Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Gis Apllication
Încărcat de
Abhi Manu0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
55 vizualizări4 paginiAbout gis
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentAbout gis
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
55 vizualizări4 paginiGis Apllication
Încărcat de
Abhi ManuAbout gis
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 4
Application of GIS And GPS in Distribution Power Sector
Anil Kumar, Arun M Shandilya & S. K. Katiyar
Manit Bhopal
E-mail : anilbaraik777@yahoo.co.in, arunshandilya@yahoo.com, skatiyar7@rediffmail.com
attribute are represented with the help of lines, points or
polygons in a geo referenced map.
Abstract - With the advancement in Software and IT
sector, our electricity utility is going to be much more
benefited in power system planning and management. The
main objective of a utility is to supply the power demand
with good quality of service but unfortunately we are
unable to do so due to uneven and variable load condition.
This had led to advance in new methods which can make
effective changes in solving the intricacy of electrical
distribution system. This paper shows the application of
new and emerging technologies like GIS (geographic
information system) and GPS (global positioning system)
which are capable of carrying out complex online and
offline power system analysis like Load flow analysis, Load
forecasting,
Route
optimization,
supply
control
distribution planning etc. using shortest path algorithm all
this we can do in a software called ARCGIS 9.3.
GPS - A global positioning system is an artificial
satellite based navigation used to get the exact location
of any physical object in term of latitude & longitude
with the help of a GPS device
II. WHY GIS IN POWER SECTOR
Keywords - ARCGIS 9.3, Geographical Information System,
(GIS) Global Position System (GPS).
I.
1.
VISUALIZATION TOOL- A conceptual model of
a GIS provides a useful way to visualize both
physical & electrical layer in a single screen
registered together to a common base map or
geographic area. Each layer typically contains one
type of data only.
2.
FLEXIBILITY IN ANALYSIS - With GIS, one can
easily manipulate and carry out different task
related to power system planning & management of
electricity with efficient results. Such as planning or
updating a new distribution network.
3.
When new facilities are installed, GIS database can
be updated easily to accommodate new features.
4.
Thus map revision and digital mapping become
easy in GIS Environment.
5.
It is useful in planning a routine maintenance.
6.
Customers enquiries can be handled easily.
7.
Sharing of data among different users like Urban
Planners, Construction Managers, Civil Engineers
is also Possible
8.
Ready-to-use tools.
INTRODUCTION
The present situation shows that the Distribution
sector in India is the weakest area compared to
Generation & Transmission. It directly affects the
consumer because most of the losses and faults occur in
this particular area. Due to insufficient attention in
transmission & distribution losses the situation is worse
in some rural areas. The average T&D losses are
currently at 28%[3] by the year 2012.Lack of proper
administration & power theft are some common reasons
for the high losses. Thus the present distribution system
requires to be upgraded to minimize the loss. Also by
applying GIS we can reduce the distribution planning
cost by reducing the material cost through Optimum
feeder path.
III. APPLICATION IN POWER SECTOR
GIS - It is a digital representation of consumers,
network elements & important landmarks on a geo
referenced map, with their attributes stored in a
database, OR we can say that it is a system used to
capture, store ,analyze and managing data and attributes
associated with it which are referenced to the earth. In
GIS software all information regarding physical
Database management.
GIS based Electrical network mapping.
Optimum feeder path.[2]
GIS based Consumer database indexing.
ISSN (Print): 2278-8948, Volume-2, Issue-5, 2013
23
International Journal of Advanced Electrical and Electronics Engineering, (IJAEEE)
Metering, Billing & Collection Efficiency.
Selection of optimal conductors.
Energy audit and accounting practices.
Load Flow analysis.
Supervisory control & Data acquisition (SCADA).
System & Distribution Automation.
Maintenance management System.
Management Information System.
Load forecasting and load planning
Inventory control.
