Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Treatment of Fistula in Ano
Încărcat de
09172216507Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Treatment of Fistula in Ano
Încărcat de
09172216507Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
www.downstatesurgery.
org
Treatment of Fistula in Ano
Johanna Basa M.D.
SUNY Downstate Medical Center
August 2, 2012
www.downstatesurgery.org
Case Presentation
HPI:54 yr old male with PMH of HTN,
presented to clinic with complaints of
3rd perianal abscess s/p incision and
drainage
ROS: Pain just left of the anal verge,
denied fevers, drainage or incontinence
www.downstatesurgery.org
Case Presentation
PMH: HTN
PSH: none
Social: non contributory
PE: 97.8, 76, 150/100
Rectal exam revealed a small external
opening on the left side with no
evidence of ertheyma or drainage
www.downstatesurgery.org
Case Presentation
Procedure performed: exam under
anesthesia and placement of non
cutting seton
Operative findings: posterior midline
fistula with anterior and posterior
fissures
www.downstatesurgery.org
www.downstatesurgery.org
Cryptoglandular Theory
Most anal glands are in the posterior
midline
8-12 anal glands that enter the canal at
the dentate line
Plugging of duct-->entry of bacteria->amplification and expansion of
perirectal spaces-->liquefaction and
abscess formation
www.downstatesurgery.org
Recurrence and development
of Fistula in Ano
Hamaliainen and Saino followed patients over
a 99 month period, 37% developed a fistula
and 10% developed a recurrent abscess
Vasilevsky and Gordon reported 37% of
patients developed persistent fistula and 11%
developed recurrent abscess
Schouton and van Varoonhaven in a RCT
reported similar results with 40.6% of patients
developing a fistula after drainage of abscess
www.downstatesurgery.org
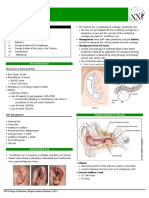
Goodsalls Rule
www.downstatesurgery.org
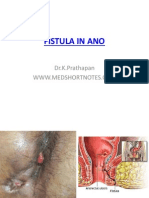
Fistula Classification
Fistula in Ano
Simple
Fistula
Intersphincteric
45-60%
Complex
Fistula
Suprasphincteric
3%
Transphincteric
25-30%
Extrasphincteric
<3%
www.downstatesurgery.org
Parks Classification of Fistula
www.downstatesurgery.org
Complex Fistula Treatment
Fistulotomy primary without seton or staged
with a seton
Fibrin Glue
Anal Fistula Plug
Endoanal/rectal advancement flap
LIFT: ligation of intersphincteric fistula tract
BioLIFT- LIFT with the addition of a
bioprosthetic in the intersphincteric plane
www.downstatesurgery.org
Seton Placement
www.downstatesurgery.org
Fistulotomy
High success rates 87-94%
Used for intersphincteric, low
transphincteric, and simple fistulas
Alteration in continence varies 6-40%,
due to differences in the definition of
incontinence
www.downstatesurgery.org
Fibrin Glue
www.downstatesurgery.org
Fibrin Glue
Lowest success rates, 14-16%
Low risk to sphincter
musculature/incontinence because
there is no dissection
More currently used as an adjunct to
other treatments +/- advancement flap
www.downstatesurgery.org
Anal Fistula Plug
www.downstatesurgery.org
Anal Fistula Plug
Success rates 35-85%
Low/No impact on sphincters, and
continence used for low transphincteric
fistulas
Highest rate post-opertive septic
complications
www.downstatesurgery.org
Endoanal mucosal
advancement flap
www.downstatesurgery.org
Endoanal mucosal
advancement flaps
Success rates 62-88%
Low/no incontinence rates as this is a
sphincter sparing procedure
No randomized controlled trials
comparing advancement flaps vs
conventional fistulotomy
www.downstatesurgery.org
LIFT procedure
Success rates 57-94%
Low incontinence rates
Used for transphincteric fistulas, may
convert hard to treat transphincteric
fistula to easier to manage
intersphincteric fistula
Relatively new procedure, data from
case series
www.downstatesurgery.org
Principles of Treatment
Treat anal sepsis
Establish relationship of fistula tract with
external and internal sphincters to
maintain continence
Provide high closure rate of fistula
No single technique is best
www.downstatesurgery.org
Questions?
