Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
HSN - 2mks With Ans
Încărcat de
archumeenabaluTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
HSN - 2mks With Ans
Încărcat de
archumeenabaluDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Sub Code & Title: EC 1009 High Speed Networks
Year & SEM: IV /VII (ECE A&B)
UNIT I
1).Define Datagram.
i. In packet switching, a packet, independent of other packets is referred to as a datagram.
ii. It carries information sufficient for routing from the originating data terminal equipment (DTE)
to the destination DTE without the necessity of establishing a connection between the DTEs and the
network.
2). Define virtual circuit.
A packet switching service in which a connection (virtual circuit) is established between 2
stations at the start of transmission. All packets follow the same route, need not carry a complete address,
and arrive in sequence.
3).What are the functions of LAPF core protocol?
LAPF core provides a minimal set of data link control functions, consists of the following:
i.
Frame delimiting, alignment, data transparency.
ii.
Frame multiplexing/de-multiplexing using the address field.
iii.
Inspection of the frame to ensure that it is neither too long nor too short.
iv.
Detection of transmission errors.
v.
Congestion control functions.
4).Define cells.
In the case of ATM, the information flow on each logical connection is organized into fixed size
packets, called cells.
5).What is the difference between VCC and VPC?
VCC:
i.
A VCC is setup between two end users through the network and a variable rate, fullii.
VPC:
i.
ii
duplex flow of fixed size cells are exchanged over the connection.
VCCs are also used for user-network exchange and network-network exchange.
A virtual path connection is a bundle of VCCs that have the same
End points.
the virtual path technique helps contain the control cost by grouping
connections
sharing common paths through the network into a single unit.
6).What is the advantages of virtual path?
i. Simplified network architecture.
ii. Increased network performance and reliability.
iii. Reduced processing and short connection setup time.
iv. Enhanced network services.
7).What are the uses of VCC?
i). Between end users:
It can be used to carry end-to-end user data and also it can
control signaling between end users.
ii). Between an end user and a network entity:
[Type text]
be used to carry
Sub Code & Title: EC 1009 High Speed Networks
Year & SEM: IV /VII (ECE A&B)
Used for user-to-network control signaling.
iii). Between two network entities:
Used for network traffic management and routing functions.
8). What are the characteristics of VPC and VCC?
i.
Quality of service
ii.
Switched and semi-permanent virtual channel connections.
iii.
Cell sequence integrity
iii.
Traffic parameter negotiation and usage monitoring
9) What is cell loss ratio?
Ratio of cells lost to cell transmitted is referred to a cell loss ratio.
10) What are the traffic parameters available in ATM?
The traffic parameters must be viewed from two different perspectives.
(i)
Source traffic descriptor
peak cell rate
sustainable cell rate
maximum burst size
minimum cell rate
maximum frame size
(ii)
connection traffic descriptor
source traffic descriptor
cell delay variation tolerance
conformance definition
11) What is the difference between switched & semi-permanent VCC?
A switched VCC is an on-demand connection, which requires call control signaling for setup and
tearing down.
A semi-permanent VCC is one that is of long duration is set up by configuration or network
management action.
12) Draw the ATM cell format.
[Type text]
Sub Code & Title: EC 1009 High Speed Networks
GFC
VPI
Year & SEM: IV /VII (ECE A&B)
Virtual Path identifier (VPI)
VPI
VPI
5
Virtual path identifier
Payload
Payload
CLP
Header error control
Information field
48 Octets
User NW interface
Virtual path identifier
CLP
Header error control
53
octets
Information field
48 Octets
NW NW interface
13) What is the function of generic flow control?
GFC can be used for control of cell flow only at the local user-network interface.
The field could be used to assist the customer in controlling the flow of traffic for different
qualities of service.
14) What is the function of payload type?
The payload type field indicates the type of information in the information field
Payload type has giving the 3 bit coding
(i)
the value of 0 in the 1st bit indicates the user information that is information from
(ii)
(iii)
next higher layer.
2nd bit indicates whether congestion has been experienced
3rd bit known as the ATM user to ATM user indicates bit is a one bit field that can
be used to convey information between end users
15) What are the service categories have been defined by ATM cell format?
There are 2 types of service categories used in ATM cell format.
(i)
Real time service
CBR constant bit rate
r-VBR real time variable bit rate
(ii)
Non-real time service
Ntr-VBR non real time VBR
UBR unspecified bit rate
ABR available bit rate
GFR guaranteed frame rate
[Type text]
Sub Code & Title: EC 1009 High Speed Networks
Year & SEM: IV /VII (ECE A&B)
16) What are the applications of constant bit rate?
Constant bit rate requires the maintenance of a timing relation is used and the transfer is
connection oriented.
