Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
4.9 Grounding: Wiring The S7-400
Încărcat de
Mathivanan AnbazhaganDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
4.9 Grounding: Wiring The S7-400
Încărcat de
Mathivanan AnbazhaganDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Wiring the S7-400
4.9
Grounding
Introduction
Grounding in accordance with regulations and conscientiously implemented is the
prerequisite for proper functioning of a programmable controller.
Each individual component of the S7-400 and of the controlled system must be
properly grounded.
Ground Connections
Low-resistance ground connections reduce the risk of electric shock in the event of
a short-circuit or faults in the system. Moreover, proper grounding (low-impedance
connections: large surface area, wide-area bonding) together with the effective
shielding of lines and devices reduces the effect of interference on the system and
the interference signal emissions.
Note
Always ensure that operating currents do not flow via ground.
Protective Ground
All equipment of Safety Class I and all large metal parts must be connected to the
protective ground. This is essential to ensure that the user of the installation is
reliably protected from electric shock.
Furthermore, this serves to discharge interference transferred via external power
supply cables, signal cables, or cables to I/O devices.
Shown in Table 4-2 are the grounding methods required for the individual
components.
Table 4-2
Methods of Protective Grounding
Device
Grounding Method
Cabinet/frame
Connection to central ground point, e.g. ground bus, via
cable with protective conductor quality
Racks
Connection to central ground point via cable with
10 mm2 min. cross-section, when racks are not installed in a
cabinet and not interconnected via large metal parts
Module
None; automatically grounded via backplane bus when fitted
I/O device
Grounded via power plug
Shields of connecting
cables
Connection to rack or central ground point (avoid ground
loops)
Sensors and actuators
Grounding according to specifications applying to the
system
Automation System S7-400 Hardware and Installation
A5E00850741-01
4-13
Wiring the S7-400
Connecting the Load Voltage Ground
Many output modules require an additional load voltage to switch the actuators.
Two different modes are possible for this load voltage:
Non-isolated operation
Floating operation
The following table shows how the load voltage ground is connected in the
individual modes.
Table 4-3
Grounded connection load voltage
Mode
Connection of Load Voltage
Non-isolated operation
Grounded configuration
to the reference point of the rack; metallic connection
between frame element and chassis ground must be
fitted.
Ungrounded configuration
to the reference point of the rack; metallic connection
between frame element and chassis ground must be
fitted.
Floating operation
Grounded and ungrounded
configuration
Left open or to any point, but not to protective ground
or reference potential M of operating voltages
The following figure shows how the load voltage ground is connected for
non-isolated operation.
Metallic connection, remove for
ungrounded configuration
Ground terminal for
load voltage
Figure 4-7 Grounded connection load voltage
4-14
Automation System S7-400 Hardware and Installation
A5E00850741-01
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- 16th Edition IEE Wiring Regulations: Design and Verification of Electrical InstallationsDe la Everand16th Edition IEE Wiring Regulations: Design and Verification of Electrical InstallationsEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- Instrument Location PlanDocument16 paginiInstrument Location PlanCezarinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solar Cathodic Protection System ManualDocument10 paginiSolar Cathodic Protection System Manualsoltani aliÎncă nu există evaluări
- MP75-MP150 Installation ManualDocument17 paginiMP75-MP150 Installation ManualMohamedGuerboujÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1101-808-1 Install Guide USDocument4 pagini1101-808-1 Install Guide USJOSE BÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coil-Lock ... Hold-in-Device: From Power Quality Solutions IncDocument2 paginiCoil-Lock ... Hold-in-Device: From Power Quality Solutions IncvelizarkoÎncă nu există evaluări
- R8501G K1RangeDocument208 paginiR8501G K1RangeRinda_RaynaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control System Grounding - Part 2 - Ground Wiring, Shield Grounds, and Power Supply GroundingDocument10 paginiControl System Grounding - Part 2 - Ground Wiring, Shield Grounds, and Power Supply Groundingwaqas_a_shaikh4348Încă nu există evaluări
- What NEC Says About Design Constraints For Grounding SystemsDocument8 paginiWhat NEC Says About Design Constraints For Grounding Systemsmatthew02012010Încă nu există evaluări
