Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Definitions Docx2
Încărcat de
Ayman KeirTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Definitions Docx2
Încărcat de
Ayman KeirDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Mach number - the speed of an object moving
through any fluid divided by the speed of sound
as it is in that substance
Speed of Sound- =
RT
ratio specific
heat*temp*R
Critical Mach number -the Mach number when
the local Mach number on the wings upper
surface reaches 1
Reynolds number-dimensionless parameter
representing ratio of inertial forces to viscous
forces. decreases with alt
Boundary layer-thin layer of slow moving fluid
flow with high viscosity on a body surface
IAS-IAS as shown on airspeed indicator uses
mean sea level density.
CAS-speed of aircraft after IAS is correct for
position errors
EAS-CAS after corrected for high speed flow
effect/compressibility. accurate air speed value
TAS- true air speed is calculated by adjusting an
IAS according to temperature, density, and
pressure.
Zero lift drag-Cdo-drag when lift =0.
dimensionless parameter that relates 0-lift drag
force to an aircraft's size, speed and flying
altitude
Ramjet-air is rammed in at high speed so no
need for compressor. efficient at M>8
Scramjet- a ramjet in which combustion takes
place in a stream of gas moving at supersonic
speed.
Turbofan- a jet engine in which a turbine-driven
fan provides additional thrust.
Flight envelope-capabilities and operating
parameters incorporating the range of
combinations of speed, AOA, n of which aircraft
is aerodynamically stable. a plot of Vmin and Vmax
as function of altitude define flight envelope.
Fuel weight fraction-ratio of fuel consumption in
a given mission leg to an aircraft's weight at the
start of the mission leg
Mass ratio-ratio of mass at start to mass at end
Thrust specific fuel consumption-fuel
consumption per thrust produced. lower values
are more efficient
Best range condition-optimum velocity to
produce the maximum range possible with min
fuel burned
Endurance-length of time an aircraft can fly per
a given load of fuel at a given set of flight
conditions
Rate of climb-an aircraft's vertical speed minus
change in altitude
Range-distance an aircraft can fly at certain
flight conditions, parameters and load of weight
Max climb angle-the steepest angle or max gain
of alt for a given horizontal distance
Velocity-rate of change of distance over time
Load factor-represents stress of which an
aircraft is subjected to
Ground speed -speed of aircraft relative to
ground calculated between two known
reference points
Position error-obtained when static vents are
located in an area of changing air flow such as
behind control surfaces
Take off-when landing gear leaves the ground,
or when the aircraft reaches 50ft from ground,
or when landing gear and flaps are fully
retracted
Specific energy-total energy/ weight
Aspect ratio-ratio of wing span(b) to chord(c) or
wing area(S) - a=(b^2)/S or a=b/c
Specific power-rate of change of specific
energy/ change in time
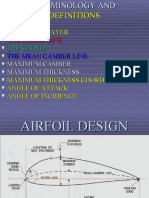
Angle of attack-angle between the mean chord
line and the relative air flow
Specific excess power-excess power/weight
Pitch angle-angle between the aircrafts
longitudinal axis and horizontal plane
Lift-force acting perpendicular to flow
Drag-force acting parallel to flow
Turboprop-uses gas turbine engine to power
prop
Turbojet-thrust produced by exit velocity
Centre of gravity- The longitudinal and lateral
point in an aircraft where it is stable; the static
balance point.
Aerodynamic centre- the point at which the
pitching moment coefficient for the airfoil does
not vary with lift coefficient (i.e. angle of
attack).
Induced drag - Induced drag occurs because of
the distribution of lift across the span of the
wing
parasitic drag- the part of the drag on an
aircraft that is contributed by nonlifting
surfaces, such as fuselage, nacelles
air speed indicator - device that measure the air
speed of aircraft through an air mass, but not its
ground speed
form drag - that part of the drag on an aerofoil
which arises from its shape.