(i)
video conference
(ii)
connection oriented and timing is important audio/video retrieval
17) What are the services provided by the AAL protocol?
* Handling of transmission errors
* Segmentation & re-assembly to enable layer blocks of data to be carried in the information field
of ATM cells
* Handling of lost and mis-inserted cell condition
* flow control & timing control
18) What is meant by SAP?
SAP service access point
Each AAL user attaches to AAL at a service access point, which is simply the address of
the application. This layer is then service dependent.
19) What is the function of CS layer & SAR layer?
CS layer:
Convergence sub-layer provides the functions needed to support specific application
using AAL. Each AAL user attaches to AAL at a SAP, which is simply the address of the application. This
Sublayer is then service dependent.
SAR layer:
The segmentation & reassembly Sublayer is responsible for packaging information
received from CS into cells for transmission & unpacking at the another end.
20) What are the advantages of AAL5 protocol compared with another?
(i)
reduced protocol processing overhead
(ii)
reduced transmission overhead
(iii)
Ensure adaptability to existing transport protocols.
These are the advantages of AAL5 protocol compared with another type.
21) What are the differences between fast & gigabit Ethernet?
Fast Ethernet
Gigabit Ethernet
Data rate used in 100Mbps
Data rate used in 10Gbps, 1Gbps
Transmission media used are UTP,STP &
It uses UTP, shielded cable and optical fiber.
optical fiber
22) Define fabric.
[Type text]
Sub Code & Title: EC 1009 High Speed Networks
Year & SEM: IV /VII (ECE A&B)
Collection of switching elements is referred to as a fabric. These elements are inter-connected by
point-point links between ports or individual nodes and switches.
23) What are the major strengths of fiber channel?
One of the major strengths is that if provides a range of option for the physical medium, the data
rate on that medium and the topology of the network.
24) What are the requirements of wireless LAN?
o Throughput
o No of nodes
o Connection to backbone LAN
o Service area
o Battery power consumption
o Transmission robustness & security
o Network operation
o License free operation
o Hand off operation
o Hand off / roaming
o Dynamic configuration
25) What is meant by access point?
A basic service set may be is isolated or it may be connected to a backbone distributed system
through an access point.
AP is the logic within a station that provides access to DS by providing DS service in addition to
acting as a station.
UNIT-2
1) What is the function of Queue?
The queue is in FIFO order, which has two buffers with a particular memory & it can accept the
frame. If memory fills, it discards the frames
2) What are the queue parameters?
average rate
1.
[Type text]
Sub Code & Title: EC 1009 High Speed Networks
2.
waiting time
3.
average no of waiting W
4.
average service time Ts
5.
utilization P
6.
average no of resident r
7.
mean residence time Tr
Year & SEM: IV /VII (ECE A&B)
3) Draw the single server queuing system.
Waiting line (queue)
Arrivals
Departure
Dispatching discipline
Server
Arrival rate
Ts Service time
P utilization
Waiting time
w items waiting
r items resident in queuing system
Tr residence time
4) Define:
Waiting time
The mean time that an item must wait is Tw
Service time:
It is the time interval between the dispatching of an item to the server & the departure of that item
from the server.
Utilization:
It is the fraction of time that the server is busy, measured over some interval of time.
Resident time:
The average time that an item spends in system, waiting & being served is referred as residence
time Tr
5) What are the char of queuing system?
The char of a queuing system are,
item population
[Type text]
queue size
dispatching discipline
Sub Code & Title: EC 1009 High Speed Networks
Year & SEM: IV /VII (ECE A&B)
6) What is the basic dispatching discipline approach?
When the server becomes free & if there is more than one item waiting, a decision must be made
as to which item to dispatch next. The simplest approach is FIFO, FCFS (first come first served) this
discipline is what is normally implied when the term queue is used.
7) Compare multi-server queue & multiple single servers.
Multi-server
Multiple single server
Server
Server
Server
Server
Arrivals
Arrivals
Departure
Queue
Server
Server
Single queue is used
Departure
N queues are used
8) Write littles formula for single server queue.
Little formula for single server queue is
(i)
P= Ts
(ii)
r=w+P
9) What is Kendalls notation P?
Kendalls notation is X/Y/N,
Where,
X refers to distribution of the inter-arrival times,
Y refers to the distribution of service times &
N refers to the no of servers
10) What are the effects of congestion?
As the load on the network continues to increase, the queue lengths of the various modes continue
to grow. Eventually, throughput drops with increased load. So, the main effect of congestion is, under
there circumstances the effective capacity of system is virtually zero.
11) What is congestion?