IV. METHODOLOGY
FIG: excel data in CSV format
FIELD SURVEY
DATA ORGANIZATION
DATA IMPORT & LAYER CREATION
ANALLYSIS
ATTRIBUTE TABLE
IX. TYPE OF LAYER DATA
V. SOFTWARE USED
ARC GIS 9.3
GPS DEVICE
GOOGLE EARTH
X. VECTOR LAYER
VI. INTRODUCTION TO ARC GIS & GPS
ARC GIS- It is a software designed & developed by
ESRI & it consists of 3 GIS software products:
1.
ARC VIEW
2.
ARC EDITOR
3.
ARC INFO
VII. FIELD SURVEY
XI. GEOREFRENCING
It consists of capturing geographical coordinates
(latitude & longitude) of electrical elements like Poles,
Transformer, HT & LT cables. With the help of a
portable GPS device in decimal degrees format.
It is a process of defining the coordinate of a map
image so that it get correctly placed concurrently with
other different shape file placed in ARC MAP window.
PROCEDURE - It require a map application like
GOOGLE EARTH
VIII. DATA ORGANIZATION
This process consist of two steps1.
2.
Step 1: Open arc catalogue & edit the spatial
property of map WGS 1984
Arranging & placing all the coordinates in
Microsoft Excel Document.
Step 2: Import map image in arc map.
Saving them with file extension-CSV (comma
delimited).
Step 3: Point & select at least 3 locations & input
the actual (X &Y) field taken Google earth.
ISSN (Print): 2278-8948, Volume-2, Issue-5, 2013
24
International Journal of Advanced Electrical and Electronics Engineering, (IJAEEE)
Fig: Geo referenced Map
Fig: Road Shape File
XII. DATA IMPORT & LAYER CREATION
This is the stage we just import all the different
layer, shape file & base map using ADD DATA button
in ARC GIS desktop.
S
NO
SHAPE
FILE TYPE
POINT
LINE
POLYGON
FILE EXTENSION
&
DISCRIPTION
1) .shp- Point Data in ARC GIS
2) .gpx-GPS Exchange
Format
3) .kml- Keyhole Markup
Language
4) .lyr- Layer Data in ARC GIS
Fig: Location of Transformer in Point Shape File
TABLE: Shape File Description
XIII. SCREEN SHOTS
Fig: Base Map
Fig: Location of Poles in Point Shape File
ISSN (Print): 2278-8948, Volume-2, Issue-5, 2013
25
International Journal of Advanced Electrical and Electronics Engineering, (IJAEEE)
XV. CONCLUSION
1.
Better customer services
2.
Reduction of technical losses
3.
Energy audit and accounting
4.
Trouble call management
5.
Real time operation of distribution network
6.
Better revenue protection
7.
Long term distribution planning etc.
XVI. REFRENCES
[1]
Philip Smith, Virgilio Centeno, Jaime De La Ree,
Mapping The Electrical Influence Of
Distributed Generation On Radial Distribution
Networks Using Geographic Information
Systems, Securing Critical Infrastructures,
Grenoble on October 2004.
[2]
Priyanka Dixit, J.D.Sharma, M.K.Singhal, Gis
And Gps Based Preliminary Distribution System
Planning, NCEEERE 2008.
[3]
Planning Commission Of India.
[4]
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gps.
Fig: Location of Buildings in Polygon Shape File
Fig: Final Screen Showing All Shape File
XIV. CREATING ATTRIBUTE TABLE
1.
Network database indexing.
2.
Creation of customer database linked to HT & LT
lines.
3.
All consumers are given a unique CIN (Consumer
Index Number).
4.
All network elements are identified and their
technical Attributes are recorded in a ARC GIS 9.3.
