor
A variable capacitor is used in a radio tuner.
Trimmer Capacitor
This type of variable capacitor (a trimmer) is operated with a small
screwdriver or similar tool. It is designed to be set when the circuit is
made and then left without further adjustment.
Diodes
Component
Circuit Symbol
Function of Component
diode symbol
Diode
A device, which only allows current to flow in one direction.
LED sy mbol
LED
Light Emitting Diode
A transducer, which converts electrical energy to light.
A special diode, which is used to maintain a fixed voltage in a
power supply.
zener diode symbol
Zener Diode
photodiode sy mbol
A light-sensitive diode. Which react when light is shine direct on it
may increase or decrease it resistance
Photodiode
Transistors
Component
Circuit Symbol
Function of Component
NPN transistor sy mbol
A transistor amplifies current. It can be used with other components to make an
amplifier or switching circuit.
Transistor NPN
PNP transistor symbol
A transistor amplifies current. It can be used with other components to make an
amplifier or switching circuit.
Transistor PNP
Phototransistor sy mbol
Phototransistor
A light-sensitive transistor.
Audio and Radio Devices
Component
Circuit Symbol
Function of Component
microphone symbol
Microphone
A transducer, which converts sound to electrical energy.
earphone symbol
Earphone
A transducer, which converts electrical energy to sound.
loudspeaker symbol
Loudspeaker
A transducer, which converts electrical energy to sound.
piezo transducer symbol
Piezo Transducer
A transducer, which converts electrical energy to sound.
amplifier symbol
Amplifier
(general symbol)
An amplifier circuit with one input. Really it is a block diagram symbol
because it represents a circuit rather than just one component.
aerial symbol
Aerial
(Antenna)
A device, which is designed to receive or transmit radio signals. It is also
known as an antenna.
Meters and Oscilloscope
Component
Circuit Symbol
Function of Component
A voltmeter is used to measure voltage.
The proper name for voltage is 'potential difference', but most people
prefer to say voltage!
v oltmeter symbol
Voltmeter
ammeter symbol
Amp-meter
An amp-meter is used to measure current. As known as amps
A galvanometer is a very sensitive meter which is used to measure tiny
currents, usually 1mA or less.
Galvanometer
ohmmeter symbol
Ohmmeter
An ohmmeter is used to measure resistance. Most Multimeter have an
ohmmeter setting.
Oscilloscope
An oscilloscope is used to display the shape of electrical signals and it
can be used to measure their voltage and time period.
Sensors (input devices)
Component
Circuit Symbol
Function of Component
A transducer which converts brightness (light) to resistance (an electrical
property).
LDR = Light Dependent Resistor
LDR
A transducer which converts temperature (heat) to resistance (an
electrical property).
thermistor symbol
Thermistor
Logic Gates
Logic gates process signals, which represent true (1, high, +Vs, on) or false (0, low, 0V, off).
There are two sets of symbols: traditional and IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission).
Gate
Type
Traditional Symbol
IEC Symbol
NO T gate traditional sy mbol
NO T gate IEC sy mbol
AND gate traditional sy mbol
AND gate IEC sy mbol
NOT
AND
Function of Gate
A NOT gate can only have one input. The 'o' on the output
means 'not'. The output of a NOT gate is the inverse (opposite)
of its input, so the output is true when the input is false. A NOT
gate is also called an inverter.
An AND gate can have two or more inputs. The output of an
AND gate is true when all its inputs are true.
NA ND gate traditional sy mbol
NA ND gate IEC sy mbol
A NAND gate can have two or more inputs. The 'o' on the output
means 'not' showing that it is a Not AND gate. The output of a
NAND gate is true unless all its inputs are true.
NAND
OR gate traditional sy mbol
OR gate IEC sy mbol
An OR gate can have two or more inputs. The output of an OR
gate is true when at least one of its inputs is true.
OR
NO R gate traditional sy mbol
NO R gate IEC sy mbol
A NOR gate can have two or more inputs. The 'o' on the output
means 'not' showing that it is a Not OR gate. The output of a
NOR gate is true when none of its inputs are true.
