Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Degumming
Încărcat de
vanessa100%(1)100% au considerat acest document util (1 vot)
38 vizualizări1 paginăsummary of degumming
Titlu original
degumming
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentsummary of degumming
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
100%(1)100% au considerat acest document util (1 vot)
38 vizualizări1 paginăDegumming
Încărcat de
vanessasummary of degumming
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 1
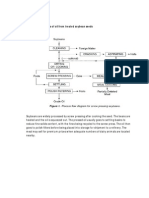
Degumming is a process, which removes phospholipids because they are not
desirable for biodiesel production. The presence of phospholipids in oil may
cause oil to settle out during shipping and storage.
TECHNOLO
GY
WATER
DEGUMMIN
G
ACID
DEGUMMIN
G
ENZYMES
DEGUMMIN
G
TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION
ADVANTAGES
DISADVANTAGES
Hot water or steam is injected
into hot oil and mixed for 3060minutes. Phospholipids
absorb water, lose lipophilic
character and agglomerate
into a gum phase. Gum is
separated by centrifugation.
Addition of acid into oil at
40-55 . Acids convert
non-hydratable phosphatides
to hydratable phosphatides.
Subsequent steps similar to
water degumming.
Simple and
established process
Requires centrifugation,
cost high
Requires hot water or steam
Removes nonhydratable
phospholipids
Simple and
established process
Addition of certain acids
will form soap, which may
not be suitable for
downstream processing
Phospholipase are used to
hydrolyze ester bonds of
phospholipids. Hydrophilic
and insoluble phospholipids
are released from glyceride
backbone of phospholipids
and are separated by
centrifugation.
Minimizes oil
Enzymes cost are high
entrained in the gum, Enzymes for degumming
resulting in
are currently unstable
improved oil yields
Utilises less water
than water and acid
degumming
processes
http://old.iupac.org/symposia/proceedings/Tunis04/logan_andrew.pdf
The chosen technology is acid degumming because the lipids from Chlamydomonas
reinhardtii consist of non-hydratable phospholipids.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- A Search For Alternative Solvent To Hexane During Neem Oil ExtractionDocument5 paginiA Search For Alternative Solvent To Hexane During Neem Oil ExtractiontramiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oil and Fat Technology Lectures IIIDocument42 paginiOil and Fat Technology Lectures IIIaulger100% (1)
- Hungrystock CPO OutlookDocument28 paginiHungrystock CPO OutlooknindyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Crude Palm OilDocument19 paginiCrude Palm OilmarpadanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering Proposal and Quotation: 50T/D Continuous Refining Workshop EquipmentDocument26 paginiEngineering Proposal and Quotation: 50T/D Continuous Refining Workshop EquipmentMuhammad aliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Enrollment No.:-1814320004: Electrical EngineeringDocument29 paginiEnrollment No.:-1814320004: Electrical EngineeringGavit AniketÎncă nu există evaluări
- Downstream Products from VCODocument78 paginiDownstream Products from VCOjosephine mataÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecithin - A Useful Byproduct of Edible Oil ExtractionDocument11 paginiLecithin - A Useful Byproduct of Edible Oil Extractionadda100% (1)
- Wenzhou Bangcheng Grain and Oil Machinery Co.,Ltd: 20T/D Soybean & Sunflower Oil Full Continuous Refinery Plant QuotationDocument3 paginiWenzhou Bangcheng Grain and Oil Machinery Co.,Ltd: 20T/D Soybean & Sunflower Oil Full Continuous Refinery Plant QuotationMuhammad aliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Properties and Uses of Palm StearinDocument4 paginiProperties and Uses of Palm StearinShu ShuadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study Palm Oil Refinery NewDocument2 paginiCase Study Palm Oil Refinery NewFong Leong Chee 馮亮智100% (2)
- Processing of Vegitable OilDocument11 paginiProcessing of Vegitable OilAJAGUN JOHNSON100% (1)
- A General Review of Palm Oil Mill EffluentDocument3 paginiA General Review of Palm Oil Mill EffluentMykel-Deitrick Boafo DuoduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vegetable Oil Extraction - Vegetable Refinery - Solvent Extraction Plant - MectechDocument9 paginiVegetable Oil Extraction - Vegetable Refinery - Solvent Extraction Plant - Mectechmectech50% (2)
- Refining and Degumming Systems for Edible OilsDocument7 paginiRefining and Degumming Systems for Edible Oilsjaymie_llanera100% (1)
- Palm Kernel & Coconut Oils - Analytical Characteristics - JAOCS - 1983Document6 paginiPalm Kernel & Coconut Oils - Analytical Characteristics - JAOCS - 1983EtsABD100% (1)
- Fractionation of Palm Oil: Processes and ProductsDocument10 paginiFractionation of Palm Oil: Processes and ProductsShriram PrasadÎncă nu există evaluări
- VCO Brochure EngDocument4 paginiVCO Brochure EngYuneza MutyaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 - Part 1 RefiningDocument46 paginiChapter 3 - Part 1 RefiningAzhan FikriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Properties of Palm Oil MargarineDocument7 paginiProperties of Palm Oil Margarinemcalidonio5656Încă nu există evaluări
