Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Muscles of The Back PDF
Încărcat de
jsdlzjDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Muscles of The Back PDF
Încărcat de
jsdlzjDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
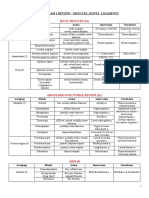
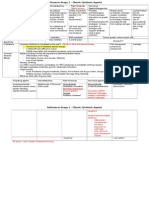
6.
2, p755)
Innervation
Main Action
Trapezius
medial third of superior nuchal line;
external occipital protuberance; nuchal
ligament; spinous processes of C7-C12
vertebrae
Lateral third of clavicle; acromion &
spine of scapula
-accessory nerve (CN
XI) (motor fibers) &
-C3, C4 spinal nerves
(pain & proprioceptive
fibers)
Latissimus Dorsi
spinous processes of inferior 6 thoracic
vertebrae, thoracolumbar fascia, iliac
crest, & inferior 3 or 4 ribs
floor of intertubercular groove of
humerus
thoracodorsal nerve C6C8
Descending part elevates; ascending part
depresses; & middle part (or all parts
together) retracts scapula; descending &
ascending parts act together to rotate
glenoid cavity superiorly
extends, adducts, & medially rotates
humerus; raises body toward arms during
climbing
Levator Scapulae
posterior tubercles of transverse
processes of C1-C4 vertebrae
medial border of scapula superior to
root of spine
dorsal scapular (C5) &
cervical (C3, C4) nerves
Elevates scapula & tilts its glenoid cavity
inferiorly by rotating scapula
Spinous processes of T2-T5
vertebrae
nuchal ligament; spinous processes of
C7 & T1 vertebrae
nuchal ligament, spinous processes of
C7-T3 vertebrae
medial border of scapula from level
of spine to inferior angle
smooth triangular area at medial end
of scapular spine
Dorsal scapular nerve
(C4, C5)
Retracts scapula & rotates it to depress
glenoid cavity; fix scapula to thoracic wall
Superior borders of 2nd to 4th ribs
2nd-5th intercostal
space
elevate ribs
inferior borders of 8th-12th ribs near
their angles
anterior rami of T9-T12
thoracic spinal nerves
depresses ribs
Posterior rami of spinal
nerves
Acting along: laterally flex neck & rotate
head to side of active muscles -Acting
together: extend head & neck
Rhomboid Minor
4.5, p537)
1.2 p94)
Serratus Posterior
Superior
4.6, p538)
Superficial
Intrinsic (Table
Intermediate Intrinsic (Table
Insertion
Rhomboid Major
Intermediate
Extrinsic (Table
Superficial Extrinsic Group (Table
Muscle
Serratus Posterior
Inferior
Splenius
Erector Spinae
Back v.3
Origin
spinous processes of T11-L2 vertebrae
Arises from the nuchal ligament &
spinous processes of C7-T3 or T4
vertebrae
Arises by a broad tendon from
posterior part of iliac crest, posterior
surface of sacrum, sacroiliac
ligaments, sacral & inferior lumbar
spinous processes, & supraspinous
ligament
-Splenius Capitis: fibers run
superolaterally to mastoid process of
temporal bone & lateral third of
superior nuchal line of occipital bone
-Splenius cervicis: tubercles of
transverse processes of C1-C3/4
vertebrae
-Spinalis: thoracis, cervicis, capitis;
fibers run superiorly to spinous
processes in the upper thoracic
region & to cranium
-Longissimus: thoracis, cervicis,
capitis; fibers run superiorly to ribs
between tubercles & angles to
transverse processes in thoracic &
cervical regions, & to mastoid
process of temporal bone
-Iliocostalis: lumborum, thoracis,
cervicis; fibers run superiorly to
angles of lower ribs & cervical
transverse processes
joe.seo, liz.carter & samantha.evans
Posterior rami of spinal
nerves
-Acting bilaterally: extend vertebral
column & head; as back is flexed, control
movement by gradually lengthening their
fibers
-Acting unilaterally: laterally flex vertebral
column
Muscle
Innervation
Info/Misc.