ISSN (Print): 2278-8948, Volume-2, Issue-5, 2013
26
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Delivering Water and Power: GIS for UtilitiesDe la EverandDelivering Water and Power: GIS for UtilitiesPat HohlEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- Gis and Gps Based Preliminary Distribution System PlanningDocument6 paginiGis and Gps Based Preliminary Distribution System Planningpd110382Încă nu există evaluări
- Integration of Demand Response into the Electricity Chain: Challenges, Opportunities, and Smart Grid SolutionsDe la EverandIntegration of Demand Response into the Electricity Chain: Challenges, Opportunities, and Smart Grid SolutionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- GIS-based Model For Implementation On Power Transformer Planning Within Thailand Power NetworkDocument8 paginiGIS-based Model For Implementation On Power Transformer Planning Within Thailand Power Networkalen123456Încă nu există evaluări
- Designing Geodatabases for TransportationDe la EverandDesigning Geodatabases for TransportationEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (2)
- GIS and The Smart GridDocument4 paginiGIS and The Smart GridSteve CollierÎncă nu există evaluări
- Use of Geographic Information Systems To Build and Management A Geometric Network For ElectricityDocument6 paginiUse of Geographic Information Systems To Build and Management A Geometric Network For ElectricityEditor IJTSRDÎncă nu există evaluări
- 004 FDocument8 pagini004 FŽarko MočnikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presentation On GIS Mapping of Electrical Distribution NetworkDocument15 paginiPresentation On GIS Mapping of Electrical Distribution Networkharp123Încă nu există evaluări
- GIS-Based Distribution System PlanningDocument10 paginiGIS-Based Distribution System PlanningAbu Saro DimasangkaÎncă nu există evaluări
- GIS in Kenya PowerDocument4 paginiGIS in Kenya PowerTapas RoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conference Paper: "Integration of For Mapping and Analysis of Electric Distribution Circuits"Document11 paginiConference Paper: "Integration of For Mapping and Analysis of Electric Distribution Circuits"heissenriyadhovicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Load Curve Data Cleansing and Imputation Via Sparsity and Low RankDocument9 paginiLoad Curve Data Cleansing and Imputation Via Sparsity and Low RankFlorin NastasaÎncă nu există evaluări
- GIS Based Consumer Indexing and Asset Mapping at MohaliDocument4 paginiGIS Based Consumer Indexing and Asset Mapping at MohaliJamie OrtizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lessons Learnt From Interfacing Arcgis and Digsilent Powerfactory at Başkent DiscoDocument5 paginiLessons Learnt From Interfacing Arcgis and Digsilent Powerfactory at Başkent Discoael0escalanteÎncă nu există evaluări
- SIG EmpresarialDocument13 paginiSIG EmpresarialOmar Cristián MarcaÎncă nu există evaluări
- GIS Application in Power DistributionDocument2 paginiGIS Application in Power Distributionعماد صدقيÎncă nu există evaluări
- Idea - A Gis-Based Multi Criteria Decision Platform To Evaluate Der IntegrationDocument4 paginiIdea - A Gis-Based Multi Criteria Decision Platform To Evaluate Der IntegrationkotiniÎncă nu există evaluări
- GisDocument6 paginiGisJohn Tejada IIIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gis CatDocument7 paginiGis CatMARK KIPKORIR MARITIMÎncă nu există evaluări
- GIS On JakartaDocument5 paginiGIS On JakartaSteffe ArbiniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Role of GIS in Distribution Power Systems: N. Rezaee, M Nayeripour, A. Roosta, T. NiknamDocument5 paginiRole of GIS in Distribution Power Systems: N. Rezaee, M Nayeripour, A. Roosta, T. NiknamWasiuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Subsurface Views: See The Big PictureDocument4 paginiSubsurface Views: See The Big PictureRisky AftartuÎncă nu există evaluări
- 03 - SYNOPSIS - Garry CachoDocument11 pagini03 - SYNOPSIS - Garry CachoSugar Ray0% (1)
- Performance Prediction Tools For Low Impact Building DesignDocument8 paginiPerformance Prediction Tools For Low Impact Building DesignLTE002Încă nu există evaluări
- Energies 06 03593Document29 paginiEnergies 06 03593Aditya DasÎncă nu există evaluări
- A New Method of Realistic GSM Network Planning For Rural Indian TerrainsDocument10 paginiA New Method of Realistic GSM Network Planning For Rural Indian Terrainsrfabre76Încă nu există evaluări
- Distribution Feeder One-Line Diagrams Automatic Generation From Geographic Diagrams Based On GISDocument5 paginiDistribution Feeder One-Line Diagrams Automatic Generation From Geographic Diagrams Based On GISheissenriyadhovicÎncă nu există evaluări
