Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Module Questions
Încărcat de
zulkarnainDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Module Questions
Încărcat de
zulkarnainDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
LEARNING AREA 4 : CELL
DIVISION
MITOSIS
1.
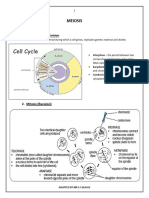
Cell Cycle
Name and state the purpose of each of these sub phases
P1
: ..
: ..
P2
: ..
: ..
: ..
2. State the definition of Mitosis.
MITOSIS
Process by which a nucleus divides to produce _____________
daughter cells, each containing the __________ number of
chromosomes as the parental cells.
LEARNING AREA 4 : CELL
DIVISION
3. Rearrange the jumbled words .
The importances of mitosis are:
a. W O T H G R
_____________________
b. ELLC
_____________________
E CALP N E TE R M
c. G E T O I R E N E N A
_____________________
d. X E S A A U L D U T C I N E R R O P
_____________________
4. Label the diagram below.
i.
ii.
5. Underline the correct words in the bracket.
Cytokinesis is occurs ( just prior to , after ) mitosis. Between divisions, cells are in
( dormant-phase , interphase ) , an active period during which chromosomal DNA is
duplicated, the cell mass ( increases, decreases) and new organelles are produced.
Nuclear DNA is replicated only during ( G1 , G2 , S ) phase. The process of mitosis
occurs in the following order : prophase, ( anaphase , metaphase ) , ( anaphase ,
metaphase ) and telophase. The mitotic spindle is a complex of ( microtubules ,
microfilaments ) that ( prevents , assists ) chromosomes movement. The spindle is
attached to each chromosome at a site called the ( connector , centromere ). Following
nuclear division, the cytoplasm of the cells is divided. The soon-to-be daughter cells are
LEARNING AREA 4 : CELL
DIVISION
separated by the cleavage ( plane , furrow ) in animals cells and the cell ( plate , furrow )
in the plant cells.
6. How does mitosis in plant cells differ from mitosis in animal cells ?
Cell division in plant and animal cells differs in two ways : (1) animal cells have
, whereas plants cells . , and (2) animal cells
have .. , whereas plant cells have ..
8. Complete the flow chart below
Tissue Culture Technique
. of carrot
Transverse section of root
Cell ( ..n )
Fragments cultured in ..
Cell division . to form
Callus cultured on .. medium and transferred to .
Adult plant
LEARNING AREA 4 : CELL
DIVISION
9. Explain briefly how Dolly the sheep was produced by cloning. Give your answer in the
form of a flow chart which shows the successive steps with explanatory notes for each
step.
LEARNING AREA 4 : CELL
DIVISION
10. ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF CLONING
Advantage
Disadvantage
Cloned plant are is
Clones are to new
size and shape
Plants can be produced the year
diseases
Clones are easily destroyed if there is a
. in the environment
Plant maintain the .. designed
characteristics of the mother plants
Tissue culture techniques are
cost
Clones can be produced in ..
numbers in a short time
MEIOSIS
11.
MEIOSIS
Process by which a nucleus divides to produce
____________ daughter cells, each containing ___________
the number of chromosomes of the parental cell.
12. Fill in the blank using the words provided.
Synapsis
Sister Chromatids
Haploid
Haploid
Two
Diploid
Metaphase II
four
Homologous chromosomes
Prophase I
Diploid
LEARNING AREA 4 : CELL
DIVISION
1. At __________ phase of meiosis are these two cells, each with sister chromatids
aligned at the spindle equator.
2. The meiotic process by which homologues are paired during prophase I is called
__________ .
3. Crossing occurs during ________ .
4. Meiosis consists of __________ nuclear divisions, producing ___________
haploid cells.
5. The function of meiosis I is to separate _________ . The function of meiosis II is
to separate _____________ .
6. Meiosis I produces two ____________ cells.
7. Meiosis II produces four ______________ cells.
13. By using two different colours show the result of crossing-over.
14. Complete the table below.
LEARNING AREA 4 : CELL
DIVISION
Name of Phase
Description
1.
Homologous chromosomes pair up and form tetrad
2.
Spindle fibers move homologous chromosomes to opposite sides
3.