Main Action
Extension
extends head & thoracic &
cervical regions of vertebral
column & rotates them
contralaterally
transverse processes
spinous processes of more
superior vertebrae
-Semispinalis
arises from transverse
processes of C4-T12
vertebrae
thoracis, cervicis, capitis;
fibers run superomedially to
occipital bone & spinour
processes in thoracic &
cervical regions, spanning 4-6
segments
the superficial member of the
transversospinal group, consists
of three parts according to their
superior attachments: capitis,
thoracis, cervicis
-Multifidus
arises from posterior sacrum,
posterior superior iliac spine
of ilium, aponeurosis of
erector spinae, sacroiliac
ligaments, mammillary
processes of lumbar
vertebrae, transverse
processes of T1-T3, articular
processes of C4-C7
thickest in lumbar region;
fibers pass obliquely
superomedially to entire
length of spinous processes
of vertebrae, located 2-4
segments superior to origin
arise from transverse
processes of vertebrae
fibers pass superomedially to
attach to junction of lamina &
transverse process or spinous
process of vertebra
immediately (brevis) or 2
segments (longus) superior to
vertebra of origin
Interspinales
Superior surfaces of spinous
processes of cervical &
lumbar vertebrae
inferior surfaces of spinous
processes of vertebra
superior to vertebra of origin
posterior rami of
spinal nerves
Intertransversarii
transverse processes of
cervical & lumbar vertebrae
transverse processes of
adjacent vertebrae
posterior &
anterior rami of
spinal nerves
Levatores costarum
tips of transverse processes
of C7 & T1-T11 vertebrae
Pass inferolaterally and insert
on rib between tubercle &
angle
Posterior rami of
C8-T11 spinal
nerves
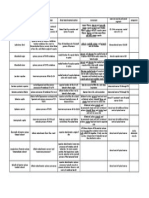
(Table 4.7, p539)
Deep Intrinsic
Insertion
deep to the erector spinae in an
obliquely disposed group of
much shorter mm called
transversospinal m group,
consisting of semispinalis,
multifidus, rotatores
Transversospinalis:
-Rotatores
Minor Deep Intrinsic
Origin
posterior rami of
spinal nerves
middle layer consists of short
triangular muscle bundles;
thickest in the lumbar region
deepest;
best developed in the thoracic
region
stabilizes vertebrae during
local movements of vertebral
column
stabilize vertebrae & assist
with local extension &
rotatory movements of
vertebral column; may
function as organs of
proprioception
aid in extension & rotation of
vertebral column;
acting bilaterally, stabilize
vertebral column
aid in lateral flexion of
vertebral column; acting
bilaterally, stabilize vertebral
column
Elevate ribs, assisting
respiration; assist with lateral
flexion of vertebral column
th
Major Sources include Moores COA 5 , Stedmans Medical Dictionary, Grants Dissector
Thank you Samantha out the Excel table version
Back v.3
joe.seo, liz.carter & samantha.evans
p541)
Principle Muscles
Producing
Movements of the
Thoracic &
Lumbar
Intervertebral (IV)
Joints Table 4.9,
p542)
Principle Muscles
Producing
Movement of the
Cervical
Intervertebral
Jionts (Table 4.8,
Flexion
Sternocleidomastoid
Bilateral action of:
Rectus abdominis
Psoas major
Gravity
(Table 4.10, p545)
Muscle
Suboccipital Muscles
Extension
Bilateral action of:
Longus coli
Scalene
Rectus capitis posterior
major
Rectus capitis posterior
minor
Inferior oblique of head
(L. m. obliquus capitis
inferior)
superior oblique of head
(L. m. obliquus capitis
superior)
Lateral bending
Deep neck muscles:
1. semispinalis cervicis &
iliocostalis cervicis
2. splenius cervicis & levator
scapulae
3. splenius capitis
4. multifidus
5. longissimus capitis
6. semispinalis capitis
T. trapezius
Bilateral action of:
Erector spinae
Multifidus
Semispinalis thoracis
Origin
Unilateral action of:
Rotatores
Semispinalis capitis & cervicis
Multifidus
Splenius cervicis
Unilateral action of:
Iliocostalis thoracis & lumborum
Longissimus toracis
Multifidus
External & internal oblique
Quadratus lumborum
Rhomboids
Serratus anterior
Unilateral action of:
Rotatores
Multifidus
Iliocostalis
Longissimus
External oblique acting synchronously with
opposite internal oblique
Splenius thoracis
(See bracket to rotatores & multifidus: Transversopinalis)
Insertion
spinous process of vertebra C2
posterior tubercle of posterior arch
of vertebra C1
transverse process of vertebra C1
Rotation (not illustrated)
Unilateral action of:
Iliocostalis cervicis
Longissimus capitis & cervicis
Splenius capitis & cervicis
Intertransverse & scalenes