- ICCA 2019 Proceedings Book-Pages-273-279Document7 paginiICCA 2019 Proceedings Book-Pages-273-279aung myoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sparse and Redundant Representation-Based Smart Meter Data Compression and Pattern ExtractionDocument10 paginiSparse and Redundant Representation-Based Smart Meter Data Compression and Pattern ExtractionKartik HansÎncă nu există evaluări
- FTTH Gis Ijeit1412201408 - 09Document9 paginiFTTH Gis Ijeit1412201408 - 09jorgefuriasseÎncă nu există evaluări
- MIS in Power Distribution SystemDocument34 paginiMIS in Power Distribution SystemAnkita KothariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wastewater Collection System Modeling and Design Using GISDocument41 paginiWastewater Collection System Modeling and Design Using GISJalijashÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thesis Paper On Smart GridDocument7 paginiThesis Paper On Smart Gridshannonsandbillings100% (2)
- Urban Data and Building EnergyDocument23 paginiUrban Data and Building Energyxinyi tangÎncă nu există evaluări
- The GIS Application For Electricity Distribution Billing and Revenue ManagementDocument24 paginiThe GIS Application For Electricity Distribution Billing and Revenue ManagementInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Erms F Eference For Distribution Network Survey, Asset Mapping and Consumer Indexing in Dhenkanal and Anugul AreaDocument2 paginiErms F Eference For Distribution Network Survey, Asset Mapping and Consumer Indexing in Dhenkanal and Anugul AreasomuÎncă nu există evaluări
- CIRED2007 0130 PaperDocument5 paginiCIRED2007 0130 PaperkotiniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project Proposal v8Document5 paginiProject Proposal v8IgweÎncă nu există evaluări
- GIS Applications Optimize Power Distribution ManagementDocument21 paginiGIS Applications Optimize Power Distribution ManagementbjfvfvÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ts22 05 JonesDocument6 paginiTs22 05 JonesGenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Automatic routing of urban MV distribution networksDocument6 paginiAutomatic routing of urban MV distribution networksbluemoon1172Încă nu există evaluări
- Base Map Generation For Utility Mapping Using High Resolution Satellite Data PDFDocument5 paginiBase Map Generation For Utility Mapping Using High Resolution Satellite Data PDFNatarajanSubramanyamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Construction and Application of Field InvestigatioDocument7 paginiConstruction and Application of Field InvestigatiomarouanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solutions For The Data Level's Representation in A Decision Support System in Wind Power PlantsDocument6 paginiSolutions For The Data Level's Representation in A Decision Support System in Wind Power PlantsMuhammad TaslimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Distribution Network Model Builder For OpenDSS in Open Source GIS SoftwareDocument6 paginiDistribution Network Model Builder For OpenDSS in Open Source GIS SoftwareDavid Jose Poma GuillenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Using Geographic Information Systems (Gis) in Industrial Water Reuse ModellingDocument9 paginiUsing Geographic Information Systems (Gis) in Industrial Water Reuse Modellingashoori79Încă nu există evaluări
- Towards 5G: Context Aware Resource Allocation For Energy SavingDocument13 paginiTowards 5G: Context Aware Resource Allocation For Energy SavingOPTICALMIMOOFDMÎncă nu există evaluări
- Content ServerDocument15 paginiContent ServerAmbika sharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Automated Energy Meter Reading System Using GSM TechnologyDocument8 paginiAn Automated Energy Meter Reading System Using GSM TechnologyBarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Graphical Editing, Network Topology, and Database Management. System ManagementDocument3 paginiGraphical Editing, Network Topology, and Database Management. System ManagementМирко ГрбићÎncă nu există evaluări
- Literature Review Smart GridDocument5 paginiLiterature Review Smart Gridbsnyfpwgf100% (1)
- SubTelForum Issue32 May2007Document3 paginiSubTelForum Issue32 May2007nautapronautaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Role of Information and Communication Technologies in The Smart GridDocument10 paginiRole of Information and Communication Technologies in The Smart GridNovia Agustiar RahmatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geo HydroDocument17 paginiGeo Hydrocarmen_andreea_Încă nu există evaluări
