Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
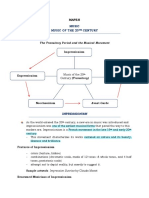
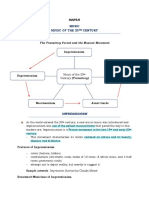
Main Composers: Stravinsky, Shosti, Cage, Ives, Schoenberg, Bartok
Încărcat de
Anonymous kDMD6iAp4F0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
17 vizualizări2 paginiComposers
Titlu original
Main Composers
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentComposers
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
17 vizualizări2 paginiMain Composers: Stravinsky, Shosti, Cage, Ives, Schoenberg, Bartok
Încărcat de
Anonymous kDMD6iAp4FComposers
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 2
Main Composers: Stravinsky, Shosti, Cage, Ives, Schoenberg, Bartok
Igor Stravinsky (1882 1971)
- Background information
o 1882 born near St. Petersburg Russia into music family he liked wagner
o studied composition/orchestration with Rimsky Korsakov
o 1909 Sergi Diaghilev commissioned Stravinsky to compose for is company
(firebird, petrushka, rite of spring)
o 1913 Paris premiere of Rite of Spring great riot
o 1914 exiled to Switzerland dealt with homesickness by using Russian
folklore for works
o 1930 symphony of psalms
o 1939 LA, USA
- Russian Period
o Rite of Spring
Adolescent girl chosen for sacrifice, dance till death
Primitivism deliberate representation of elemental, crude, uncultured,
and cast aside sophistication/styleish of modern life trained art
First scene: Danse de adolescents accented chords create
unpredictable pattern of stresses and destroy metric, yet it is still
strategically written in danceable format (8 measures).
Final dance Danse sacrale reduced meter by changing meters and
alternation of notes with rests
Dissonances based on scales from Russian classical music
(diatonic/octatonic collections
- Neoclassical Period
o 1919, Diaghilev asked Stravinsky to orchestrate pieces by 18th century
Pergolesi, this sparked neoclassicism
o he does not revive old styles but alluding to them in order to create
something new (unique combo of old and new)
o broad movement from 1910s 50s composers revived, imitated, revoked
styles of pre-romantic, he turned away from Russian folk-music and returned
to an earlier time for a source of inspiration
o Symphony of Psalms
For mixed chorus and orchestra, omits violins, violas, and clarinets
Includes perpetual motion, sequences, frequent ostinatos,
Neotonality composer finding new way of establishing single pitch as
tonal center
- Influence
o Popularized neoclassicism
o Elements had been nurtured in Russian music
o Introduced new traits (ie; change of meter, Steve Reich)
Bela Bartok (1881-1946)
- Background
o 1881 born in hungary to musical family, studied piano/composition
o 1904 heard woman singing folk song and decided to collect folk
music/dance.
o 1926 39 mikrokosmos 153 progressive piano pieces
o 1934 ethnomusicologist at academy of Sciences, prepped critical editions
of Hungarian folk music
included his top works Music for strings, percussion, celeste, high
point of career
- Stylistic Convention
o Synthesised Hungarian, Romanian, Slovak and Bulgarian peasant music with
elements of German and French classical tradition (rhythm, melodic)
o Felt Hungarian music was fresh start, free of romantic sentimentality
o Piano works (allegro barbaro) and other piano works introduced it as more of
a percussive einstrument
o Pieces after WWI pushed tonal ambiguities with Violin Sonatas
o From Hungarian music, he drew rhythmic complexity and irregular meters,
modal scales and mixed modes, resulting in complex counterpoints
- Example of Synthesis
o Many peacies in mikrokosmos demonstrate this, eg Staccato and Legatto
like Bach 2 part invention, use of inversion, cannon between hands, and
tonal structure resembles Bach, shape of melody is reminiscent of Hungarian
melodies built from a short phrase that rises and falls between the span of a
4th, repeats transposed up a 5th and returns to tonic
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Music History NotesDocument6 paginiMusic History NotesPhylicia MorrisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Q1 W1 Music Learning MaterialsDocument8 paginiQ1 W1 Music Learning MaterialsCes Michaela CadividaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Daanoy, Abpo, BerjaDocument55 paginiDaanoy, Abpo, Berjachrontius'sÎncă nu există evaluări