stall- sudden loss of lift when AOA increases to a
point where flow break away from aerofoil
interference drag- Interference Drag is drag that
is generated by the mixing of airflow
streamlines between airframe components such
as the wing and the fuselage
Steady level turn - a turn where IAS and altitude
are constant
buffet- irregular oscillations of aircraft structure
caused by turbulent airflow of conditions of
compresibility
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Aviation GlossariesDocument11 paginiAviation GlossariesramiiijavedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ace The Technical Pilot InterviewDocument6 paginiAce The Technical Pilot InterviewHarshenDesaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amte 127Document9 paginiAmte 127Jan Patrick VelosoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Climb and Cruise PerformanceDocument59 paginiClimb and Cruise PerformanceBruceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Principles of FlightDocument26 paginiPrinciples of FlightShanaya Ishi Aso100% (1)
- Airplane Performance Courtesy BoeingDocument22 paginiAirplane Performance Courtesy Boeingr100% (1)
- How Plane Flies: Presentation For Air Port Planning & DesignDocument61 paginiHow Plane Flies: Presentation For Air Port Planning & DesignJawad Amjad GhauriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aerodynamics ExplainedDocument24 paginiAerodynamics ExplainedMonica MohaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engine PerformanceDocument12 paginiEngine PerformanceJuly TadeÎncă nu există evaluări
- AP4ATCO - Factors AffectingDocument12 paginiAP4ATCO - Factors Affectingsamirsamira928Încă nu există evaluări
- Engine Glossary ExplainedDocument6 paginiEngine Glossary ExplainedM Syahral RudyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effect Temperature and AltDocument4 paginiEffect Temperature and AltFaiza SaeedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conversions and Formulas for AerodynamicsDocument15 paginiConversions and Formulas for AerodynamicsKarl Radison AbreaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MANUAL LOADSHEET HANDLING GUIDEDocument9 paginiMANUAL LOADSHEET HANDLING GUIDESara khan100% (1)
- AeroplanoDocument9 paginiAeroplanoJose Luis MÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technical Topics: Understanding MY Conversion Rules Go-MindedDocument39 paginiTechnical Topics: Understanding MY Conversion Rules Go-MindedGábor KapuyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phases of A FlightDocument3 paginiPhases of A FlightGani PateelÎncă nu există evaluări
- FPP Cat 1Document9 paginiFPP Cat 1ay9 antarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Theory of Flight PDFDocument58 paginiTheory of Flight PDFJC Burciaga100% (2)
- Cive 461 Transportation Engineering Introduction To Planning and Design of Airport FacilitiesDocument29 paginiCive 461 Transportation Engineering Introduction To Planning and Design of Airport Facilitiessamir el-khodariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aviation DefinitionDocument22 paginiAviation DefinitionFahmi PrayogiÎncă nu există evaluări
- FPPDocument5 paginiFPPSteven PaulÎncă nu există evaluări
- For Flight DynamicsDocument125 paginiFor Flight DynamicsSNADAÎncă nu există evaluări
- RYAN DOMANDE New (61 PG)Document61 paginiRYAN DOMANDE New (61 PG)Filippo CiaravoloÎncă nu există evaluări
- United (UAL) Performance ManualDocument64 paginiUnited (UAL) Performance Manualpereira2106100% (1)
- QDB 15 PerformanceDocument48 paginiQDB 15 PerformanceKueh Chew Chai90% (10)
- Lec#12, Aircraft Characterisitcs (Compatibility Mode)Document46 paginiLec#12, Aircraft Characterisitcs (Compatibility Mode)Nawaz AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- ABC SummaryDocument65 paginiABC SummaryIslam AbdelshafyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aircraft Runway LengthDocument43 paginiAircraft Runway LengthLuiz AlvesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aircraft Characteristics: (B-Section) Instructor: SATISH SajjaDocument44 paginiAircraft Characteristics: (B-Section) Instructor: SATISH SajjaPavan KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 AerofoilsDocument40 paginiChapter 3 Aerofoilstopgun320Încă nu există evaluări
- (Class 19) Introduction To Aeronautical EngineeringDocument48 pagini(Class 19) Introduction To Aeronautical EngineeringFabian Torres100% (2)
- CHAPTER 11. Air Data Computer (ADC) : 11.1. General 11.1.1 AirspeedDocument8 paginiCHAPTER 11. Air Data Computer (ADC) : 11.1. General 11.1.1 AirspeedCypher_192Încă nu există evaluări
- Flight Planning ATP Chapter 1Document15 paginiFlight Planning ATP Chapter 1zest aviation100% (3)
