Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Modal Verbs (1BACH)
Încărcat de
Enrique FerreroDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Modal Verbs (1BACH)
Încărcat de
Enrique FerreroDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
MODAL VERBS
What are modal verbs?
The most common modal verbs are:
Can
Could
May
They are auxiliary verbs that provide
additional and specific meaning to the
main verb of the sentence
Might
Must
Should
Would
Modal verbs are sometimes referred to as
Modal auxiliary verbs because they help
other verbs
MODAL VERBS
How do we use modal verbs?
Subject
Verb
Example: Mary could play the piano
They do not accept conjugation
They do not need other auxiliary verbs
How do we use modal verbs?
MODAL VERBS
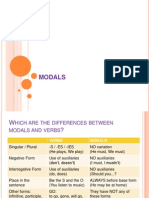
There is no s in singular
There is no do / does in the question
There is no dont / doesnt in the negative
He can ski
He cans ski or He can skis
Would you like to come with me?
Do you would like to come with me?
They cant be serious
They dont can be serious
How do we use modal verbs?
MODAL VERBS
Modal verbs do not have all the tenses
Modal verbs use other verbs to complete the tenses
Can is completed with be able to
Must is completed with have to
They can play the piano
They will be able to play the piano in the future
You must come early
You had to come early yesterday
They have different meanings depending
on the situation:
MODAL VERBS
Obligation and prohibition
Must for obligation; mustnt for prohibition (law, rules, orders):
You must wear a school uniform; you mustnt eat chewing gum in class
Have to / need to when we know its important to do something (tengo que):
I have to / need to remember this, the teacher says itll be in the exam
Dont have to / neednt when there is no obligation (its not necessary to):
You dont have to / neednt wear the uniform to the school party
Ability
Can(t) to speak about ability in the present:
Sam can say hello in more than twenty languages.
Could(nt) to speak about ability in the past:
I could play chess when I was a child, but I forgot how to do it.
Possibility and certainty
Can when something is possible You can buy tickets online.
May (not) / might(nt)* / could(nt)* when were not sure if something will happen
It may/might/could rain tomorrow.
*might/could: the possibility is more remote
Must / cant when we are sure that something is/isnt possible or true:
That must be John, he was about to arrive.
Those girls cant be Jackie and Jill, they are on holiday in France.
They have different meanings depending
on the situation:
MODAL VERBS
Advice, recommendations and opinions
Should(nt) / ought to*:
You should / ought to look before you cross the road
* ought to is not very common in the negative and interrogative forms; should is
the most used modal of advice in affirmative, negative and interrogative
Requests (asking somebody to do something, or if you can do something)
Can for requests:
Can I go to the concert?
May / could for polite requests:
Could you take me to the concert?
Would for formal requests (Would _____, please?):
Would you stop singing that song, please?
May I borrow your phone for a moment?
Suggestions
Can / could*:
You can use my guitar tonight. You could invite them to your party.
* could is more polite
Polite offers (Would you like to___?)
Would:
Would you like to sing in the concert with us today?
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Modal VerbsDocument29 paginiModal VerbsJanita Nikoliva100% (2)
- Modal Verbs PPT ClassDocument20 paginiModal Verbs PPT ClassKarlita Ruela100% (2)
- Modal VerbsDocument24 paginiModal Verbsjoemacarra100% (5)
- Introduction..Polysemy and HomonymyDocument6 paginiIntroduction..Polysemy and HomonymyClaudia Elena NegurăÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toaz - Info Headway Elementary Workbook 5th Edition PRDocument98 paginiToaz - Info Headway Elementary Workbook 5th Edition PRGm Sanu67% (6)
- Modalverbs-Final 2Document61 paginiModalverbs-Final 2api-252190418Încă nu există evaluări
- Test 2Document19 paginiTest 2Maja VrsaljkoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modal Verbs-BatxDocument21 paginiModal Verbs-BatxMinhang Lin LinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ought Rachel To Be Here So Early? Ought They To Live There?Document12 paginiOught Rachel To Be Here So Early? Ought They To Live There?Roy ToyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Verbos ModalesDocument3 paginiVerbos ModalesEsther GilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modal Auxiliary VerbDocument19 paginiModal Auxiliary VerbYuninda Novita PutriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mo Dals Obligation 2Document8 paginiMo Dals Obligation 2Mirjana IvancevÎncă nu există evaluări