If packets arrive too fast for the node to process them or faster than packets can be cleared from
the outgoing buffers, the queue will overflow & leads to congestion.
[Type text]
Sub Code & Title: EC 1009 High Speed Networks
Year & SEM: IV /VII (ECE A&B)
12) What are the congestion control techniques?
The congestion control techniques are,
(i)
backpressure
(ii)
choke packet
(iii)
implicit signaling
(iv)
explicit signaling
backward signaling
forward signaling
13) What is the concept of backpressure tech & writes its application?
Backpressure can be selectively applied to logical connections, so that the flow from one node to
the next is restricted or halted & this restriction propagates back along the connections t the source
Application:
(i)
X.25 based packet switching network
(ii)
IP based internets
14) What is choke packet & its application?
A choke packet is a control packet generated at a congested node& transmitted back to a source
node restrict traffic flow. (e.g.) ICMP
Application:
Source quench message can be used by a route or host to discard IP datagram because of a full
buffer.
15) What is implicit signaling & when it is used?
If a source is able to detect increased delays & packet discards, then it has implicit evidence of
network congestion. It is used when
(i)
transmission delay is increased
(ii)
packets are discarded
16) Compare forward & backward signaling.
Backward signaling
Notifies
the
source
that
congestion
avoidance procedures should be initiated
Forward signaling
Notifies the user that congestion avoidance
procedures should be initiated
[Type text]
Where applicable for traffic in opposite
Where applicable for traffic of the received
direction of the received packet
packet
Sub Code & Title: EC 1009 High Speed Networks
Year & SEM: IV /VII (ECE A&B)
17) What are explicit congestion signaling approaches?
It is of three general categories
(i)
Binary: A bit is set in a data packet and it is forwarded by the congested node.
(ii)
Credit based: It is based on providing an explicit credit to a source over a logical
connection.
(iii)
Rate based: It is based on providing an explicit data rate limit.
18) What is fairness in congestion control?
If all of the queue buffers are of equal length, then the queues with the highest traffic load will
suffer discards more often allowing lower- traffic connections a fair share of the capacity.
19) What are congestion control techniques used in PSN?
1. choke packet
2. Relay on routing information
3. Make use of an end-to-end probe packet
4. Allow packet switching nodes to add congestion information to packets as they go by.
20) What is congestion avoidance?
Congestion avoidance provides guidance to end systems about congestion in network. The
technique used is forward & backward explicit congestion notification.
21) What is the concept of CIR?
CIR (committed information rate is the rate, in bits per second, that the network agrees to support
for a particular frame mode connections
22) What is relation between CIR & access rate?
The relation between CIR & Access rate is
CIR i,j
< Access rate j
Where,
CIR i,j CIR for connection i on channel j.
Access rate j data rate of user access channel j.
[Type text]
Sub Code & Title: EC 1009 High Speed Networks
Year & SEM: IV /VII (ECE A&B)
UNIT III
1) What are the different types of TCP implementation policy?
*Sent policy.
*Deliver policy.
*Accept policy.
*Retransmit policy.
*Acknowledgement policy.
2) Define Back off?
A more sensible policy used in TCP source increase its RTO each time, the same segment is
retransmitted, this is known as back off RTO process
3) State the condition that must be met for a cell to conform.
In case of ATM, the information flow on each logical connection is organized into fixed size
packets called cells. Cells should arrive with in theoretical arrive time but with in CDVT (limitation) cell
is conformed.
4) What are the mechanisms used in ATM traffic control to avoid congestion condition?
Resource management
Connection admission control
Usage parameter control
Traffic shaping
5) How is a time useful to control congestion in TCP?
The value of RTO (Retransmission time out) has a critical effect on TCPs reaction to congestion. Hence
by calculating RTO effectively congestion can be controlled.
6) Why congestion control is difficult to implement in TCP?
The end system is expected to exercise flow control upon the source end system at a higher layer. Thus it
is difficult to implement in TCP.
7) What are the accept policies used in TCP traffic control?
In order policy
In window Policy
8) What is meant by silly window syndrome?
[Type text]
Sub Code & Title: EC 1009 High Speed Networks
Year & SEM: IV /VII (ECE A&B)
If frequently data are sending as small segment, the response will be speed in sender side but it cause
degradation in performance. This degradation is called silly window syndrome.
9) What is meant by cell insertion time?
Cell insertion time is the time taken to insert a single cell on to the network.
10) What are the mechanisms used in TCP control congestion?
RTO timer management
Window management
11) What is meant by allowed cell rate?.
The current rate at which source is permitted to send or transmit cell in ABR mechanism is called allowed
cell rate.
12) Define behavior class selector?
BCS enables an ATM network to provide different service levels among UBR connections by associating
each connection with one of a set of behavior class.
