Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Dysrhythmias
Încărcat de
zooDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Dysrhythmias
Încărcat de
zooDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Rhythm and Strip
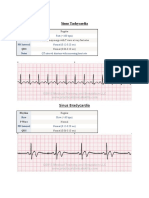
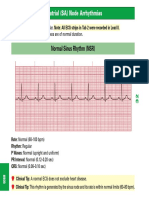
Normal sinus rhythm
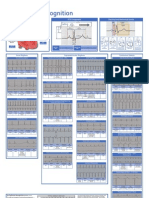
Cardiac Rhythms and Dysrhythmias
ECG Characteristics
Rate: 60 100 bpm
Rhythm: regular
There is one P for every QRS
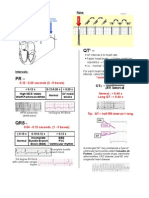
PR interval: 0.12 0.20 seconds
QRS complex: 0.06 0.10 seconds
Management
This is a normal heart rhythm so no
treatment is required
Sinus tachycardia
Rate: 101 150 bpm
Rhythm: regular
There is one P for every QRS but may
be hidden with T wave due to speed
PR interval: 0.12 0.20 seconds
QRS complex: 0.06 0.10 seconds
This is only treated if client is
symptomatic or is at risk for
myocardial damage
If there is an underlying cause, betablockers or verapamil can be used
Sinus bradycardia
Rate: < 60 bpm
Rhythm: regular
There is one P for every QRS
PR interval: 0.12 0.20 seconds
QRS complex: 0.06 0.10 seconds
This is only treated if client is
symptomatic; administer IV atropine,
isoproterenol, and/or pacemaker may
be used
Premature atrial contractions (PAC)
Rate: varies
Rhythm: regular with early beats
originating in atria
There is one P for every QRS
PR interval: not measured
QRS complex: 0.06 0.10 seconds
Rate: atrial 240 360 bpm, ventricular
rate depends on degree of AV block
Rhythm: regular
P:QRS ratio: 2:1. 4:1, 6:1, or variable
PR interval: not measured
QRS complex: 0.06 0.10 seconds
This usually requires no treatment.
Advise client to reduce alcohol intake,
reduce stress, and stop smoking
Atrial flutter
This is treated with synchronized
cardioversion; meds to reduce
ventricular response such as betablocker or calcium channel blocker
followed by a class I antidysrhythmic
or amiodarone
Atrial fibrillation
Rate: 300 600 bpm; ventricular 100
180 bpm in untreated clients
Rhythm: irregularly regular
P:QRS ratio is variable
PR interval: not measured
QRS complex: 0.06 0.10 seconds
This is treated with synchronized
cardioversion; meds to reduce
ventricular response rate such as
metoprolol, diltiazem, or digoxin;
anticoagulant therapy to reduce risk of
clot formation and stroke
Premature ventricular contractions (PVC)
Rate: variable
Rhythm: irregular; PVC interrupts
underlying rhythm and followed by a
compensatory pause
No P wave noted before a PVC
PR interval: absent
QRS complex: wide, > 0.12 seconds
Rate: 100 250 bpm
Rhythm: regular
No indentifiable P wave
PR interval: not measured
QRS complex: 0.12 seconds; bizarre
shape
This is treated if client is symptomatic;
advise against using stimulants
(caffeine, nicotine); drug therapy
includes, class I and III
antidysrhythmics and possibly addition
of a beta blocker
Ventricular tachycardia
Ventricular fibrillation
Rate: too rapid to count
Rhythm: grossly irregular
No identifiable P waves
PR interval: none
QRS complex: bizzare, varying in
shape and direction
First-degree AV block
Rate: 60 10 bpm
Rhythm: regular
There in one P for every QRS
PR interval: > 0.20 seconds
QRS complex: 0.06 0.10 seconds
This is treated if VT is sustained or if
client is symptomatic; treatment
includes IV procainamide, lidocaine.