- Music Music of The 20 Century: MapehDocument16 paginiMusic Music of The 20 Century: MapehApril Sophie DavidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Music Music of The 20 Century: MapehDocument26 paginiMusic Music of The 20 Century: MapehApril Sophie DavidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Music 10-Q1-Summary-LessonDocument4 paginiMusic 10-Q1-Summary-LessonNorham AzurinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Music of The 20TH Century 1ST Quarter LessonDocument44 paginiMusic of The 20TH Century 1ST Quarter LessonMaurice OlivaresÎncă nu există evaluări
- MusicStyles Sinopsis XXDocument14 paginiMusicStyles Sinopsis XXLuis Monge FernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Music 1Document24 paginiMusic 1Francisco GellyÎncă nu există evaluări
- LAS MAPEH 10 Q1 W1 MusicDocument6 paginiLAS MAPEH 10 Q1 W1 MusicJemalyn Hibaya LasacaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maximilian SteinbergDocument5 paginiMaximilian SteinbergDmitry KalinichenkoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Music of The 20TH CenturyDocument30 paginiMusic of The 20TH CenturyAhaki SwzenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summary in Mapeh 10Document4 paginiSummary in Mapeh 10Rasel Santillan100% (2)
- Presentation1 Q1 Music Lesson1 G10 ImpressionismDocument84 paginiPresentation1 Q1 Music Lesson1 G10 Impressionismcheeneerain banaganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Soviet ComposersDocument3 paginiSoviet ComposersQuynh NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rachmaninoff's Complete Songs: A Companion with Texts and TranslationsDe la EverandRachmaninoff's Complete Songs: A Companion with Texts and TranslationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Musicofthe20thcentury 180729202354Document54 paginiMusicofthe20thcentury 180729202354rommelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Music 10-QUARTER 1Document33 paginiMusic 10-QUARTER 1Homer ParungaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Music 10 Q1 W1 Day 1 ClassDocument31 paginiMusic 10 Q1 W1 Day 1 ClassAverill BollosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Romantic Lecture 19Document4 paginiRomantic Lecture 19Clare CooneyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reviewer in Mapeh 3RD GradingDocument8 paginiReviewer in Mapeh 3RD GradingCarlos, Jolina R.Încă nu există evaluări
- Music of The 21st CenturyDocument88 paginiMusic of The 21st CenturyRechelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Music of The 20th CenturyDocument24 paginiMusic of The 20th CenturyHanna Fernando100% (3)
- Primitivism and Neo ClassicismDocument11 paginiPrimitivism and Neo ClassicismKeshia Faith RizonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Music Las 1 - Q1Document7 paginiMusic Las 1 - Q1Justine Dave rubaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Music 10 - Quarter 1Document41 paginiMusic 10 - Quarter 1Icy PÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hadap I. LT Mapeh 9Document104 paginiHadap I. LT Mapeh 9Jep Jep PanghulanÎncă nu există evaluări
- MUSIC10 Q1 KylaDocument6 paginiMUSIC10 Q1 Kylacorpuzkyla2115Încă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 2 - Composers 20th CenturyDocument14 paginiLesson 2 - Composers 20th CenturyKimberly De torresÎncă nu există evaluări
- g10 Music q1Document93 paginig10 Music q1Yhunize reign CadenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2oth Century MusicDocument39 pagini2oth Century MusicPrincess Rhona PaulinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- First Quarter Music10Document63 paginiFirst Quarter Music10Ysabelle TagarumaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Music 10 Reviewer. Quarter 1Document5 paginiMusic 10 Reviewer. Quarter 1mitchbalonzo7Încă nu există evaluări
- HabaDocument3 paginiHabanotmelbrooksÎncă nu există evaluări
- Student Recital Program TemplateDocument3 paginiStudent Recital Program TemplateAlyssaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ExpressionismDocument15 paginiExpressionismEmily T. NonatoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3rd Grading Module in Music 9Document4 pagini3rd Grading Module in Music 9Dominique Lim Yañez35% (17)
