Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Nursing Care Plans
Încărcat de
BeyotchsangreMesswithurownlifeDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Nursing Care Plans
Încărcat de
BeyotchsangreMesswithurownlifeDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
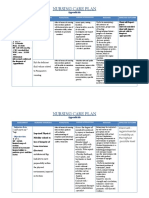
NURSING CARE PLANS
1. Impaired Skin Integrity related to pressure ulcer secondary to prolonged immobility and
unrelieved pressure as evidenced by :
- pressure ulcers on sacral area ( stage 3 )
- left thigh( stage 3)
- left ankle
- prolonged immobility
- bedridden since 2014
- 4 months prior to admission redness over affected areas noted
Nursing Interventions:
Asses between folds of skin also assess under oxygen tubing especially on the ears and the
cheek, and under medical devices.
Note objective data of pressure ulcer ( stage, length, width, depth, wound bed, appearance,
drainage and condition of Periulcer tissue )
Increase the frequency of turning to sides every 2 hours. Position the client to stay off the
ulcer. If there is no turning surface without a pressure ulcer, use a pressure redistribution bed
and continue turning the client.
Elevate heels of bed by using pillows or heel elevation boots.
Maintain head of bed at lowest elevation, if client must have the head elevated to prevent
aspiration, reposition to 30 degree lateral position. Use seat cushions and assess sacral ulcers
daily.
Follow body substance isolation precautions; use clean gloves and clean dressings for wound
care.
Dependent /Collaborative:
Ensure adequate dietary intake, review dieticians recommendations. Prevent the ulcer from
being exposed to urine and feces. Use indwelling catheters, bowel containing system, and
topical creams and dressings.
Supplement the diet with vitamins and minerals. Vitamins C and zinc are commonly
prescribed.
Provide oral supplementations, tube feedings or hyperalimentation to achieve positive
nitrogen balance.
Removed devitalized tissue from the wound bed except from the avascular tissue or on the
heels. Began by cleansing the ulcer bed with normal saline, then use appropriate technique for
debridement. Once the ulcer is free of devitalized tissue, apply dressing the wound bed moist
and the surrounding skin dry. Do not use the occlusive dressing on ulcer.
Rationale:
Pressure ulcers under medical devices are commonly overlooked.
Reassessment of ulcer is completed each time dressing are changed or sooner if ulcer shows
manifestations or deterioration. Analyses of the trends in healing are more important step in
assessment.
To disperse pressure overtime or decreasing the tissue load
Heel covers do not relieve the pressure, but they can reduce friction.
To prevent further occurrence of pressure ulcer
To reduce risk of infection and promote faster healing.
To prevent malnutrition and delayed healing.
To prevent spread of infection/contamination.
To promote wound healing on clients who do not have adequate calories.
Pressure ulcers cannot heal clients with severe malnutrition.
To promote faster healing and reduce infection.
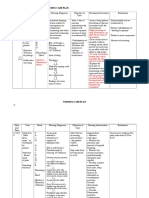
2. Self-care deficit related to muscle weakness secondary to paralysis as evidenced by:
- Stroke in 2014 made the client bedridden
- Client has weak lower extremities
- Clients left arm is weaker than the right
- Client depends on another person in maintaining activities of daily living
Nursing interventions:
Assess abilities and level of deficit (04 scale) for performing ADLs.
Avoid doing things for patient that patient can do for self, but provide assistance
as necessary.
Be aware of impulsive actions suggestive of impaired judgment.
Maintain a supportive, firm attitude. Allow patient sufficient time to accomplish
tasks. Dont rush the patient.
Provide positive feedback for efforts and accomplishments.
Create plan for visual deficits that are present: Place food and utensils on the tray
related to patients unaffected side; Situate the bed so that patients unaffected
side is facing the room with the affected side to the wall; Position furniture against
wall/out of travel path.
Provide self-help devices: extensions with hooks for picking things up from the
floor, toilet risers, long-handled brushes, drinking straw, leg bag for catheter,
shower chair. Encourage good grooming and makeup habits.
Encourage SO to allow patient to do as much as possible for self
Assess patients ability to communicate the need to void and/or ability to use
urinal, bedpan. Take patient to the bathroom at periodic intervals for voiding if
appropriate.