www.downstatesurgery.org
Questions
3 weeks after drainage of a perianal abscess a 44 yr old fema presents with
ongoing low volume serosanguinous drainage from the site of abscess incision
and draiange. On examination a 3mm opening in the perianal skin is seen and a
firm cord between the opening and anal canal is palpated. Which of the following
is TRUE?
A. Goodsalls rule states that an external opening posterior to a line drawn
transversely across the perineum will originate from an internal opening in the
posterior midline
B. Fistulas associated with an anterior location in women or inflammatory bowel
disease or those that course through significant amounts of sphincter muscle
are amenable to fistulotomy
C.One advanctage of a cutting seton is that is avoids the discomfort associated
with a non cutting seton
D. The main benefit of a seton is that it serves as an anatomic guide for
subsequent procedures including lateral internal sphincterotomy
E. Although associated with high success rates, advancement flaps are also
assicated with high rates of incontinence
www.downstatesurgery.org
Questions
3 weeks after drainage of a perianal abscess a 44 yr old fema presents with
ongoing low volume serosanguinous drainage from the site of abscess incision
and draiange. On examination a 3mm opening in the perianal skin is seen and a
firm cord between the opening and anal canal is palpated. Which of the following
is TRUE?
A. Goodsalls rule states that an external opening
posterior to a line drawn transversely across the
perineum will originate from an internal opening in the
posterior midline
B. Fistulas associated with an anterior location in women or inflammatory bowel
disease or those that course through significant amounts of sphincter muscle
are amenable to fistulotomy
C.One advanctage of a cutting seton is that is avoids the discomfort associated
with a non cutting seton
D. The main benefit of a seton is that it serves as an anatomic guide for
subsequent procedures including lateral internal sphincterotomy
E. Although associated with high success rates, advancement flaps are also
assicated with high rates of incontinence
www.downstatesurgery.org
Questions
Two months after draiange of a perianal abscess, a 62 yr old male presents with
signs and symptoms concerning for a preianal fistula (low volume,
serosanguinous drainage from the site of abscess incision and drainage). He is
taken to the operating room for examination under anesthesia. While in the
operating room, an external opening is easily appreciated, but an internal
opening cannot be found. Which of the following is indicated?
A. Creation of an artificial opening with a lacrimal duct probe so that the fistula
can drain internally
B. Fistulotomy
C. Placement of a mushroom catheter and injection of methylene blue to search
for the internal opening
D. Aborting the procedure and returning to the operating room in 2-4 weeks for a
repeat examination under anesthesia
E. Fistulectomy
www.downstatesurgery.org
Questions
Two months after draiange of a perianal abscess, a 62 yr old male presents with
signs and symptoms concerning for a preianal fistula (low volume,
serosanguinous drainage from the site of abscess incision and drainage). He is
taken to the operating room for examination under anesthesia. While in the
operating room, an external opening is easily appreciated, but an internal
opening cannot be found. Which of the following is indicated?
A. Creation of an artificial opening with a lacrimal duct probe so that the fistula
can drain internally
B. Fistulotomy
C. Placement of a mushroom catheter and injection
of methylene blue to search for the internal opening
D. Aborting the procedure and returning to the operating room in 2-4 weeks for a
repeat examination under anesthesia
E. Fistulectomy
www.downstatesurgery.org
Questions
A 41 yr old female with a history of Crohn disease presents with signs
and symptoms concerning for a fistula in ano. Which of the following is
TRUE regarding her condition?