- Mapeh 9: Prepared By: Ezekiel Ranel G. HadapDocument60 paginiMapeh 9: Prepared By: Ezekiel Ranel G. HadapJep Jep PanghulanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Charles Ives and His WorldDe la EverandCharles Ives and His WorldJ. BurkholderEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (2)
- LECTURE NOTES IN MUSIC 1st and 2nd ExaminationDocument12 paginiLECTURE NOTES IN MUSIC 1st and 2nd ExaminationMarissa Altarejos BrionesÎncă nu există evaluări
- MAPEH ReviewerDocument12 paginiMAPEH ReviewerCassandra Jeurice UyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gallagher Alyssa Janacek PaperDocument6 paginiGallagher Alyssa Janacek PaperAlyssaGallagherÎncă nu există evaluări
- 20th Century MusicDocument37 pagini20th Century MusicGEMINO JIM MONTERONAÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1ST Music of The 20TH 1STWKDocument48 pagini1ST Music of The 20TH 1STWKNICOLE QUEJARROÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mapeh Grade 10 Module 1Document12 paginiMapeh Grade 10 Module 1Jorely Barbero Munda100% (7)
- Music of 20th CeenturyDocument20 paginiMusic of 20th CeenturyJerick SubadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Music Composers in Romantic PeriodDocument33 paginiMusic Composers in Romantic PeriodClarissa Joyce BagosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uneventful Music in Eventful TimesDocument4 paginiUneventful Music in Eventful TimesRaymond DeaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Saint-Saens and His Danse MacabreDocument2 paginiSaint-Saens and His Danse MacabreSeunghyun RyuÎncă nu există evaluări
- LAS MAPEH 9 Q2 W1 MusicDocument7 paginiLAS MAPEH 9 Q2 W1 MusicJemalyn Hibaya Lasaca67% (3)
- 20th CENTURY MUSIC Grade 10Document48 pagini20th CENTURY MUSIC Grade 10Eduard PanganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 10 Music First Quarter PPT1 SC 2023Document56 paginiGrade 10 Music First Quarter PPT1 SC 2023Kian CamaturaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stravinsky The Rite of Spring (Elective Music Students) PDFDocument21 paginiStravinsky The Rite of Spring (Elective Music Students) PDFandyvitale16Încă nu există evaluări
- Music of 20th CeenturyDocument20 paginiMusic of 20th CeenturyJerick SubadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Las 10 4TH Q Week 1Document4 paginiLas 10 4TH Q Week 1richard ferolinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Small Ternary Form: Tightly-Knit Than BDocument2 paginiSmall Ternary Form: Tightly-Knit Than BAnonymous kDMD6iAp4FÎncă nu există evaluări
- Writing Better LyricsDocument20 paginiWriting Better LyricsAnonymous kDMD6iAp4FÎncă nu există evaluări
- Untitled DocumentDocument3 paginiUntitled DocumentAnonymous kDMD6iAp4FÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Assessment Sheets-Editable) Gr.1 - Needs and Characteristics of Living ThingsDocument5 pagini(Assessment Sheets-Editable) Gr.1 - Needs and Characteristics of Living ThingsAnonymous kDMD6iAp4FÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan Gym VolleyballDocument9 paginiLesson Plan Gym VolleyballAnonymous kDMD6iAp4FÎncă nu există evaluări
- (End of Unit Task) Gr.1 - Daily & Seasonal ChangesDocument3 pagini(End of Unit Task) Gr.1 - Daily & Seasonal ChangesAnonymous kDMD6iAp4FÎncă nu există evaluări
- Snacks - Maple Cinnamon Trail Mix - Chili Lime Crispy Chickpeas - Sweet & Salty Roasted Almonds - Peanut Butter Balls - SaladsDocument6 paginiSnacks - Maple Cinnamon Trail Mix - Chili Lime Crispy Chickpeas - Sweet & Salty Roasted Almonds - Peanut Butter Balls - SaladsAnonymous kDMD6iAp4FÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lang AnalysisDocument77 paginiLang AnalysisAnonymous kDMD6iAp4FÎncă nu există evaluări
- Names: - Music vs. NoiseDocument1 paginăNames: - Music vs. NoiseAnonymous kDMD6iAp4FÎncă nu există evaluări
- SelfDocument1 paginăSelfAnonymous kDMD6iAp4FÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kalangfarbenmelodien o Orchestration Very Interesting. Notates Things One Note o Orchestration and Compositional Techniques Are WonderfullDocument1 paginăKalangfarbenmelodien o Orchestration Very Interesting. Notates Things One Note o Orchestration and Compositional Techniques Are WonderfullAnonymous kDMD6iAp4FÎncă nu există evaluări