- ModalsDocument46 paginiModalsblossom buenaventura100% (1)
- Modal Verbs 2Document7 paginiModal Verbs 2pepemusicaantequeraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gramatica InglesaDocument11 paginiGramatica InglesaANGIE LIZET RIVERA PRADOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 4 GramáticaDocument11 paginiUnit 4 GramáticaLILIAN DEL CARMEN RAMIREZ RIVASÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modals and Semi-ModalsDocument11 paginiModals and Semi-Modalsmarinela100% (1)
- All Modal VerbsDocument8 paginiAll Modal VerbsIonut TomaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modal VerbsDocument5 paginiModal VerbsCarlos Paz ChanganaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 3 Modal VerbsDocument26 paginiLesson 3 Modal VerbsAlpha Joy ProvidoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modal Verbs PDFDocument20 paginiModal Verbs PDFbelenxxu97Încă nu există evaluări
- Modal VerbsDocument32 paginiModal Verbssusie fallariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- BK 1 Unit 21 To 24 Modal AuxiliariesDocument21 paginiBK 1 Unit 21 To 24 Modal AuxiliariesSheena SuicoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modals and Perfect Modals in PastDocument11 paginiModals and Perfect Modals in PastLuz Andrea Castillo CaicedoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ingles SeptimoDocument18 paginiIngles Septimomargarita giraldoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Welcome To The Class... How Are You?Document32 paginiWelcome To The Class... How Are You?Isabel VC100% (1)
- Modal VerbsDocument24 paginiModal VerbspasaceviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Can BE ABLEDocument8 paginiCan BE ABLEjuanetitoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modal Auxilary Verbsclass2Document24 paginiModal Auxilary Verbsclass2MiCkeyTorresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modality: Introduction: English Grammar TodayDocument13 paginiModality: Introduction: English Grammar TodaySilvia Alejandra SuarezÎncă nu există evaluări
- MODALVERBS FinalDocument32 paginiMODALVERBS FinalKAMALÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modals of NecessityDocument10 paginiModals of Necessityalexferreire1Încă nu există evaluări
- L2 - Modals LamDocument35 paginiL2 - Modals LamQui RainÎncă nu există evaluări
- UNIT 4 - Modal VerbsDocument15 paginiUNIT 4 - Modal VerbsOliver TorresÎncă nu există evaluări
- 18eng32l U4Document75 pagini18eng32l U4Ruchi KhannaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modal Verbs For Upper SecondaryDocument20 paginiModal Verbs For Upper SecondaryfergarcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modals Semi-Modals: Always The Same Form. Change Form According To The SubjectDocument9 paginiModals Semi-Modals: Always The Same Form. Change Form According To The SubjectMaría RodríguezÎncă nu există evaluări
- MODAL VERBS (Simple Forms)Document3 paginiMODAL VERBS (Simple Forms)David Sánchez GarcíaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4TH Eso Modal Verbs RevisionDocument11 pagini4TH Eso Modal Verbs RevisionJccd JccdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument30 paginiGerunds and InfinitivesPatrícia Argôlo Rosa100% (1)
- Modals of Ability: Can, Could, Be Able To, May, MightDocument5 paginiModals of Ability: Can, Could, Be Able To, May, Mightsyarief asy-syahidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Verbos ModalesDocument3 paginiVerbos ModalesZulema Tapia LluscoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mo Bab Ity: Dal Verbs of Pro IlDocument20 paginiMo Bab Ity: Dal Verbs of Pro Illarisa444Încă nu există evaluări
- Modals and Semi-ModalsDocument22 paginiModals and Semi-ModalsBianca ChircuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modal VerbsDocument23 paginiModal Verbsrap manÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mod Al VerbsDocument79 paginiMod Al VerbsSeda SezerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modals of Ability: Can, Could, Be Able To, May, MightDocument3 paginiModals of Ability: Can, Could, Be Able To, May, MightsabamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mod Al VerbsDocument32 paginiMod Al VerbsKris Bernadette Perez DavidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modal VerbsDocument8 paginiModal VerbsMariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 2 ModalsDocument28 paginiWeek 2 ModalsNur Aliaa100% (1)