Identify previous bowel habits and re-establish normal regimen. Increase bulk in
diet, encourage fluid intake, increased activity.
Teach the patient to comb hair, dress, and wash.
Refer patient to physical and occupational therapist.
Rationale:
Aids in planning for meeting individual needs.
To maintain self-esteem and promote recovery, it is important for the patient to do
as much as possible for self. These patients may become fearful and
independent, although assistance is helpful in preventing frustration.
May indicate need for additional interventions and supervision to promote patient
safety.
Patients need empathy and to know caregivers will be consistent in their
assistance.
Enhances sense of self-worth, promotes independence, and encourages patient
to continue endeavors.
Patient will be able to see to eat the food. Will be able to see when getting in/out
of bed and observe anyone who comes into the room. Provides for safety when
patient is able to move around the room, reducing risk of tripping/falling over
furniture.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 paginiAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationJhoizel VenusÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Disturbed Body ImageDocument2 paginiNCP Disturbed Body ImageDoneva Lyn MedinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument5 paginiDecreased Cardiac Outputshuang81Încă nu există evaluări
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 paginăNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationCharina AubreyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plans For Activity IntoleranceDocument4 paginiNursing Care Plans For Activity IntolerancethebigtwirpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Constipation NCPDocument2 paginiConstipation NCPKaren Pili100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Acute PainDocument4 paginiNursing Care Plan: Acute PainEvet VaxbmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Disturbed Body Image Nursing InterventionsDocument11 paginiDisturbed Body Image Nursing InterventionsNdel LindaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Acute Pain Related To Presence of Postoperative Surgical IncisionDocument2 paginiNCP Acute Pain Related To Presence of Postoperative Surgical IncisionPebbles PangilinanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Objective Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 paginiCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Objective Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationjomsportg0% (1)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 paginiAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationgabbyÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP For HemorrhoidsDocument3 paginiNCP For HemorrhoidsTADURAN RENE MAE ANGELLI F.Încă nu există evaluări
- Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation: Nursing Care PlanDocument1 paginăCues Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation: Nursing Care Planaprilrosehibaya100% (1)
- Impaired Physical MobilityDocument3 paginiImpaired Physical MobilityCharmaine ChuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP MRMDocument2 paginiNCP MRMKhloe Cristel Llanes Torres100% (1)
- Seizure NCPDocument2 paginiSeizure NCPChristine Dela CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCPDocument2 paginiNCPCamille VirayÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCPDocument10 paginiNCPNefre Dayap DarrocaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Acitivity IntoleranceDocument3 paginiNCP Acitivity IntolerancegizelleÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCPDocument1 paginăNCPVictor MurilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Impaired Physical MobilityDocument1 paginăImpaired Physical MobilitySheena Yen de Pano-PagdalianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Renal Failure NCPDocument3 paginiRenal Failure NCPjsksÎncă nu există evaluări
- Healthcare - Nursing Care Plan - Excess Fluid VolumeDocument4 paginiHealthcare - Nursing Care Plan - Excess Fluid VolumeBenjamin CañalitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Total Abdominal Hysterectomy Bilateral Salpingo Oophorectomy (Tahbso) Nursing Responsibilities Rationale Pre-OperativeDocument2 paginiTotal Abdominal Hysterectomy Bilateral Salpingo Oophorectomy (Tahbso) Nursing Responsibilities Rationale Pre-OperativeMiar QuestÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Impaired ComfortDocument2 paginiNCP Impaired ComfortGia P. de VeyraÎncă nu există evaluări
- LortabDocument1 paginăLortabSheri490Încă nu există evaluări