NOR
EX-O R gate traditional sy mbol
EX-O R gate IEC sy mbol
An EX-OR gate can only have two inputs. The output of an EXOR gate is true when its inputs are different (one true, one false).
EX-OR
EX-NOR gate traditional sy mbol
EXNOR
EX-NOR gate IEC sy mbol
An EX-NOR gate can only have two inputs. The 'o' on the output
means 'not' showing that it is a Not EX-OR gate. The output of
an EX-NOR gate is true when its inputs are the same (both true
or both false).
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Wires and ConnectionsDocument22 paginiWires and ConnectionsDanilo AlbayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Component Circuit Symbol Function of ComponentDocument8 paginiComponent Circuit Symbol Function of ComponentNelson CabingasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simbologia Eletrica 1Document4 paginiSimbologia Eletrica 1SarjitoÎncă nu există evaluări
- LegendDocument8 paginiLegendhassanpour5882Încă nu există evaluări
- Circuit Symbols: Wires and Connections Component Circuit Symbol Function of ComponentDocument8 paginiCircuit Symbols: Wires and Connections Component Circuit Symbol Function of ComponentdasfagagÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circuit Symbols of Electronic ComponentsDocument8 paginiCircuit Symbols of Electronic ComponentsEBEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circuit Symbol T1Document8 paginiCircuit Symbol T1Islam AtiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circuit Symbols of Electronic ComponentsDocument8 paginiCircuit Symbols of Electronic ComponentsCasandra ClarkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circuit Symbols: Wires and ConnectionsDocument8 paginiCircuit Symbols: Wires and ConnectionsAnonymous BwLfvuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circuit Symbols: Wires and Connections Compone NT Circuit Symbol Function of ComponentDocument7 paginiCircuit Symbols: Wires and Connections Compone NT Circuit Symbol Function of ComponentRalph MedinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circuit Symbols Electronics ClubDocument6 paginiCircuit Symbols Electronics Clubayodeledamilola124Încă nu există evaluări
- MODULE in Consumer ElectronicsDocument129 paginiMODULE in Consumer ElectronicsNyepni NelmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Practice-1 (Circuit Symbols)Document7 paginiLab Practice-1 (Circuit Symbols)awien28Încă nu există evaluări
- Servicio Nacional de Aprendizaje Centro de Electricidad Electronica Y Telecomnunicaciones Circuit SymbolsDocument4 paginiServicio Nacional de Aprendizaje Centro de Electricidad Electronica Y Telecomnunicaciones Circuit Symbols伊文伊文Încă nu există evaluări
- Basic Electronics by Cel - Phon PDFDocument12 paginiBasic Electronics by Cel - Phon PDFDaniel Etsey50% (2)
- Engineering Practices Laboratory: Lab ManualDocument51 paginiEngineering Practices Laboratory: Lab ManualKarthikeyan100% (1)
- Wires: Electronic Component Circuit Symbol DescriptionDocument9 paginiWires: Electronic Component Circuit Symbol DescriptionMarkAngeloCabañasRosasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering Practices Laboratory (12F1Z9) : Lab ManualDocument51 paginiEngineering Practices Laboratory (12F1Z9) : Lab ManualJoao Carlos DrumondÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electronic Components: Symbols & FunctionsDocument6 paginiElectronic Components: Symbols & FunctionsAlexander San Juan92% (112)
- Circuit SymbolsDocument6 paginiCircuit SymbolsFarhan SaadatÎncă nu există evaluări
- ELECTRIC WORKSHOP Student VersionDocument25 paginiELECTRIC WORKSHOP Student Versionnaqirustambajwa90Încă nu există evaluări
- Symbols in Edc LabDocument13 paginiSymbols in Edc LabmkrishnadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical and Electronic Schematic SymbolsDocument16 paginiElectrical and Electronic Schematic SymbolsSanjana Singh100% (1)
- Electrical DiagramDocument18 paginiElectrical Diagramabhishek kalshettiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Symbols of Electronic ComponenetsDocument21 paginiSymbols of Electronic ComponenetsMehmet KARAHANLIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electronic Circuit SymbolsDocument15 paginiElectronic Circuit Symbolsramash75Încă nu există evaluări
- Workshop Practice (Electric Shop)Document13 paginiWorkshop Practice (Electric Shop)muhammad omer100% (1)
