Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
CE 326 F2013 Lecture 6-7 Trip Distribution
Încărcat de
Arod Caliber0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
27 vizualizări12 paginik
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentk
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
27 vizualizări12 paginiCE 326 F2013 Lecture 6-7 Trip Distribution
Încărcat de
Arod Caliberk
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 12
CE 326:
Transportation
Planning
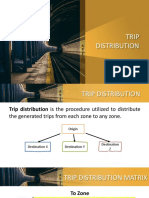
TRIP DISTRIBUTION
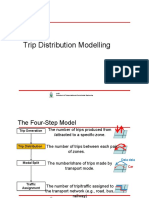
Goal of Trip Distribution
To distribute productions among attractions
To obtain inter-zonal flows
Trip Conservation
Production Conservation
=
where Tij is the trip interchange from zone i to zone j
Pi is the total number of productions from zone i
Attraction Conservation
=
Aj is the total number of attractions to zone j
Trip Distribution Models
Growth Factor Model (e.g. Fratar model)
Gravity Model
Growth Factor Model
Theory: Preserves historical relationships
Often used to estimate external trips (those either
produced and/or attracted outside of study region)
Fratar Model Steps
1) Given: Observed average interzonal trips from zone i to zone j (0 )
2) Compute zonal growth factors based on expected changes in land
use ( = )
3)Estimate expected future trips per zone
= 0
4) Apply growth factors directly to observed trips to estimate expected
trips for each zone pair
0
0
=
0
5) Estimate expected trips for individual zone pairs
+
=
2
6) Calculate new Growth Factor; stop when sufficiently close to 1
+1
Limitations of Growth Factor
Models
Advantages
Simple
No LOS information needed
Disadvantages
May break down mathematically when a new zone is
added
Convergence to the target-year generation totals is not
always possible
The model is not sensitive to impedance (No project/policy
effect)
No congestion impact
Newtons Law of Gravitation
The force of attraction between two bodies is
directly proportional to the product of the masses of
the two bodies and inversely proportional to the
square of the distance between them
Trip Distribution Formula
The interchange volume between a trip-producing zone i and
a trip-attracting zone j is directly proportional to the magnitude
of the trip productions of zone i and the trip attractions of zone j
and is inversely proportional to a function of the impedance Wij
between the zones
Dependent variable: i to j volume
Independent variables: Productions, attractions, impedance
Model Parameters: k, c; estimated through calibration
Friction Factor
Friction factor (or travel time factor)
Fij is a measure of the impedance from i to j
We need to know the relative impedance to zone j compared
to all zones
Socioeconomic Adjustment Factors
Fij is often estimated as a function of only one variable (usually
travel time)
Kij incorporates the effects not captured by the limited number
of independent variables in the model
Relative attractiveness
of zone j compared to
all other zones
Limitations of the Gravity
Model
Does not consider individual user or household characteristics in trip
decision-making process (although separate models can be
developed for stratified groups)
K-factors difficult to interpret, may not remain constant between
observed and predicted years
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Gravity ModelDocument5 paginiThe Gravity Modelcaoboi1980Încă nu există evaluări
- TransportationDocument129 paginiTransportationFaith Rezza Mahalia F. BETORIOÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 Trip Distribution Lecture 12-13.unlockedDocument23 pagini5 Trip Distribution Lecture 12-13.unlockedTanmay Sahni100% (1)
- Transporation Forecasting ProcessDocument53 paginiTransporation Forecasting ProcessVince AlanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module-4 UTP NotesDocument13 paginiModule-4 UTP NotesGladi A ThorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Estimating Demand IIDocument83 paginiEstimating Demand IIManpreet SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trip Generation: Socioeconomic Data Land Use DataDocument23 paginiTrip Generation: Socioeconomic Data Land Use DataCheGanJiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument146 paginiIlovepdf MergedJoshua A. EboraÎncă nu există evaluări
- MODULE 4 UnlockedDocument12 paginiMODULE 4 UnlockedRockstar AnilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 4Document12 paginiModule 4RohithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 5. Transportation Systems Planning: Civil Engineering Department 8 SemesterDocument19 paginiUnit 5. Transportation Systems Planning: Civil Engineering Department 8 SemesterBadal NayakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 4Document11 paginiModule 4monika hcÎncă nu există evaluări