UNIT IV
1) What is need for IS and DS?
To cope with the demand of
(i)
high volume client server applications
(ii)
tremendous volume of web traffic
(iii)
increasing graphics intensive
it is not enough to increase internet capacity but sensible and effective methods for managing the traffic
and controlling congestion are needed. That is IS and DS are needed.
2) Compare IS and DS.
IS
Reserve network resources for a particular
DS
Does not attempt to reserve
QOS
views totality of the current traffic
Does not attempt to total traffic
[Type text]
Sub Code & Title: EC 1009 High Speed Networks
Year & SEM: IV /VII (ECE A&B)
3) What is elastic and inelastic traffic? Write its applications.
Elastic traffic:
It is that which can adjust over wide ranges to changes in delay and throughput across an internet
and still meet the needs of its applications
Applications:
It is used in TCP or UDP including FTP , SMTP, Telnet, SNMP, HTTP etc
Inelastic traffic:
It does not easily adapt, if it all to changes in delay and throughput across an internet
Applications:
Teleconferencing, stock trading etc.,
4) What are the requirements of inelastic traffic?
(i) Throughput
(ii) Delay
(iii)jitter
(iv) packet loss
5) What are the functions to manage congestion and provide in QOS in ISA?
ISA makes use of the following functions to manage congestion and provide QOS support.
(i)
Admission control
(ii)
Routing algorithm
(iii)
Queuing discipline
(iv)
Discard policy
6) What are functions of packet scheduler?
(i) It manages one or more queues for each output port
(ii) It determines the order in which queued packets are transmitted and selection of packets for
discard, if necessary
7) What are the components in ISA?
1. Reservation protocol
2. Admission control
3. Management agent
4. Routing protocol
5. Classifier and route selection
6. Packet scheduler
8) What are services available in ISA?
(i) Guaranteed Service
(ii) Controlled Load
(iii) Best Effort
9) What is concept of token bucket scheme ?
The bucket represents a counter that indicates the allowable no of octets of IP data that can be
sent at any time, the two specifications of this scheme are
(i)
Token replenishment rate R
(ii)
Bucket size B
[Type text]
Sub Code & Title: EC 1009 High Speed Networks
Year & SEM: IV /VII (ECE A&B)
10) What are the advantages of token bucket scheme?
(i) Many traffic sources can easily and accurately be defined
(ii) It provides a concise description of the load to be imposed by flow
(iii)It provides input parameters to a policing function
11) What are the key elements of guaranteed service?
1. The service provides assured capacity level or data rate
2. There is a specified upper bound on the queuing delay through the network
3. No queuing losses
12) What are the key elements of controlled load?
1. The service tightly approximates the behavior visible to applications receiving best effort
service under unloaded conditions.
2. No specified upper bound on the queuing delay through the network
3. Almost no queuing losses
13) What is fair queuing?
With fair queuing, each incoming packet is placed in appropriate queue and these queues are
serviced in round robin fashion, taking one packet from each non empty queue in turn and empty queues
are skipped over.
14) What is drawback FIFO?
i.
No special treatment is given to packets from flow that or of higher priority or are more delay
ii.
iii.
sensitive
FIFO queuing results in large average delay/ packet
Also FIFO queuing results in congestion in a greedy TCP connection
15) What is queuing approach based in ISA?
The queuing approach used in ISA is FIFO queuing discipline also known as FCFS (First Come
First Served) at each output port
16) What is concept of BRFQ?
BRFQ ( Bit round fair queuing) is designed to emulate a bit by bit round robin discipline. It is
implemented by computing virtual starting and finishing times on the fly as if ps where running.
17) What is processor sharing?
In particular, if there are N queues and each of the queue always has a packet to send, then each
queue receives exactly 1/N of the available capacity. This bit-by-bit approach is known is processor
sharing.
18) What is concept of RED?
The most important of pro-active packet discard is knows as RED( Random early detection) the
design goals are
[Type text]
Sub Code & Title: EC 1009 High Speed Networks
i.
ii.
iii.
iv.
Year & SEM: IV /VII (ECE A&B)
The congestion avoidance
Global synchronization avoidance
Avoidance of bias against busty traffic
Bound on average queue length
19) What are the characteristics of DS?
i.
IP packets are labeled for differing QOS treatment using IPV4 type of service field.
ii.
SLA( Service level agreement) is established
iii.
It provides a built in aggregation mechanism.
20) What is SLA?
A service contract between a customer and a service provider that specifies the forwarding service
a customer should receive.
21) Draw DS field format.
DSCP
Class selector code points
DS field
7
X
Precedence
TOS
7
X
X - Unused
IPV4 type of service field
22) What are the traffic conditioning system elements and its function in DS?