- Electrical Engineering SymbolDocument8 paginiElectrical Engineering SymbolAnupam BanerjeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electric Shop Lab ManualDocument13 paginiElectric Shop Lab ManualHuzaifaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Electronics NotesDocument5 paginiBasic Electronics NotesRolando Carlos FloresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electronic Circuit Symbols: Power Supplies Component Circuit Symbol Function of ComponentDocument8 paginiElectronic Circuit Symbols: Power Supplies Component Circuit Symbol Function of ComponentImran AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Symbols & Electronic SymbolsDocument7 paginiElectrical Symbols & Electronic SymbolsSilviu IlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notes: 3.1 Laser ClassesDocument9 paginiNotes: 3.1 Laser ClassesAmlan BhuyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Diagram and SymbolsDocument7 paginiTypes of Diagram and SymbolsPrince John Rabano100% (1)
- Electrical and Electronics SymbolsDocument52 paginiElectrical and Electronics SymbolssorcererpcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Symbols & Electronic SymbolsDocument7 paginiElectrical Symbols & Electronic Symbolsmksamy2021Încă nu există evaluări
- Electric Circuit and SymbolDocument3 paginiElectric Circuit and SymbolAlvie MontejoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wiring SymbolsDocument13 paginiWiring SymbolsStalin TagoreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical SymbolDocument3 paginiElectrical SymbolGener TanizaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Electrical SymbolDocument42 paginiBasic Electrical SymbolMuzammal HamadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Electrical Symbols and Their MeaningsDocument5 paginiBasic Electrical Symbols and Their MeaningsJasjeet SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Symbols & Electronic SymbolsDocument6 paginiElectrical Symbols & Electronic SymbolsJeric Gader BriosoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Symbols & Electronic SymbolsDocument21 paginiElectrical Symbols & Electronic SymbolsHassaan ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter No 1Document6 paginiChapter No 1rajamudasarjavedÎncă nu există evaluări
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10De la EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10Încă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Wire: Table of Electrical SymbolsDocument7 paginiElectrical Wire: Table of Electrical SymbolsMoneth Aquino BrionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circuit SymbolsDocument9 paginiCircuit SymbolsMAHESWARA RAO CHALLAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Table of Electrical SymbolsDocument6 paginiTable of Electrical SymbolsArgo Arjieanto0% (1)
- Power Supplies: Types of Power SupplyDocument18 paginiPower Supplies: Types of Power SupplyArasu LoganathanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical SymbolsDocument7 paginiElectrical SymbolsZativa AlyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simboli CircuitiDocument6 paginiSimboli CircuitiLuca MarzarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment No: 1 Familiarization of Electronic Components AimDocument49 paginiExperiment No: 1 Familiarization of Electronic Components Aimarun joseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wires and Connections Component Circuit Symbol Function of ComponentDocument8 paginiWires and Connections Component Circuit Symbol Function of ComponentHanim HusaifÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wires and Connections Component Circuit Symbol Function of ComponentDocument8 paginiWires and Connections Component Circuit Symbol Function of ComponentHanim HusaifÎncă nu există evaluări
- KMT#4Document5 paginiKMT#4RomanHerreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Term Paper On Construction of 12 Volts Power SupplyDocument15 paginiTerm Paper On Construction of 12 Volts Power SupplyVictor ImehÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1De la EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Evaluare: 2.5 din 5 stele2.5/5 (3)
- Employability Skills: Brush up Your ElectronicsDe la EverandEmployability Skills: Brush up Your ElectronicsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Past Year Q For Chargeman L1 PDFDocument53 paginiPast Year Q For Chargeman L1 PDFFaizal Fezal50% (4)