A. The internal opening of the fistulas whose external opening is in the
posterior quadrant are always in the posterior midline.
B. The most common type of fistula is intersphincteric.
C. Excision of the entire fistula tract is necessary for cure.
D. Fistulas associated with Crohns disease are usually lower and less
complex than spontaneous ones.
E. Fibrin glue is the most effective means of treating most fistulas.
www.downstatesurgery.org
Questions
A 41 yr old female with a history of Crohn disease presents with signs
and symptoms concerning for a fistula in ano. Which of the following is
TRUE regarding her condition?
A. The internal opening of the fistulas whose external opening is in the
posterior quadrant are always in the posterior midline.
B. The most common type of fistula is
intersphincteric.
C. Excision of the entire fistula tract is necessary for cure.
D. Fistulas associated with Crohns disease are usually lower and less
complex than spontaneous ones.
E. Fibrin glue is the most effective means of treating most fistulas.
www.downstatesurgery.org
References
Abbas, Mm Jackson, CH, Haigh, P. Predictors of Outcome for Anal
Fistula Surgery. Arcg Surg. 2011; 146(9):1011-1016
Bleier JI, Moloo H, Goldberg SM. Ligation of the intersphincteric fistula
tract: an effective new technique for complex fistulas. Dis Colon
Rectum. 2010;53:43-46.
Christoforidis D, Pieh MC, Madoff RD, Mellgren AF. Treatment of
transsphincteric anal fistulas by endorectal advancement flap or
collagen fistula plug: a comparative study. Dis Colon Rectum.
2009;52:18-22
Garcia-Aguilar J, Belmonte C, Wong DW, Goldberg SM, Madoff RD.
Cutting seton versus two-stage seton fistulotomy in the surgical
management of high anal fistula. Br J Surg. 1998;85:243-245.
Hyman, N. OBrien, S Osler, T. Outcomes of Fistulotomy:results f a
prospective , multicenter regional study. Dis Colon Rectum. 2009. 52
2022-7
www.downstatesurgery.org
References
Jacob,TJ, Perakath, B, Keighley, MR. Surgical intervention for anorectal fistula
(Review) Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2010; 5
Schouten WR, van Vroonhoven TJ. Treatment of anorectal abscess with or
without primary fistulectomy. Results of a prospective randomized trial. Dis
Colon Rectum. 1991;34:60-63.
Song, K.H. New Techniques for Treating Anal Fistula. J. Korean Soc Coloproctol
2012;28 (1):7-12
Steele, SR, Kumar, R, et al. Practice Parameters for the Management of
Perianal abscess and Fistula-in-Ano. Dis Colon Rectum. 2011;54:1465-1474
Fazio. Current Therapy in Colon and Rectal Surgery. 2nd ed.Philadelphia, PA
2005 Print
Cameron: Current Surgical Therapy. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA. 2011 Print
Yeo:Shakelfords Surgery of the Alimentary Tract. 6th ed Philadelphia, PA.
