Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Sum
Încărcat de
MuhammadAbdullahTariqDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Sum
Încărcat de
MuhammadAbdullahTariqDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
2009
Some data related to airship:
A good airship model should include
1. Dynamic Modeling of the Airship Using Analytical Aerodynamic Model.
2. Control performance.
3. Flight modes of the airship.
This paper uses geometrical characteristics in order to find vehicle aerodynamics forces
and moments
Uses MATLAB which is easily available and is user friendly.
Lifting gases used are usually Hydrogen, Helium or Hot air gas.
Airships may be Rigid, Non-Rigid, Metal clad or Hybrid types.
Uses Vectored Thrust.
This paper:
Used S.B.V. Gomes model, it is 6 DOF non-linear Mathematical model. This model
describes the Dynamics, Gravitation, Propulsion, Aerodynamics and Control.
Two orthogonal axes sets
1. Body axes pointing towards the three orthogonal X, Y and Z directions
centered at airship center of volume (C.V).
2. Main concept is calculation of the three linear velocities, u, v and w, and
the three angular velocities, p, q and r, with reference to X, Y and Z,
respectively.
3. Inertial or Earth axes. Where 0X axis is aligned with the North direction,
0Y with the East and 0Z axis points downwards to the center of Earth.
4. Earth axes set stays stationary throughout
5. Body axes set moves along with the vehicle.
6. Effects of the Earth curvature are not taken into account (flat Earth is
assumed).
Airship is assumed to be rigid, aero-elastic effects are ignored.
Flight at small height
1. Temperature and pressure conditions remains almost constant.
2. C.G location is fixed.
LTA vehicles is a mass with forces and moments applied.
Added or virtual masses and inertias which arise due to the vehicle mass being of the same
order of magnitude as mass of the displaced air.
2013
Some data related to airship
Six degrees-of-freedom dynamic model of a non-rigid airship.
Small perturbation modeling technique is recently used.
System identification approach for determining flight dynamic characteristics of an airship
from flight data is also used.
Flexible and non-flexible airship is also illustrated.
Hull shape optimization is also being used.
A detailed work for investigation of flight dynamics using wind tunnel database is also used
for airship.
Focus of this paper
A comprehensive six degrees of freedom dynamic model.
Non-rigid airship modified for its aerodynamic part.
Model is based on that of a remotely operated underwater vehicle (ROV)
Upgraded to model airship dynamics
The model has all inertial, dynamic, aerodynamic, buoyant, gravitational, and
propulsion forces
Validation for YEZ-2A airship is demonstrated.
Details about model
Mathematical model used for Remotely Operated Underwater Vehicle (ROV).
Small perturbation model is used as a basis for study of the airship flight dynamics.
Model by S.B.V. Gomes to draw a full six degrees of freedom (6-DOF) non-linear
mathematical model.
This model includes the dynamic, gravitation, propulsion, aerodynamic and control
behavior.
Can explain the stability and control performance as well as flight modes of the
airship.
Used analytical method to develop a model and wind tunnel data in order to
estimate parameters.
Base paper
Uses Guidance-Based Path Following (GBPF) principle and Trajectory Linearization
Control (TLC) theory
Dynamic model of the stratospheric airship with kinematics and dynamics
equations.
Path following control strategy integrated GBPF principle and TLC theory is deduced.
Control system possesses a cascaded structure
consists of guidance law subsystem, attitude control loop and velocity control loop.
Stability analysis shows that the controlled closed-loop system is asymptotically
stable.
Linearized models are only effect in equilibrium state of airship.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Projectile Motion PPT FR RefDocument17 paginiProjectile Motion PPT FR RefR K100% (2)
- EPQ Full Project Version 2Document52 paginiEPQ Full Project Version 2nsjÎncă nu există evaluări
- BookDocument20 paginiBookIvicaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vibrating Plate 2D Viscous Flow 53Document7 paginiVibrating Plate 2D Viscous Flow 53Dr-Ateeq Ur RehmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- MM302 4 Lecture Note 4Document13 paginiMM302 4 Lecture Note 4Emre100% (1)
- Hydraulic Calculations & MudpumpDocument1 paginăHydraulic Calculations & MudpumpUok Ritchie100% (1)
- Wind Turbine Airfoils and Blades Optimization Design Theory by Chen, Jin Wang, QuanDocument393 paginiWind Turbine Airfoils and Blades Optimization Design Theory by Chen, Jin Wang, QuanAli ShahinÎncă nu există evaluări
- ST Venant EquationsDocument13 paginiST Venant EquationsHelun Ben LiuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project Name: Booster Pump CalculationsDocument2 paginiProject Name: Booster Pump CalculationsJohn AÎncă nu există evaluări
- McDonnell USAF Datcom 1979 Volume 1 User ManualDocument313 paginiMcDonnell USAF Datcom 1979 Volume 1 User ManualFabian ZenderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modeling and CFD Analysis of Flow Over Aircraft Split Winglet and Blended WingletDocument6 paginiModeling and CFD Analysis of Flow Over Aircraft Split Winglet and Blended WingletArif AdjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- JAFM Engine Nozzle Journal 2018Document10 paginiJAFM Engine Nozzle Journal 2018arslansayaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- EcaseDocument5 paginiEcasesanjaymata1542Încă nu există evaluări
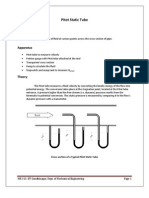
- Pitot Static TubeDocument4 paginiPitot Static TubeVrushiket PatilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Progress Report Week#9 UlubeluDocument6 paginiProgress Report Week#9 UlubelutiantaufikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Development of Francis Turbine Using CFDDocument40 paginiDevelopment of Francis Turbine Using CFDaashish386Încă nu există evaluări
- Air Combat ManeuveringDocument176 paginiAir Combat Maneuveringcontrollerhead100% (5)
- Liquid Flowmeters: Reynolds NumbersDocument12 paginiLiquid Flowmeters: Reynolds NumbersAsaithambi DorairajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physicalsciences Grade 12 Term 1 PDFDocument141 paginiPhysicalsciences Grade 12 Term 1 PDFRose Ann CruzadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Awwa C600Document8 paginiAwwa C600张守冲Încă nu există evaluări
- Numerical Design of Multi Element AirfoilDocument105 paginiNumerical Design of Multi Element AirfoilChristiano Pereira de OliveiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unsteady Friction ModelsDocument32 paginiUnsteady Friction ModelsWalter F SilvaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydraulic Reference Manual IberDocument56 paginiHydraulic Reference Manual Iberचन्द्र प्रकाशÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course Content On Engineering PhysicsDocument3 paginiCourse Content On Engineering PhysicsNimeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- ProblemsDocument1 paginăProblemsAngela SedanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- EM Dis CH 4 Part 4Document26 paginiEM Dis CH 4 Part 4Fawzi Al-TawilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Two Equation Eddy Viscosity Turbulence Models For EngineeringDocument8 paginiTwo Equation Eddy Viscosity Turbulence Models For EngineeringGerardo CanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 199 Department of Civil EngineeringDocument6 pagini199 Department of Civil EngineeringMARSDEN RONNYÎncă nu există evaluări