- R8505 KVTR100Document88 paginiR8505 KVTR100Rinda_RaynaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MANUAL For Inverter 3.5 KW LNCDocument78 paginiMANUAL For Inverter 3.5 KW LNCEduardo Gonzalez OleaÎncă nu există evaluări
- OK4U 100W Grid Tie Inverter ManualDocument4 paginiOK4U 100W Grid Tie Inverter Manualdavidmc6375Încă nu există evaluări
- MT506V46Install 060223 PDFDocument8 paginiMT506V46Install 060223 PDFHoa Lưu LyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Service Manual Type LFCB102 Digital Current Differential RelayDocument211 paginiService Manual Type LFCB102 Digital Current Differential RelayRinda_RaynaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Installation Instructions: Netcontroller IiDocument10 paginiInstallation Instructions: Netcontroller IinandodefariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lmu PDFDocument4 paginiLmu PDFceverthÎncă nu există evaluări
- Installation: This Chapter Describes The Setup of The Access Point and Includes The Following SectionsDocument8 paginiInstallation: This Chapter Describes The Setup of The Access Point and Includes The Following SectionsAngel Bernardo Gomez LizanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Service Manual Type MHOA 04, MHOB 04, MHOC 04 Translay Feeder Protection SchemesDocument36 paginiService Manual Type MHOA 04, MHOB 04, MHOC 04 Translay Feeder Protection SchemesRinda_RaynaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Delta SOLIVIA Inverter 2.5APG3 Installation GuideDocument148 paginiDelta SOLIVIA Inverter 2.5APG3 Installation Guidekselvan_1Încă nu există evaluări
- Diary Report SirDocument14 paginiDiary Report SirNeeraj PurohitÎncă nu există evaluări
- FC 3000 SDocument60 paginiFC 3000 SMohamedElsawiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 100 Amp 3000UC ManualDocument47 pagini100 Amp 3000UC ManualAshish Jain50% (2)
- Nec 250 Part Ix InstrumentsDocument6 paginiNec 250 Part Ix Instrumentsvladimir rosas ayalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECX 400 SeriesDocument16 paginiECX 400 SeriesGeneral Electronic Facility LandsideÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3com WLAN Managed AP3150: Quick Start GuideDocument16 pagini3com WLAN Managed AP3150: Quick Start GuideMarcelo PiresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rev EDocument12 paginiRev EDanilo SkateÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mvaa Manual GBDocument22 paginiMvaa Manual GBAbdullah Ghannam0% (1)
- Nec 250Document7 paginiNec 250Sujeet ManolkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5A To 9A Stroker. Electronic Controller Conversion Guideline ManualDocument20 pagini5A To 9A Stroker. Electronic Controller Conversion Guideline Manualabuzer1981Încă nu există evaluări
- 9 Recommended Practices For Grounding: Basis For Safety and Power QualityDocument11 pagini9 Recommended Practices For Grounding: Basis For Safety and Power QualityPrabu Baskaran100% (1)
- AGN 038 - Earthing: Application Guidance Notes: Technical Information From Cummins Generator TechnologiesDocument10 paginiAGN 038 - Earthing: Application Guidance Notes: Technical Information From Cummins Generator TechnologiesariwibowoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Enclosure Design Handbook Rev. 1Document20 paginiEnclosure Design Handbook Rev. 1cristoinhumanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Distribution Circuits: Learning OutcomeDocument22 paginiElectrical Distribution Circuits: Learning OutcomeMandeep MalikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Service Manual Type MRSU 04 Rotor Earth Fault RelayDocument24 paginiService Manual Type MRSU 04 Rotor Earth Fault RelayRinda_RaynaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Moxa Eds 2005 El Elp Series Qig v1.4Document15 paginiMoxa Eds 2005 El Elp Series Qig v1.4pham huyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Accessories: Test and Training Set Switchgear SimulatorDocument4 paginiAccessories: Test and Training Set Switchgear SimulatorJoseph KrauseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Controllogix Voltage/Current Input Module: Installation InstructionsDocument20 paginiControllogix Voltage/Current Input Module: Installation InstructionsMarco RojasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asco 4000 Manual Transfer Switch PDFDocument12 paginiAsco 4000 Manual Transfer Switch PDFPedro Bermudez100% (1)
- Areva MFACDocument30 paginiAreva MFACFerry A ViawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Basics of Personal Protective GroundingDocument5 paginiThe Basics of Personal Protective GroundingRobertoHerediaJacoboÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9 1 2013 SinicolaDocument21 pagini9 1 2013 SinicolaAnonymous Wu6FDjbÎncă nu există evaluări