2007. Print
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Problem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyDe la EverandProblem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyJohn N. PlevrisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Define of Rectal ExaminationDocument18 paginiDefine of Rectal ExaminationMohd Hafiz Al-Muslim Bin YusoffÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fistula in Ano Treatment Options and ClassificationDocument49 paginiFistula in Ano Treatment Options and ClassificationsitalcoolkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiovascular DiseasesDocument8 paginiCardiovascular DiseasesRebecca MarshallÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluid and ElectrolytesDocument107 paginiFluid and ElectrolytesStephenus JavedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Screening of Breast CancerDocument19 paginiScreening of Breast CancerIncredible DivineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding the prostate gland and BPH symptomsDocument14 paginiUnderstanding the prostate gland and BPH symptomsRheena PadayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment of Pituitary Function and Hormone EvaluationDocument114 paginiAssessment of Pituitary Function and Hormone Evaluationmalex33yÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Transplantation of Human Organs Act, 1994: DR Amit Gupta Associate Professor Dept of SurgeryDocument63 paginiThe Transplantation of Human Organs Act, 1994: DR Amit Gupta Associate Professor Dept of SurgeryDr Suhas BavikarÎncă nu există evaluări
- MEDICALLY COMPROMISED Patients in Orthodontics / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental AcademyDocument107 paginiMEDICALLY COMPROMISED Patients in Orthodontics / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental Academyindian dental academyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lung CancerDocument9 paginiLung CancerMahmood SaeedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medical Case 1: Language Centre of Malahayati University at 2010Document16 paginiMedical Case 1: Language Centre of Malahayati University at 2010putri1114Încă nu există evaluări
- ENT Emergencies GuideDocument8 paginiENT Emergencies GuideAbegail IbañezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Euthanasia .Mercy Killing: DR - Temur Barkalaia, MD Tbilisi, Georgia 2020Document26 paginiEuthanasia .Mercy Killing: DR - Temur Barkalaia, MD Tbilisi, Georgia 2020Ashish SainiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Soil Transmitted Helminth PDFDocument90 paginiSoil Transmitted Helminth PDFMinarni HoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fistula in AnoDocument17 paginiFistula in Anoapi-216828341Încă nu există evaluări
- Chronic Gastritis: Pentti Sipponen & Heidi-Ingrid MaaroosDocument11 paginiChronic Gastritis: Pentti Sipponen & Heidi-Ingrid MaaroosFiorella Portella CordobaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Joint Pain - ApproachDocument32 paginiJoint Pain - ApproachHassan Bin AjmalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparison of Serum Microseminoprotein-Beta (MSMB) With Total Prostate Specific Antigen (TPSA) in The Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer in African MenDocument7 paginiComparison of Serum Microseminoprotein-Beta (MSMB) With Total Prostate Specific Antigen (TPSA) in The Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer in African MenInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Having A Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL)Document4 paginiHaving A Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL)Mukesh KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organ TransplantDocument17 paginiOrgan Transplantapi-392813642Încă nu există evaluări
- Vastu Tips For Diagonal Plot JAJPURDocument5 paginiVastu Tips For Diagonal Plot JAJPURhunky11Încă nu există evaluări
- AdhdDocument9 paginiAdhdapi-501702185Încă nu există evaluări
- Consent To Participate in ResearchDocument2 paginiConsent To Participate in Researchapi-372331210Încă nu există evaluări
- Multiple Myeloma-My NotesDocument8 paginiMultiple Myeloma-My NotesMitra Sadrameli100% (1)