lateral part of inferior nuchal line of
occipital bone
medial part of inferior nuchal line of
occipital bone
Aspect of
Structures
superomedial boundary
rectus capitis posterior major
rectus capitis posterior minor
transverse process of vertebra C1
inferolateral boundary
obliquus capitis inferior
occipital bone between superior &
inferior nuchal lines
superolateral boundary
obliquus capitis superior
posterior atlanto-occipital membrane
& posterior arch of vertebra C1
semispinalis capitis
vertebral artery & suboccipital nerve
floor
roof
contents
Principle Muscles Producing Movement of the Atlanto-Occipital Joints
(Table 4.11, p546)
(Table 4.12, p546)
Flexion
Extension
Longus capitis
Rectus capitis anterior
Anterior fibers of
sternocleidomastoid
Suprahyoid & infrahyoid muscles
Rectus capitis posterior major & minor
Obliquus capitis superior
Splenius capitis
longissimus capitis
trapezius
Back v.3
Principle Muscles Producing Movement of the AtlantoAxial Joints
Lateral bending
sternocleidomastoid
obliquus capitis superior
rectus capitis lateralis
longissimus capitis
splenius capitis
joe.seo, liz.carter & samantha.evans
Ipsilateral
obliquus capitis inferior
rectus capitis posterior, major & minor
longissimus capitis
splenius capitis
Contralateral
sternocleidomastoid
semispinalis capitis
Back v.3
joe.seo, liz.carter & samantha.evans
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Muscle of Upper LimbsDocument5 paginiMuscle of Upper LimbsFong Yu-heng100% (1)
- Muscles of The BackDocument38 paginiMuscles of The BackPrashanth KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- კუნთებიDocument6 paginiკუნთებიPlay ListÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lower Limb & HipDocument9 paginiLower Limb & HipEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Subclavius Pectoralis Minor: Axial Skeleton To Shoulder Girdles (Ventral Side)Document6 paginiSubclavius Pectoralis Minor: Axial Skeleton To Shoulder Girdles (Ventral Side)馮素琴Încă nu există evaluări
- L14-Arteries of The Lower Limb-DoneDocument47 paginiL14-Arteries of The Lower Limb-Doneyakuza444Încă nu există evaluări
- Anterior Triangle of The Neck IIDocument49 paginiAnterior Triangle of The Neck IIvrajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Muscle Origin Insertion Action Nerve: SartoriusDocument3 paginiMuscle Origin Insertion Action Nerve: SartoriusJim VargheseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy Exam 1 Review - Muscles of the Back, Shoulder, Arm, Forearm & HandDocument27 paginiAnatomy Exam 1 Review - Muscles of the Back, Shoulder, Arm, Forearm & Handgdubs215Încă nu există evaluări
- Cranial Nerves 7-12 Functions and Integrity TestsDocument62 paginiCranial Nerves 7-12 Functions and Integrity TestsjangyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neck Axilla BackDocument24 paginiNeck Axilla BackmoregutsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Upper Limb Muscle AttachmentDocument7 paginiUpper Limb Muscle Attachmenterwilli5Încă nu există evaluări
- Muscles of The Neck PDFDocument1 paginăMuscles of The Neck PDFEdreyn DellosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lower Limb - Clinical AnatomyDocument18 paginiLower Limb - Clinical Anatomyewijayapala100% (2)
- Upper Limb ChartDocument6 paginiUpper Limb ChartDianeLumintooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gluteal Region, Posterior Compartment of The Thigh and Popliteal FossaDocument4 paginiGluteal Region, Posterior Compartment of The Thigh and Popliteal FossaSteph SantosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lower Limb: Muscle Charts: Cheat Sheet (English Terminology)Document9 paginiLower Limb: Muscle Charts: Cheat Sheet (English Terminology)yinose7198Încă nu există evaluări
- Muscles ReviewDocument32 paginiMuscles ReviewCorine RepatoÎncă nu există evaluări
- MeningesDocument43 paginiMeningesRehab NaeemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hip Joint: Important PointsDocument4 paginiHip Joint: Important PointsNamrah AfzalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Axillary Artery: Branches First (1 Branch) Second Part (2 Branches) Third (3 Branches) 1 2 4Document14 paginiAxillary Artery: Branches First (1 Branch) Second Part (2 Branches) Third (3 Branches) 1 2 4foster18Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 8 Lab Assignment - Appendicular Skeleton LabelingDocument6 paginiChapter 8 Lab Assignment - Appendicular Skeleton Labelingadriana blanco galianoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blue Boxes Lower LimbDocument4 paginiBlue Boxes Lower LimbZllison Mae Teodoro MangabatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cubital Fossa PDFDocument18 paginiCubital Fossa PDFKyle TongolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy - Anterior Forearm and Palm PDFDocument5 paginiAnatomy - Anterior Forearm and Palm PDFAngel Kim100% (2)