- ModalsDocument24 paginiModalsUmair Ejaz ButtÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modal Verbs BACHDocument26 paginiModal Verbs BACHZulcka TTVÎncă nu există evaluări
- ModalsDocument27 paginiModalsThess Flores CabreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grammar Reference: Modal AuxiliariesDocument10 paginiGrammar Reference: Modal AuxiliariesAndrei IvanovichÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modals Verbs: Advanced English GrammarDocument21 paginiModals Verbs: Advanced English GrammarRoberto FlotaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modals To ExpressDocument16 paginiModals To ExpressDia PasereÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modal Verbs (Obligation, Permission, Requests, Offers) : - o o o oDocument4 paginiModal Verbs (Obligation, Permission, Requests, Offers) : - o o o oluchador86Încă nu există evaluări
- Modal Verb CANDocument9 paginiModal Verb CANanali gallardo arreolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modals and Perfect ModalsDocument14 paginiModals and Perfect ModalsCF CarolinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- English Grammar– Do, Does, Did: Patterns and ExamplesDe la EverandEnglish Grammar– Do, Does, Did: Patterns and ExamplesÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 ESO: Unit 7 RevisionDocument3 pagini3 ESO: Unit 7 RevisionEnrique Ferrero0% (1)
- 4 ESO: Unit 5 (Revision)Document1 pagină4 ESO: Unit 5 (Revision)Enrique FerreroÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 ESO: Unit 3 (Revision)Document2 pagini3 ESO: Unit 3 (Revision)Enrique FerreroÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 BACHILLERATO: 2nd Term Grammar RevisionDocument45 pagini2 BACHILLERATO: 2nd Term Grammar RevisionEnrique FerreroÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 ESO: Unit 6 (Revision)Document1 pagină4 ESO: Unit 6 (Revision)Enrique FerreroÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 ESO: Unit 7 RevisionDocument3 pagini4 ESO: Unit 7 RevisionEnrique FerreroÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 ESO: Unit 4 (Revision)Document1 pagină4 ESO: Unit 4 (Revision)Enrique Ferrero0% (1)
- Units 2-3 Revision 4ESODocument4 paginiUnits 2-3 Revision 4ESOEnrique FerreroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gerunds in EnglishDocument3 paginiGerunds in EnglishEnrique FerreroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bachillerato 2 - 1st Term - Grammar Units 1-3Document29 paginiBachillerato 2 - 1st Term - Grammar Units 1-3Enrique FerreroÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1BACH - Verb TensesDocument3 pagini1BACH - Verb TensesEnrique FerreroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bachillerato 2 - 1st Term - Verb TensesDocument20 paginiBachillerato 2 - 1st Term - Verb TensesEnrique Ferrero100% (2)
- Unit 2 Revision 3ESODocument2 paginiUnit 2 Revision 3ESOEnrique FerreroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paragraph 1:: What Is The Name of The City? Where Is It?Document8 paginiParagraph 1:: What Is The Name of The City? Where Is It?Enrique FerreroÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Passive Voice: IntroductionDocument1 paginăThe Passive Voice: IntroductionEnrique FerreroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Countries, Nationalities and LanguagesDocument1 paginăCountries, Nationalities and LanguagesEnrique FerreroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Past PerfectDocument1 paginăPast PerfectEnrique FerreroÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 ESO: Unit 6 RevisionDocument2 pagini3 ESO: Unit 6 RevisionEnrique FerreroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Passive of Reporting VerbsDocument2 paginiPassive of Reporting VerbsEnrique Ferrero100% (2)
- 4ESO Units 0-1 RevisionDocument2 pagini4ESO Units 0-1 RevisionEnrique FerreroÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 ESO: Unit 6 RevisionDocument2 pagini1 ESO: Unit 6 RevisionEnrique FerreroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 5 Revision 1ESODocument1 paginăUnit 5 Revision 1ESOEnrique FerreroÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Bachillerato: 3rd Term RevisionDocument4 pagini1 Bachillerato: 3rd Term RevisionEnrique FerreroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 5 Revision 3ESODocument2 paginiUnit 5 Revision 3ESOEnrique FerreroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Videogame TreatmentDocument2 paginiVideogame TreatmentEnrique FerreroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Passive Voice With Reporting VerbsDocument2 paginiPassive Voice With Reporting VerbsEnrique Ferrero75% (28)