If unstable, a class III antidysrhythmic
and immediate cardioversion; ablation
surgery or internal defibrillator for
repeated episodes
Immediate defibrillation
No treatment required
Second-degree AV block type 1 (Mobitz 1, Wenckebach)
Second-degree AV block type 2 (Mobitz 2)
Third-degree block (complete heart block)
Rate: 60 100 bpm
Rhythm: atrial regular, ventricular
irregular
P:QRS ratio: 1:1 until P wave is
blocked w/ no QRS following
PR interval: progressively lengthens in
regular pattern
QRS complex: 0.06 0.10 seconds;
sudden absence of QRS complex
Rate: atrial 60 -100 bpm, ventricular <
60 bpm
Rhythm: atrial regular, ventricular
irregular
P:QRS ration: typically 2:1, may vary
PR interval: constant PR interval for
each conducted QRS
QRS complex: 0.06 0.10 seconds
Rate: atrial 60 100 bpm; ventricular
15 60 bpm
Rhythm: both atrial and ventricular are
regular
Independent rhythm (no relationship
between P and QRS)
PR interval: not measured
QRS complex:
Treatment includes monitoring and
observation; atropine and isoproterenol
if client is symptomatic (rarely
progresses to a higher level of block)
Treatment includes atropine or
isoproterenol; pacemaker therapy
Immediate pacemaker therapy
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Cardiac DysrhythmiasDocument3 paginiCardiac DysrhythmiasKatherine Santiago92% (62)
- Cardiac Rhythms and Dysrhythmias GuideDocument14 paginiCardiac Rhythms and Dysrhythmias GuideShawn Gaurav Jha100% (1)
- Ekg Strip NotesDocument13 paginiEkg Strip NotesNick Loizzo100% (2)
- BASIC ECG READING For Nle NOVEMBER 2018Document63 paginiBASIC ECG READING For Nle NOVEMBER 2018Sharmaine KimmayongÎncă nu există evaluări
- EKG and ECG Interpretation: Learn EKG Interpretation, Rhythms, and Arrhythmia Fast!De la EverandEKG and ECG Interpretation: Learn EKG Interpretation, Rhythms, and Arrhythmia Fast!Încă nu există evaluări
- EKG | ECG: An Ultimate Step-By-Step Guide to 12-Lead EKG | ECG Interpretation, Rhythms & Arrhythmias Including Basic Cardiac DysrhythmiasDe la EverandEKG | ECG: An Ultimate Step-By-Step Guide to 12-Lead EKG | ECG Interpretation, Rhythms & Arrhythmias Including Basic Cardiac DysrhythmiasEvaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (5)
- Dysrhythmias ChartDocument6 paginiDysrhythmias Chartjkrix100% (1)
- Basic Arrhythmia RulesDocument3 paginiBasic Arrhythmia Rulesgreenflames0997% (30)
- EKG Flash CardsDocument5 paginiEKG Flash CardsRyann Sampino FreitasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiac Rhythm Abnormalities GuideDocument7 paginiCardiac Rhythm Abnormalities GuideAya KamajayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECG Rhythm Interpretation GuideDocument3 paginiECG Rhythm Interpretation Guideis_aradanas0% (1)
- Critical Care - Hemodynamic Monitoring TableDocument7 paginiCritical Care - Hemodynamic Monitoring TableVictoria Romero100% (2)
- Lab ValuesDocument3 paginiLab Valuessurviving nursing schoolÎncă nu există evaluări
- ArrhythmiaDocument2 paginiArrhythmiaChris Pritchard93% (30)
- ECG StripsDocument5 paginiECG Stripssurviving nursing school100% (1)
- Ecg StripsDocument39 paginiEcg StripsNursyNurse100% (3)
- EKG Practice Test QuizDocument16 paginiEKG Practice Test QuizAbdul Rohim100% (1)
- Ekg Cheat SheetDocument2 paginiEkg Cheat Sheetdectricdf26505100% (1)
- Inherent Rates: Cardiovascular System Alterations Module BDocument7 paginiInherent Rates: Cardiovascular System Alterations Module Bmp_329Încă nu există evaluări
- Mini Test QUIZDocument9 paginiMini Test QUIZAbdul RohimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiac Notes NursingDocument16 paginiCardiac Notes NursingYemaya8494% (17)