- PTE Travel Demand ForecastingDocument29 paginiPTE Travel Demand ForecastinghithereÎncă nu există evaluări
- Travel Demand ForecastingDocument51 paginiTravel Demand ForecastingGraciele Sera-RevocalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 4Document11 paginiModule 4Abhishek BiradarÎncă nu există evaluări
- TPE-Lecture# 5Document32 paginiTPE-Lecture# 5mamoona aliÎncă nu există evaluări
- TR 631 LT 2.3 Trip Distribution ModellingDocument36 paginiTR 631 LT 2.3 Trip Distribution ModellingGilbert MaroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trip Generation and DistributionDocument33 paginiTrip Generation and DistributionNabeelSaleemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 3.transportion ModellingDocument7 paginiTopic 3.transportion ModellingCivil EngineeringÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trip Distribution: Calibrated Base YearDocument11 paginiTrip Distribution: Calibrated Base YearAngelo AdiaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trip Distribution Synthetic Models: 1. Gravity ModelDocument11 paginiTrip Distribution Synthetic Models: 1. Gravity ModelManjunatha A GoudaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trip GenerationDocument36 paginiTrip GenerationsatishsajjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Automatic Determination of PID Controlle PDFDocument20 paginiAutomatic Determination of PID Controlle PDFJosafa AstroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trip Distribution WordDocument10 paginiTrip Distribution WordDushan SenarathneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Regional Transport Plan & Trip Distribution ModelDocument53 paginiRegional Transport Plan & Trip Distribution ModelPRITI DASÎncă nu există evaluări
- Minggu 5 - Spatial Interaction Modelling PDFDocument29 paginiMinggu 5 - Spatial Interaction Modelling PDF3Agatha Aldivane PetrasatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trip Generation & Trip DistributionDocument14 paginiTrip Generation & Trip DistributionHari PÎncă nu există evaluări
- Town-Planning PPT 2Document45 paginiTown-Planning PPT 2arsabanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 3 Trip DistributionDocument10 paginiLecture 3 Trip DistributionYimkum Ozzy100% (1)
- Calibrating A Trip Distribution Gravity Model Stratified by The Trip Purposes For The City of AlexandriaDocument13 paginiCalibrating A Trip Distribution Gravity Model Stratified by The Trip Purposes For The City of AlexandriaMohamed Hassan Abd ElatyÎncă nu există evaluări
- TranspoDocument6 paginiTranspoEri EliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trip DistributionDocument15 paginiTrip DistributionAqeel Younis100% (1)
- Traffic ForecastingDocument46 paginiTraffic ForecastingLyka AnchetaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trip DistributionDocument23 paginiTrip DistributionqphungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transportation Forecasting ProcessDocument36 paginiTransportation Forecasting ProcessKristelle GinezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trip-Distribution 1Document11 paginiTrip-Distribution 1Patrick Henry Dela VegaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture3 Trip DistributionDocument10 paginiLecture3 Trip DistributionEng Bedri BederÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trip Generation: The First Step in Transportation ForecastingDocument27 paginiTrip Generation: The First Step in Transportation ForecastingJohn BarrogaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transportation Planning and Engineering: Transportation Planning Process (Data Collection Methods - Cont'd)Document17 paginiTransportation Planning and Engineering: Transportation Planning Process (Data Collection Methods - Cont'd)Fortiter FysproÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transportation Demand AnalysisDocument32 paginiTransportation Demand AnalysisAgerico FunelasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 3 - FRATAR AlgorithmDocument27 paginiLecture 3 - FRATAR Algorithmethernalx100% (1)
- Nptel CeTEI L08Document9 paginiNptel CeTEI L08Sulabh Biswas100% (1)
- Transportmodelling 461B LUDocument70 paginiTransportmodelling 461B LUMd Habibur RahmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analisis Regional. GEOGRAFI TENTANG KERUANGANDocument56 paginiAnalisis Regional. GEOGRAFI TENTANG KERUANGANNovi ArisÎncă nu există evaluări
- UEMX 3813 Highway and TransportationDocument39 paginiUEMX 3813 Highway and TransportationMOBA UNIÎncă nu există evaluări
- TR 631 LT 2.2 Trip Generation ModellingDocument12 paginiTR 631 LT 2.2 Trip Generation ModellingGilbert MaroÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8 TransportationDocument9 pagini8 Transportationmpe1Încă nu există evaluări