Classifier: separates submitted packets into different classes
Meter: measures submitted traffic for conformance to a profile
Marker: policies traffic by re-marking packets with code points as needed
Shaper: Policies traffic by delaying packets
Dropper: drops packets
23) What is PHB?
As part of the DS standardization effort, specific types of PHBs need to be defined, which can
be associated with specific DS services. The two types of PHBs are
i.
Expedited forwarding PHB
ii.
Assured forwarding PHB
24) What is premium service?
EFPHB is a mechanism that can be used to support the premium service. A premium service is
low loss, low delay, low jitter, assured bandwidth, end-end service through DS domains.
25) What is Best effort service?
[Type text]
Sub Code & Title: EC 1009 High Speed Networks
Year & SEM: IV /VII (ECE A&B)
AFPHB is designed to provide a service superior to best effort but one that does not require the
reservation of resources with in an internet and does not require the use of detailed discrimination among
flows from different users.
UNIT V
1) What are the reservations attributes and styles in RSVP.
Sender Selection
Explicit
Wild card
Reservation Attributes
Distinct
Shared
Fixed-Filter style(FF style)
Shared-Explicit(SE)style
Wild-card Filter(WF)style
2) Draw the diagram showing relationship among session, flow spec & filter spec
Packets that
Pass filter
Packet scheduler
Packets of one session
Flowspec
Filterspec
QOS
delivery
Best-Effort
Delivery
Other Packets
3) Define session RSVP.
Once a reservation is made at a router by a particular destination, the router considers this as a
session and allocates resources for the life of that session.
Session has Destination IP address,IP protocol identifier, Destination Port.
4) Define Flow specification in RSVP.
The flow specification of RSVP specifies a desired QoS and is used to set parameters in a nodes packet
scheduler. Flow specification defined by Service class, Reserve Spec , Traffic Spec.
5) What is the types reservation style used in RSVP?
[Type text]
Sub Code & Title: EC 1009 High Speed Networks
Year & SEM: IV /VII (ECE A&B)
Wild card filter reservation style
Fixed filter reservation style
Shared explicit reservation style
6) Define Label swapping in MPLS.
The basic operation of looking up an incoming label to determine the outgoing label and forwarding is
called Label swapping
7) Define Label switched HOP in MPLS.
The hop between two MPLS nodes on which forwarding is done using labels is called Label switch.
8) Define label switched router in MPLS
An MPLS network consists of a set of nodes called label switched router (LSR) capable of switching and
routing packets on the basis of which a label has been added to each packets.
9) What is the purpose of time to live field in label format?
The value of this field is decremented at each router and the packet is dropped if the count falls to zero.
10) What is meant by integrated layer processing in RTP?
In TCP/IP each layer processed sequentially, where as in integrated layer processing, adjacent layers are
tightly coupled and they function properly.
[Type text]
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- ECE1009 High Speed Networks Questions and AnswersDocument16 paginiECE1009 High Speed Networks Questions and AnswersarevazhagunvcÎncă nu există evaluări
- High Speed Networks Two Marks Questions and Answers 2MARKS-LibreDocument27 paginiHigh Speed Networks Two Marks Questions and Answers 2MARKS-Librethangam8891Încă nu există evaluări
- Ec1008 Becse HSN 2marks With AnswersDocument12 paginiEc1008 Becse HSN 2marks With AnswerssansunameÎncă nu există evaluări
- HSN 2 Marks LatestDocument81 paginiHSN 2 Marks LatestmrarunpsgÎncă nu există evaluări
- High Speed Networks - Cs2060 Two Marks Questions and AnswersDocument28 paginiHigh Speed Networks - Cs2060 Two Marks Questions and Answersbikkinpark1Încă nu există evaluări
- AN1630 - High Performance Communication NetworksDocument17 paginiAN1630 - High Performance Communication NetworksPavithra SunÎncă nu există evaluări
- UNIT3NGNDocument5 paginiUNIT3NGNshubham chauhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cs2060-High Speed Networks Question Bank Department:ECE Unit - 1 Part-ADocument5 paginiCs2060-High Speed Networks Question Bank Department:ECE Unit - 1 Part-AFrank IssÎncă nu există evaluări
- NetworkDocument156 paginiNetworkavi0341Încă nu există evaluări
- 2 Basic ATM Technical CharacteristicsDocument10 pagini2 Basic ATM Technical Characteristicsz88zaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCNA Interview QuestionsDocument6 paginiCCNA Interview QuestionsGarryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medi-Caps University 2020-2021Document11 paginiMedi-Caps University 2020-2021Krati ChhabraÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCNA1 Final ExamDocument74 paginiCCNA1 Final ExamDidi SunardiÎncă nu există evaluări