- Spotlight On Cardiac DrugsDocument2 paginiSpotlight On Cardiac Drugspauerish100% (2)
- Ekg Guidelines PDFDocument7 paginiEkg Guidelines PDFd.ramadhan100% (1)
- MAP, CO, and SV+HRDocument11 paginiMAP, CO, and SV+HRjenwiley318096% (73)
- ECG Interpretation Cheat SheetDocument14 paginiECG Interpretation Cheat Sheetrenet_alexandre75% (4)
- Cardiac MedicationsDocument9 paginiCardiac Medicationsnovikane100% (1)
- Reading A EKGDocument10 paginiReading A EKGMayer Rosenberg100% (15)
- Cardiac Dysrhythmia Chart Med-Surg NUR4Document3 paginiCardiac Dysrhythmia Chart Med-Surg NUR4ktfosterfd2096% (96)
- ACLS EKG Rhythms and InterpretationDocument10 paginiACLS EKG Rhythms and Interpretationdonheyzz_02Încă nu există evaluări
- ECG ReadingDocument11 paginiECG ReadingSuresh Shrestha100% (1)
- ECG Interpretation GuideDocument4 paginiECG Interpretation GuidePRaDo PATÎncă nu există evaluări
- EKG ExamplesDocument9 paginiEKG ExamplesMayer Rosenberg99% (235)
- Pakya ECG BasicsDocument5 paginiPakya ECG BasicsFrederick CokroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dysrhythmia Recognition Pocket Reference Card PDFDocument14 paginiDysrhythmia Recognition Pocket Reference Card PDFjenn1722100% (2)
- Adult III Cardiac Study GuideDocument15 paginiAdult III Cardiac Study GuideNursingSchoolNotes100% (6)
- Ecg Reading NotesDocument17 paginiEcg Reading NotesMarian FloresÎncă nu există evaluări
- EKG Cheat SheetDocument9 paginiEKG Cheat SheetAlert Twitter100% (5)
- Cardiac Medications and Treatments GuideDocument10 paginiCardiac Medications and Treatments GuideNursePoor98% (47)
- Ekg PracticeDocument7 paginiEkg PracticeMichelle Cobb Matthews100% (1)
- ECG Interpretation - Axis and Conduction AbnormalitiesDocument9 paginiECG Interpretation - Axis and Conduction Abnormalitiesradha1000100% (1)
- Basic EKG Review: Identify Rhythms & InterventionsDocument31 paginiBasic EKG Review: Identify Rhythms & Interventionsmeb100% (1)
- A Simplified ECG GuideDocument4 paginiA Simplified ECG Guidejalan_z96% (25)
- Cardiac DrugsDocument5 paginiCardiac Drugseric100% (17)
- Cardiac Dysrhythmia Chart Med Surg NUR4 PDFDocument3 paginiCardiac Dysrhythmia Chart Med Surg NUR4 PDFlml100% (1)
- Heart FailureDocument1 paginăHeart Failurehannahhwolf100% (3)
- The 12-Lead Electrocardiogram for Nurses and Allied ProfessionalsDe la EverandThe 12-Lead Electrocardiogram for Nurses and Allied ProfessionalsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dimensional Analysis For Nursing StudentsDe la EverandDimensional Analysis For Nursing StudentsÎncă nu există evaluări
- EKG/ECG Interpretation Made Easy: A Practical Approach to Passing the ECG/EKG Portion of NCLEXDe la EverandEKG/ECG Interpretation Made Easy: A Practical Approach to Passing the ECG/EKG Portion of NCLEXEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (2)
- Fluid and Electrolytes for Nursing StudentsDe la EverandFluid and Electrolytes for Nursing StudentsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (12)
- EKG Technician: Passbooks Study GuideDe la EverandEKG Technician: Passbooks Study GuideÎncă nu există evaluări
- CRITICAL CARE NURSE: Passbooks Study GuideDe la EverandCRITICAL CARE NURSE: Passbooks Study GuideÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECG Characteristics and Management of Cardiac RhythmsDocument6 paginiECG Characteristics and Management of Cardiac RhythmsJeffrey Viernes100% (1)