- Travel Demand ForecastingDocument25 paginiTravel Demand ForecastingFrederick BarutÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter - 7 Trip Distribution: I J IjDocument4 paginiChapter - 7 Trip Distribution: I J IjSwopnil KalikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2ND Exam Written ReportDocument29 pagini2ND Exam Written ReportLance Moral GumtangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ijcet: International Journal of Computer Engineering & Technology (Ijcet)Document10 paginiIjcet: International Journal of Computer Engineering & Technology (Ijcet)IAEME PublicationÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trip Distribution: Is IsDocument2 paginiTrip Distribution: Is IsBalogun IbrahimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Several Methods of Trip Distribution Analysis: Fratar Method Intervening Opportunity Model Gravity ModelDocument7 paginiSeveral Methods of Trip Distribution Analysis: Fratar Method Intervening Opportunity Model Gravity ModelJoeylene Fabros MallorcaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modal Split TextDocument5 paginiModal Split Textbestebozkurt1Încă nu există evaluări
- Cee350 TP 6Document10 paginiCee350 TP 6Rafsanul HaqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Study On Road Accidents Forecasting Model Based On Multi-Level Recursive MethodDocument7 paginiThe Study On Road Accidents Forecasting Model Based On Multi-Level Recursive MethodAbhishek JainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Space Economy: The New Frontier for DevelopmentDe la EverandSpace Economy: The New Frontier for DevelopmentÎncă nu există evaluări
- Almaty–Issyk-Kul Altnernative Road Economic Impact AssessmentDe la EverandAlmaty–Issyk-Kul Altnernative Road Economic Impact AssessmentÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neues verkehrswissenschaftliches Journal - Ausgabe 16: Capacity Research in Urban Rail-Bound Transportation with Special Consideration of Mixed TrafficDe la EverandNeues verkehrswissenschaftliches Journal - Ausgabe 16: Capacity Research in Urban Rail-Bound Transportation with Special Consideration of Mixed TrafficÎncă nu există evaluări
- Landscape dimensions: Reflections and proposals for the implementation of the European Landscape ConventionDe la EverandLandscape dimensions: Reflections and proposals for the implementation of the European Landscape ConventionÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Play GuitarDocument51 paginiHow To Play GuitarAlin Costescu80% (5)
- E46 m3 Torque Specs LRDocument98 paginiE46 m3 Torque Specs LRArod Caliber100% (4)
- Presentations TipsDocument21 paginiPresentations Tipsapi-253601657Încă nu există evaluări
- Presentations TipsDocument21 paginiPresentations Tipsapi-253601657Încă nu există evaluări
- CE-45000 - Civil Engineering Management Problem Set #3 - Professor's SolutionDocument1 paginăCE-45000 - Civil Engineering Management Problem Set #3 - Professor's SolutionArod CaliberÎncă nu există evaluări
- SaveDocument1 paginăSaveArod CaliberÎncă nu există evaluări
- CE 326 F2013 Lecture 2 Public Sector PlanningDocument26 paginiCE 326 F2013 Lecture 2 Public Sector PlanningArod CaliberÎncă nu există evaluări
- HW#9Document3 paginiHW#9Arod CaliberÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Bid Sheet and Final Schedule PDFDocument2 paginiFinal Bid Sheet and Final Schedule PDFArod Caliber0% (1)
- CE 326 Fall 2013 Alternative Evaluation Practice ProblemsDocument4 paginiCE 326 Fall 2013 Alternative Evaluation Practice ProblemsArod CaliberÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2012 Sample Test 1Document6 pagini2012 Sample Test 1Arod CaliberÎncă nu există evaluări
- HW 1Document1 paginăHW 1Arod CaliberÎncă nu există evaluări
- CE 326 F2013 Lecture 4-5 Trip GenerationDocument35 paginiCE 326 F2013 Lecture 4-5 Trip GenerationArod CaliberÎncă nu există evaluări
- CE 326 F2013 Lecture 2 Public Sector PlanningDocument26 paginiCE 326 F2013 Lecture 2 Public Sector PlanningArod CaliberÎncă nu există evaluări
- Do The Following Problems From Textbook: 1. 8.2 2. 8.4 3. 8.8 4. 8.9 5. 8.13 Case 3 6. 8.14 Case 1 7. 8.22 8. 8.24Document1 paginăDo The Following Problems From Textbook: 1. 8.2 2. 8.4 3. 8.8 4. 8.9 5. 8.13 Case 3 6. 8.14 Case 1 7. 8.22 8. 8.24Arod CaliberÎncă nu există evaluări
- Release Conditions ExerciseDocument1 paginăRelease Conditions ExerciseArod CaliberÎncă nu există evaluări