- Industrial Training Presentation ROHIT YADAVDocument15 paginiIndustrial Training Presentation ROHIT YADAVROHIT YADAVÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pdvsa: Engineering Design ManualDocument17 paginiPdvsa: Engineering Design ManualRafael GarciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Revisions Rev Description Date Approved: Third Angle ProjectionDocument11 paginiRevisions Rev Description Date Approved: Third Angle ProjectionMokhtar AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- MOT Spot Welder: Food Living Outside Play Technology WorkshopDocument11 paginiMOT Spot Welder: Food Living Outside Play Technology Workshopprivate 2Încă nu există evaluări
- PTW 5.0 Enhancements PDFDocument28 paginiPTW 5.0 Enhancements PDFangel lozadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transformer Life Extension Pdmsa Southafrica 2010Document17 paginiTransformer Life Extension Pdmsa Southafrica 2010Eddy Fernando Queca CadizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tesla Coil (2K19EE219) R1Document11 paginiTesla Coil (2K19EE219) R1Sanyam JainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electro-Motion Devices: Lecture 6-Power Transformer - 2Document11 paginiElectro-Motion Devices: Lecture 6-Power Transformer - 2Junaid KhattakÎncă nu există evaluări
- L42 ECEN5817 NotesDocument17 paginiL42 ECEN5817 NotesMuhammad Uzair BilalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Works - Write UpDocument63 paginiElectrical Works - Write UpKenzo Braye GeraleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Electronics QuestionsDocument7 paginiBasic Electronics Questionsvind_hya1Încă nu există evaluări
- Differance Between ELCB and RCCB?: Answer:For Lighting Loads, Neutral Conductor Is Must and Hence The SecondaryDocument3 paginiDifferance Between ELCB and RCCB?: Answer:For Lighting Loads, Neutral Conductor Is Must and Hence The SecondaryBeere GangadharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Product Guide - RED615Document68 paginiProduct Guide - RED615ronald_chan_2Încă nu există evaluări
- High Voltage On Ships, Safety, Equipment Testing: (Adapted from:D.T. Hall:Practical Marine Electrical Knowledge)Document18 paginiHigh Voltage On Ships, Safety, Equipment Testing: (Adapted from:D.T. Hall:Practical Marine Electrical Knowledge)World GamesÎncă nu există evaluări
- IGBT Retrofit Inverters-SIBAS Device Manual - Rev1.1 PDFDocument254 paginiIGBT Retrofit Inverters-SIBAS Device Manual - Rev1.1 PDFLuis Carlos Durazo100% (1)
- ACC SVN61A en (Installer's Guide)Document24 paginiACC SVN61A en (Installer's Guide)jfisher54Încă nu există evaluări
- Eht Earthing ThesisDocument28 paginiEht Earthing ThesisAnonymous 2l8XJIVÎncă nu există evaluări
- New Energy Technologies Issue 13Document78 paginiNew Energy Technologies Issue 13blameitontherain9877Încă nu există evaluări
- PSSE ReleaseDocument34 paginiPSSE ReleaseAshutosh SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Updated IEEE Power, Distribution, & Regulating Transformers Standards 2016 CollectionDocument2 paginiUpdated IEEE Power, Distribution, & Regulating Transformers Standards 2016 CollectionAkash VermaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Motor: 220-250VDC/AC Diagram: 0889461H: ScaleDocument28 paginiMotor: 220-250VDC/AC Diagram: 0889461H: ScaleMiuta IrinelÎncă nu există evaluări
- ABB RED 615 ManualDocument68 paginiABB RED 615 Manual2008shivaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transformers-Tolerances On Guaranteed Technical ParametersDocument5 paginiTransformers-Tolerances On Guaranteed Technical Parameterssalemg82Încă nu există evaluări
- Activity 1.3Document2 paginiActivity 1.3Niño John JaymeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Demag Test Card Presentation PDFDocument27 paginiDemag Test Card Presentation PDFsimitzuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 6: Electrical and Electronic PrinciplesDocument16 paginiUnit 6: Electrical and Electronic Principlesশাজারাতুল ইসলাম রাসেলÎncă nu există evaluări
- 800 KVA Transformer SpecificationsDocument3 pagini800 KVA Transformer SpecificationsRavi Bapodra100% (1)
- SECTION 26 05 73 Overcurrent Protective Device Coordination StudyDocument5 paginiSECTION 26 05 73 Overcurrent Protective Device Coordination StudyEzana EzanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electricity and MagnetismDocument17 paginiElectricity and Magnetismaddy 05Încă nu există evaluări