- Superficial Back Proximal Insertion Distal Insertion Innervation Blood Supply Function Latissimus DorsiDocument23 paginiSuperficial Back Proximal Insertion Distal Insertion Innervation Blood Supply Function Latissimus Dorsimeyouhere100% (1)
- Manual Muscle Testing: RD TH TH TH TH TH TH TH THDocument6 paginiManual Muscle Testing: RD TH TH TH TH TH TH TH THAljon S. TemploÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy - Upper LimbDocument72 paginiAnatomy - Upper LimbAiman ArifinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lower LimbDocument25 paginiLower LimbLalanFernandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Upper Extremity: Sufitni Megasari SitorusDocument37 paginiThe Upper Extremity: Sufitni Megasari SitorusFakhrur RaziÎncă nu există evaluări
- Upper LimbDocument31 paginiUpper LimbNandhana Kattuparambil SunojÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy-1 PDFDocument50 paginiAnatomy-1 PDFSaransh Ghimire100% (1)
- Upper Limb - Pectoral Region, Scapular Region, Axilla & Brachial PlexusDocument12 paginiUpper Limb - Pectoral Region, Scapular Region, Axilla & Brachial PlexusewijayapalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Midbrain ("Mesencephalon")Document56 paginiMidbrain ("Mesencephalon")Полина Бауэр100% (1)
- Upper Limb: Pectoral RegionDocument13 paginiUpper Limb: Pectoral RegionMariam Alavidze0% (1)
- Study Sheet - Gross Anatomy Lower - ExtremityDocument12 paginiStudy Sheet - Gross Anatomy Lower - ExtremityMuhammad BilalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lower Limb Anatomy Flashcards - QuizletDocument5 paginiLower Limb Anatomy Flashcards - QuizletAsif HanifÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lower Limb: Front and Medial Aspect of ThighDocument8 paginiLower Limb: Front and Medial Aspect of ThighErnie G. Bautista II, RN, MDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy MnemonicsDocument2 paginiAnatomy MnemonicsPia Boni0% (1)
- Popliteal Fossa: Dr.P.Sasikala, Assistant Professor of AnatomyDocument18 paginiPopliteal Fossa: Dr.P.Sasikala, Assistant Professor of AnatomySasikala Mohan100% (1)
- Muscle Origin Insertion Innervation Action: (Branch of The Brachial Plexus)Document58 paginiMuscle Origin Insertion Innervation Action: (Branch of The Brachial Plexus)sdfs sdfdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mnemonics Anatomy 1st SemDocument4 paginiMnemonics Anatomy 1st SemNastassja Callmedoctor Douse67% (3)
- Upper LimbDocument20 paginiUpper LimbsamzailÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 7 Lab Assignment - Axial Skeleton BonesDocument5 paginiChapter 7 Lab Assignment - Axial Skeleton Bonesadriana blanco galianoÎncă nu există evaluări
- UMass Medical School Mind Brain Behavior 1 Spinal Cord Atlas OverviewDocument11 paginiUMass Medical School Mind Brain Behavior 1 Spinal Cord Atlas Overviewnon_zense100% (1)
- PS 01 - Lower Limb Muscles Table From Gray'sDocument4 paginiPS 01 - Lower Limb Muscles Table From Gray'szivp610% (1)
- 01 Muscle Tables Upper LimbDocument7 pagini01 Muscle Tables Upper LimbhawkreadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Axilla and Brachial PlexusDocument22 paginiAxilla and Brachial Plexusromaisa akhtarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 14Document14 paginiLab 14Lueshen Wellington100% (1)
- Muscles of Lower LimbsDocument7 paginiMuscles of Lower LimbsFong Yu-hengÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mnemonic SDocument8 paginiMnemonic Smueen hashmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Muscle Flash CardsDocument127 paginiMuscle Flash Cardsjoelh9100% (3)
- The Back and Spinal Cord AnatomyDocument6 paginiThe Back and Spinal Cord AnatomyjsdlzjÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2nd Order (Unit 1 - B)Document5 pagini2nd Order (Unit 1 - B)uberjunk426801Încă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy Chart2Document16 paginiAnatomy Chart2Jeff WuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Musculoskeletal Anatomy GuideDocument9 paginiMusculoskeletal Anatomy Guidesimone dumbrell100% (1)