Nuclear membrane reforms, cytoplasm divides, 4 daughter cells
formed
4.
Chromosomes line up along equator, not in homologous pairs
5.
Crossing-over occurs
6.
Sister chromatids separate
7.
Homologous chromosomes line up alone equator
8.
Cytoplasm divides, 2 daughter cells are formed
15. Name the stages in the diagrams above.
16. If a diploid cell has two chromosomes ( 2n = 4 ) , Draw and describe the events that
occur in each stage in mitosis and meiosis.
LEARNING AREA 4 : CELL
DIVISION
Mitosis Prophase
Meiosis I Prophase
Meiosis II Prophase
Chromosome
behaviour
Chromosome
Mitosis Metaphase
Meiosis I Metaphase
Meiosis II Metaphase
behaviour
Mitosis Anaphase
Meiosis I Anaphase
Meiosis II Anaphase
LEARNING AREA 4 : CELL
DIVISION
Chromosome
Mitosis Telophase
Meiosis I Telophase
behaviour
Meiosis II
Telophase
Chromosome
behaviour
17. COMPARE AND CONTRAST
1. Complete the table below.
Meiosis I
Similarities
Meiosis II
LEARNING AREA 4 : CELL
DIVISION
10
1. The chromosomes become . and .
during prophase.
2. The chromosomes are arranged at the . plate.
MEIOSIS I
Aspect compared
Homologous chromosomes pair Prophase
Synapsis
up and ...
chromosomes
between non-sister chromatids
.between
occurs.
non- sister chromatids does not
. Metaphase
take place
.
align at the metaphase plate of
the metaphase plate ( equator)
the cell
Homologous
of the cell
Sister
chromosomes Anaphase
MEIOSIS II
of
homologous
and
align
at
chromatids
and move to
becoming
opposite
daughter
poles.
Sister
chromosomes
that
chromatids are still attached
move to opposite poles.
together and move as a unit.
.. haploid daughter cells Telophase
. haploid daughter are
are formed.
Each daughter cell has only Set of chromosome
formed.
Each daughter cell has the
of
chromosome:
paternal
or
each
type
either
the
of
number
the
chromosome as the haploid cell
maternal
produced in meiosis I but each
chromosome.
cell has only one of the sister
chromatids.
18. Complete the table below.
Mitosis
1. A nuclear division process
Similarities
Meiosis
Aspect compared
Place occur
MEIOSIS
2. Nuclear division occur
MITOSIS
of
LEARNING AREA 4 : CELL
DIVISION
Role
Number of
cytokinesis
Synapsis of
homologous
chromosomes
Number of
daughter cells
Set of
chromosomes
Genetic
composition of
daughter cells
Variation
EXERCISES
1. Diagram 1.1 shows phases M and N during meiosis I.
11
LEARNING AREA 4 : CELL
DIVISION
M phase :
Description :
12
N phase :
Description :
a. In the space provided,
i.
State the both stages in M and N
ii.
Describe the behaviour of both chromosomes in above stages.
b. Diagram 1.2 shows the chromosome behaviour during Prophase I in
meiosis.
LEARNING AREA 4 : CELL
DIVISION
13
uv ray
i.
State the M process
..
ii.
State the part of chromatids where the M process occurs.
...
c. Based on diagram 1.2, draw the chromosome behaviour during Prophase
II.
Statement :
Case :
Meiosis is a process to
produce gametes that take
place in sex organ.
In a family, there are
variability occurs in
offspring.
d. Based on the above statement, explain how the situation happens.
LEARNING AREA 4 : CELL
DIVISION
14
.
e. Diagram 1.3 shows the formation of cancer cell in epithelium.
Epithelium cells
Cancerous cells
Based on diagram 1.3 , explain how the cancer happens.
2. Meiosis is involved in the production of gametes for sexual reproduction. Offspring
produced by sexual reproduction differ genetically from one another and from the
parents. Draw a diagram and explain briefly how meiosis makes genetic variation
possible.
LEARNING AREA 4 : CELL
DIVISION
15
..
3. Diagram shows the differences that occur in a family member.
Based on diagram 8, identify the differences among the family members. Discuss how
the differences are inherited.
..