- CIRED2017 0061 FinalDocument5 paginiCIRED2017 0061 FinalChris ParkinsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Distributed SystemDocument15 paginiDistributed Systemvijay9994Încă nu există evaluări
- A Real-Time Conductor Sag Measurement System Using A Differential GPSDocument6 paginiA Real-Time Conductor Sag Measurement System Using A Differential GPSBalaji Narayanan NÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11 KV Feeder Analysis Using GPS Mapping For Improving The Network PDFDocument3 pagini11 KV Feeder Analysis Using GPS Mapping For Improving The Network PDFmdasifhassanapspdclÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experion Scada PinDocument7 paginiExperion Scada PinKhalid AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bottom Ash HopperDocument8 paginiBottom Ash HopperBhargav ChaudhariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final ReportDocument33 paginiFinal ReporttsutsenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Loading Equipment For Amsco Evolution™ Steam Sterilizers: ApplicationDocument4 paginiLoading Equipment For Amsco Evolution™ Steam Sterilizers: ApplicationniÎncă nu există evaluări
- January2016page1to36 Layout 1Document36 paginiJanuary2016page1to36 Layout 1c737Încă nu există evaluări
- SRSUNTOUR General Fork GlossaryDocument23 paginiSRSUNTOUR General Fork GlossaryThomas JunkersfeldÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 7: Cylinders: Basic Hydraulic SystemsDocument12 paginiLesson 7: Cylinders: Basic Hydraulic Systemsoscar el carevergaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 3: Temperature Measurement MethodDocument12 paginiExperiment 3: Temperature Measurement Methodmohamad munzirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Customize ADFS sign-in page brandingDocument4 paginiCustomize ADFS sign-in page brandingmicu0% (1)
- Estimating/ Construction Planning/ Scheduling and Programming/ Feasibility Project StudiesDocument4 paginiEstimating/ Construction Planning/ Scheduling and Programming/ Feasibility Project StudiesVholts Villa VitugÎncă nu există evaluări
- NUSTian Final July SeptDocument36 paginiNUSTian Final July SeptAdeel KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Please Note That This Form Details Exploration and Production Api Titles Available For OrderDocument8 paginiPlease Note That This Form Details Exploration and Production Api Titles Available For Orderhaotran68Încă nu există evaluări
- 3RInternational Tetzner Model Based Pipeline LDS 07-2003 PDFDocument6 pagini3RInternational Tetzner Model Based Pipeline LDS 07-2003 PDFRene ParedesÎncă nu există evaluări
- RCC BEAM DESIGN AND SERVICEABILITYDocument15 paginiRCC BEAM DESIGN AND SERVICEABILITYprashmceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Foxpro For O LevelDocument3 paginiFoxpro For O LevelShiv PathakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technical Publications: Direction 2190775 100Document21 paginiTechnical Publications: Direction 2190775 100zakaria alhosinyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mixers Towable Concrete Essick EC42S Rev 8 Manual DataId 18822 Version 1Document84 paginiMixers Towable Concrete Essick EC42S Rev 8 Manual DataId 18822 Version 1Masayu MYusoffÎncă nu există evaluări
- Distribution A9F74240Document3 paginiDistribution A9F74240Dani WaskitoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Customer Targeted E-CommerceDocument4 paginiCustomer Targeted E-CommercepriyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Synergies of Hybridizing CNC and Additive ManufacturingDocument8 paginiThe Synergies of Hybridizing CNC and Additive ManufacturingdemuxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Demographically Similar EntriesDocument1 paginăDemographically Similar EntriesTahsildar MydukurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Applied Fluid Mechanics: Viscosity of FluidsDocument22 paginiApplied Fluid Mechanics: Viscosity of FluidsMaggie HepditchÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dow Corning (R) 200 Fluid, 50 Cst.Document11 paginiDow Corning (R) 200 Fluid, 50 Cst.Sergio Gonzalez GuzmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Models - Rf.bowtie Antenna OptimizationDocument14 paginiModels - Rf.bowtie Antenna OptimizationbkmmizanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Airflex 728 Vinyl Acetate-Ethylene Copolymer Modified With Vinyl ChlorideDocument2 paginiAirflex 728 Vinyl Acetate-Ethylene Copolymer Modified With Vinyl ChlorideNissim Hazar CasanovaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CAD1 AssignmentDocument11 paginiCAD1 AssignmentJohn2jÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Report On Workability of Fresh Concrete by Slump TestDocument5 paginiA Report On Workability of Fresh Concrete by Slump TestRishabhJain100% (1)