- Acute Poststreptococcal GlomerulonephritisDocument69 paginiAcute Poststreptococcal GlomerulonephritisJirran CabatinganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Breast Cancer ScreeningDocument12 paginiBreast Cancer ScreeningCare Diagnostic CenterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 7 - Organ TransplantationDocument14 paginiLesson 7 - Organ Transplantationapi-307592530Încă nu există evaluări
- Antiemetic Prophylaxis For CINV NEJM 2016Document12 paginiAntiemetic Prophylaxis For CINV NEJM 2016tcd_usaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Critical Appraisal RCTDocument7 paginiCritical Appraisal RCTAisya FikritamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Savior Siblings - The Ethical Debate PDFDocument25 paginiSavior Siblings - The Ethical Debate PDFAna Widia SimanjuntakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Benign Prostatic HyperthropyDocument54 paginiBenign Prostatic HyperthropyPrawira Buntara PutraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pregnancy Case with Placenta Praevia and BleedingDocument9 paginiPregnancy Case with Placenta Praevia and BleedingAngeline RodriguesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Total Abdominal HysterectomyDocument19 paginiTotal Abdominal HysterectomyMeidina Rachma Amanda100% (1)
- Woman With DysuriaDocument26 paginiWoman With DysuriaAlFi KamaliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS)Document26 paginiLower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS)Ayi Abdul BasithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Road Traffic AccidentDocument35 paginiRoad Traffic AccidentHomer MoeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Belle Cervical DiseaseDocument7 paginiBelle Cervical DiseaseRashed ShatnawiÎncă nu există evaluări
- TherapyDocument25 paginiTherapyHagai MagaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- TheNurembergCode ACritiqueDocument6 paginiTheNurembergCode ACritiqueserenity limÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ca COLORECTALDocument19 paginiCa COLORECTALRaudhiatul AzzahraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Essential Hypertension - A Review ArticleDocument3 paginiEssential Hypertension - A Review ArticleHolly JonesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Appendectomy GuidelinesDocument12 paginiAppendectomy GuidelinesJessa Frances FranciscoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Non Hodgkin LymphomaDocument53 paginiNon Hodgkin LymphomaMeilina Elin WardhaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drowning: DR K.B.Suryakumar Prof & HOD Dept of Forensic Medicine KVG Medical College Sullia - KarnatakaDocument33 paginiDrowning: DR K.B.Suryakumar Prof & HOD Dept of Forensic Medicine KVG Medical College Sullia - KarnatakaSuryakumar KilarÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Current Clinica (Current - Clinical - Strategies) - Gynecology - and - Obstetrics - 2004l Strategies) - Gynecology and Obstetrics 2004Document125 pagini(Current Clinica (Current - Clinical - Strategies) - Gynecology - and - Obstetrics - 2004l Strategies) - Gynecology and Obstetrics 2004Eliza Stochita100% (1)
- Rbs Ogtt Final PresentDocument40 paginiRbs Ogtt Final PresentFrances GrefalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Myasthenia Gravis Case Study 01Document3 paginiMyasthenia Gravis Case Study 01PJHG0% (1)
- Brief - Sickle Cell AnemiaDocument6 paginiBrief - Sickle Cell AnemiaJologs AggasidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 23 - Management of Patients With Chest and Lower Respiratory Tract Disorders (PrepUDONE)Document7 paginiChapter 23 - Management of Patients With Chest and Lower Respiratory Tract Disorders (PrepUDONE)Mary SingletonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Massive Blood Transfusion Protocol (MBTP) Definition and ManagementDocument17 paginiMassive Blood Transfusion Protocol (MBTP) Definition and ManagementevanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP)Document7 paginiIdiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP)Rizqka PertiwiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Surgical Ethics in 40 CharactersDocument10 paginiSurgical Ethics in 40 CharactersHafizur Rashid100% (1)
- Types of Arthritis: SOLOMON SALLFORSDocument3 paginiTypes of Arthritis: SOLOMON SALLFORSSolomon Seth SallforsÎncă nu există evaluări
- MED - Finals 1.5 - Asthma PDFDocument12 paginiMED - Finals 1.5 - Asthma PDFYestin Reece Corpus ArcegaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Colour of UrineDocument1 paginăColour of Urinetmunroe961Încă nu există evaluări