LEARNING AREA 4 : CELL
DIVISION
16
4.
Diagram 2.1 shows phase X and phase Y in the cell cycle of an organism.
Phase X consists of three sub-phases, P, Q and R. Phase Y involves two
processes, U and Y.
Diagram 2.1
(a)
(i)
Name process U.
(ii)
State two roles of process U in an organism.
(b)
Diagram 2.2 shows the various stages in process U.
LEARNING AREA 4 : CELL
DIVISION
17
Diagram 2.2
(i)
Based on Diagram 2.2 complete the correct sequence of stages in
process U.
Stage
IV
(ii)
Stage
Stage
Stage
Name the stages in process U.
Stage
Name of stage
I
II
III
IV
(c) (i)
Name phase X in Diagram 2.1.
(ii)
Describe what happens in the cell during phase X.
LEARNING AREA 4 : CELL
DIVISION
(d)
18
A technique which involves the cell cycle shown in Diagram 2.1 could
used in cattle farming. A researcher use the technique to increase the
number of beef cattle. Describe the technique.
..
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (894)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- 2008 A Level H2 Biology P2 AnsDocument8 pagini2008 A Level H2 Biology P2 Ansjoannetzy0% (1)
- Mitosis and Meiosis WorksheetDocument4 paginiMitosis and Meiosis WorksheetAutumn Jackson-ButlerÎncă nu există evaluări
- IB Biology SL GeneticsDocument8 paginiIB Biology SL GeneticsAliciaChing24Încă nu există evaluări
- Dentistry Note First Year - 1Document398 paginiDentistry Note First Year - 1tuturuÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.6 Cell Division - AnswersDocument36 pagini1.6 Cell Division - AnswersEunice LeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seminar Bio P2 SMART 2018Document179 paginiSeminar Bio P2 SMART 2018zulkarnain100% (1)
- Rumus BiologiDocument1 paginăRumus Biologizulkarnain100% (3)
- Paper 1, SPMRSM 2016Document48 paginiPaper 1, SPMRSM 2016zulkarnainÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6.1 Types of NutritionDocument15 pagini6.1 Types of Nutritionzulkarnain0% (1)
- XAPlus 2016 MiauDocument24 paginiXAPlus 2016 Miauzulkarnain100% (1)
- 4.5 EnzymesDocument21 pagini4.5 Enzymeszulkarnain100% (1)
- Paper 3, SPMRSM 2016Document14 paginiPaper 3, SPMRSM 2016zulkarnainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analysis of SPM Bio Qs 2016Document3 paginiAnalysis of SPM Bio Qs 2016zulkarnainÎncă nu există evaluări
- XAPlus 2016 Answer MiauDocument24 paginiXAPlus 2016 Answer MiauzulkarnainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paper 2, SPMRSM 2016Document32 paginiPaper 2, SPMRSM 2016zulkarnain100% (1)
- Trial Kedah Biologi SPM 2015 k2 SoalanDocument22 paginiTrial Kedah Biologi SPM 2015 k2 SoalanzulkarnainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trial Kedah Biologi SPM 2015 k3 SoalanDocument11 paginiTrial Kedah Biologi SPM 2015 k3 SoalanYk TayÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4.4 LipidsDocument10 pagini4.4 Lipidszulkarnain100% (1)
- 5.1 MitosisDocument18 pagini5.1 MitosiszulkarnainÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.1 Cell Structure and FunctionDocument13 pagini2.1 Cell Structure and FunctionpjolÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4.2 CarbohydratesDocument6 pagini4.2 CarbohydrateszulkarnainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trial SPM 2015 Biology Paper 1 Answer Scheme NO Answer NO AnswerDocument1 paginăTrial SPM 2015 Biology Paper 1 Answer Scheme NO Answer NO AnswerzulkarnainÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4.3 - ProteinsDocument13 pagini4.3 - ProteinszulkarnainÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4551-Skema BIO Trial SPM 2015Document22 pagini4551-Skema BIO Trial SPM 2015zulkarnain100% (1)
- Paper 3 Biology Fe Pahang 2008Document11 paginiPaper 3 Biology Fe Pahang 2008zulkarnainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biologi Ting 4 ModulDocument20 paginiBiologi Ting 4 ModulNoine AiniÎncă nu există evaluări