- Back MusclesDocument38 paginiBack MusclesAsmithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Muscles of Breathing and Posture - Functions and InnervationDocument6 paginiMuscles of Breathing and Posture - Functions and Innervatione jeighÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5-Scapular RegionDocument36 pagini5-Scapular Regionsama rasmyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oina MusclesDocument73 paginiOina MusclesShen AndradeÎncă nu există evaluări
- IV Fluid Management As An InternDocument2 paginiIV Fluid Management As An InternjsdlzjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analgesia For InternsDocument4 paginiAnalgesia For InternsjsdlzjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uni of Melb 2005 Mcqs EditedjrDocument19 paginiUni of Melb 2005 Mcqs EditedjrjsdlzjÎncă nu există evaluări
- INTERN Referee Process and Sample FormDocument2 paginiINTERN Referee Process and Sample FormjsdlzjÎncă nu există evaluări
- VMAT Protocol - Victorian Medical Assistance TeamDocument27 paginiVMAT Protocol - Victorian Medical Assistance TeamjsdlzjÎncă nu există evaluări
- DrugsDocument11 paginiDrugsjsdlzjÎncă nu există evaluări
- OsteoporosisDocument5 paginiOsteoporosisjsdlzjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Second StripeDocument1 paginăSecond StripejsdlzjÎncă nu există evaluări
- DKA: Diabetic Ketoacidosis Signs, Causes and TreatmentDocument3 paginiDKA: Diabetic Ketoacidosis Signs, Causes and TreatmentjsdlzjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hyperosmolar Hyperglycaemic StateDocument3 paginiHyperosmolar Hyperglycaemic StatejsdlzjÎncă nu există evaluări
- AMSA Rural Health SurveyDocument3 paginiAMSA Rural Health SurveyjsdlzjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mock Peg Stem: Zhengjie Lim 2018Document7 paginiMock Peg Stem: Zhengjie Lim 2018jsdlzjÎncă nu există evaluări
- FibroidsDocument4 paginiFibroidsjsdlzjÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHARGE SyndromeDocument1 paginăCHARGE SyndromejsdlzjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Explanation StationDocument4 paginiExplanation StationjsdlzjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prediction of Perinatal Depression From Adolescence and Before Conception (VIHCS) : 20-Year Prospective Cohort StudyDocument9 paginiPrediction of Perinatal Depression From Adolescence and Before Conception (VIHCS) : 20-Year Prospective Cohort StudyjsdlzjÎncă nu există evaluări
- MED1022 Study Guide 2014Document213 paginiMED1022 Study Guide 2014jsdlzj100% (1)
- PolypsDocument2 paginiPolypsjsdlzjÎncă nu există evaluări
- ArrhythmiasDocument4 paginiArrhythmiasjsdlzjÎncă nu există evaluări
- AAFP - Evaluation of Acute Abdomen in AdultsDocument8 paginiAAFP - Evaluation of Acute Abdomen in AdultsTe HineahuoneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Social Determinants of Health and Health PromotionDocument1 paginăSocial Determinants of Health and Health PromotionjsdlzjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Articular System and Joints OverviewDocument9 paginiArticular System and Joints OverviewjsdlzjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Overview of neuromuscular blocking agents and their mechanisms of actionDocument2 paginiOverview of neuromuscular blocking agents and their mechanisms of actionjsdlzjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute InflammationDocument38 paginiAcute InflammationjsdlzjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Muscles of The BackDocument1 paginăMuscles of The BackjsdlzjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zee's Autoimmunity, Basic Concept and ExamplesDocument2 paginiZee's Autoimmunity, Basic Concept and ExamplesjsdlzjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Epidemiology Summary - Weeks 1 To 6Document2 paginiEpidemiology Summary - Weeks 1 To 6jsdlzjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Own Notes-Anticancer 2Document2 paginiOwn Notes-Anticancer 2jsdlzjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Own Notes-Anticancer 1Document2 paginiOwn Notes-Anticancer 1jsdlzjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pott's DiseaseDocument30 paginiPott's DiseaseLucila Lugo100% (1)