- Epidemiologic study designs and analytic conceptsDocument78 paginiEpidemiologic study designs and analytic conceptsYosief DemissieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Researchpaper AbortionDocument21 paginiResearchpaper AbortionKaryl UyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Factors Influencing Blood Pressure Control and Medication AdherenceDocument88 paginiFactors Influencing Blood Pressure Control and Medication AdherenceLover TeddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anal Fistula Dont DeleteDocument28 paginiAnal Fistula Dont DeleteRazeen RiyasatÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2010 Philippine Cancer Facts EstimatesDocument70 pagini2010 Philippine Cancer Facts Estimates09172216507Încă nu există evaluări
- Iraq-Journal Drain PediaDocument5 paginiIraq-Journal Drain Pedia09172216507Încă nu există evaluări
- Burn OintmentDocument8 paginiBurn Ointment09172216507Încă nu există evaluări
- Determinants of The Nutritional Status of Mothers and Children in EthiopiaDocument36 paginiDeterminants of The Nutritional Status of Mothers and Children in EthiopiaJoe FeghaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Prospective Randomised Trial To Compa... Chlorhexidine 2% For Skin DisinfectionDocument8 paginiA Prospective Randomised Trial To Compa... Chlorhexidine 2% For Skin Disinfection09172216507Încă nu există evaluări
- Learn The Brachial Plexus in Five Minutes or LessDocument21 paginiLearn The Brachial Plexus in Five Minutes or LesskavithaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tracheal MassesDocument6 paginiTracheal Masses09172216507Încă nu există evaluări
- Japanese Gastric Cancer Treatment 2014Document19 paginiJapanese Gastric Cancer Treatment 201409172216507Încă nu există evaluări
- DelormeDocument6 paginiDelorme09172216507Încă nu există evaluări
- Medical Gross Anatomy-MusclesDocument66 paginiMedical Gross Anatomy-Muscles09172216507Încă nu există evaluări
- Board Exam PrimerDocument9 paginiBoard Exam PrimerEngr Jibril Naval Labiao67% (3)
- Aha Acls Algorithms 2010Document13 paginiAha Acls Algorithms 2010Imania AssagafÎncă nu există evaluări
- Learn The Brachial Plexus in Five Minutes or LessDocument21 paginiLearn The Brachial Plexus in Five Minutes or LesskavithaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abdomen ArteriesDocument18 paginiAbdomen Arteries09172216507Încă nu există evaluări
- r4f Pastest MnemonicsDocument23 paginir4f Pastest MnemonicsplayuhzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cap Guidelines :) Please ReadDocument101 paginiCap Guidelines :) Please ReadkaznielsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Med Mnemonic SDocument149 paginiMed Mnemonic S09172216507Încă nu există evaluări
- Learn The Brachial Plexus in Five Minutes or LessDocument21 paginiLearn The Brachial Plexus in Five Minutes or LesskavithaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lymphatic FilariasisDocument3 paginiLymphatic Filariasis09172216507Încă nu există evaluări
- Educ NutritionDocument4 paginiEduc Nutrition09172216507Încă nu există evaluări
- COPD AsthmaDocument16 paginiCOPD Asthma09172216507Încă nu există evaluări
- CBS ModulesDocument1 paginăCBS Modules09172216507Încă nu există evaluări
- GastroschisisDocument1 paginăGastroschisis09172216507Încă nu există evaluări
- Topics 4 TH Bi PCMDocument1 paginăTopics 4 TH Bi PCM09172216507Încă nu există evaluări
- Print - Normal Newborn - History and Physical Exam OutlineDocument3 paginiPrint - Normal Newborn - History and Physical Exam Outline09172216507Încă nu există evaluări
- Installation 1. Install Advanced System Care Pro 2. Disconnect From The Internet 3. Enter Key: DFF7A-8204E-69ADE-0D5AA 4. DoneDocument1 paginăInstallation 1. Install Advanced System Care Pro 2. Disconnect From The Internet 3. Enter Key: DFF7A-8204E-69ADE-0D5AA 4. Done09172216507Încă nu există evaluări
- Patho - Salivary GlandsDocument2 paginiPatho - Salivary Glands09172216507Încă nu există evaluări
- Installation 1. Install Advanced System Care Pro 2. Disconnect From The Internet 3. Enter Key: DFF7A-8204E-69ADE-0D5AA 4. DoneDocument1 paginăInstallation 1. Install Advanced System Care Pro 2. Disconnect From The Internet 3. Enter Key: DFF7A-8204E-69ADE-0D5AA 4. Done09172216507Încă nu există evaluări