- J1939 Gateway™: Installation and Operation GuideDocument27 paginiJ1939 Gateway™: Installation and Operation GuideEmrol2Încă nu există evaluări
- LexiumDocument32 paginiLexiumIbrahima DiawÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shielding and GroundingDocument4 paginiShielding and GroundingSaibuOluwaseyiÎncă nu există evaluări
- MEN System of EarthningDocument6 paginiMEN System of EarthningstarykltÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multiple Earthed NeutralDocument6 paginiMultiple Earthed Neutralrajpre1213Încă nu există evaluări
- Operator's Manual: Rating LabelDocument20 paginiOperator's Manual: Rating LabelNeptali NaveaÎncă nu există evaluări
- R8017G MBCHDocument52 paginiR8017G MBCHmjbriceno@gmail.com100% (1)
- KEPCO Quick Start GuideDocument8 paginiKEPCO Quick Start Guideankara271828Încă nu există evaluări
- Type MCAG 14, 34: High Stability Circulating Current RelaysDocument30 paginiType MCAG 14, 34: High Stability Circulating Current Relaysrenjithas2005100% (2)
- R8005C MvawDocument20 paginiR8005C MvawRinda_RaynaÎncă nu există evaluări
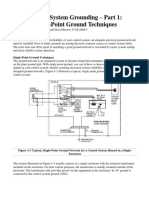
- Control System Grounding - Part 1 - Single-Point Ground TechniquesDocument7 paginiControl System Grounding - Part 1 - Single-Point Ground Techniqueswaqas_a_shaikh4348Încă nu există evaluări
- Inversor Abb 5kwDocument2 paginiInversor Abb 5kwapi-290643326Încă nu există evaluări
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionDe la EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionDe la EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2De la EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Încă nu există evaluări
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1De la EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Evaluare: 2.5 din 5 stele2.5/5 (3)
- RAZDocument178 paginiRAZMathivanan Anbazhagan100% (1)
- Attachment To K2207/M2/513, Sep 10 '03 Comments On APIL's P&ID For TGDocument1 paginăAttachment To K2207/M2/513, Sep 10 '03 Comments On APIL's P&ID For TGMathivanan AnbazhaganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Security LocksDocument12 paginiSecurity LocksMathivanan AnbazhaganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Performance ModelDocument5 paginiPerformance ModelMathivanan AnbazhaganÎncă nu există evaluări
- KKS Classification SystemDocument227 paginiKKS Classification SystemMathivanan Anbazhagan100% (2)
- GCCDocument1 paginăGCCMathivanan AnbazhaganÎncă nu există evaluări
- PV Data SheetDocument2 paginiPV Data SheetMathivanan AnbazhaganÎncă nu există evaluări
- LEED v4 Ballot Version (BDC) - 13 11 13Document159 paginiLEED v4 Ballot Version (BDC) - 13 11 13rasheedillikkalÎncă nu există evaluări
- TenderDocument3 paginiTenderMathivanan AnbazhaganÎncă nu există evaluări
- RFQ-Supply of Field InstrumentsDocument2 paginiRFQ-Supply of Field InstrumentsMathivanan AnbazhaganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alfanar: Emmar The Economic CityDocument1 paginăAlfanar: Emmar The Economic CityMathivanan AnbazhaganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mepl-Design and Engg StatusDocument170 paginiMepl-Design and Engg StatusMathivanan AnbazhaganÎncă nu există evaluări
- 16 - Annexures A and BDocument74 pagini16 - Annexures A and BMathivanan AnbazhaganÎncă nu există evaluări
- XV Data SheetDocument1 paginăXV Data SheetMathivanan Anbazhagan100% (1)
- Software ManualDocument7 paginiSoftware ManualMathivanan AnbazhaganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Instrument Specification SheetDocument1 paginăInstrument Specification SheetMathivanan AnbazhaganÎncă nu există evaluări
- PT Data SheetDocument2 paginiPT Data SheetMathivanan AnbazhaganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Schedule B - Attachment IiiDocument5 paginiSchedule B - Attachment IiiMathivanan AnbazhaganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Show Floor Cutout As Per Your 2D Drawing in Your 3D Model AlsoDocument1 paginăShow Floor Cutout As Per Your 2D Drawing in Your 3D Model AlsoMathivanan AnbazhaganÎncă nu există evaluări
- FI Data SheetsDocument1 paginăFI Data SheetsMathivanan AnbazhaganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scope of WorkDocument4 paginiScope of WorkMathivanan AnbazhaganÎncă nu există evaluări
- SH 51MW Bop 033 I 001 Rev.2Document15 paginiSH 51MW Bop 033 I 001 Rev.2Mathivanan AnbazhaganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Instrument Installation Material List (BM Bulk Material List), Rev 1Document1 paginăInstrument Installation Material List (BM Bulk Material List), Rev 1Mathivanan AnbazhaganÎncă nu există evaluări
- FO Data SheetDocument1 paginăFO Data SheetMathivanan AnbazhaganÎncă nu există evaluări