- Oil Extraction Processes: Screw Pressing, Solvent Extraction & Extruding-ExpellingDocument6 paginiOil Extraction Processes: Screw Pressing, Solvent Extraction & Extruding-ExpellingNahid Akhter KathaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oleochemical - WikipediaDocument3 paginiOleochemical - WikipediaNur Atiqah Ahmad100% (1)
- Sesame ProteinDocument10 paginiSesame ProteinJulius BudiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Preparation of Laundry Soap From Used Cooking Oils: Getting Value Out of WasteDocument10 paginiPreparation of Laundry Soap From Used Cooking Oils: Getting Value Out of WasteGshsghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Groundnutdpr 04.08.23Document17 paginiGroundnutdpr 04.08.23TNRTP SALEMÎncă nu există evaluări
- Twinkle Palm Oil Ventures Set to Redefine Standard Palm Oil ProcessingDocument35 paginiTwinkle Palm Oil Ventures Set to Redefine Standard Palm Oil ProcessingMumtahinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DegummingDocument3 paginiDegummingKhairi Maulida Azhari100% (1)
- Palm Oil and Palm Kernel OilDocument26 paginiPalm Oil and Palm Kernel OilRachel Yessica WinartiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mango Butter Yield Ed Casas Et AlDocument35 paginiMango Butter Yield Ed Casas Et AlAri HalosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Principles and Methods of Manufacture of Ghee and Butter OilDocument16 paginiPrinciples and Methods of Manufacture of Ghee and Butter OilNishkarsh AgarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activation of Spent Bleaching Earth For Dehumidification ApplicationDocument8 paginiActivation of Spent Bleaching Earth For Dehumidification ApplicationWorld-Academic JournalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coconut Oil - WikipediaDocument11 paginiCoconut Oil - WikipediaYusuf Aliyu UÎncă nu există evaluări
- Corn BleachingDocument3 paginiCorn BleachingMaria Elaine AlbiusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Palm Oil Mills Targets Zero EmissionDocument5 paginiPalm Oil Mills Targets Zero EmissionscreenscreamerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Edible Oil SourcesDocument22 paginiEdible Oil Sourcesshym hjrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oil Refining ProcessDocument5 paginiOil Refining Processhaisamdo100% (2)
- Chemical Enzymatic InteresterificationDocument37 paginiChemical Enzymatic Interesterificationjlcheefei9258Încă nu există evaluări
- Palm Oil Manufacturing and Application Che 323Document14 paginiPalm Oil Manufacturing and Application Che 323Amirul HaikalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Report LiDocument68 paginiReport Lipitt8780% (5)
- World Bank Group - Palm Oil - Econsultation On Draft Framwork For Engagement - EtranscriptDocument131 paginiWorld Bank Group - Palm Oil - Econsultation On Draft Framwork For Engagement - EtranscriptRichard Anthony AitkenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Recovery of Glycerine From Spent Palm Kernel Soap and Palm Oil Soap LyeDocument8 paginiRecovery of Glycerine From Spent Palm Kernel Soap and Palm Oil Soap LyeNadya Larasati KrdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Declaration: Liquid Detergent Production From Castor SeedDocument117 paginiDeclaration: Liquid Detergent Production From Castor SeedZemariyam BizuayehuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Natural Blush Cosmetics: Setting A Science-Based Carbon Reduction TargetDocument6 paginiNatural Blush Cosmetics: Setting A Science-Based Carbon Reduction TargetdanielÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oleochemical Industry Future Through Biotechnology: ReviewDocument10 paginiOleochemical Industry Future Through Biotechnology: ReviewAmanda SartikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Waxes Are A Diverse Class of Organic Compounds That Are Hydrophobic, MalleableDocument5 paginiWaxes Are A Diverse Class of Organic Compounds That Are Hydrophobic, MalleableAmmar SiddiquiÎncă nu există evaluări
- DegummingDocument41 paginiDegummingTan Han Kiat100% (2)
- 3.4 DeodorizationDocument33 pagini3.4 DeodorizationLaila FaeizahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oil, Fat, Soap and Lubricants-Merged PDFDocument133 paginiOil, Fat, Soap and Lubricants-Merged PDFEshanth RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oil Extraction MachineDocument3 paginiOil Extraction MachineiqbalindiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oils, Fats and WaxesDocument23 paginiOils, Fats and WaxesIvy JoyceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Castor Oil & Its Derivatives Oleoresin, Turkey Red Oil, Dco, Hco, Sebacic Acid, 12-Hydroxy Stearic AcidDocument5 paginiCastor Oil & Its Derivatives Oleoresin, Turkey Red Oil, Dco, Hco, Sebacic Acid, 12-Hydroxy Stearic Acidkunal agiwaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Palm Acid Oil MSDSDocument3 paginiPalm Acid Oil MSDSFermanton SiagianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Company ProfileDocument4 paginiCompany Profileravi150888Încă nu există evaluări
- PIPOC 2011 Congress on Palm Oil Fortification and EnergizationDocument42 paginiPIPOC 2011 Congress on Palm Oil Fortification and EnergizationBung HarunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Palm Fatty Acid Distillate BiodieselDocument4 paginiPalm Fatty Acid Distillate Biodieseldwi anggraeniÎncă nu există evaluări