- ENGR 204 Test 2Document7 paginiENGR 204 Test 2Arod CaliberÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2011 Fall Test 2Document5 pagini2011 Fall Test 2inrhgoiwnowbÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reinforced Concrete Design PDFDocument1 paginăReinforced Concrete Design PDFhallelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ferrero A.M. Et Al. (2015) - Experimental Tests For The Application of An Analytical Model For Flexible Debris Flow Barrier Design PDFDocument10 paginiFerrero A.M. Et Al. (2015) - Experimental Tests For The Application of An Analytical Model For Flexible Debris Flow Barrier Design PDFEnrico MassaÎncă nu există evaluări
- World of Self, Family and Friends UNIT 4 - Lunchtime Speaking 37 Wednesday Friendship LanguageDocument11 paginiWorld of Self, Family and Friends UNIT 4 - Lunchtime Speaking 37 Wednesday Friendship LanguageAin NawwarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ass AsDocument23 paginiAss AsMukesh BishtÎncă nu există evaluări
- LT3845ADocument26 paginiLT3845Asoft4gsmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5 IppDocument24 paginiChapter 5 IppRoseann EnriquezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ims DB DCDocument90 paginiIms DB DCpvnkraju100% (1)
- Calendar of Activities A.Y. 2015-2016: 12 Independence Day (Regular Holiday)Document3 paginiCalendar of Activities A.Y. 2015-2016: 12 Independence Day (Regular Holiday)Beny TawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nails Care: Word Search: Name: - DateDocument1 paginăNails Care: Word Search: Name: - DateDeverly Hernandez Balba-AmplayoÎncă nu există evaluări
- S3 U4 MiniTestDocument3 paginiS3 U4 MiniTestĐinh Thị Thu HàÎncă nu există evaluări
- X Lube Bushes PDFDocument8 paginiX Lube Bushes PDFDavid TurnerÎncă nu există evaluări
- PID Marcado Operación Del Paquete Del Compresor de Hidrogeno PHP-K-002 PDFDocument7 paginiPID Marcado Operación Del Paquete Del Compresor de Hidrogeno PHP-K-002 PDFDenisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cella Di Carico Sartorius MP77 eDocument3 paginiCella Di Carico Sartorius MP77 eNCÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 3: Theories and Principles in The Use and Design of Technology Driven Learning LessonsDocument5 paginiUnit 3: Theories and Principles in The Use and Design of Technology Driven Learning Lessons서재배Încă nu există evaluări
- What Is The Difference Between Newtonian and Non-Newtonian Fluid and Give Example For Each Case?Document11 paginiWhat Is The Difference Between Newtonian and Non-Newtonian Fluid and Give Example For Each Case?MOHAMED ABD ELGHANYÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ec 0301Document25 paginiEc 0301Silvio RomanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 3 Alds 2202Document13 paginiWeek 3 Alds 2202lauren michaelsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shelly Cashman Series Microsoft Office 365 Excel 2016 Comprehensive 1st Edition Freund Solutions ManualDocument5 paginiShelly Cashman Series Microsoft Office 365 Excel 2016 Comprehensive 1st Edition Freund Solutions Manualjuanlucerofdqegwntai100% (10)
- 1.classification of Reciprocating PumpsDocument8 pagini1.classification of Reciprocating Pumpsgonri lynnÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progression (Ex 5.1) Exercise 5.1Document8 paginiNCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progression (Ex 5.1) Exercise 5.1Akash DasÎncă nu există evaluări
- VERGARA - RPH Reflection PaperDocument2 paginiVERGARA - RPH Reflection PaperNezer Byl P. VergaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- A-1660 11TH Trimester From Mcdowell To Vodafone Interpretation of Tax Law in Cases. OriginalDocument18 paginiA-1660 11TH Trimester From Mcdowell To Vodafone Interpretation of Tax Law in Cases. OriginalPrasun TiwariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bearing 1Document27 paginiBearing 1desalegn hailemichaelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kursus Jabatan Kejuruteraan Mekanikal Sesi Jun 2014Document12 paginiKursus Jabatan Kejuruteraan Mekanikal Sesi Jun 2014ihsanyusoffÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Schottel) Aspects of The Design Procedure For Propellers Providing Max Bollard PullDocument10 pagini(Schottel) Aspects of The Design Procedure For Propellers Providing Max Bollard Pulldevu2chodankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iso Iec 25030 2007 eDocument44 paginiIso Iec 25030 2007 eAngélica100% (1)
- LAB REPORT - MGCLDocument5 paginiLAB REPORT - MGCLKali stringsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coating Resins Technical Data SYNOCURE 867S - 60Document1 paginăCoating Resins Technical Data SYNOCURE 867S - 60Heramb TrifaleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Furniture AnnexDocument6 paginiFurniture AnnexAlaa HusseinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Essay On Stem CellsDocument4 paginiEssay On Stem CellsAdrien G. S. WaldÎncă nu există evaluări