- Takeoff 3Document2 paginiTakeoff 3a2962109Încă nu există evaluări
- Lect - 1Document26 paginiLect - 1zay yassineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Airframe Loads Types and FactorsDocument27 paginiBasic Airframe Loads Types and FactorsMeenakshi NathanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Weight & Balance RASDocument55 paginiWeight & Balance RASToni NiniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study Project (Ayyub Achilev)Document18 paginiStudy Project (Ayyub Achilev)Ayyub AchilevÎncă nu există evaluări
- 12222major ComponentsDocument41 pagini12222major ComponentsPokemon GoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1-Introduction To Aircraft PerformanceDocument66 paginiChapter 1-Introduction To Aircraft PerformancesemayatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Propeller NewDocument12 paginiPropeller NewMaruf AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Selection of Lightweight Materials for Aircraft Structural ComponentsDocument24 paginiSelection of Lightweight Materials for Aircraft Structural ComponentssasisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aircraft General & Performance: Aerodynamic Force Created by The AerofoilDocument49 paginiAircraft General & Performance: Aerodynamic Force Created by The Aerofoilpeter stanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aerodynamics: Lift and DragDocument4 paginiAerodynamics: Lift and DragJuly TadeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aerodrome PPT 4.2Document109 paginiAerodrome PPT 4.2John Client Aclan RanisÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 Airfoil DesignDocument56 pagini3 Airfoil DesignMaheshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geoffs Private Pilot Study GuideDocument28 paginiGeoffs Private Pilot Study Guideajcd110Încă nu există evaluări
- Qatar AssessmentDocument43 paginiQatar AssessmentBAZOUK95% (20)
- NASA Information Summaries Sawtooth ClimbsDocument5 paginiNASA Information Summaries Sawtooth ClimbsBob AndrepontÎncă nu există evaluări
- PerformanceDocument140 paginiPerformanceOleacov SergiuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aircraft comparison report summarizes key specsDocument50 paginiAircraft comparison report summarizes key specsMukesh KarunanethyÎncă nu există evaluări
- NASA Information Summaries Maximum Performance LandingDocument5 paginiNASA Information Summaries Maximum Performance LandingBob Andrepont100% (1)
- Wing Loading During CruiseDocument2 paginiWing Loading During CruiseAina KhairunnisaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Performance LandingDocument17 paginiPerformance LandingBFBGFD100% (1)
- Basic TermsDocument2 paginiBasic TermsMuhammad Tanveer ul HaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Edit Air Density Lift Coefficient Temperature Altitude Density Altitude International Standard Atmosphere V-SpeedsDocument1 paginăEdit Air Density Lift Coefficient Temperature Altitude Density Altitude International Standard Atmosphere V-Speedsa2962109Încă nu există evaluări
- Optimum Altitude for Maximum Aircraft RangeDocument9 paginiOptimum Altitude for Maximum Aircraft RangeRoger Maqueda NoguerÎncă nu există evaluări
- StudentDocument15 paginiStudentGhino San DiegoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Definitions Docx2Document2 paginiDefinitions Docx2Ayman KeirÎncă nu există evaluări
- SGP.. 24th JulyDocument1 paginăSGP.. 24th JulyAyman KeirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Boundary LayerDocument14 paginiIntroduction To Boundary LayerAyman KeirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Materials Lab Extruded PolymersDocument3 paginiMaterials Lab Extruded PolymersAyman KeirÎncă nu există evaluări
- 78 4.25 0 39.15 23 45.051 50 46.453 100 40.91 Mild Steel: Testing Temperature ( C) Energy Absorbed (J)Document6 pagini78 4.25 0 39.15 23 45.051 50 46.453 100 40.91 Mild Steel: Testing Temperature ( C) Energy Absorbed (J)Ayman KeirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tensile Strength and Deformation Characteristics of Engineering MaterialsDocument13 paginiTensile Strength and Deformation Characteristics of Engineering MaterialsAyman KeirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Materials Lab Extruded PolymersDocument3 paginiMaterials Lab Extruded PolymersAyman KeirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Impact Lab - : Observation of Temperature Effects During Fracture of Materials Under ImpactDocument7 paginiImpact Lab - : Observation of Temperature Effects During Fracture of Materials Under ImpactAyman KeirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ayman Trains 