- EKG RhythmsDocument10 paginiEKG RhythmsQueenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of ArrhythmiaDocument10 paginiTypes of ArrhythmiaRonilyn Mae AlvarezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Memory JoggersDocument2 paginiNursing Memory JoggersMarcus, RN96% (24)
- 5 Written QuestionsDocument4 pagini5 Written QuestionszooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Business Letter Format SampleDocument1 paginăBusiness Letter Format SamplezooÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2014 2015CatalogWEBDocument158 pagini2014 2015CatalogWEBzooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Answering NCLEX QuestionsDocument19 paginiAnswering NCLEX QuestionsNorma Zamudio92% (24)
- Vasopressors Drug BulletsDocument19 paginiVasopressors Drug BulletszooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carbidopa-Levodopa Treatment for Parkinson's DiseaseDocument3 paginiCarbidopa-Levodopa Treatment for Parkinson's DiseaseTodd ColeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Memory JoggersDocument2 paginiNursing Memory JoggersMarcus, RN96% (24)
- Hot One Hundred Sample Worksheet-2Document3 paginiHot One Hundred Sample Worksheet-2zooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Epidural Anesthesia GuideDocument3 paginiEpidural Anesthesia GuidezooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vasopressors Drug BulletsDocument19 paginiVasopressors Drug BulletszooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Patient Care SheetDocument2 paginiPatient Care SheetzooÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHPA Pediatrics DosingChart FINALDocument1 paginăCHPA Pediatrics DosingChart FINALTodd ColeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Epidural Anesthesia GuideDocument3 paginiEpidural Anesthesia GuidezooÎncă nu există evaluări
- ABG Poster A3Document1 paginăABG Poster A3Araceli Ecot Calunod100% (2)
- Nursing Memory JoggersDocument2 paginiNursing Memory JoggersMarcus, RN96% (24)
- Goal: Control PainDocument2 paginiGoal: Control PainzooÎncă nu există evaluări
- GASTROINTESTINALDocument5 paginiGASTROINTESTINALRizMarie100% (3)
- NCSBN Learning Extension's Nclex RN & PN Review: 3-Week PlanDocument2 paginiNCSBN Learning Extension's Nclex RN & PN Review: 3-Week PlanzooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diabetes ArticleDocument2 paginiDiabetes ArticlezooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Business Letter Format SampleDocument1 paginăBusiness Letter Format SamplezooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acetaminophen Dosage ChartDocument1 paginăAcetaminophen Dosage ChartTodd ColeÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHPA Pediatrics DosingChart FINALDocument1 paginăCHPA Pediatrics DosingChart FINALTodd ColeÎncă nu există evaluări
- IBUPROFENDocument1 paginăIBUPROFENYuni PratiwiÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHPA Pediatrics DosingChart FINALDocument1 paginăCHPA Pediatrics DosingChart FINALTodd ColeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Goal: Control PainDocument2 paginiGoal: Control PainzooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutrition test 1 study guideDocument4 paginiNutrition test 1 study guideTodd Cole50% (2)
- Activate and Connect Fubo TV On Fire Stick TVDocument4 paginiActivate and Connect Fubo TV On Fire Stick TVBaron SilvaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hide and Seek Fun in Decodable Reader 26Document5 paginiHide and Seek Fun in Decodable Reader 26BaxiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 150 MinoriesDocument2 pagini150 MinoriesBE OfficesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Farnsworth House Architecture in Detail PDFDocument2 paginiFarnsworth House Architecture in Detail PDFEdwin50% (2)