- R.O. Appendicitis.: Nursing Care Plan (NCP)Document2 paginiR.O. Appendicitis.: Nursing Care Plan (NCP)Karen Joy ItoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plans for Pain Management and Self-CareDocument15 paginiNursing Care Plans for Pain Management and Self-CareKarl Vincent Soso100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan for Diabetic Patient with DehydrationDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan for Diabetic Patient with DehydrationRodolfo Bong SemaneroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Cues for Managing Osteosarcoma PainDocument2 paginiNursing Cues for Managing Osteosarcoma Painkasandra dawn BerisoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan for Post-Surgical PainDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan for Post-Surgical PainAngelgodess Athena-envyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan: Determine Cause of Activity - Determining The Cause of A Disease CanDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan: Determine Cause of Activity - Determining The Cause of A Disease Canrix07Încă nu există evaluări
- Improve Patient Satisfaction ScoresDocument5 paginiImprove Patient Satisfaction ScoresAce TabioloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Impaired Physical Mobility. Impaired CommunicationDocument5 paginiImpaired Physical Mobility. Impaired CommunicationJovania Liza R. Baguilat100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective DataDocument4 paginiNursing Care Plan: Subjective DataAbdallah AlasalÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Skin IntegrityDocument3 paginiNCP Skin IntegrityAlfie Ayro50% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal and Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan: Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal and Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationCalimlim KimÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP BronchopneumoniaDocument8 paginiNCP BronchopneumoniaCrisantaCasliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan (Acute Pain)Document1 paginăNursing Care Plan (Acute Pain)kyaw100% (2)
- Managing Fatigue Through Activity Pacing and RestDocument2 paginiManaging Fatigue Through Activity Pacing and ResthaniehaehaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Impaired Physical MobilityDocument1 paginăNCP Impaired Physical MobilityCharmaine SolimanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan for Hypokalemia: Monitoring and Maintaining Serum Potassium LevelsDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan for Hypokalemia: Monitoring and Maintaining Serum Potassium LevelsDoneva Lyn MedinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP SicuDocument6 paginiNCP SicuChoco MuchoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Disturbed Sleeping Pattern NCPDocument4 paginiDisturbed Sleeping Pattern NCPSamVelascoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan for Suicidal PatientDocument4 paginiNursing Care Plan for Suicidal PatientJennifer ArdeÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP PainDocument1 paginăNCP Painsitz04Încă nu există evaluări
- Fistula NCPDocument1 paginăFistula NCPHasna LisnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Planning: NCP #1 Chronic Pain Related To Compression of Spinal Nerves As Evidenced byDocument10 paginiPlanning: NCP #1 Chronic Pain Related To Compression of Spinal Nerves As Evidenced byNicole Anne TungolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Diagnosis: Impaired Physical Mobility Assessment Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 paginiNursing Diagnosis: Impaired Physical Mobility Assessment Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationSheril Sularte CasanesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Incomplete Spinal Cord Injury Nursing CareDocument6 paginiIncomplete Spinal Cord Injury Nursing CareTherese MargaretÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing assessment and intervention plan for fall riskDocument1 paginăNursing assessment and intervention plan for fall riskAyeÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Decreased Cardiac Output 1Document2 paginiNCP Decreased Cardiac Output 1Arnel MacabalitaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Self CaRE DeficitDocument1 paginăNCP Self CaRE Deficitnicole pageÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 1 Am Activity On Prioritization v2Document5 paginiModule 1 Am Activity On Prioritization v2KeanuÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Risk For InfectionDocument2 paginiNCP Risk For InfectionlinnaroueyakÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCPDocument5 paginiNCPMcmc Ryan Ferdinand GutierrezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case IcuDocument5 paginiCase IcuTrisha SuazoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan for Peptic UlcerDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan for Peptic UlcerJefferson Baluyot PalmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP-Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument2 paginiNCP-Impaired Skin IntegrityMikee Ann Valdez96% (26)