2Document4 paginiAyman Trains 2Ayman KeirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Investigating boundary layer separation using Tecquipment's AF41 wind tunnelDocument4 paginiInvestigating boundary layer separation using Tecquipment's AF41 wind tunnelAyman KeirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tata Steel Mechanical Engineer ApplicationDocument1 paginăTata Steel Mechanical Engineer ApplicationAyman KeirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sr-71 Blackbird-: Presented by Ayman, Phil, Aiden, Jacob and MattDocument5 paginiSr-71 Blackbird-: Presented by Ayman, Phil, Aiden, Jacob and MattAyman KeirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Crystallizers: Chapter 16 Cost Accounting and Capital Cost EstimationDocument1 paginăCrystallizers: Chapter 16 Cost Accounting and Capital Cost EstimationDeiver Enrique SampayoÎncă nu există evaluări
- CDI-AOS-CX 10.4 Switching Portfolio Launch - Lab V4.01Document152 paginiCDI-AOS-CX 10.4 Switching Portfolio Launch - Lab V4.01Gilles DellaccioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Meet Joe Black (1998) : A Metaphor of LifeDocument10 paginiMeet Joe Black (1998) : A Metaphor of LifeSara OrsenoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guidelines - MIDA (Haulage)Document3 paginiGuidelines - MIDA (Haulage)Yasushi Charles TeoÎncă nu există evaluări
- PeopleSoft Security TablesDocument8 paginiPeopleSoft Security TablesChhavibhasinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ielts Practice Tests: ListeningDocument19 paginiIelts Practice Tests: ListeningKadek Santiari DewiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Form 4 Additional Mathematics Revision PatDocument7 paginiForm 4 Additional Mathematics Revision PatJiajia LauÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guia de Usuario GPS Spectra SP80 PDFDocument118 paginiGuia de Usuario GPS Spectra SP80 PDFAlbrichs BennettÎncă nu există evaluări
- Qad Quick StartDocument534 paginiQad Quick StartMahadev Subramani100% (1)
- ISO 13485-2016 - DR - Pack - Control of Non Conforming ProductsDocument4 paginiISO 13485-2016 - DR - Pack - Control of Non Conforming ProductskmasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Masteringphys 14Document20 paginiMasteringphys 14CarlosGomez0% (3)
- Equilibruim of Forces and How Three Forces Meet at A PointDocument32 paginiEquilibruim of Forces and How Three Forces Meet at A PointSherif Yehia Al MaraghyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Link Ratio MethodDocument18 paginiLink Ratio MethodLuis ChioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Master SEODocument8 paginiMaster SEOOkane MochiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Special Power of Attorney: Benedict Joseph M. CruzDocument1 paginăSpecial Power of Attorney: Benedict Joseph M. CruzJson GalvezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ansible Playbook for BeginnersDocument101 paginiAnsible Playbook for BeginnersFelix Andres Baquero Cubillos100% (1)
- Busbar sizing recommendations for Masterpact circuit breakersDocument1 paginăBusbar sizing recommendations for Masterpact circuit breakersVikram SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- New Hire WorkbookDocument40 paginiNew Hire WorkbookkÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1st SemDocument3 pagini1st SemARUPARNA MAITYÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test Bank For Fundamental Financial Accounting Concepts 10th by EdmondsDocument18 paginiTest Bank For Fundamental Financial Accounting Concepts 10th by Edmondsooezoapunitory.xkgyo4100% (47)
- Key Fact Sheet (HBL FreedomAccount) - July 2019 PDFDocument1 paginăKey Fact Sheet (HBL FreedomAccount) - July 2019 PDFBaD cHaUhDrYÎncă nu există evaluări
- Damcos Mas2600 Installation UsermanualDocument26 paginiDamcos Mas2600 Installation Usermanualair1111Încă nu există evaluări
- Propoxur PMRADocument2 paginiPropoxur PMRAuncleadolphÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dolni VestoniceDocument34 paginiDolni VestoniceOlha PodufalovaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SNC 2p1 Course Overview 2015Document2 paginiSNC 2p1 Course Overview 2015api-212901753Încă nu există evaluări
- Flowmon Ads Enterprise Userguide enDocument82 paginiFlowmon Ads Enterprise Userguide ennagasatoÎncă nu există evaluări
- CBT For BDDDocument13 paginiCBT For BDDGregg Williams100% (5)
- AD Chemicals - Freeze-Flash PointDocument4 paginiAD Chemicals - Freeze-Flash Pointyb3yonnayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Form Active Structure TypesDocument5 paginiForm Active Structure TypesShivanshu singh100% (1)