- TCP/IP PROTOCOL SUITE AND ATM LAYERSDocument12 paginiTCP/IP PROTOCOL SUITE AND ATM LAYERSsravan123Încă nu există evaluări
- Erode Sengunthar Engineering College (An Autonomous Institution)Document16 paginiErode Sengunthar Engineering College (An Autonomous Institution)mohanapriyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- QB3Document14 paginiQB3prakash_oxfordÎncă nu există evaluări
- Frequently Asked Ccna Interview QuestionsDocument11 paginiFrequently Asked Ccna Interview QuestionsDavid ChungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Virtual-Circuit Networks: Frame Relay and ATM TechnologiesDocument58 paginiVirtual-Circuit Networks: Frame Relay and ATM TechnologiesMythili NatarajanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter Eight Network Control and Monitoring: Circuit SwitchingDocument7 paginiChapter Eight Network Control and Monitoring: Circuit Switchingshavali56Încă nu există evaluări
- Wiley Encyclopedia of Computer Science and Engineering - 1st Edition (5 Volume Set) (2009) PDFDocument2.365 paginiWiley Encyclopedia of Computer Science and Engineering - 1st Edition (5 Volume Set) (2009) PDFManoj Kumar Gunturi100% (2)
- CCNADocument5 paginiCCNADevesh Kumar VermaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCNA Interview Questions and AnswersDocument12 paginiCCNA Interview Questions and AnswersChakibMedchakibÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCN Lab Interview QuestionsDocument13 paginiCCN Lab Interview QuestionsMurali MC MirleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Examen 4-7Document10 paginiExamen 4-7Jhon RojasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Qos and Atm: Kimmo Ahonen Nokia TelecommunicationsDocument6 paginiQos and Atm: Kimmo Ahonen Nokia TelecommunicationsSandhya SandyÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Core FAQ FileDocument165 paginiThe Core FAQ Fileapi-3736604Încă nu există evaluări
- Ccna InterviewDocument22 paginiCcna InterviewRahul RocksÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Do You Understand by Internet? List The Uses. What Does Protocol Layering Mean?Document20 paginiWhat Do You Understand by Internet? List The Uses. What Does Protocol Layering Mean?jagan19781978Încă nu există evaluări
- Dc1621 High Speed Switching ArchitectureDocument18 paginiDc1621 High Speed Switching ArchitectureVisakh VijayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Department of Computer Science and Engineering: PREPARED BY: Mr. D. Ramkumar - A.P-CSEDocument38 paginiDepartment of Computer Science and Engineering: PREPARED BY: Mr. D. Ramkumar - A.P-CSEanish.t.pÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cs9251 Mobile Computing 2marks 16marks Question PapersDocument11 paginiCs9251 Mobile Computing 2marks 16marks Question PapersNivithaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Encyclopedia of Computer Science and EngineeringDocument1.770 paginiEncyclopedia of Computer Science and Engineeringmythulasi100% (2)
- Missing AnswersDocument8 paginiMissing AnswersManzil TanvirÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is CPRI & eCPRI?Document4 paginiWhat Is CPRI & eCPRI?Pushpendra Kumar0% (1)
- 3G Communication Protocols: 4.1 UTRAN Protocol Structure: The Encryption Mechanism Is Built Into RadioDocument9 pagini3G Communication Protocols: 4.1 UTRAN Protocol Structure: The Encryption Mechanism Is Built Into RadioSithija AlwisÎncă nu există evaluări
- A) Guided MediaDocument12 paginiA) Guided Mediabharath5911Încă nu există evaluări
- How Many Numbers of Addresses Are Usable For Addressing in A Class C Network?Document13 paginiHow Many Numbers of Addresses Are Usable For Addressing in A Class C Network?repovinodhÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4G Interveiw QqquestionsDocument25 pagini4G Interveiw QqquestionssamehÎncă nu există evaluări
- Juenal CorbaDocument12 paginiJuenal CorbaLaura Veronika Diah MousehunterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asynchronous Transfer Mode ATM NetworksDocument21 paginiAsynchronous Transfer Mode ATM Networkssurya selvamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asynchronous Transfer Mode: Presenters: Shahid Iqbal & Haris TariqDocument45 paginiAsynchronous Transfer Mode: Presenters: Shahid Iqbal & Haris TariqHusnainÎncă nu există evaluări