- Energetics in Acupuncture Pages 2Document99 paginiEnergetics in Acupuncture Pages 2Geeta SajjanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4.abdomen and Pelvis Gross SpottersDocument122 pagini4.abdomen and Pelvis Gross Spottersmatt medmedmedicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gross Anatomy I OsteologyDocument42 paginiGross Anatomy I OsteologySonia FelixÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yamamoto New Scalp Acupuncture | Fast Musculoskeletal ReliefDocument5 paginiYamamoto New Scalp Acupuncture | Fast Musculoskeletal ReliefMaria Agustina Flores de Seguela100% (1)
- MANUAL THERAPY Course OutlineDocument6 paginiMANUAL THERAPY Course OutlineDanish LatifÎncă nu există evaluări
- NEET GT-5 SolutionsDocument12 paginiNEET GT-5 Solutionsabcxyz7799Încă nu există evaluări
- Support and movementDocument96 paginiSupport and movementmercynjesh20Încă nu există evaluări
- KSM Orthopedi New1Document20 paginiKSM Orthopedi New1rspku mayongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pedicles Are Short Projections, From The Superior Part of The Vertebral Body To TheDocument3 paginiPedicles Are Short Projections, From The Superior Part of The Vertebral Body To ThebarbacumlaudeÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Transmutation of Sexual EnergyDocument25 paginiThe Transmutation of Sexual EnergyCassandraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group 38 CaseDocument73 paginiGroup 38 CaseMarjune DimayugaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thorax and Chest WallDocument6 paginiThorax and Chest WallDale P. PolvorosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pott 6Document8 paginiPott 6Jeanie WangsaÎncă nu există evaluări
- EMG Analysis of Latissimus Dorsi Erector Spinae and Middle TrapDocument68 paginiEMG Analysis of Latissimus Dorsi Erector Spinae and Middle TrapYuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture Activities No. 6 Skeletal System: Guide Questions AnswersDocument13 paginiLecture Activities No. 6 Skeletal System: Guide Questions AnswersPrancheska Abigayle Peneyra SantiagoÎncă nu există evaluări
- FIU - Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Clinical EvaluationDocument51 paginiFIU - Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Clinical Evaluationmursyid nasruddinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and Physiology Test 2 PrepDocument21 paginiAnatomy and Physiology Test 2 PrepNicholas SirunoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manipulations For TuinaDocument95 paginiManipulations For TuinaFabrizio F. Caragnano100% (2)
- Thoracic Spine Rotation in Healthy Adults - Scurt PDFDocument6 paginiThoracic Spine Rotation in Healthy Adults - Scurt PDFBondreaTiberiuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Equine Body Condition ScoringDocument7 paginiEquine Body Condition ScoringAlbert Villasevil Florensa100% (1)
- DR Ara Khan Marwat: Join My Watssap Group For Part-1 Books, Papers and UpdatesDocument25 paginiDR Ara Khan Marwat: Join My Watssap Group For Part-1 Books, Papers and UpdatesmisdduaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy of Bone and JointDocument48 paginiAnatomy of Bone and JointKamalia Bint MuhammadÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2946 1308 00 Leroy Somer LSA47.2 Installation & MaintenanceDocument20 pagini2946 1308 00 Leroy Somer LSA47.2 Installation & MaintenanceJORGE ARMANDO CARRASCO TICLLEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Axial Body - Muscles (Head, Neck & Trunk)Document14 paginiAxial Body - Muscles (Head, Neck & Trunk)HaleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- ANP 300 Exam 1 ReviewDocument8 paginiANP 300 Exam 1 ReviewNerdy Notes Inc.Încă nu există evaluări
- Traumatology Orthopaedic EXAMDocument219 paginiTraumatology Orthopaedic EXAMElo GonçalvesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elaine Atkins - Jill Kerr - Emily Goodlad-A Practical Approach To Orthopaedic Medicine - A Practical Approach-Elsevier Health Sciences UK, Churchill Livingstone (2010)Document481 paginiElaine Atkins - Jill Kerr - Emily Goodlad-A Practical Approach To Orthopaedic Medicine - A Practical Approach-Elsevier Health Sciences UK, Churchill Livingstone (2010)Anonymous AoZDT6Încă nu există evaluări
- Revised CompendiumDocument46 paginiRevised CompendiumEvon GohÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brachial Plexus InjuriesDocument346 paginiBrachial Plexus InjuriesvinaymanÎncă nu există evaluări