- R: Die Walkure - R: For 16 - Ride of The Valkyries and Finale (Wotan's Lament (From Act 3)Document1 paginăR: Die Walkure - R: For 16 - Ride of The Valkyries and Finale (Wotan's Lament (From Act 3)Anonymous kDMD6iAp4FÎncă nu există evaluări
- Berlioz Handout 2Document3 paginiBerlioz Handout 2Abby Schwab Zarimba100% (1)
- Registration Manual 2012 SUFADocument239 paginiRegistration Manual 2012 SUFAJared WilliamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Poulenc - Gloria Motets PDFDocument25 paginiPoulenc - Gloria Motets PDFjose_mote8147100% (2)
- Mapeh 9 Music 2nd Grading 1Document3 paginiMapeh 9 Music 2nd Grading 1Aian Cortez71% (7)
- BBC Radio 3 - Schedules, 07 Sunday April 2019Document2 paginiBBC Radio 3 - Schedules, 07 Sunday April 2019Luis HernándezÎncă nu există evaluări
- S.L. Weiss - Moscow Partita 94Document11 paginiS.L. Weiss - Moscow Partita 94Metatron S100% (3)
- List 4Document1 paginăList 4Mr GorillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Teaching Intermediate-Level Technical and Musical Skills ThroughDocument109 paginiTeaching Intermediate-Level Technical and Musical Skills ThroughNayaneNogueiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basics in Arranging PDFDocument84 paginiBasics in Arranging PDFAnthony TreÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Great Locomotive Chase-PartsDocument57 paginiThe Great Locomotive Chase-PartsAnonymousEnnoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amazing Grace - String QuartetDocument2 paginiAmazing Grace - String QuartetBernardo Lourenço100% (2)
- Teaching The Music of Our TimeDocument8 paginiTeaching The Music of Our TimePamela HernándezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ornamentation and Improvisation in Mozart. by Frederick NeumannDocument6 paginiOrnamentation and Improvisation in Mozart. by Frederick Neumannchristina7angell0% (1)
- Telemann C-Moll - FagotDocument8 paginiTelemann C-Moll - FagotJan TineÎncă nu există evaluări
- NSM Baritone Solo1Document21 paginiNSM Baritone Solo1AntonioBrasiliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Handel KeyboardDocument4 paginiHandel KeyboardAurora SeasonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Got To Get You Into My Life 2 8 2 2 2 2 4: Q 140 (Sing 8vb)Document22 paginiGot To Get You Into My Life 2 8 2 2 2 2 4: Q 140 (Sing 8vb)Joseph Christian Panganiban100% (2)
- Kurt Weill - Der LindberghflugDocument2 paginiKurt Weill - Der LindberghflugKelsey K. RogersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Black Codes - Kenny Kirkland's SoloDocument16 paginiBlack Codes - Kenny Kirkland's SoloNishimura Kohei100% (5)
- 12 Suites From The London and Dresden ManuscriptsDocument1 pagină12 Suites From The London and Dresden ManuscriptsMaria Tellini FÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Development of Alban Bergs Compositional StyleDocument397 paginiThe Development of Alban Bergs Compositional StylessiiuullLL100% (1)
- RondofromAbdelazar Orchestra 329Document27 paginiRondofromAbdelazar Orchestra 329Kevin David Otero SeñasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Donizetti Flute Sonata in C Minor PDFDocument17 paginiDonizetti Flute Sonata in C Minor PDFerato79Încă nu există evaluări
- Choral and Orchestral ConductiDocument77 paginiChoral and Orchestral ConductiCleiton Xavier100% (3)
- PillsDocument65 paginiPillsAntonio MerilliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kwazulu-Natal Philharmonic Orchestra Vacancy: Co-Principal TrumpetDocument1 paginăKwazulu-Natal Philharmonic Orchestra Vacancy: Co-Principal TrumpetStefanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mariss JansonsDocument25 paginiMariss JansonsAlyssa GalangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contoh Paragraf Sebab Akibat 1 Akibat 2Document3 paginiContoh Paragraf Sebab Akibat 1 Akibat 2SapandriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Apontamentos ABRSM Cello 3Document18 paginiApontamentos ABRSM Cello 3Joel ReisÎncă nu există evaluări