- New Version: CCNA 1 Final Exam Answers v6.0Document25 paginiNew Version: CCNA 1 Final Exam Answers v6.0cÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atm Networks: A Seminar OnDocument24 paginiAtm Networks: A Seminar OnAmbati Naga VishnuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cs9251 Mobile Computing 2marks 16marks Question PapersDocument11 paginiCs9251 Mobile Computing 2marks 16marks Question PapersValar MathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Telecom Source 10 Slide Technology SeriesDocument12 paginiThe Telecom Source 10 Slide Technology SeriesPrasant Nag KellaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Com FactsDocument8 paginiCom Factsapi-3713843Încă nu există evaluări
- What Are The Two Types of Transmission Technology Available?Document6 paginiWhat Are The Two Types of Transmission Technology Available?sandy14312Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 23: Data-Link Protocols and Data Communications NetworksDocument7 paginiChapter 23: Data-Link Protocols and Data Communications NetworksSarah Rivie Mae BeloroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Top 70 CCNA Interview Questions & AnswersDocument8 paginiTop 70 CCNA Interview Questions & AnswersMurali DharanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Netwirk 2 Marks 1Document40 paginiComputer Netwirk 2 Marks 1Amirtharajan RengarajanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Part-A (University Questions) : Sengunthar College of Engineering, TiruchengideDocument31 paginiPart-A (University Questions) : Sengunthar College of Engineering, TiruchengideAlwarsamy RamakrishnanÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesDe la EverandCCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesÎncă nu există evaluări
- CISA Exam-Testing Concept-OSI Architecture (Domain-5)De la EverandCISA Exam-Testing Concept-OSI Architecture (Domain-5)Încă nu există evaluări
- Implementing IP and Ethernet on the 4G Mobile NetworkDe la EverandImplementing IP and Ethernet on the 4G Mobile NetworkEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Handbook of Serial Communications Interfaces: A Comprehensive Compendium of Serial Digital Input/Output (I/O) StandardsDe la EverandHandbook of Serial Communications Interfaces: A Comprehensive Compendium of Serial Digital Input/Output (I/O) StandardsEvaluare: 1 din 5 stele1/5 (4)
- WAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksDe la EverandWAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksÎncă nu există evaluări
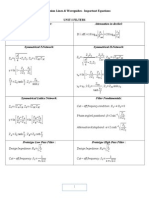
- Attenuation in Neper: Attenuation in Decibel:: 1 2 LN 20 LogDocument3 paginiAttenuation in Neper: Attenuation in Decibel:: 1 2 LN 20 LogarchumeenabaluÎncă nu există evaluări
- Attenuation in Neper: Attenuation in Decibel:: 1 2 LN 20 LogDocument3 paginiAttenuation in Neper: Attenuation in Decibel:: 1 2 LN 20 LogarchumeenabaluÎncă nu există evaluări
- HSN SyllabusDocument1 paginăHSN SyllabusarchumeenabaluÎncă nu există evaluări
- September 2015 Current AffairsDocument10 paginiSeptember 2015 Current AffairsarchumeenabaluÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tele MedicineDocument11 paginiTele MedicinearchumeenabaluÎncă nu există evaluări
- TrigonometruyDocument3 paginiTrigonometruyRitu SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SSC CGL Exam 101113Document20 paginiSSC CGL Exam 101113archumeenabaluÎncă nu există evaluări
- July 2015 Current AffairsDocument4 paginiJuly 2015 Current AffairsarchumeenabaluÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quants-Points 2 Remember For CAT and XATDocument10 paginiQuants-Points 2 Remember For CAT and XATbilalak1990Încă nu există evaluări
- GeometryDocument31 paginiGeometryarchumeenabalu100% (1)
- SYLLABUSDocument2 paginiSYLLABUSarchumeenabaluÎncă nu există evaluări
- CryptographyDocument38 paginiCryptographyAmar SawriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bus Arbitration Means Settlement Among Different ModulesDocument1 paginăBus Arbitration Means Settlement Among Different ModulesarchumeenabaluÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fundamental IntroductiontothePracticeofTelemedicineDocument7 paginiFundamental IntroductiontothePracticeofTelemedicinearchumeenabaluÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced pipelining techniques for instruction level parallelismDocument108 paginiAdvanced pipelining techniques for instruction level parallelismAmit7837Încă nu există evaluări
- In Computer ProgrammingDocument1 paginăIn Computer ProgrammingarchumeenabaluÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Optical CommunicationDocument13 paginiIntroduction To Optical CommunicationJitendra ThakurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter08 MultiprocessorsDocument24 paginiChapter08 MultiprocessorsarchumeenabaluÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cryptography & Network SecurityDocument63 paginiCryptography & Network Securityrubyamala100% (1)