- An Example To FollowDocument2 paginiAn Example To FollowEnrique FerreroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Passive Voice RevisionDocument2 paginiPassive Voice RevisionEnrique FerreroÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 ESO: Unit 4 (Revision)Document1 pagină1 ESO: Unit 4 (Revision)Enrique FerreroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mirror GanDocument10 paginiMirror GanRohit KeshavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contrastive AnalysisDocument5 paginiContrastive AnalysisFaeZeh ZAreiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Traveling Might Satisfy Your Desire For New Experiences.: Shaken, He Walked Away From The Wrecked CarDocument5 paginiTraveling Might Satisfy Your Desire For New Experiences.: Shaken, He Walked Away From The Wrecked CarRholdan Simon AurelioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gramática - Adjetivos PosesivosDocument1 paginăGramática - Adjetivos PosesivosBeile Instituto de IdiomasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Dictionary Skills QuizDocument5 paginiAdvanced Dictionary Skills Quizhrazak_5Încă nu există evaluări
- Adverbs of Degree: Professional English I Judit Saraí Sarmiento PárragaDocument35 paginiAdverbs of Degree: Professional English I Judit Saraí Sarmiento PárragaJuan RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Synonyms and Their ExamplesDocument3 paginiSynonyms and Their ExamplesEdmondDantesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grammer TenseDocument23 paginiGrammer TenseAjay SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rina Desitarahmi 07202244120Document175 paginiRina Desitarahmi 07202244120Dwi Yanti ManaluÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rangkuman Introducing To Morphology Syntax BAB 3 - 7Document10 paginiRangkuman Introducing To Morphology Syntax BAB 3 - 7YesiRatna100% (1)
- Deverbal Reflexive and Passive in Chuvash: Merja S (Helsinki)Document33 paginiDeverbal Reflexive and Passive in Chuvash: Merja S (Helsinki)LêNgọcTùngÎncă nu există evaluări
- ConjunctionsDocument6 paginiConjunctionsJervin CoronelÎncă nu există evaluări
- HandoutsDocument17 paginiHandoutsMíša HodanováÎncă nu există evaluări
- There Are No Criteria of Identity Over Time - Trenton MerricksDocument27 paginiThere Are No Criteria of Identity Over Time - Trenton MerricksJhonny JaramilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 06Document22 paginiUnit 06John BhuiyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lehmann, Christian. Thoughts On GrammaticalizationDocument183 paginiLehmann, Christian. Thoughts On Grammaticalizationprinnn24100% (1)
- Summary Nouns: Name: Jusy Permata NPM: A1B019106 Lecturer: Wisma YunitaDocument4 paginiSummary Nouns: Name: Jusy Permata NPM: A1B019106 Lecturer: Wisma YunitaRetno Nurul AnnissaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Politeness and Translation: ApterDocument9 paginiPoliteness and Translation: ApterAna Belen Martinez AmaroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Expresiones - Chengyu - Idioms in ChineseDocument15 paginiExpresiones - Chengyu - Idioms in ChineseNacho BerlínÎncă nu există evaluări
- Morphology Tabel Derivational AffixesDocument2 paginiMorphology Tabel Derivational AffixesSam BahriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Roberto G. de Almeida, Christina Manouilidou (Eds.) - Cognitive Science Perspectives On Verb Representation and Processing-Springer International Publishing (2015)Document309 paginiRoberto G. de Almeida, Christina Manouilidou (Eds.) - Cognitive Science Perspectives On Verb Representation and Processing-Springer International Publishing (2015)nellyUNÎncă nu există evaluări
- DLL - Eng 17Document6 paginiDLL - Eng 17Reesee ReeseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adjectives and Adjectives PhrasesDocument14 paginiAdjectives and Adjectives PhrasesPrince BostonÎncă nu există evaluări
- AdjectivesDocument53 paginiAdjectivesjambyvillarsadsad123Încă nu există evaluări
- Substitution Tables LongDocument7 paginiSubstitution Tables LongAngela MaldonadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Introduction To Linguistic Stylistics, I. MURARDocument188 paginiAn Introduction To Linguistic Stylistics, I. MURARPuenea Ionut Marius100% (1)
- Seminar Paper SociolinguisticsDocument17 paginiSeminar Paper SociolinguisticsIvan SusilovicÎncă nu există evaluări
- VUnit 1 - Regular or Irregular VerbDocument27 paginiVUnit 1 - Regular or Irregular VerbAnonymous 3gASOtJJhBÎncă nu există evaluări