- PEDs and InterferenceDocument28 paginiPEDs and Interferencezakool21Încă nu există evaluări
- Strong Is the New Beautiful: Embrace Your Natural Beauty, Eat Clean, and Harness Your PowerDe la EverandStrong Is the New Beautiful: Embrace Your Natural Beauty, Eat Clean, and Harness Your PowerEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5)
- Guidelines for Auditing Process Safety Management SystemsDe la EverandGuidelines for Auditing Process Safety Management SystemsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersDe la EverandRules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (12)
- Guidelines for Implementing Process Safety ManagementDe la EverandGuidelines for Implementing Process Safety ManagementÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisDe la EverandGuidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Introduction to Petroleum Process SafetyDe la EverandIntroduction to Petroleum Process SafetyEvaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (2)
- The Darkest White: A Mountain Legend and the Avalanche That Took HimDe la EverandThe Darkest White: A Mountain Legend and the Avalanche That Took HimEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsDe la EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Poison Like No Other: How Microplastics Corrupted Our Planet and Our BodiesDe la EverandA Poison Like No Other: How Microplastics Corrupted Our Planet and Our BodiesEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Nutritional and Therapeutic Interventions for Diabetes and Metabolic SyndromeDe la EverandNutritional and Therapeutic Interventions for Diabetes and Metabolic SyndromeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Training for the Uphill Athlete: A Manual for Mountain Runners and Ski MountaineersDe la EverandTraining for the Uphill Athlete: A Manual for Mountain Runners and Ski MountaineersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (8)
- Trevor Kletz Compendium: His Process Safety Wisdom Updated for a New GenerationDe la EverandTrevor Kletz Compendium: His Process Safety Wisdom Updated for a New GenerationÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inherently Safer Chemical Processes: A Life Cycle ApproachDe la EverandInherently Safer Chemical Processes: A Life Cycle ApproachEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Two Planks and a Passion: The Dramatic History of SkiingDe la EverandTwo Planks and a Passion: The Dramatic History of SkiingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Safety Fundamentals and Best Practices in Construction IndustryDe la EverandSafety Fundamentals and Best Practices in Construction IndustryÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Art of Fear: Why Conquering Fear Won't Work and What to Do InsteadDe la EverandThe Art of Fear: Why Conquering Fear Won't Work and What to Do InsteadEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (10)
- The Art of Fear: Why Conquering Fear Won't Work and What to Do InsteadDe la EverandThe Art of Fear: Why Conquering Fear Won't Work and What to Do InsteadEvaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (5)
- Incidents That Define Process SafetyDe la EverandIncidents That Define Process SafetyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Radium Girls: Women and Industrial Health Reform, 1910-1935De la EverandRadium Girls: Women and Industrial Health Reform, 1910-1935Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (4)
- LNG Risk Based Safety: Modeling and Consequence AnalysisDe la EverandLNG Risk Based Safety: Modeling and Consequence AnalysisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nobody Cares: The Story of the World from SafetymanDe la EverandNobody Cares: The Story of the World from SafetymanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practical Industrial Safety, Risk Assessment and Shutdown SystemsDe la EverandPractical Industrial Safety, Risk Assessment and Shutdown SystemsEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (11)
- Chemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesDe la EverandChemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (14)
- The ISO 45001:2018 Implementation Handbook: Guidance on Building an Occupational Health and Safety Management SystemDe la EverandThe ISO 45001:2018 Implementation Handbook: Guidance on Building an Occupational Health and Safety Management SystemÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersDe la EverandA Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- Safety and Intelligent Transport Systems Development in the People’s Republic of ChinaDe la EverandSafety and Intelligent Transport Systems Development in the People’s Republic of ChinaÎncă nu există evaluări