- 07 JPNT Bio f4 Modul5Document17 pagini07 JPNT Bio f4 Modul5jyen92Încă nu există evaluări
- Biology Module Inheritance3Document23 paginiBiology Module Inheritance3widad.osmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 07 JPNT Bio f4 Modul4Document15 pagini07 JPNT Bio f4 Modul4Komalesh TheeranÎncă nu există evaluări
- 07 JPNT Bio f4 Modul1Document19 pagini07 JPNT Bio f4 Modul1Hazimah YusofÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module QuestionsDocument11 paginiModule QuestionszulkarnainÎncă nu există evaluări
- 07 JPNT Bio f4 Modul3Document15 pagini07 JPNT Bio f4 Modul3zulkarnainÎncă nu există evaluări
- VariationDocument21 paginiVariationzulkarnainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module QuestionsDocument14 paginiModule QuestionszulkarnainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module QuestionDocument19 paginiModule Questionzulkarnain100% (1)
- Crop Science Notes 2 2015Document67 paginiCrop Science Notes 2 2015Alfred Magwede100% (1)
- Variation in OrganismsDocument12 paginiVariation in OrganismsNur TasnimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell CycleDocument1 paginăCell Cyclenica onicaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 7 Study Guide With AnswersDocument8 paginiUnit 7 Study Guide With AnswersfklÎncă nu există evaluări
- Meiosis PowerPointDocument22 paginiMeiosis PowerPointLary Bags100% (1)
- Brooker2014 COHESINAS PDFDocument38 paginiBrooker2014 COHESINAS PDFMary MontoyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Meiosis SimulationDocument6 paginiMeiosis SimulationLittle Ar-RaziÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chromosomes and MitosisDocument10 paginiChromosomes and MitosisCorry SepviaÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Mcqs PDFDocument5 paginiGeneral Mcqs PDFJunaid ahmad lucky sahaa100% (1)
- MITOSIS and MEIOSIS: A Concise Guide to Cell Division and GeneticsDocument45 paginiMITOSIS and MEIOSIS: A Concise Guide to Cell Division and GeneticsJhon dave SurbanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division - NotesDocument9 paginiCell Cycle and Cell Division - NotesSaloni GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MEIOSIS NotesDocument11 paginiMEIOSIS Notesnoxolo dwane100% (2)
- Biology Class 10 Icse Boards!Document10 paginiBiology Class 10 Icse Boards!nark.jf4Încă nu există evaluări
- Meiosis Worksheet 13 KeyDocument2 paginiMeiosis Worksheet 13 KeyFarhan Pranadarmesta Merch100% (1)
- Unit 3 BiologyDocument183 paginiUnit 3 BiologyBeverly Crawford75% (8)
- Exp No 7 Meiosis in Onion Bud CellDocument3 paginiExp No 7 Meiosis in Onion Bud CellShadab AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Meiosis WorksheetDocument6 paginiBiology Meiosis Worksheetapi-502781581Încă nu există evaluări
- Lab Exercise # 7 - MeiosisDocument3 paginiLab Exercise # 7 - MeiosisMei KurunoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exersice Mitosis 1 Biology Form 4Document22 paginiExersice Mitosis 1 Biology Form 4Delima Adan0% (1)
- 11 Biology Notes Ch10 Cell Cycle and Cell DevisionDocument7 pagini11 Biology Notes Ch10 Cell Cycle and Cell DevisionRohit ThakranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Meiosis: Ms. Beall BiologyDocument27 paginiMeiosis: Ms. Beall BiologyChupenmeElPeneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocument8 paginiMitosis and MeiosisShiela BelandresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology - ANSWERS - Peeters, Talbot and Mayrhofer - Third Edition - IBID 2008Document27 paginiBiology - ANSWERS - Peeters, Talbot and Mayrhofer - Third Edition - IBID 2008rosafuenfloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology 140 Lab 2 Cell DivisionDocument11 paginiBiology 140 Lab 2 Cell DivisionParidhi TiwariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Meiotic DriveDocument16 paginiMeiotic DriveAdam ZHUÎncă nu există evaluări