- NCP Icu-CcuDocument6 paginiNCP Icu-CcuJohn CenasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guidelines On Ethical Issues in The Provision of Medical Genetics Services in MalaysiaDocument47 paginiGuidelines On Ethical Issues in The Provision of Medical Genetics Services in Malaysiaput3 eisyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evwoman M00o03Document33 paginiEvwoman M00o03Nader AlsheikhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercise Prescription in Pre and Post-NatalDocument63 paginiExercise Prescription in Pre and Post-NatalSim ShkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Planning and Designing An Isolation Facility in Hospitals Need of The Hour PDFDocument9 paginiPlanning and Designing An Isolation Facility in Hospitals Need of The Hour PDFdzakyzahidÎncă nu există evaluări
- CONSENT FOR BIOPSY v2Document1 paginăCONSENT FOR BIOPSY v2Bhumika SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Patau SindromDocument4 paginiPatau SindromOgnjen IvkovićÎncă nu există evaluări
- Buenas ReciproDocument60 paginiBuenas ReciproChristianOcampodaCruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0008 Hydrochlorothiazide and Prevention of Kidney-Stone Recurrence Nejmoa2209275Document11 pagini0008 Hydrochlorothiazide and Prevention of Kidney-Stone Recurrence Nejmoa2209275Iana Hércules de CarvalhoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Managing Amphetamine Dependence: Malcolm BruceDocument8 paginiManaging Amphetamine Dependence: Malcolm BrucejuraiddinÎncă nu există evaluări
- First Announcement Pdpi Update 1Document25 paginiFirst Announcement Pdpi Update 1sheeno2607Încă nu există evaluări
- Emergency Codes PDFDocument59 paginiEmergency Codes PDFRaviraj PisheÎncă nu există evaluări
- Health Assessment Assignment 1 Nursing ProcessDocument2 paginiHealth Assessment Assignment 1 Nursing ProcessDiana MuañaÎncă nu există evaluări
- UrbiztondoDocument3 paginiUrbiztondoEmmánÎncă nu există evaluări
- The MedTrak ProgramDocument11 paginiThe MedTrak ProgramInBalanceÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Resin-Bonded Fixed Partial Denture As The First Treatment Consideration To Replace A Missing ToothDocument3 paginiThe Resin-Bonded Fixed Partial Denture As The First Treatment Consideration To Replace A Missing ToothAngelia PratiwiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summary of Product Characteristics: 4.1 Therapeutic IndicationsDocument3 paginiSummary of Product Characteristics: 4.1 Therapeutic IndicationsasdwasdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Care Plan - Arsenault 1031575Document10 paginiCare Plan - Arsenault 1031575api-282962289100% (1)
- Veterinarians List CharlottesvilleDocument5 paginiVeterinarians List CharlottesvilleDoug OhnemusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analisa Jurnal Kelompok 9 (The History of Evidence-Based Practice in Nursing Education and Practice)Document9 paginiAnalisa Jurnal Kelompok 9 (The History of Evidence-Based Practice in Nursing Education and Practice)Viola AlvionitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Patient Satisfaction With Hospital Care and Nurses in England: An Observational StudyDocument10 paginiPatient Satisfaction With Hospital Care and Nurses in England: An Observational StudySelfa YunitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gcu Nrs410 Week 4 Assignment Benchmark Nursing Process Approach To Care Latest 2019 JulyDocument3 paginiGcu Nrs410 Week 4 Assignment Benchmark Nursing Process Approach To Care Latest 2019 JulyDoreenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Baby Friendly Cheat Sheet Nov 2020Document2 paginiBaby Friendly Cheat Sheet Nov 2020Lars OrdonezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chronic Pain ManagementDocument16 paginiChronic Pain Managementpuchio100% (2)
- Lectureready Scripts Level1 3Document8 paginiLectureready Scripts Level1 3waffloÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2019 Guide For ImmunizationDocument195 pagini2019 Guide For ImmunizationReigner paul DavidÎncă nu există evaluări
- FMLA PolicyDocument10 paginiFMLA PolicyJustinFinneranÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Smtebooks - Com) Clinical Trials in Neurology - Design, Conduct, Analysis 1st Edition PDFDocument385 pagini(Smtebooks - Com) Clinical Trials in Neurology - Design, Conduct, Analysis 1st Edition PDFnarasimhahanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Space Standards For Community Health Care Facilities: Health Capital Investment Branch March 2017Document29 paginiSpace Standards For Community Health Care Facilities: Health Capital Investment Branch March 2017Pratheeka ShettyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Principles of CHN New UpdatedDocument4 paginiPrinciples of CHN New Updatediheart musicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Health Shield 360 Retail - PWDocument30 paginiHealth Shield 360 Retail - PWcmpn.20102a0032Încă nu există evaluări