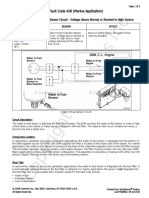
- 06-Fc428mar Water-in-Fuel Indicator Sensor Circuit - Voltage Above Normal or Shorted To High SourceDocument3 pagini06-Fc428mar Water-in-Fuel Indicator Sensor Circuit - Voltage Above Normal or Shorted To High SourceSuryadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sodium Citrate AUDocument3 paginiSodium Citrate AUKrishna OgotÎncă nu există evaluări
- CompoundingDocument5 paginiCompoundingMajester RigsÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Big, Bad Book of Botany: The World's Most Fascinating FloraDe la EverandThe Big, Bad Book of Botany: The World's Most Fascinating FloraEvaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (10)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingDe la EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (4)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingDe la EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (32)
- Last Child in the Woods: Saving Our Children From Nature-Deficit DisorderDe la EverandLast Child in the Woods: Saving Our Children From Nature-Deficit DisorderEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (283)
- The Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorDe la EverandThe Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (137)
- Why Fish Don't Exist: A Story of Loss, Love, and the Hidden Order of LifeDe la EverandWhy Fish Don't Exist: A Story of Loss, Love, and the Hidden Order of LifeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (699)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildDe la EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (44)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldDe la EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (18)
- The Mind of Plants: Narratives of Vegetal IntelligenceDe la EverandThe Mind of Plants: Narratives of Vegetal IntelligenceEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (11)
- The Secret Life of Lobsters: How Fishermen and Scientists Are Unraveling the Mysteries of Our Favorite CrustaceanDe la EverandThe Secret Life of Lobsters: How Fishermen and Scientists Are Unraveling the Mysteries of Our Favorite CrustaceanÎncă nu există evaluări
- World of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsDe la EverandWorld of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (221)
- Soil: The Story of a Black Mother's GardenDe la EverandSoil: The Story of a Black Mother's GardenEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (16)
- Spoiled Rotten America: Outrages of Everyday LifeDe la EverandSpoiled Rotten America: Outrages of Everyday LifeEvaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (19)
- The Hummingbirds' Gift: Wonder, Beauty, and Renewal on WingsDe la EverandThe Hummingbirds' Gift: Wonder, Beauty, and Renewal on WingsEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (60)
- The Hidden Life of Trees: What They Feel, How They CommunicateDe la EverandThe Hidden Life of Trees: What They Feel, How They CommunicateEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1002)
- Gathering Moss: A Natural and Cultural History of MossesDe la EverandGathering Moss: A Natural and Cultural History of MossesEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (347)
- The Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsDe la EverandThe Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (63)
- Come Back, Como: Winning the Heart of a Reluctant DogDe la EverandCome Back, Como: Winning the Heart of a Reluctant DogEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (10)
- A Garden of Marvels: How We Discovered that Flowers Have Sex, Leaves Eat Air, and Other Secrets of PlantsDe la EverandA Garden of Marvels: How We Discovered that Flowers Have Sex, Leaves Eat Air, and Other Secrets of PlantsÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Nature Fix: Why Nature Makes us Happier, Healthier, and More CreativeDe la EverandThe Nature Fix: Why Nature Makes us Happier, Healthier, and More CreativeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (157)
- Remnants of Ancient Life: The New Science of Old FossilsDe la EverandRemnants of Ancient Life: The New Science of Old FossilsEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (2)