- ClarificationsDocument1 paginăClarificationsMathivanan AnbazhaganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activities For Doing ProjectDocument1 paginăActivities For Doing ProjectMathivanan AnbazhaganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Projects Activities - ElectricalDocument4 paginiProjects Activities - ElectricalMathivanan Anbazhagan100% (1)
- Tce Consulting Engineers Limited Quality Assurance Compliance Report For Enquiry SpecificationsDocument2 paginiTce Consulting Engineers Limited Quality Assurance Compliance Report For Enquiry SpecificationsMathivanan AnbazhaganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jayamoorthy Mugunthan MR 26oct RuhDocument3 paginiJayamoorthy Mugunthan MR 26oct RuhMathivanan AnbazhaganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jayamoorthy Mugunthan MR 14nov MaaDocument3 paginiJayamoorthy Mugunthan MR 14nov MaaMathivanan AnbazhaganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cars 2 Activity Book Printable 0511 PDFDocument5 paginiCars 2 Activity Book Printable 0511 PDFGustavo VydraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maintenance and Repair of Centrifugal PumpsDocument4 paginiMaintenance and Repair of Centrifugal Pumpsaserf251Încă nu există evaluări
- 1 s2.0 S0017931021011261 MainDocument27 pagini1 s2.0 S0017931021011261 MainKuwar Ranvijay Singh (B19ME040)Încă nu există evaluări
- Samsung DVM Chiller InstallationManualDocument56 paginiSamsung DVM Chiller InstallationManualjlmoleroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flame HardeningDocument2 paginiFlame Hardenings_manikandanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Certificado Brida 3Document1 paginăCertificado Brida 3juan aguilarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical Property AnalyzersDocument211 paginiPhysical Property AnalyzersabbutalibbÎncă nu există evaluări
- APLIKASI Cee Dan Zee Purlin: Pt. Bluescope Lysaght Indonesia June 2014Document34 paginiAPLIKASI Cee Dan Zee Purlin: Pt. Bluescope Lysaght Indonesia June 2014gama adisetiantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 40W Solar Panel Specifications: Main FeaturesDocument2 pagini40W Solar Panel Specifications: Main FeaturesthoroidÎncă nu există evaluări
- BODOR User Manual of Fiber Metal Cutting MachineDocument50 paginiBODOR User Manual of Fiber Metal Cutting Machinesebastian carreño100% (2)
- ConclusionDocument2 paginiConclusionRohit Kumar75% (4)
- FIR and APPENDICES PHMSA WUTC Williams Plymouth 2016 04 28 REDACTEDDocument39 paginiFIR and APPENDICES PHMSA WUTC Williams Plymouth 2016 04 28 REDACTEDrty2Încă nu există evaluări
- Listino Sea RecoveryDocument117 paginiListino Sea RecoveryEduardo Harold ChapuzÎncă nu există evaluări
- JotamTechnologies ProfileDocument12 paginiJotamTechnologies ProfileProjecte2Încă nu există evaluări
- Control of Simple Distillation TowerDocument46 paginiControl of Simple Distillation TowerDian Ardiansyah100% (1)
- Silastic® HCM 60-1225-GRAY Silicone RubberDocument6 paginiSilastic® HCM 60-1225-GRAY Silicone RubberZENGJIAQIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Method Statement Sipchem-2201 B PDFDocument10 paginiMethod Statement Sipchem-2201 B PDFCharlie TacanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Machine FoundationDocument4 paginiMachine Foundationp kishorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4 Jobbing and BatchDocument39 paginiChapter 4 Jobbing and BatchDavid HồÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gear Manufacturing Methods: Prepared by Kaushal PatelDocument42 paginiGear Manufacturing Methods: Prepared by Kaushal Patelashoku24007Încă nu există evaluări
- VN Ensival Moret PumpDocument1 paginăVN Ensival Moret PumpsitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1970 Richart Et Al - Vibrations of Soils and FoundationsDocument39 pagini1970 Richart Et Al - Vibrations of Soils and FoundationsAlejandro PlazasÎncă nu există evaluări
- PDFDocument3 paginiPDFJoaquin UreñaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hyundai Steel Products GuideDocument40 paginiHyundai Steel Products GuidecarloÎncă nu există evaluări
- D 7264 - D 7264M - 15Document10 paginiD 7264 - D 7264M - 15AMAR SAI PRABHUÎncă nu există evaluări
- TRI SHiELD Brochure FLTR Purple Engineering 1Document6 paginiTRI SHiELD Brochure FLTR Purple Engineering 1FLTR PURPLE E.Încă nu există evaluări
- Power Source CharacteristicsDocument22 paginiPower Source CharacteristicsKyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fosc-230j 2014V1 0Document3 paginiFosc-230j 2014V1 0Francisco LaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- ACT Lab ManualDocument55 paginiACT Lab ManualDusk Slayer100% (1)
- Timing Cover 190EDocument8 paginiTiming Cover 190ESergio Belmar CrisostoÎncă nu există evaluări