- 3DDocument37 pagini3DJubin JainÎncă nu există evaluări
- GeometryDocument31 paginiGeometryarchumeenabalu100% (1)
- DefibrillationDocument11 paginiDefibrillationarchumeenabaluÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 12Document74 paginiChapter 12archumeenabaluÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 - Fundamentals of Computer DesignDocument40 paginiChapter 1 - Fundamentals of Computer Designarchumeenabalu100% (1)
- Op-Amp Fundamentals ExplainedDocument32 paginiOp-Amp Fundamentals ExplainedMd Asadul HoqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data Communicatin and NetworkingDocument30 paginiData Communicatin and NetworkingarchumeenabaluÎncă nu există evaluări
- CommunicationsDocument56 paginiCommunicationsarchumeenabaluÎncă nu există evaluări
- SYLLABUSDocument2 paginiSYLLABUSarchumeenabaluÎncă nu există evaluări
- GCTC Public Wifi BlueprintDocument74 paginiGCTC Public Wifi BlueprintepraetorianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quotation PT - SNET 20230524 KCC KTI Rev1Document1 paginăQuotation PT - SNET 20230524 KCC KTI Rev1bajoesapoetraÎncă nu există evaluări
- All Units MC PDFDocument332 paginiAll Units MC PDFNahidaNigarÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCN - Lab - Manual (17 Scheme)Document41 paginiCCN - Lab - Manual (17 Scheme)Vijay PatilÎncă nu există evaluări
- NetSDK Programming ManualDocument49 paginiNetSDK Programming ManualRodrigo VieiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux-6Document809 paginiRed Hat Enterprise Linux-6lamsal123Încă nu există evaluări
- Ariva! Events Management, IncDocument18 paginiAriva! Events Management, IncJoeyDeGuzmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- MDM Clix CommandsDocument11 paginiMDM Clix CommandsSunnyInd786Încă nu există evaluări
- DS 5400Rzl2SwitchSeriesDocument23 paginiDS 5400Rzl2SwitchSeriesyandi solahudinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Networks - Grade 9Document5 paginiNetworks - Grade 9ijsjhsaogÎncă nu există evaluări
- Virtuoso: Distributed Computing Using Virtual Machines: Peter A. DindaDocument49 paginiVirtuoso: Distributed Computing Using Virtual Machines: Peter A. DindaakashreeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sep - Nov 2011Document44 paginiSep - Nov 2011JosephatNjorogeMÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ultrasonic Parking Guidance System OverviewDocument38 paginiUltrasonic Parking Guidance System OverviewarmasciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digital Literacy Skills-Finding, Using, Creating Information and Understanding Digital Practices Not Confident Somewhat Confident Very ConfidentDocument3 paginiDigital Literacy Skills-Finding, Using, Creating Information and Understanding Digital Practices Not Confident Somewhat Confident Very ConfidentJana Luz Dumam-ag PabalayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cain & Abel DescriptionDocument3 paginiCain & Abel Descriptionmango1812Încă nu există evaluări
- Department of Education: (If Recipient Pls. Check)Document3 paginiDepartment of Education: (If Recipient Pls. Check)Ice JimenezÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3G Air InterfaceDocument29 pagini3G Air Interfaceavigupta91Încă nu există evaluări
- Public Perception Country: Tweets About Qatar (ACM WebSci '17)Document2 paginiPublic Perception Country: Tweets About Qatar (ACM WebSci '17)Shahan Ali MemonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lenovo S5Document16 paginiLenovo S5gmusic2Încă nu există evaluări
- Vlan ImpDocument26 paginiVlan ImpSathya SathyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5.3.1.3 Lab - Observing DNS Name ResolutionDocument3 pagini5.3.1.3 Lab - Observing DNS Name ResolutionMuhammad MusyawirÎncă nu există evaluări
- PCM92 Manual 5047784-A OriginalDocument62 paginiPCM92 Manual 5047784-A OriginaltaatuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Smartphone Troubleshooting & RepairDocument308 paginiSmartphone Troubleshooting & RepairMusa88% (51)
- Dhi xvr5204 08 16a s2 DatasheetDocument3 paginiDhi xvr5204 08 16a s2 DatasheetcitracandikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Command Reference) DMC-B140 - Rev.1.0Document223 pagini(Command Reference) DMC-B140 - Rev.1.0Chee An QuekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manejo de Librería Solaris 11Document4 paginiManejo de Librería Solaris 11rotwailerÎncă nu există evaluări
- LandStar Manual EN PDFDocument132 paginiLandStar Manual EN PDFFx AndrianoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linux Admin ProblemDocument2 paginiLinux Admin ProblemmethukupallyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Arista 7500 DatasheetDocument7 paginiArista 7500 DatasheetFranco ManuelÎncă nu există evaluări