- The Pianist (2002)Document8 paginiThe Pianist (2002)আলটাফ হুছেইনÎncă nu există evaluări
- HCD-GSX100W SMDocument72 paginiHCD-GSX100W SMmarialixd4472Încă nu există evaluări
- Novomatic PercentageDocument3 paginiNovomatic PercentagePVL Mwanza0% (1)
- ABYSSDocument102 paginiABYSSlucas100% (3)
- Bracket SDocument37 paginiBracket SRheynaldi Lintang SusilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bambulabp 1 PDocument21 paginiBambulabp 1 PAlexe Andrei - ClaudiuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elton JohnDocument51 paginiElton JohnGiorgio Paganelli100% (1)
- Sams ComputerFacts - Apple IIeDocument73 paginiSams ComputerFacts - Apple IIeOscar Arthur KoepkeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1. Wood Structure: F 1-4. Consideration of Grain Direction WhenDocument19 paginiChapter 1. Wood Structure: F 1-4. Consideration of Grain Direction WhenrobinyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Common Errors in English GrammarDocument13 paginiCommon Errors in English GrammarPavan GollakotiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Boltec LC DHDocument4 paginiBoltec LC DHjiaozhongxingÎncă nu există evaluări
- 07 Quiz 1Document1 pagină07 Quiz 1Joseph Benedict DeLeonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pokémon Scarlet & Violet - Version Exclusives - PokémonDocument1 paginăPokémon Scarlet & Violet - Version Exclusives - PokémonTomaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MContent WhitePaper V2.15Document30 paginiMContent WhitePaper V2.15Goalsss 2017Încă nu există evaluări
- Turkish Language Euphemisms and Cultural InsightsDocument13 paginiTurkish Language Euphemisms and Cultural InsightsUnior10% (1)
- A Four Element Rectangular Dielectric Resonator Antenna Array For Wireless ApplicationsDocument4 paginiA Four Element Rectangular Dielectric Resonator Antenna Array For Wireless ApplicationsSubhanjali MyneniÎncă nu există evaluări
- DLP in English 5 Summarizing Various Text Types Based On ElementsDocument13 paginiDLP in English 5 Summarizing Various Text Types Based On Elementspaolaagustin027Încă nu există evaluări
- FortiOS 7.4.0 New Features GuideDocument565 paginiFortiOS 7.4.0 New Features Guidexoreg93494Încă nu există evaluări
- Avantree SP850 UManualDocument6 paginiAvantree SP850 UManualVenuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Speech For PresentationDocument2 paginiSpeech For PresentationMuhammad AsyraafÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHAN 9363 BOOK - QXD 16/7/07 12:19 PM Page 2: John AdamsDocument9 paginiCHAN 9363 BOOK - QXD 16/7/07 12:19 PM Page 2: John AdamskapukapucarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Piano Mastery TalkDocument297 paginiPiano Mastery Talknunomgalmeida-1100% (4)
- Fabian TheoryDocument9 paginiFabian TheoryPierre AnfrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Star Trek Online Mogh Battle Cruiser Stats and Bortasqu Build (Warmog)Document3 paginiStar Trek Online Mogh Battle Cruiser Stats and Bortasqu Build (Warmog)Aleks OpsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ajedrez Sakaev Konstantin The Petroff An Expert Repertoire For Blackpdf PDF FreeDocument294 paginiAjedrez Sakaev Konstantin The Petroff An Expert Repertoire For Blackpdf PDF FreeEny oneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Doraemon movies in Hindi with original Japanese titlesDocument4 paginiDoraemon movies in Hindi with original Japanese titlesArjun Kabir0% (1)