- Clinical Guide SHR ModuleDocument7 paginiClinical Guide SHR ModuleNisroc MorrisonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cor PulmonaleDocument13 paginiCor PulmonaleHayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCM 106 - ABCDE AssessmentDocument35 paginiNCM 106 - ABCDE Assessmentエルミタ ジョイ ファティマÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of EmphysemaDocument3 paginiPathophysiology of EmphysemaApple Maiquez GarciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interpreting and Implementing The 2018 Pain, Agitation:Sedation, Delirium, Immobility, and Sleep Disruption Clinical Practice Guideline - Balas2018Document7 paginiInterpreting and Implementing The 2018 Pain, Agitation:Sedation, Delirium, Immobility, and Sleep Disruption Clinical Practice Guideline - Balas2018RodrigoSachiFreitasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anemia Effect On Burn Wound HealingDocument5 paginiAnemia Effect On Burn Wound HealingAgung Widya PramanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asperger's Syndrome Definition and CharacteristicsDocument2 paginiAsperger's Syndrome Definition and CharacteristicsSamakab MohamedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brunjes Cathy FanslowDocument1 paginăBrunjes Cathy FanslowAntea AssociazioneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Care For Patients With Alteration in Perception and CoordinationDocument12 paginiCare For Patients With Alteration in Perception and Coordinationevlujtrep9690100% (1)
- Cleanse & Restore Kit and ProtocolDocument2 paginiCleanse & Restore Kit and ProtocolEmese MagdásÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparative Health Information Management 4th Edition Peden Solutions Manual DownloadDocument15 paginiComparative Health Information Management 4th Edition Peden Solutions Manual DownloadVickie Montejo100% (28)
- Urinary Tract InfectionDocument2 paginiUrinary Tract InfectionChiel MagnoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practical Living With FibromyalgiaDocument62 paginiPractical Living With FibromyalgiaMaurice ClarkeÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Gentle Way to Give Birth: Hypnosis Birthing TechniquesDocument12 paginiA Gentle Way to Give Birth: Hypnosis Birthing TechniquesEkha-ekha HumairahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Questions G 2Document8 paginiQuestions G 2Nader Smadi100% (1)
- Selfassessment Nurs 151Document10 paginiSelfassessment Nurs 151api-315083210Încă nu există evaluări
- Tos From PRCDocument2 paginiTos From PRCOnele OrvenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hairy Leukoplakia As An Early OralDocument4 paginiHairy Leukoplakia As An Early OralJessicaLisaNugrohoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Food and NutritionDocument5 paginiFood and NutritionCes Blanco LicerioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mcguinness2020 - SulforaphaneDocument12 paginiMcguinness2020 - SulforaphaneSITI KHOLIFAHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hospital Pharmacy ManagementDocument17 paginiHospital Pharmacy ManagementMuhammad MuhlisÎncă nu există evaluări
- CDHO Factsheet LupusDocument3 paginiCDHO Factsheet LupusWayan Sutresna YasaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Speech and language disorders explainedDocument22 paginiSpeech and language disorders explainedJaren NadongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Temperoray Internal Jugular Catheter (Ijc) For Chronic Hemodialysis PatientsDocument2 paginiTemperoray Internal Jugular Catheter (Ijc) For Chronic Hemodialysis PatientsBobby Chin SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wound Bed PreparationDocument18 paginiWound Bed PreparationSaurabh AgrawalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diagnosis of cow milk allergy in infants and childrenDocument2 paginiDiagnosis of cow milk allergy in infants and childrenMaya FikriÎncă nu există evaluări
- For Printing Grand Case Group1Document37 paginiFor Printing Grand Case Group1Joco Bordeos AripÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Act of KindnessDocument4 paginiAn Act of KindnessKai Xuen LooÎncă nu există evaluări
- H MoleDocument7 paginiH MoleRaymond Christopher LimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tacrine Induce Hepatotoksik PDFDocument9 paginiTacrine Induce Hepatotoksik PDFItamahYulaikhaÎncă nu există evaluări